INSTRUMENTAL DELIVERY
INSTRUMENTAL DELIVERY
DEFINIFITION: delivery of a baby vaginally using an instrument for assistanceINDICATIONS
Fetal indication: fetal distress or cord prolapse during the second stage of labor, malposition of fetal headMaternal indications: maternal exhaustion and distress during second stage of labor or certain maternal medical disease that necessitate shortening second stage like heart disease
Ellective use in epidural anesthesia, premature baby, delivery of after coming head in breach vaginal delivery.
FORCEPS DELIVERY
Classification
• low forceps(Wrigley's)short and light
used if deeply engaged head
used in caesarian section
• Mid cavity non rotational forceps (Simpsons)
engaged head
direct occiput anterior
• Midcavity rotational forceps (Keillands)
engaged head
reduce pelvic curve on the blades of the forceps allow rotation about the axis of the handle
help to correct asynclitism and malposition
must only attempt by an experienced operator
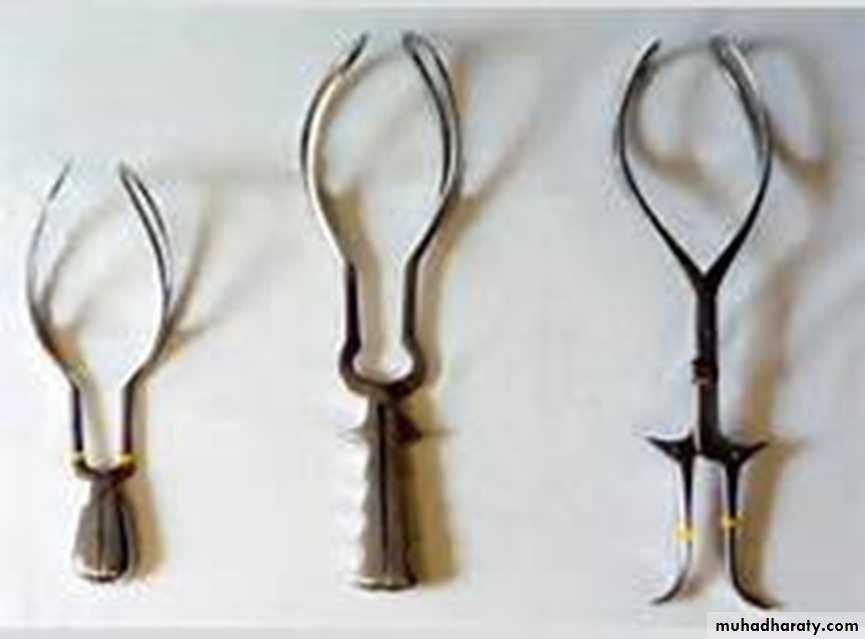
• Forceps vary in size and shape
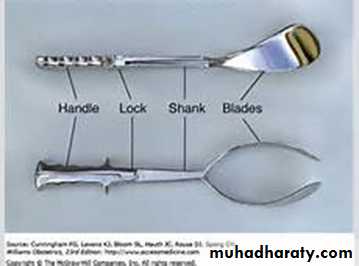
• Consist basically two crossing branching introduce separately into the vagina• Each one has four components: plate shank lock handle
• Shank short or long, plate contain cephalic and pelvic curve
Condition necessary for application of forceps
• fully dilated cervix• rupture membrane
• suitable presentation (vertex, mentoanterior face)
• position is well known
• the head must be engaged
• empty bladder
• exclude obstruction :no obstruction below the head
Technique of use
adequate analgesia or anesthesia.female in lithotomy position.
