Bacterial Skin Infections
Impetigo ContagiosaIt is a common superficial skin infection.
There are two forms:
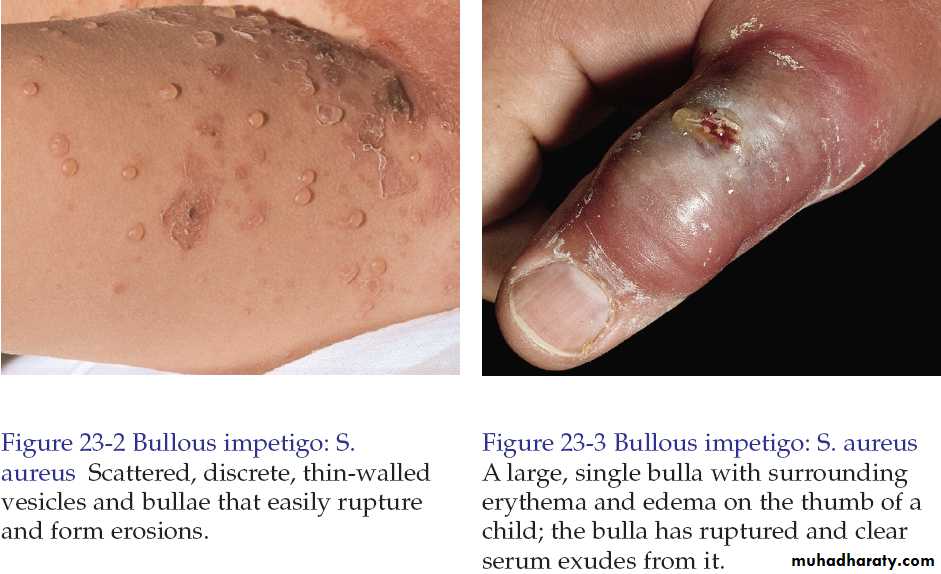
Bullous impetigo.
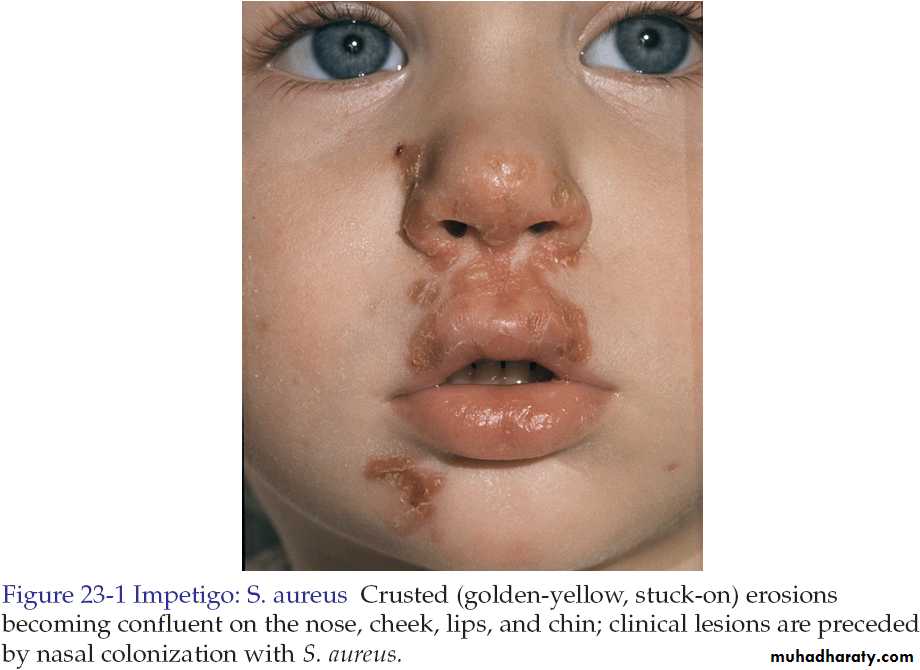
Non-bullous impetigo.
Both begin as vesicles with a very thin fragile roof consisting of only stratum corneum.
The lesions are asymptomatic.
Bullous impetigo is caused by staphylococcus aureus.
Non-bullous impetigo in majority caused by S. aureus but occasionally caused by group A beta hemolytic streptococci or both.
In both the disease is common in children.
