UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of
Pedodontics,
Orthodontics and Preventive Dentistry
Department of:
HERE
Orthodontic diagnosis
د نعم فخري
Dr Neam Fakhri
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
BRANCHES OF ORTHODONTICS
Orthodontics can be divided into three categories based on the nature and time of intervention.
• Preventive orthodontics
• interceptive orthodontics
• Corrective orthodontics
020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYIt is defined as the action taken to preserve the integrity of what appears to be a normal occlusion at a specific time. supervision of the growth and development of the dentition and the cranio-facial structures, the diagnostic procedures undertaken to predict the appearance of malocclusion and the treatment procedures instituted to prevent the onset of malocclusion .
1. Caries control
2. Parent counseling
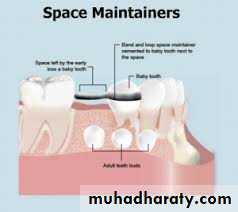
3. Space maintenance
4. Exfoliation of deciduous teeth
5. Abnormal frenal attachments
6. Treatment of locked permanent first molars
PREVENTIVE ORTHODONTICS
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Is that phase of orthodontics that recognize and eliminate potential irregularities and malpositions in the developing dentofacial complex. It implies that corrective measures may be necessary to prevent a potential irregularity from progressing into a more severe malocclusion, The basic interceptive procedures that are undertaken by the interceptive pedodontist are:
