بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
14/2/202
رجب الاصب 1442
Sleep-disordered breathing
A variety of respiratory disorders affect sleep or are affected by sleepAbnormal lung
Asthma Cough and wheeze disturbing sleephypoventilation that accompanies normal sleep can precipitate respiratory failure in patients with disordered ventilation due to kyphoscoliosis, diaphragmatic palsy or muscle disease (e.g. muscular dystrophy).
Normal lung
Patients with these may have normal daytime respiratory function,but during sleep
1-abnormalities of ventilatory drive (central sleep apnoea)
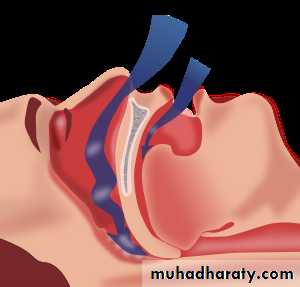
2-upper airway obstruction (obstructive sleep apnoea). Of these, the
obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome
The sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome
2–4% of the middle-aged population suffer from
recurrent upper airway obstruction during sleep.
sleep fragmentation.
daytime sleepiness.
risk of road traffic accidents.
Apnoea
(10 secsDesaturation)
Hypnoea
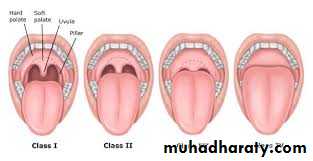
MALLAMPATI CLASSIFICATION
Clinical Features
SomnolenceNormal subjects average 5.9 (SD 2.2) and patients with