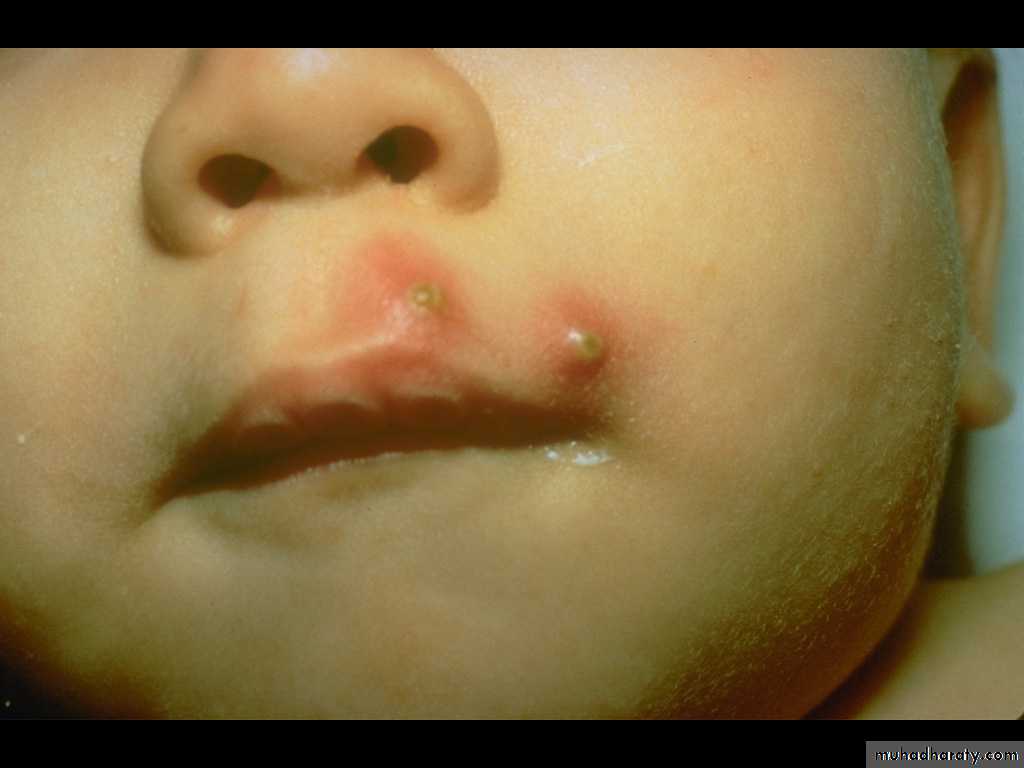
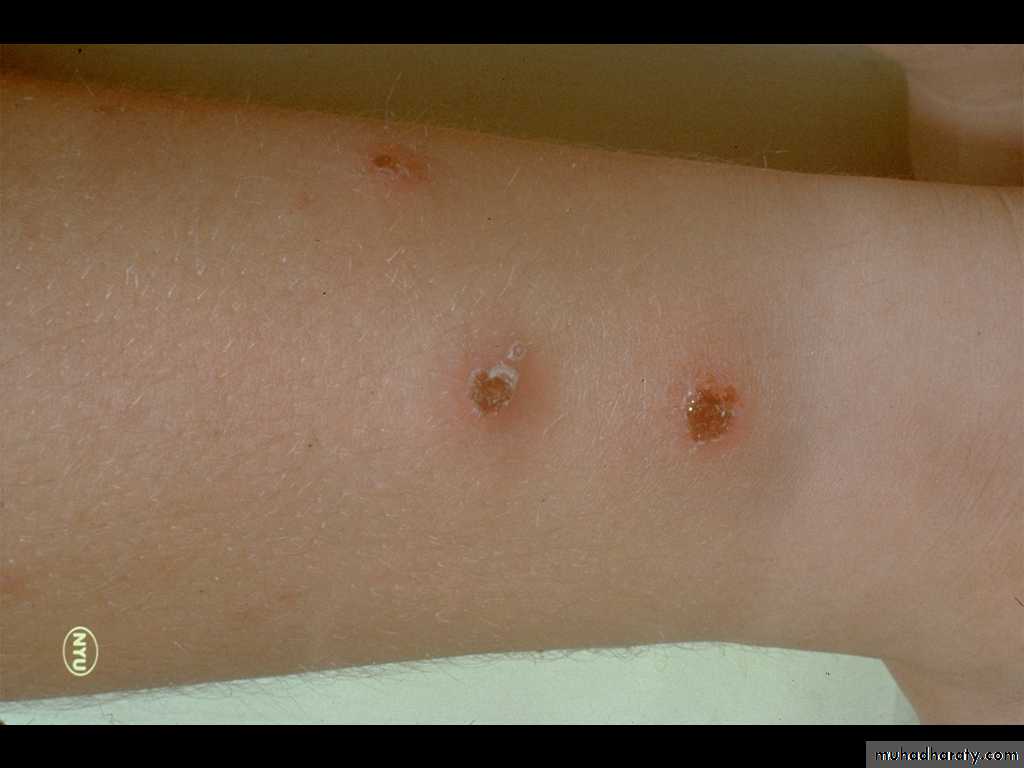
In bullous form, one or more vesicles enlarge rapidly to form bullae then the center of the thin roofed bulla collapses to form a thin flat honey yellow colored crust appear in the center. The face is common site of involvement.
In non-bullous impetigo the small vesicle or pustule ruptures to expose a red moist base (erosion). A honey-yellow to brown firmly adherent crust accumulates as the lesions extend radially. The skin around nose, mouth and the limbs are commonly involved.
Impetigo (Pustules)
Impetigo Contagiosa
The complications of impetigoPost-streptococcal glomerulonephritis usually develop 1-3 weeks following acute infection with specific nephritogenic strains of group A beta hemolytic streptococci.
Lymphadenitis is common with streptococcal infections.
Urticaria.
Erythema multiforme.
Treatment
If the area is solitary and small use topical antibiotics like fusidic acid.
If the infection is widespread, severe or accompanied by lymphadenopathy then oral antibiotics are indicated like flucloxacillin.
Removal of infected crusts by washing with soap and water is bacteriologically and cosmetically helpful.
Lesions heal without scarring.