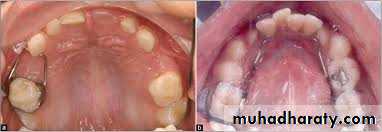
1. Space regaining
2. Correction of anterior and posterior cross bites
3. Elimination of oral habits
4. Muscle exercises
5. Removal of soft or hard tissue present in the pathway of emption
INTERCEPTIVE ORTHODONTICS
Space regaining
Space maintainingSpace regaining
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
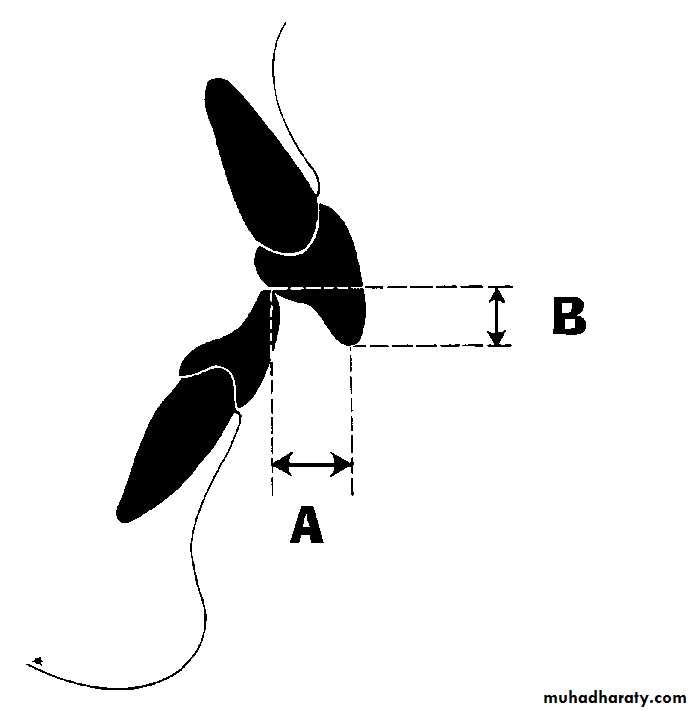
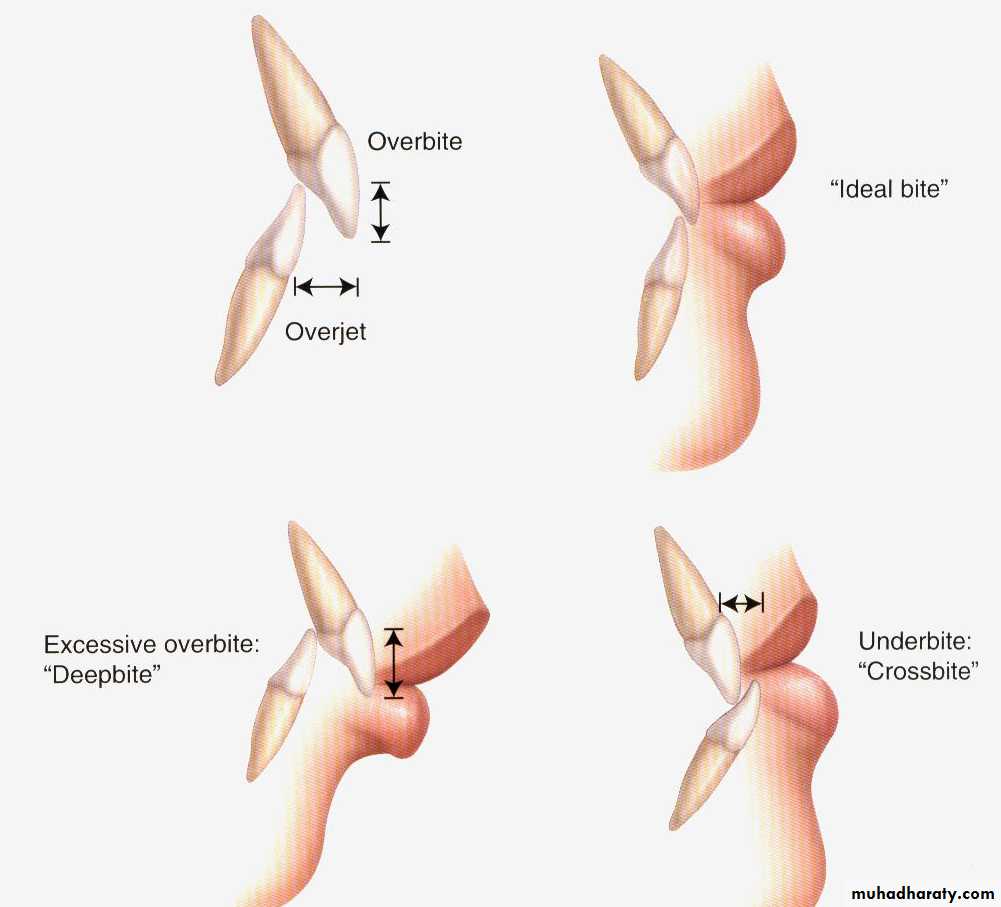
Overbite is the vertical overlap of the incisors.
Overjet is the horizontal distance between upper and lower incisors.Anterior open bite is failure of incisors to meet in maximum intercuspation.
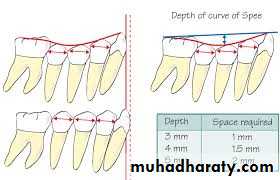
Overbite and OverjetPrimate space
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
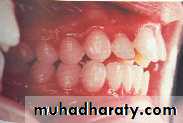
• Mal posed tooth
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
• Increase overjet
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
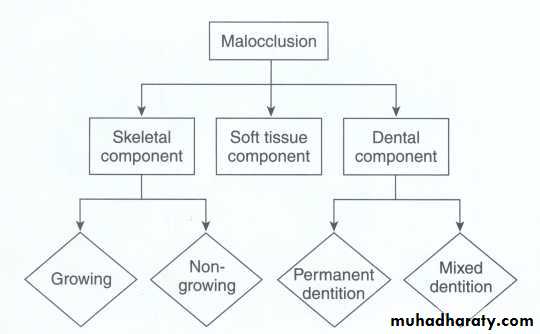
In diagnosis and treatment planning, the orthodontist must:
recognize the various characteristics of malocclusion and dentofacial deformity;
define the nature of the problem, including the etiology if possible;
design a treatment strategy based on the specific needs and desires of the individual;
present the treatment strategy to the patient in such a way that the patient fully understands his/her decision.