severe obstructive sleep apnoea average 16.0 (SD 4.4).≥ 9/24
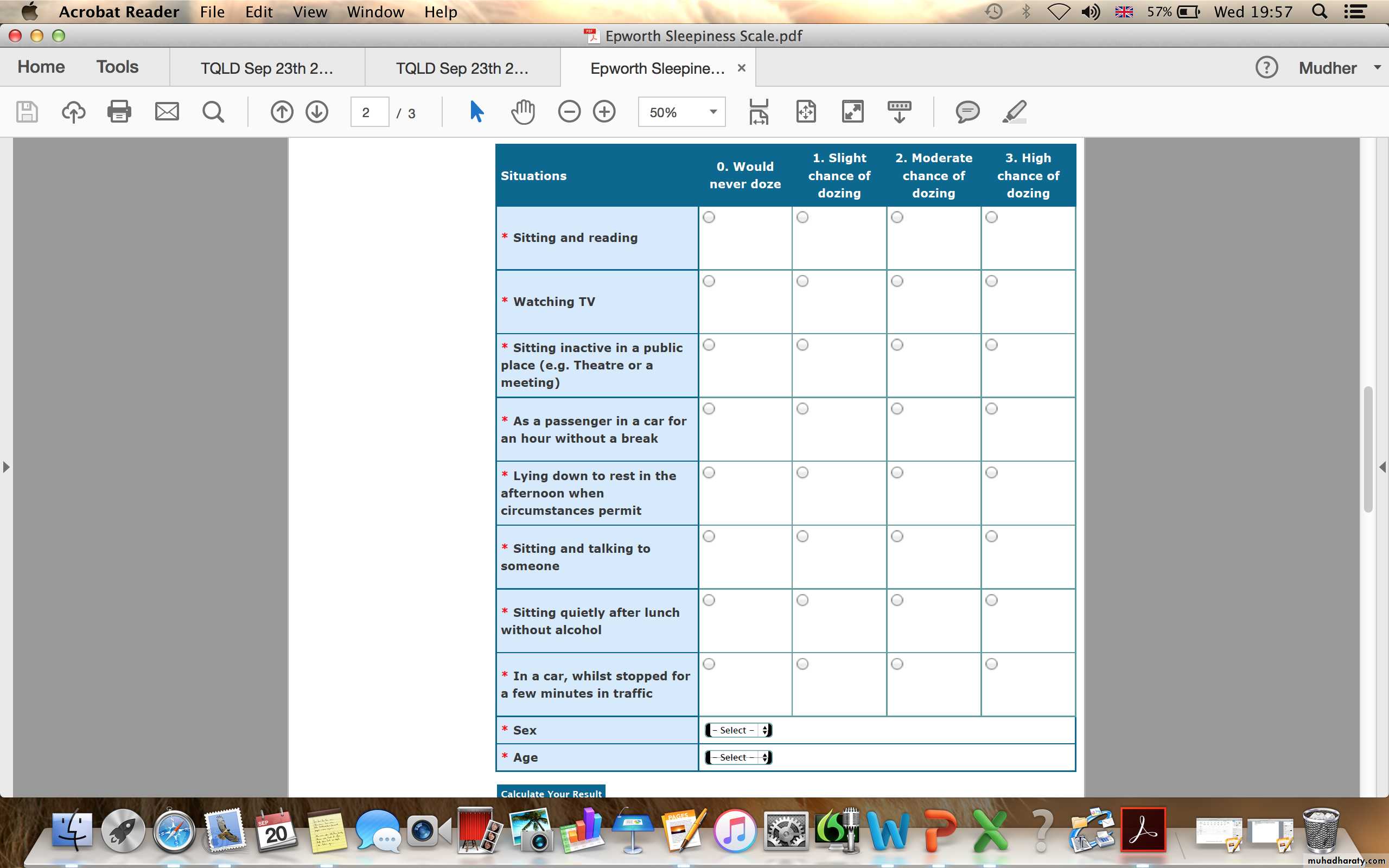
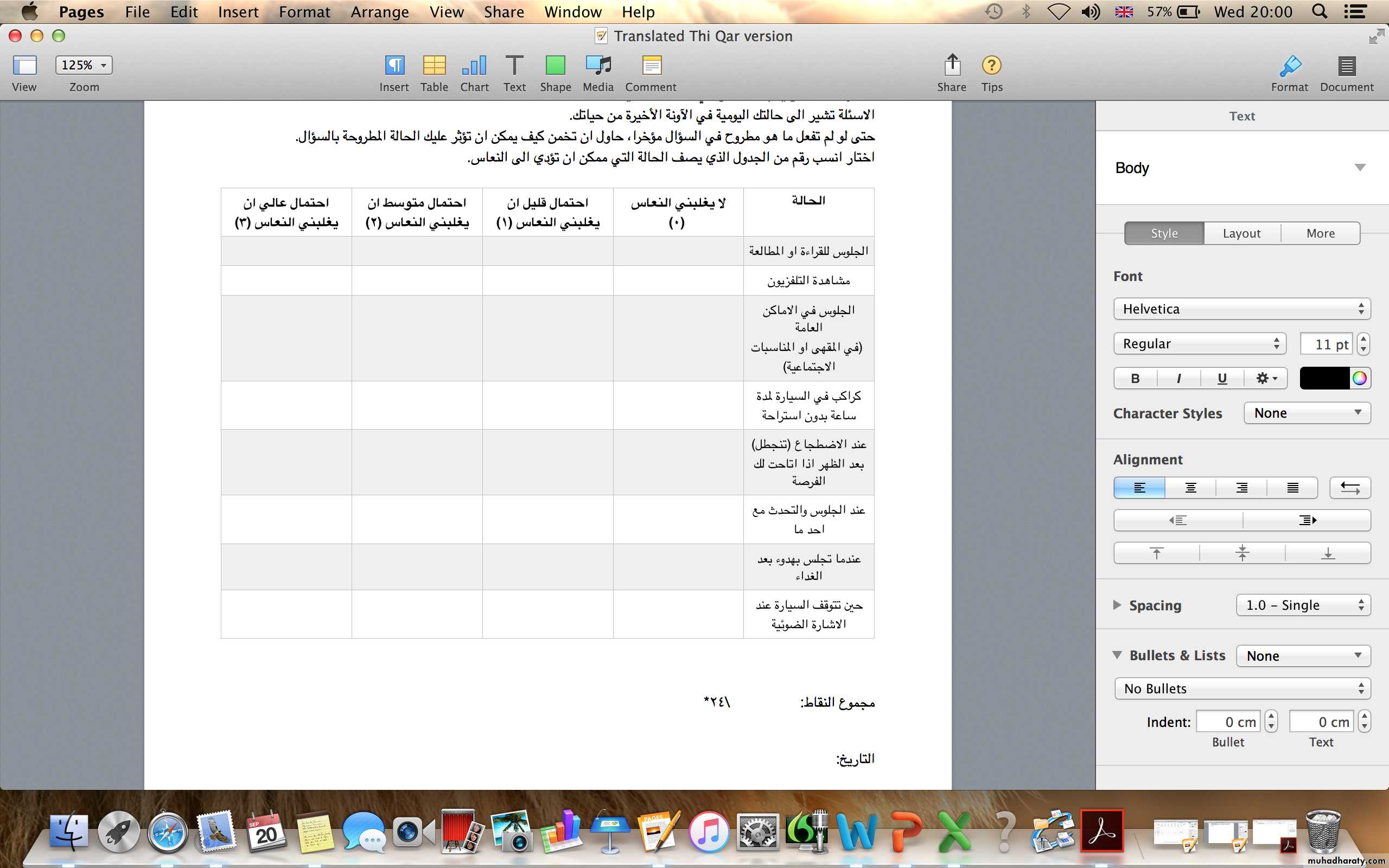
Epworth sleepiness scale
How likely are you to doze off or fall asleep :0 = would never doze
1 = slight chance of dozing
2 = moderate chance of dozing
3 = high chance of dozing
• Sitting and reading
• Watching TV
• Sitting inactive in a public place (e.g. a theatre or a meeting)
Sitting and talking to someone
• Lying down to rest in the afternoon when circumstances permit
• Sitting quietly after a lunch without alcohol• As a passenger in a car for an hour without a break