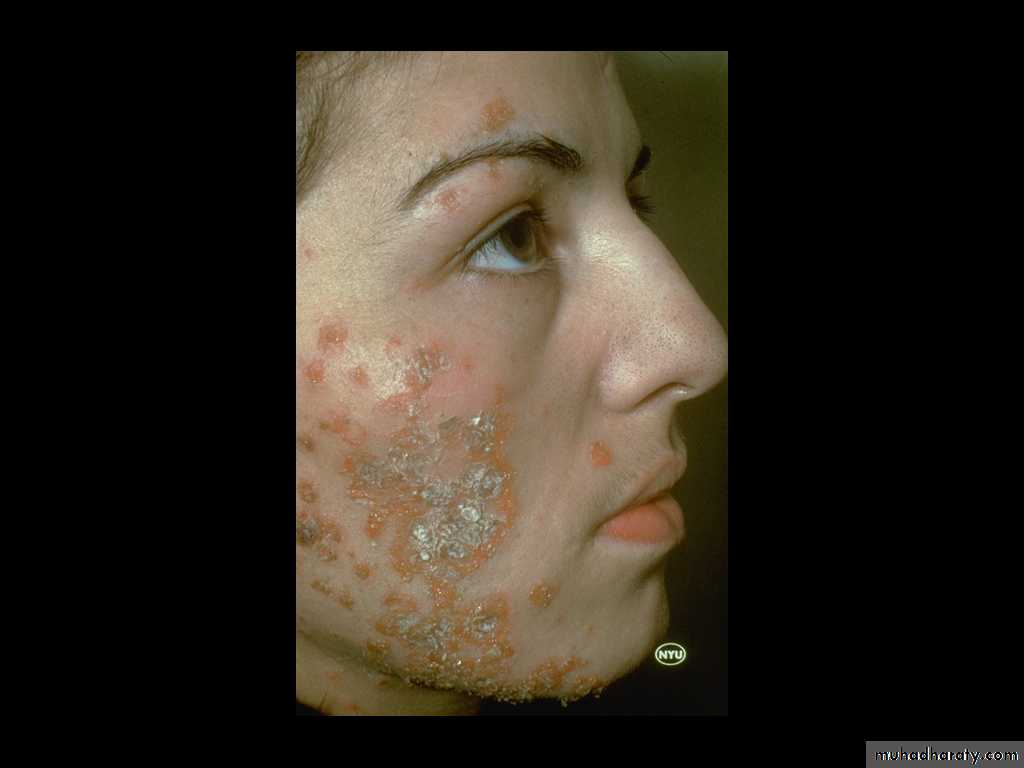
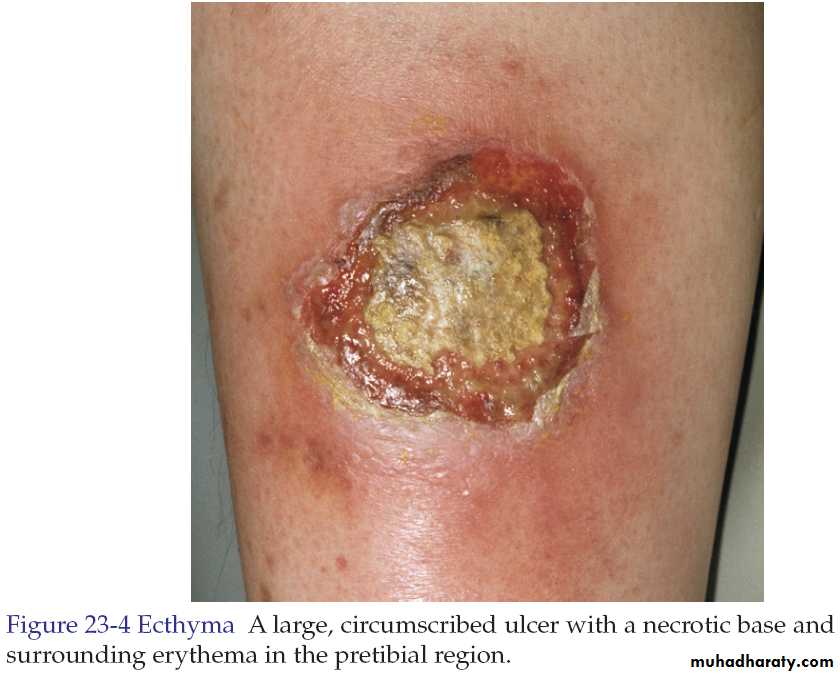
Ecthyma(ta)
Ecthyma is a deep bacterial infection that involves the dermis. It is caused by streptococci, staphylococci or both.It characterized by punched out ulcer that is covered by adherent crust surrounded by erythema.
Buttocks, thighs and legs are common sites.
Poor hygiene, immunosuppression, and malnutrition are a predisposing factors.
Treatment is by systemic antibiotics.
Healing occurs in few weeks with scarring.