• Diagnosis
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
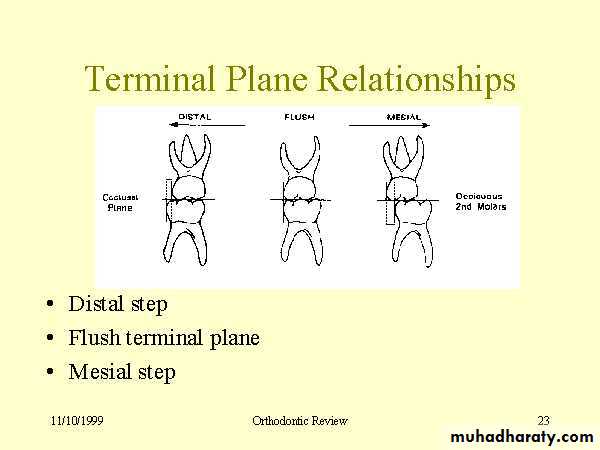
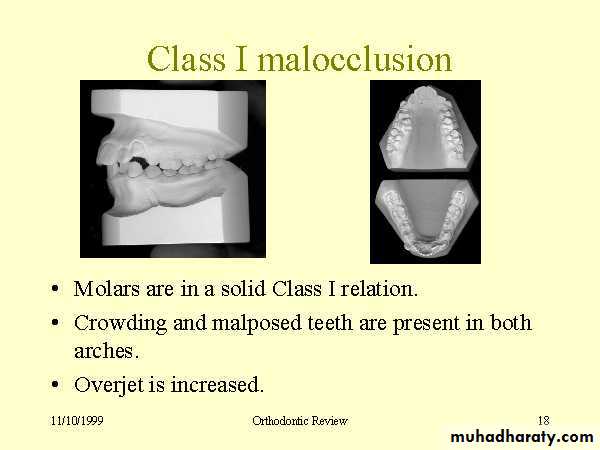
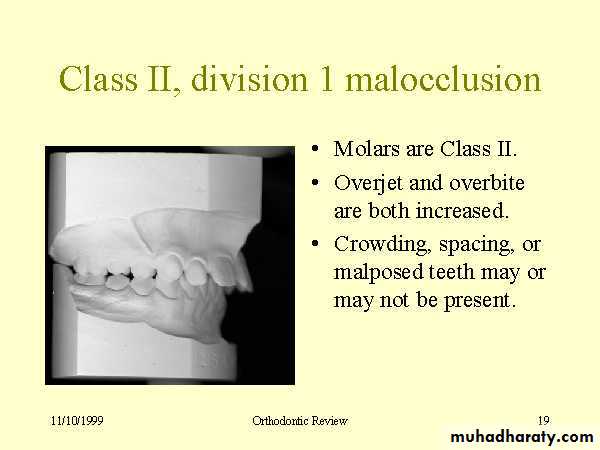
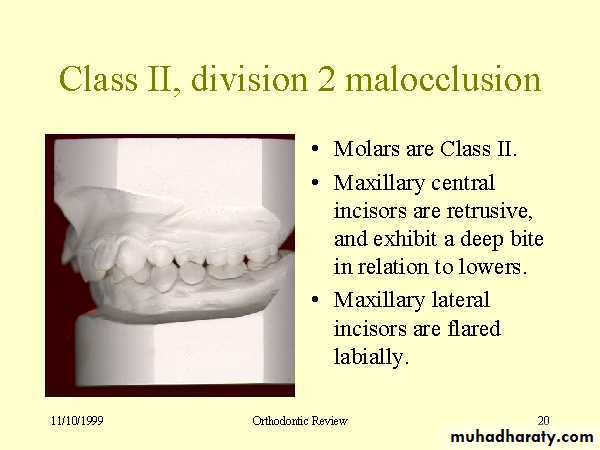
Relationships of the teeth and jaws :
• Arch alignment and symmetry
• Anteroposterior characteristics
• Transverse characteristics
• Vertical characteristics
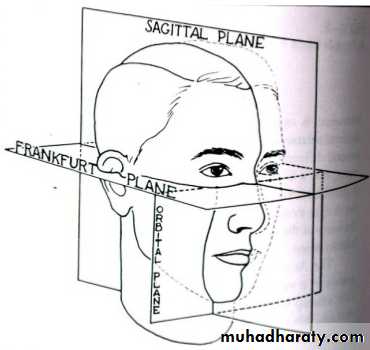
• Orientation of the occlusal plane in NHP(natural head position) i.e., standing or sitting up), not with the patient prone in a dental chair.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Department of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
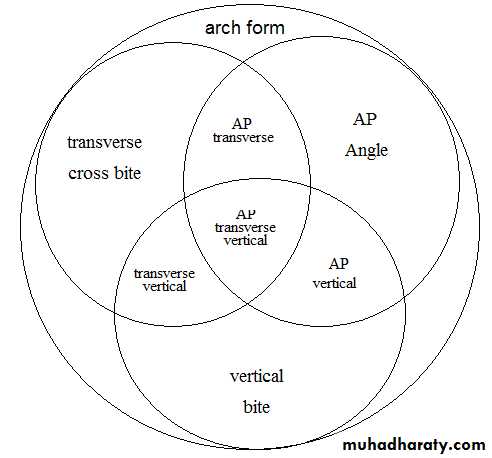
• Ackerman-Proffit orthogonal analysis. representing arch form in three planes of space
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYEssential diagnostic aids
1. Case history2. Clinical examination
3. Study models
4. Certain radiographs:
Periapical radiographs
Lateral radiographs(cephalometric radiograph)
Orthopantomograms
Bite wing radiographs.
5. Facial photographs.
Orthodontic Diagnosis
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
1. Specialized radiographs; like
Occlusal views of maxilla and/or mandible.