• In a car, while stopped for a few minutes in the trafficClinical Features
SomnolenceSnoring
Gasping (Apnoea/Hypopnoea)
Nocturia
Headache/Cognitive Impairment
Sexual Dysfunction
Differential diagnosis ofpersistent sleepiness
Lack of sleep
Sleep disruption
Sleepiness with relatively normal sleep
Psychological/psychiatric
Associated Medical Conditions
PregnancyCHF ,ESRD
Chronic Respiratory Disease
CVD
Acromegaly ,Hypothyroid
PCOS
.Metabolic syndrome and T2DM
Risk Factors
SmokingMale Gender
Obesity
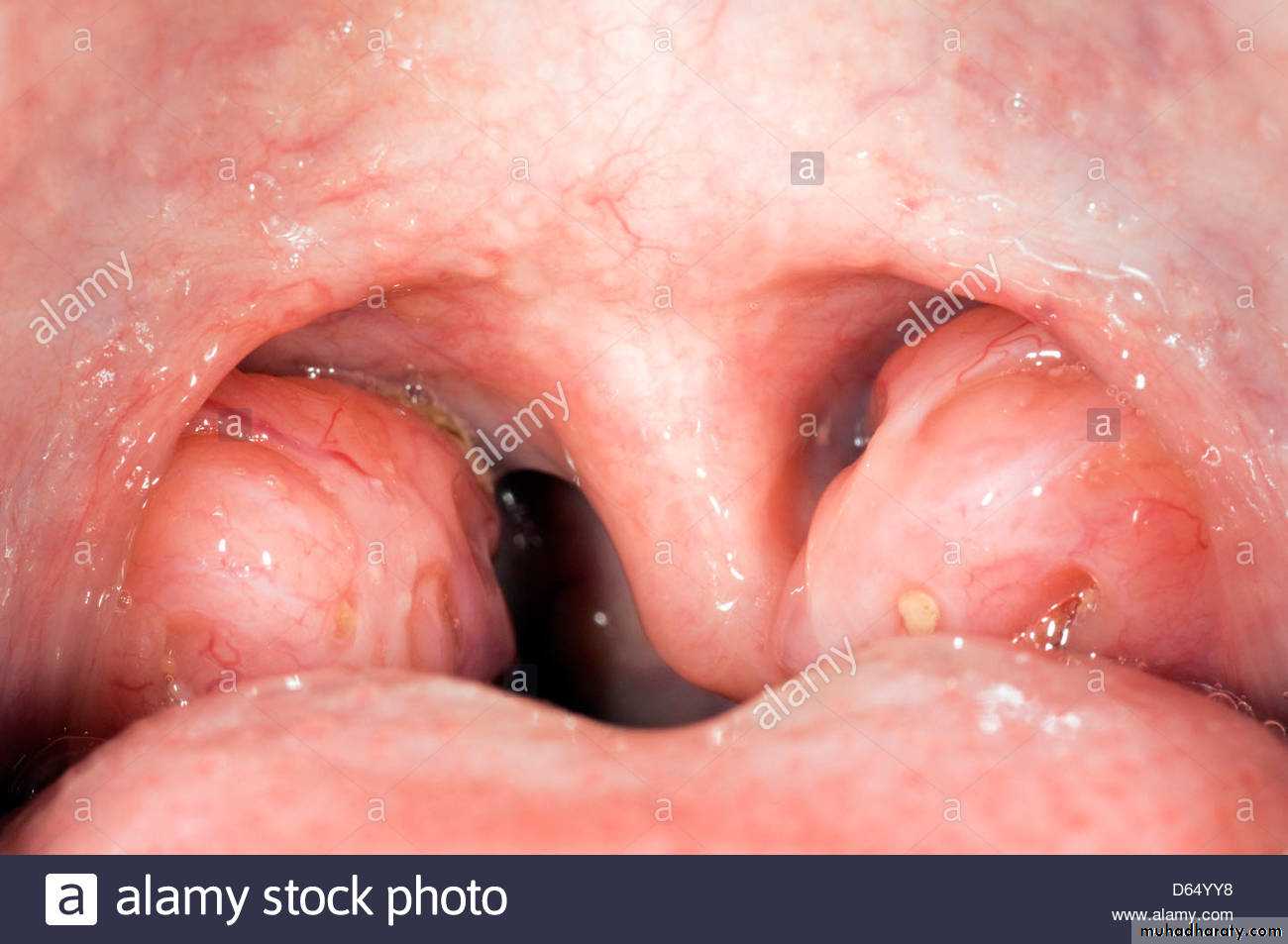
Micrognathia.