Ecthyma
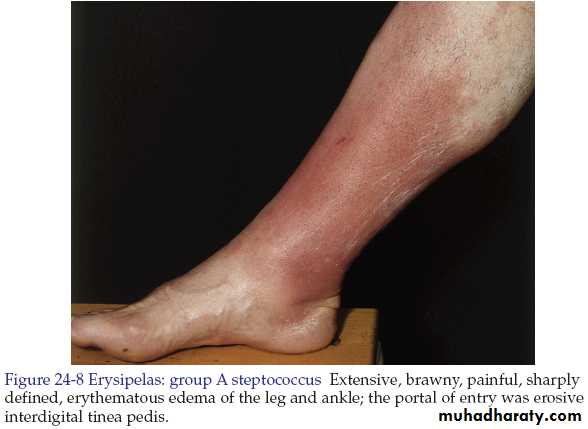
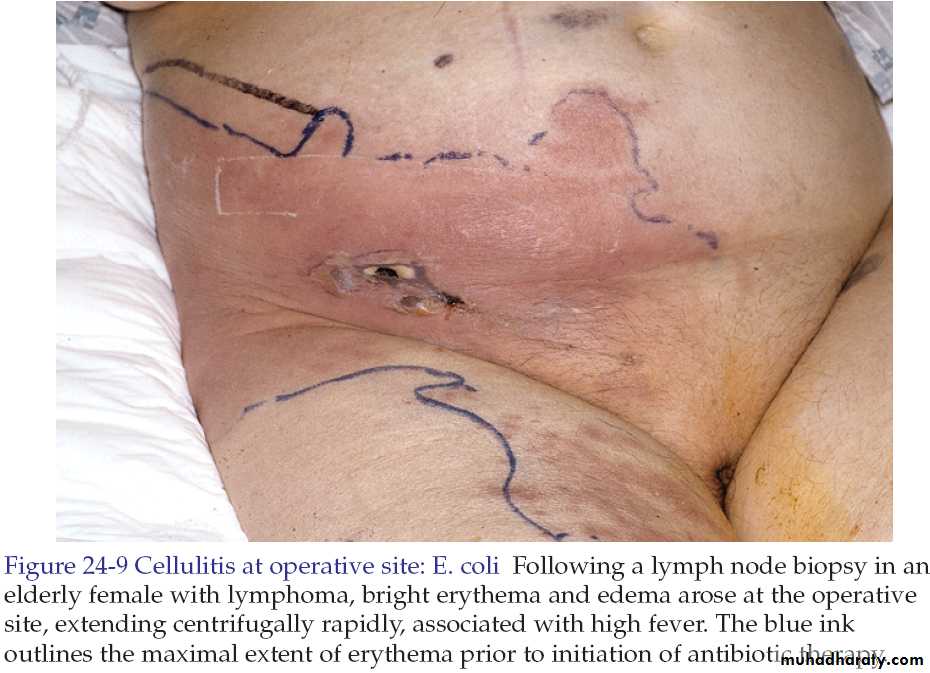
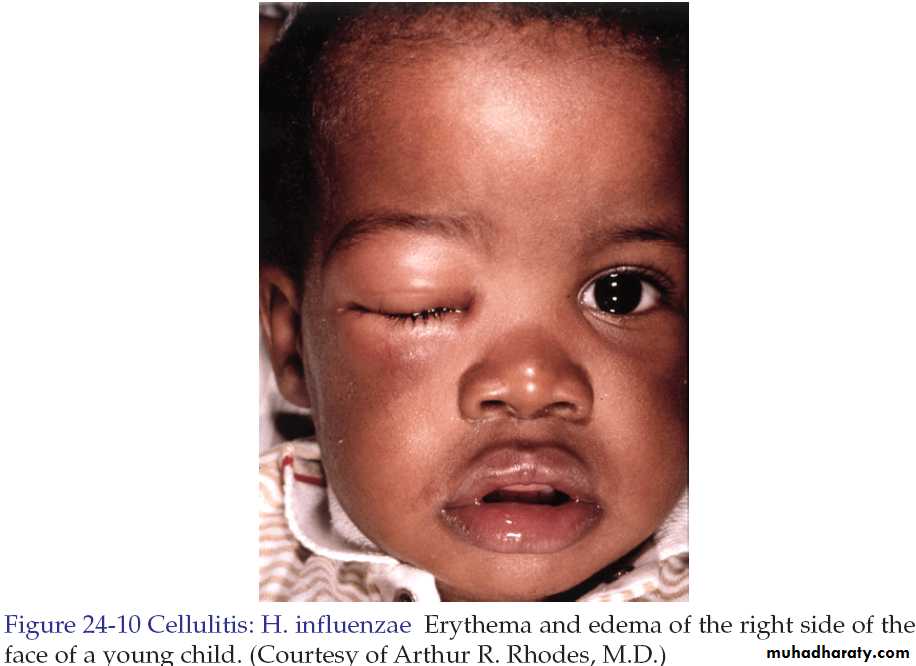
Cellulitis and Erysipelas
Both are skin infections characterized by erythema, edema and pain.In most instances there is fever.
Both may be accompanied by lymphangitis and lymphadenitis.
Pathogens enter at the site of local trauma or abrasions and psoriatic, eczematous or tinea lesions.
• Cellulitis
• Erysipelas• Feature
• Dermis and subcutaneous tissues
• Dermis
• Pathology site
• Streptococci, S. aureus, H. influenzae and others
• Usually streptococci
• Cause
• Indistinct
• Distinct
• Margin between involved and uninvolved skin
• Any site
• Lower legs, face and ear
• Common sites
• Not prominent
• Prominent
• Lymphatic involvement (streaking)
Table shows the differences between erysipelas and cellulitis
Treatment
Flucloxacillin (penicillinase resistant penicillin) 500 mg every 6 hours orally for 10 days.Or
Cephalexin 500 mg every 6 hours orally for 10 days.
Or
Gentamycin 80 mg 2-3 times daily for 7 days if gram-negative infection is suspected.