Selected lateral jaw views, etc.
2. Electromyographic examination of muscle activity
3. Hand-wrist radiographs
4. Computed axial tomography (CT scan)
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
6. Endocrine tests and/or other blood tests
7. Estimation of the basal metabolic rate
8. Sensitivity (vitality) tests
9. Biopsy.
Non-essential or supplemental diagnostic aids
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
• Case history:
• NameAge and date of birth
Address and occupation
Chief complaint
Medical history
Dental history
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Department of:
HERE
Clinical Examination
General Examination
The orthodontist should make some diagnostic determinations “from the doorway” regarding the patient’s face, posture, and expression. One can often tell from the first moment whether the orthodontic problem will be largely a dental one or a difficult skeletal or facial problem.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
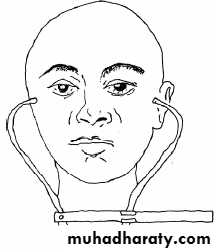
Maximum skull width
I = ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Maximum skull length
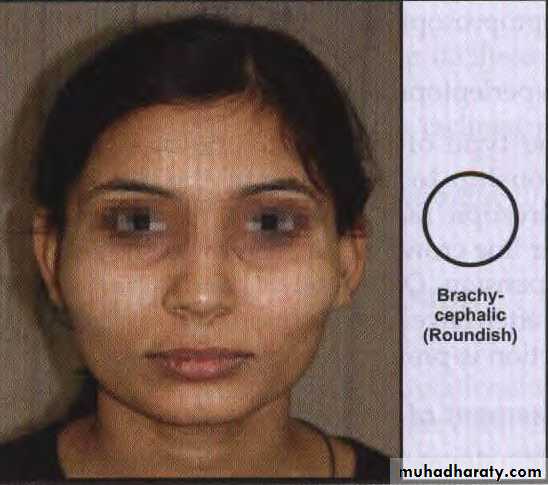
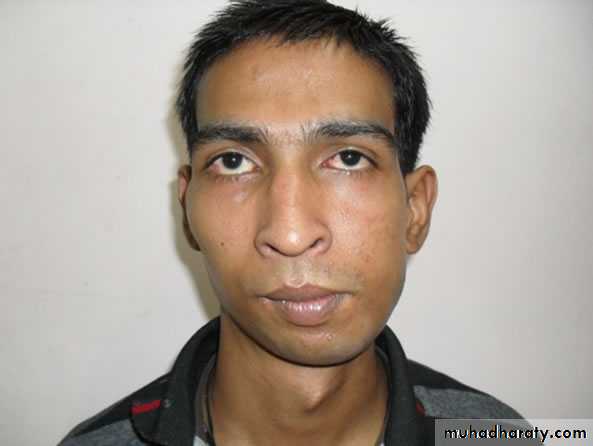
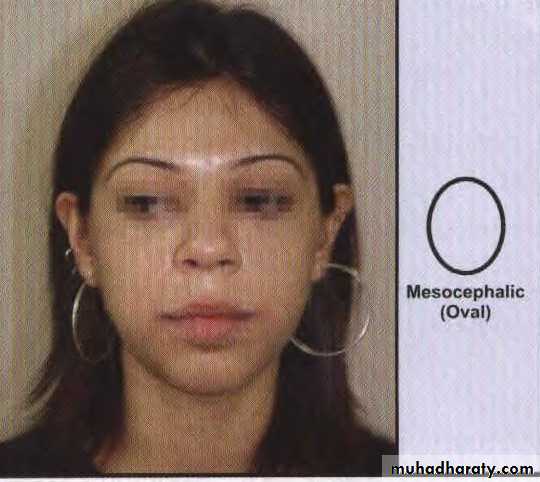
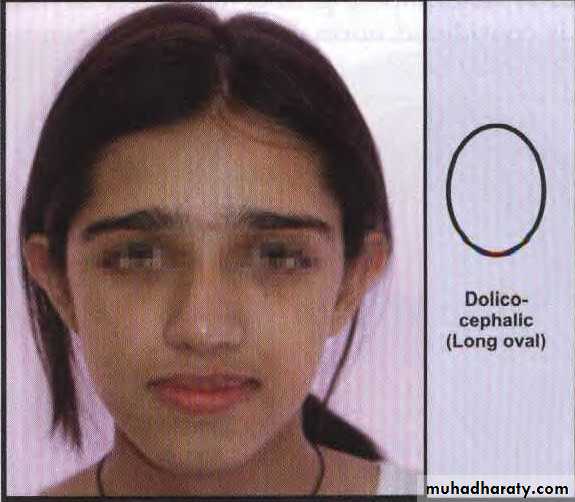
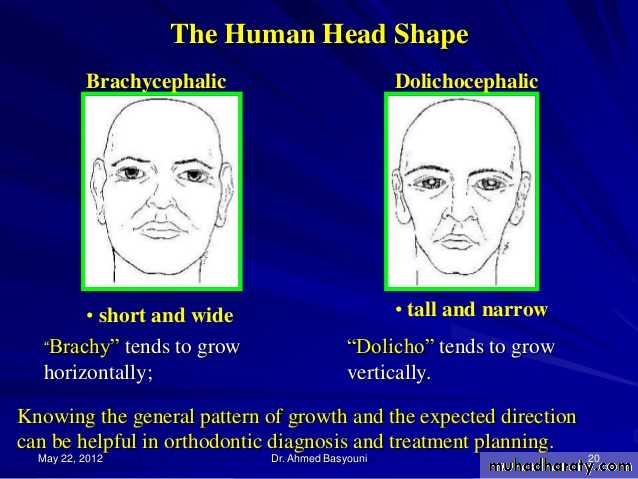
Cephalic Examination
• Mesocephalic (average) skull
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
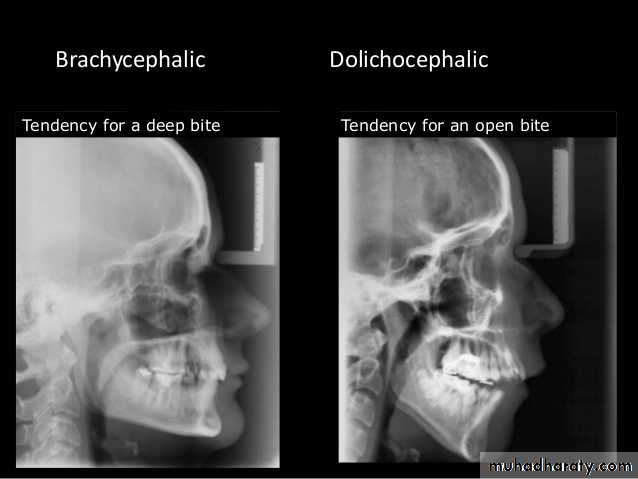
Brachycephalic (short, broad skull)
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Dolicocephalic (long, narrow skull)
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Morphologic facial height (distance between nasion & gnathion)
I = ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Bizygomatic width (distance between zygomatic points)
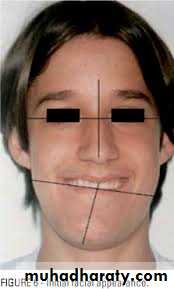