Diagnosis
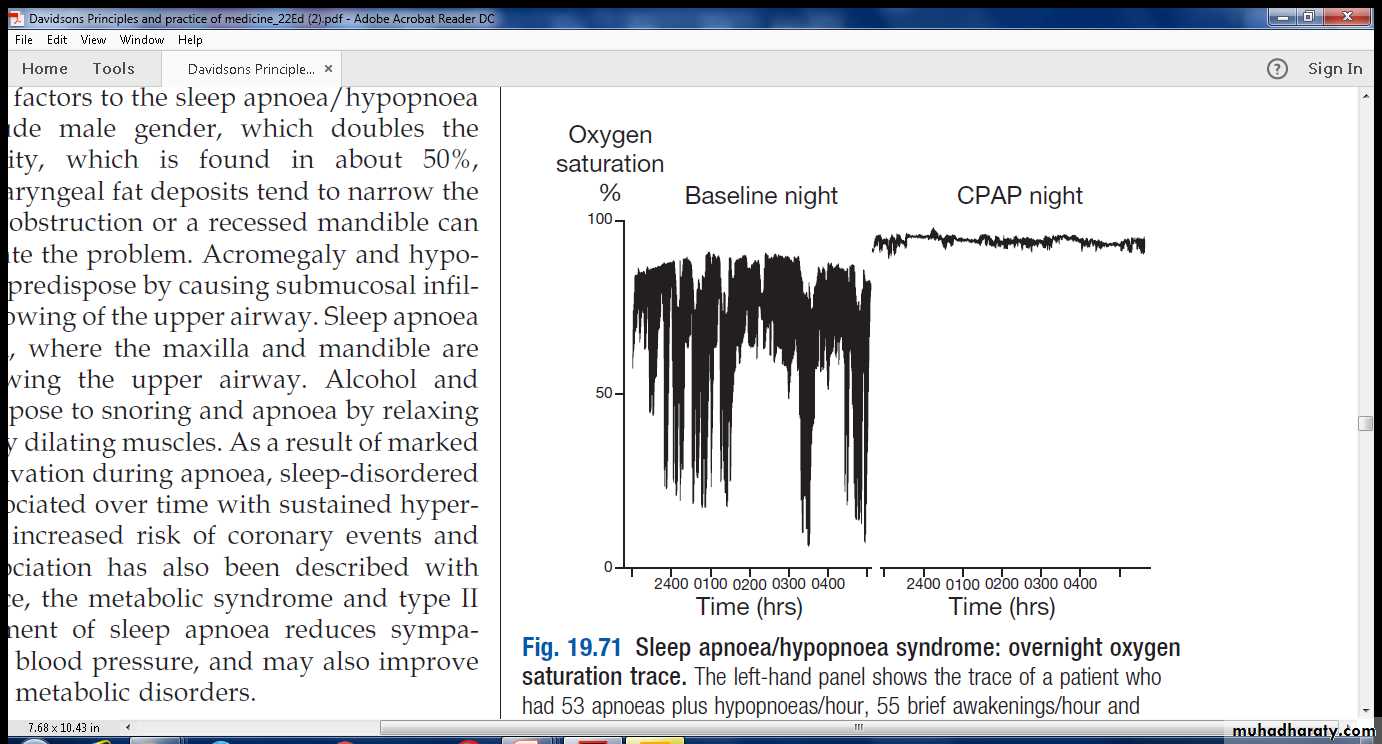
Sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome: overnight oxygensaturation trace. The left-hand panel shows the trace of a patient whohad 53 apnoeas plus hypopnoeas/hour, 55 brief awakenings/hour andmarked oxygen desaturation. The right-hand panel shows the effect ofcontinuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) of 10 cm H2O deliveredthrough a tight-fitting nasal mask: it abolished his breathing irregularity andawakenings, and improved oxygenation.
Diagnosis
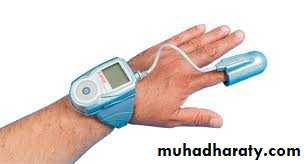
Nocturnal Pulse OximetryLimited (Ambulatory PSG)
95% sensitivity
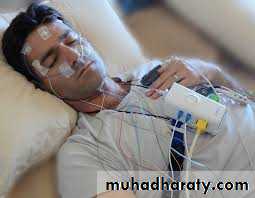
Full PSG (EEG)
RDI >10/Min
RESPIRATORY DISTURBANCE INDEXManagement
TreatmentWeight Loss
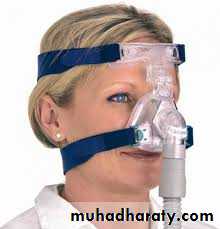
CPAP
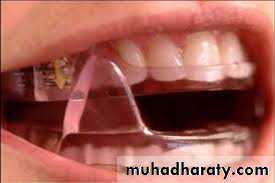
Mandibular Advancement Device
Upper airway surgery
Nasal Devices.
Others