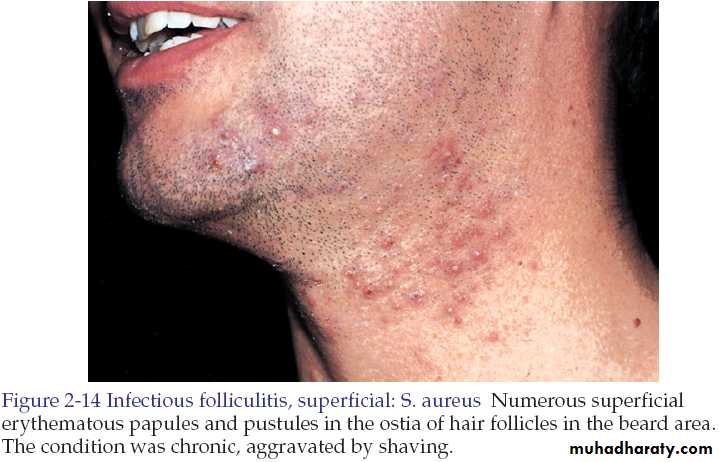
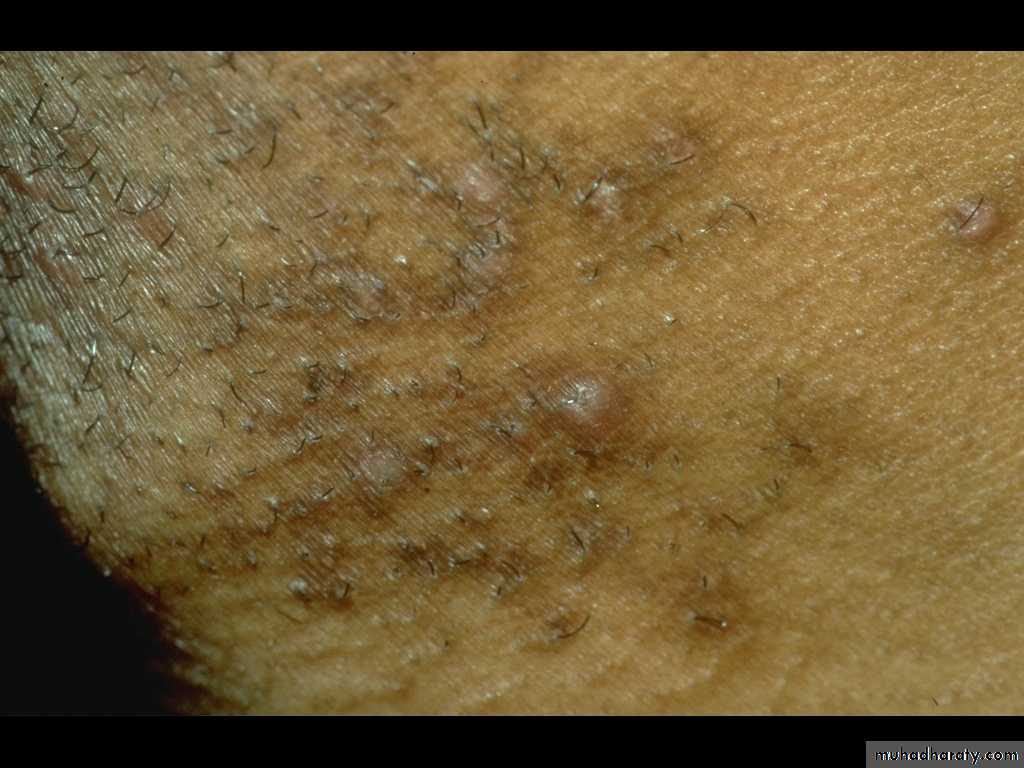
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicle caused by infection, chemical irritation or physical injury.
In superficial folliculitis, the inflammation is confined to the upper part of the hair follicle. It manifested as a painless or tender pustule that eventually heals without scarring.
In deep folliculitis, the inflammation involves the deeper portion of the hair follicle or the entire follicle. The lesions are painful and may heal with scarring.
• Deep folliculitis
• Superficial folliculitis• Furuncle and Carbuncle
• Staphylococcal folliculitis
• Sycosis barbae
• Pseudofolliculitis barbae (from shaving)
Diseases initially manifesting as folliculitis
Staphylococcal folliculitis
It occur because of injury, abrasion, nearby surgical wounds or draining abscesses.It may also be a complication of occlusive topical steroid therapy.
Oral antistaphylococcal antibiotics like flucloxacillin is used in the treatment.
Staphylococcal folliculitis (Bockhart's Impetigo)
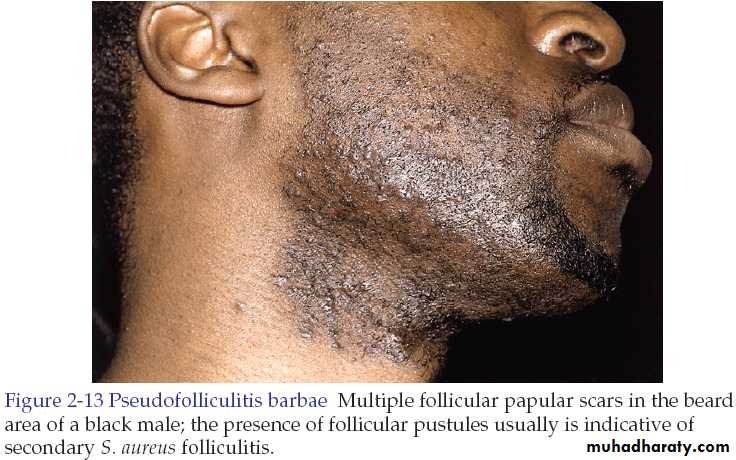
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
It is a foreign body reaction to hair. The condition occurs on the cheeks and neck in individuals who are genetically inclined to have tightly curled spiral hair, which become ingrown.Secondary bacterial infection may supervene.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
TreatmentStop shaving.