Assessment of Facial Symmetry
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Department of:
HERE
• Sagittal (mesial-distal)
• Vertical (deep bite, open bite)
• Transversal (narrow)
• Orthodontic directions for treatment
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Gross facial asymmetries may be seen in patients with:
1. Hemifacial hypertrophy / atrophy
ii. Congenital defects.
iii. Unilateral condylar hyperplasia
iv. Unilateral Ankylosis, etc.
• facial asymmetry
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Hemifacial hypertrophy / atrophy
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
• II. Congenital defects
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
• iii. Unilateral condylar hyperplasia
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY• iv. Unilateral Ankylosis
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
• Cant of occlusal plane
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Department of:
HERE
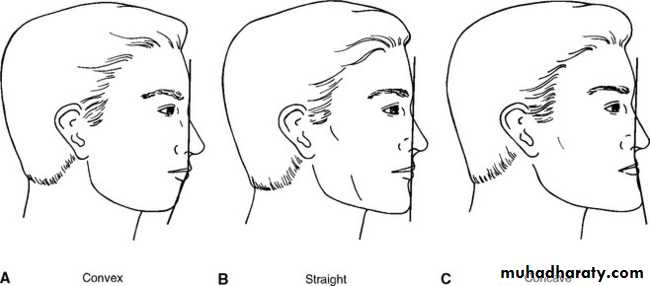
Clinically extraoral photographs, the profile can be obtained by joining two reference lines:
a. Line joining forehead and soft tissue point A
b. Line joining point A and soft tissue pogonion.
Three types of profiles are seen:
Straight orOrthognathic profile : The two lines form an almost straight line• Facial Profile
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Convex profile : The two lines form an acute angle with the concavity facing the tissues. This type of profile is seen in Class II div 1 patients due to either a protruded maxilla or a retruded mandible.
Concave profile : The two lines form an obtuse angle with the convexity facing the tissues. This type of profile is seen in Class III patients due to either a protruded mandible or a retruded maxilla.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021