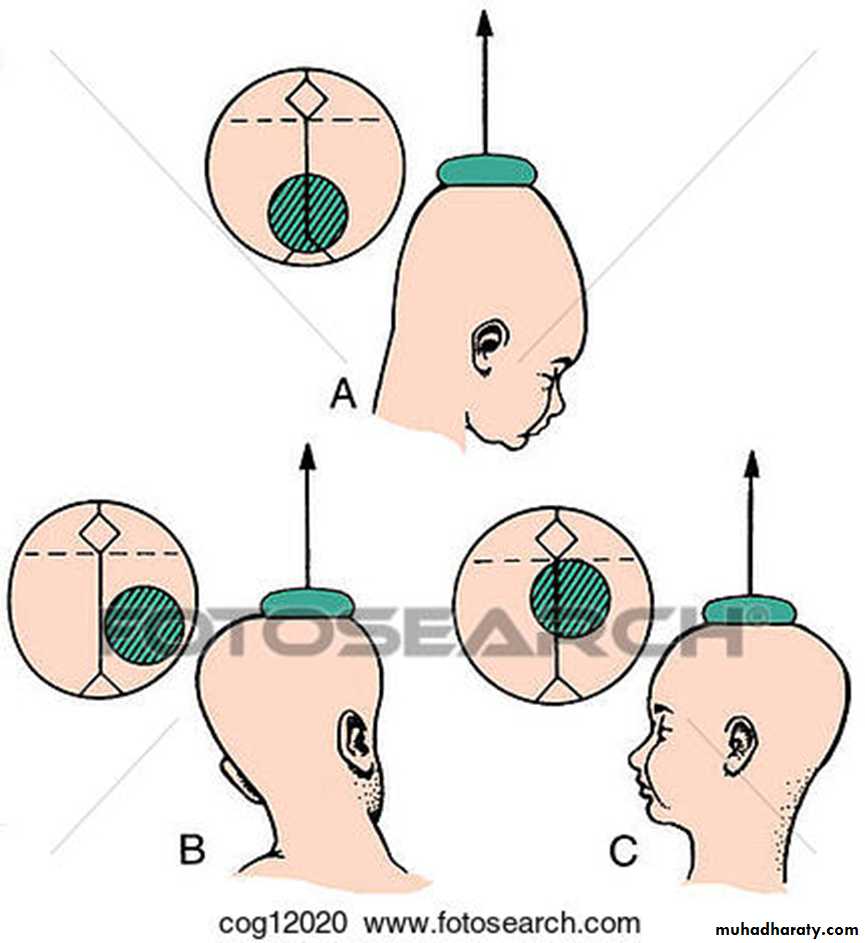
identification of position of fetal head by feeling sagittal suture and fontanel
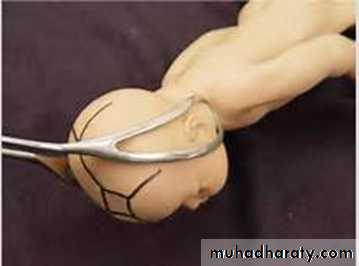
application of forceps after checking both plate of the forceps outside the pelvis and locked them.