Dislodge embedded hair shafts by inserting a firm pointed instrument such as syringe needle under the hair loop and firmly elevating it.
A short course of antibiotics may hasten resolution.
Corticosteroid (prednisone at 40-60 mg/day for 5-10 days) may be used in moderate to severe cases to reduce inflammation around the hair follicles until the hair grows and is no longer an aggravating factor.
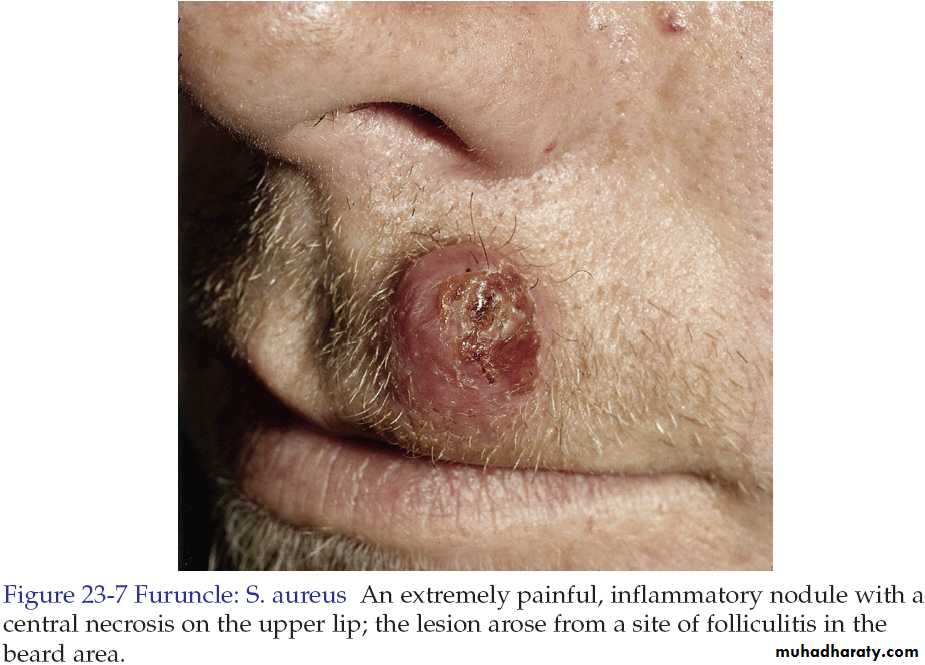
Furuncles and Carbuncles
Furuncle is a walled-off collection of pus that is a painful, firm or fluctuant nodule or abscess that evolves from folliculitis.
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common pathogen.
Lesions favor areas prone to friction or minor trauma such as underneath a belt, buttocks or axillae.
Furuncle (Boil)
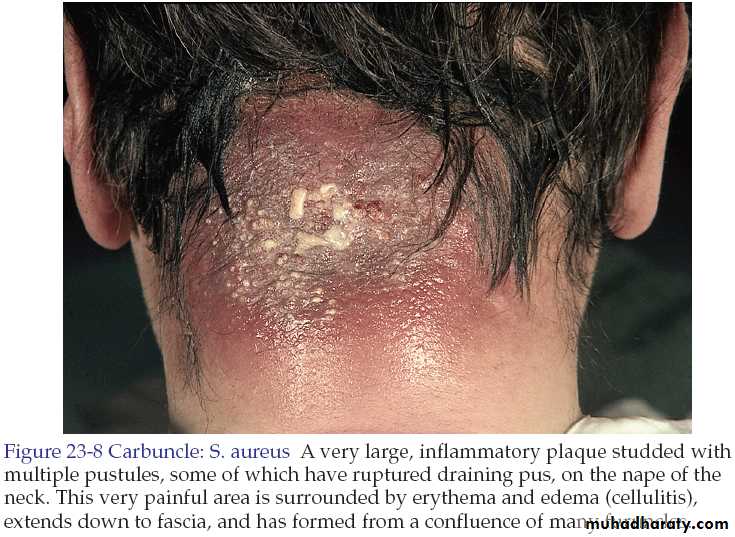
Carbuncle is an aggregate of infected follicles.
The infection originates deep in the dermis and the subcutaneous tissue consisting of interconnecting abscesses usually arising in several contiguous hair follicles forming a broad red swollen deep painful mass that points and drains through multiple openings.Carbuncle
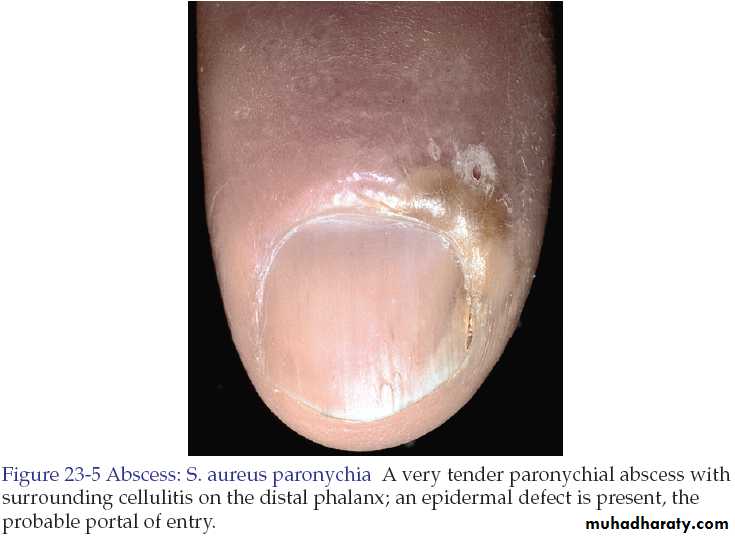
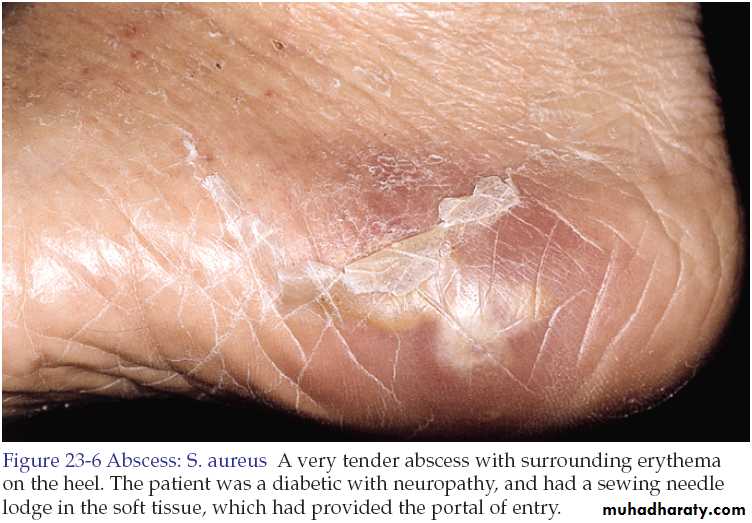
Abscess
An abscess is a circumscribed collection of pus appearing as an acute or chronic localized infection and associated with tissue destruction.Treatment
Many furuncles are self-limited and respond well to frequent applications of a moist warm compress.The primary management of cutaneous abscesses should be incision and drainage. The abscess is not ready for drainage until the skin has thinned and the underlying mass becomes soft and fluctuant.
Antistaphylococcal antibiotics for 5-10 days like cloxacillin, or flucloxacillin.
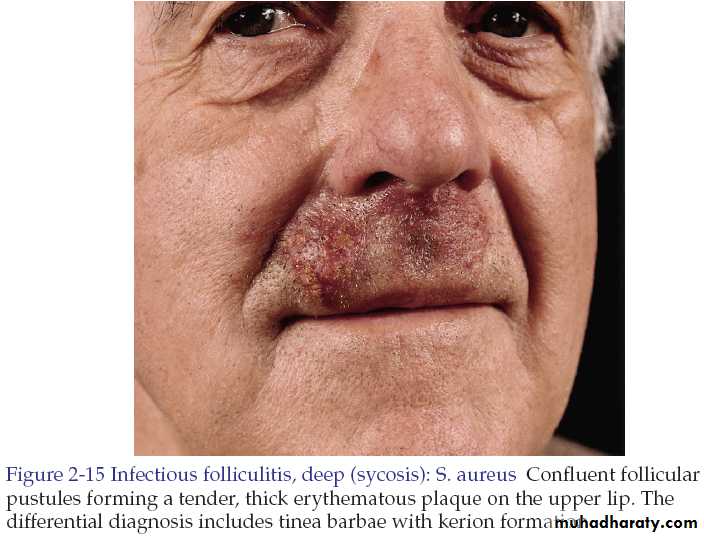
Sycosis barbae
It implies subacute or chronic pyogenic infection of the entire depth of the hair follicle in the beard and moustache areas.Staphylococcus aureus is the most common pathogen.
It begins with appearance of papules and pustules and rapidly becomes more diffuse as shaving continues. They may coalesce to form plaques studded with pustules.
The condition should differentiated from tinea barbae which is a dermatophyte fungal infection.
Fungal infections tend to be more severe, producing deeper and wider areas of inflammation while bacterial infections usually present with discrete papules and pustules.
Hair pulling is easy in fungal infections while difficult and pinful in bacterial infections.
Hair should be removed and examined for fungi by KOH examination and the purulent material should be cultured and examined by gram stain.
Treatment
Localized inflammation is treated with topical antibiotics like fucidic acid cream.Extensive disease is treated with oral antibiotics like cephalexin 500 mg 6 hourly orally for at least 2 weeks.