the left plate is introduce by the left hand into the left side of the pelvis and the right by the right hand in the same way
then two handle should be articulated and attached each other without difficulties
then gentle intermittent horizontal traction with each contraction until the vulva extended by the occiput then episiotomy done then the handle gradually elevated and pointed up
Complication and danger
Maternal:• trauma to birth canal (rupture uterus, cx tear, cx evulsion, multiple vaginal tear )
• postpartum hemorrhage
• infection
• injury to bladder ,rectum or fistulae
• uterovaginal prolapse
Infant
• trauma and death or long term morbidity, cerebral palsy, low IQ ,ICH,frature skull
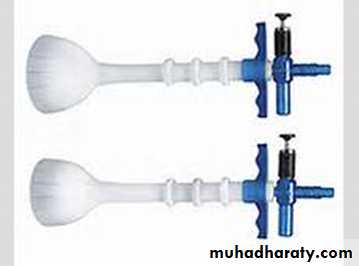
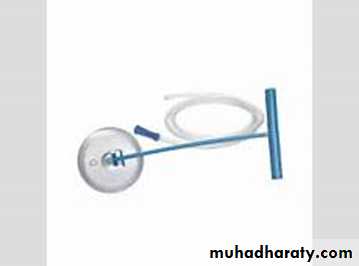
Vacum extractor (ventose )
Is that a suction cup of silastic or rigid construction of three different size 4,5,6 cm in diameter is connected via a tubing to vacume source ,either directly through the tubing or via connecting chain direct traction can then be applied to presenting part to expedite delivery
Technique
prior to application checking the patient in regard to dilation, presenting part, station and position. empty bladder, local analgesia or anesthesia. After checking the equipment for a leak the cup is placed in the vagina as closed as possible to the posterior fontanel over the sagittal suture .negative pressure of 0.2 kg\cm2 is applied and is increase gradually within 1 -2 reaching o.8 kg \cm2 traction applied in the same direction of birth canal with each uterine contraction the handle should be held perpendicular to the cup ,the thumb of the other hand is applied on the cup to counteract destruction in order to avoid cup dislodgement .the presenting part should be descend with each pull and the cup should not be dislodged more than one .if the baby is not delivered within three pulls and within 15 minute the procedure should be stopped
INDICATION
FETAL DISTRESS in the second stage of labor i.e fully dilated cervix or near fully (8 cm )Maternal indication :physical distress ,medical disease that necessitate shortening the second stage like maternal cardiac disease
Contra indication
absolute cephalopelvicdisproportion
malpresentation face ,breech ,transverse lie
cervix is insufficiently dilated
premature fetus
if suspected fetal coagulopathy and should be perform with care if prior scalp sample was perform during labor
Complications
Maternal :postpartum hemorrhage and genital tract laceration and injuries
Fetal : ICH greater incidence in premature and its related to number of pulls and duration of cup application
cephal hematoma is commonly associated with ventose cerebral irritation and asphyxia
scalp effect :scalp laceration and avulsions rarely alopecia on long term sequellae ,formation of shignon which its artificial cuputretinal haemorrhge
neonatal jaundice due to degradation of large volume of blood in the cephalhaematomalong term morbidity :less than with forceps (neurological and intellectual development )
Episiotomy
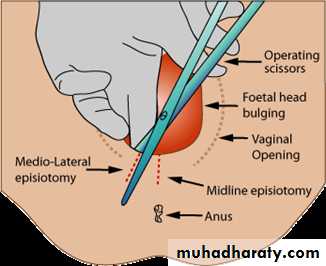
Definition :is an incision through the perineum made to enlarge the vulval outlet and assist childbirthTypes of episiotomy
Medio lateral episiotomy extents from the fourchette laterallyMidline episiotomy :extends from the fourchette towards the anus
Indication
complicated vaginal delivery (breech ,shoulder dystocia ,forceps )if there is extensive lower genital tract scarring (female genital mutilation ,poorly healed third or forth degree tears )
when there is fetal distress
Complication
Bleeding
HaematomaPain
Infection
Scarring
Dyspareunia
Rarely fistulae formation
Technique
is performed in the second stage usually when the perineum is being stretchedgood analgesia if no epidural anesthesia
incision is made mid line or Medio lateral involving skin ,perineal muscle ,vaginal wall (second degree tear )
after delivery of the fetus and the placenta the incision is repaired in layer
Mid line episiotomy less bleeding, rapid healing, less scaring. easy to repair but there is risk of extension to the anal sphincter and anal canal so Medio lateral episiotomy preferred
KEY POINT
should only be used by those trained to do so.the prerequisites for an instrumental delivery must be met before forceps or ventouse be applied .
failure rate higher with soft than rigid cups and with ventose than forceps.
use of second instrument increases the risks of fetal and maternal damage.
ventose safer to the mother than forceps.
Forceps safer to the fetus
Cephalhaematoma and retinal detachment common with ventose
forceps used in face ,after coming head in breech ,casseran section while ventose not
ventose can be used in near fully cervix while forceps not