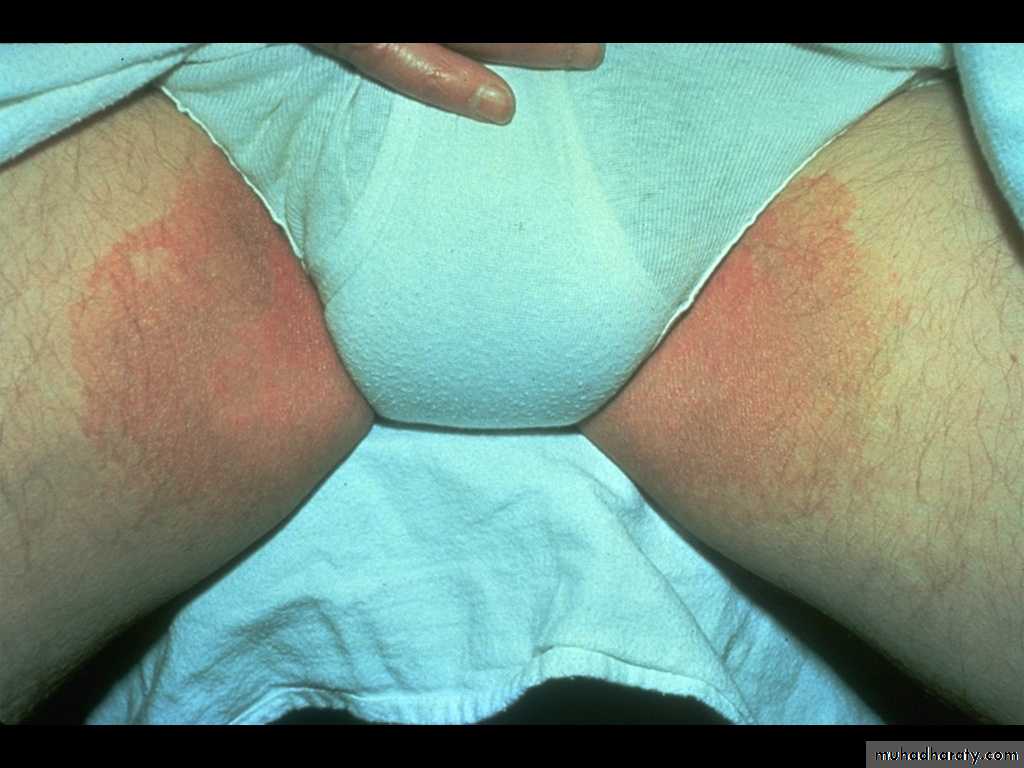
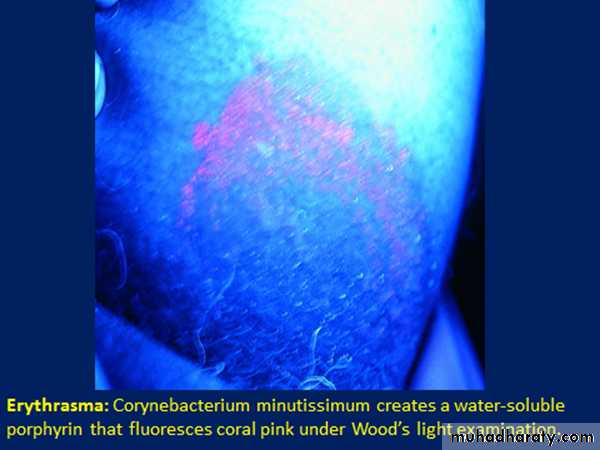
Erythrasma
It is a mild, chronic, localized superficial infection of the skin caused by bacteria known as Corynebacterium minutissimum.It affects mainly toe clefts, groins, axillae, intergluteal and submammary flexures.
There are irregular sharply marginated red-brown patches. Either smooth in new lesions or finely creased or scaly in older ones.
Usually the lesions are symptomless or with occasional itching.
Gives coral-red fluorescence under wood’s light
Erythrasma
Treatment
Topical erythromycin for 2 weeks.Or
For extensive lesions erythromycin orally 250mg 6 hourly for 10 days.
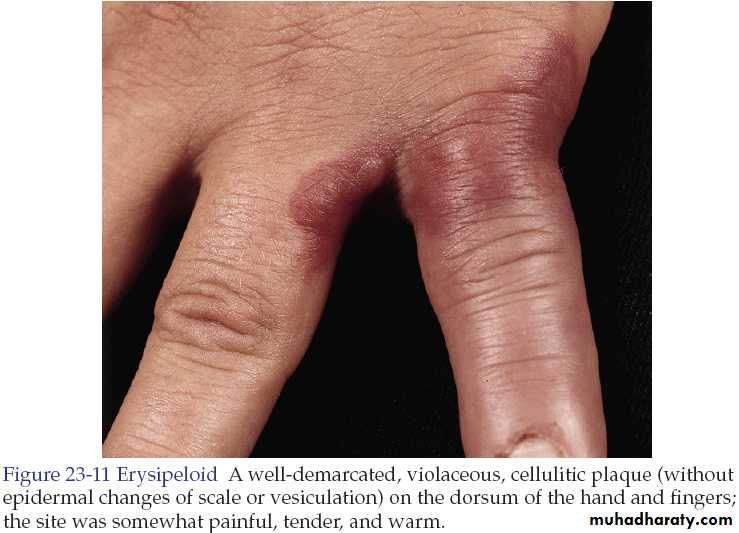
Erysipeloid
It is an acute infection of skin with Erysipelothrix rusiopathiae.The disease is transmitted from animals so it is common in butchers, cooks, fishermen, farmers and veterinary surgeons.
In the localized cutaneous type, there is violaceous and tender erythema on the inoculation site with extending irregular sharp border. Hands, fingers and forearm are common sites.
Treatment
It is self-limited disease heals without sequel within 2 weeks.In rare severe systemic infection erythromycin or ciprofloxacin.
Good luck