DR SAMI SALMAN, FRCP, MRCP, DMR, CES, MB,ChB
PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE & RHEUMATOLOGY

By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to:
Describe briefly the pathophysiology of Cervical
and Back pain
List the common causes, clinical features and how
to diagnose the different conditions leading to
back pain and cervical pain
Have a good idea as to how each condition can be
managed.
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
2

A '
human
condition‘
60-80%
of the world's population
Reported disability and absence
from work due to back pain have
increased
significantly in 30 years
.
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
3

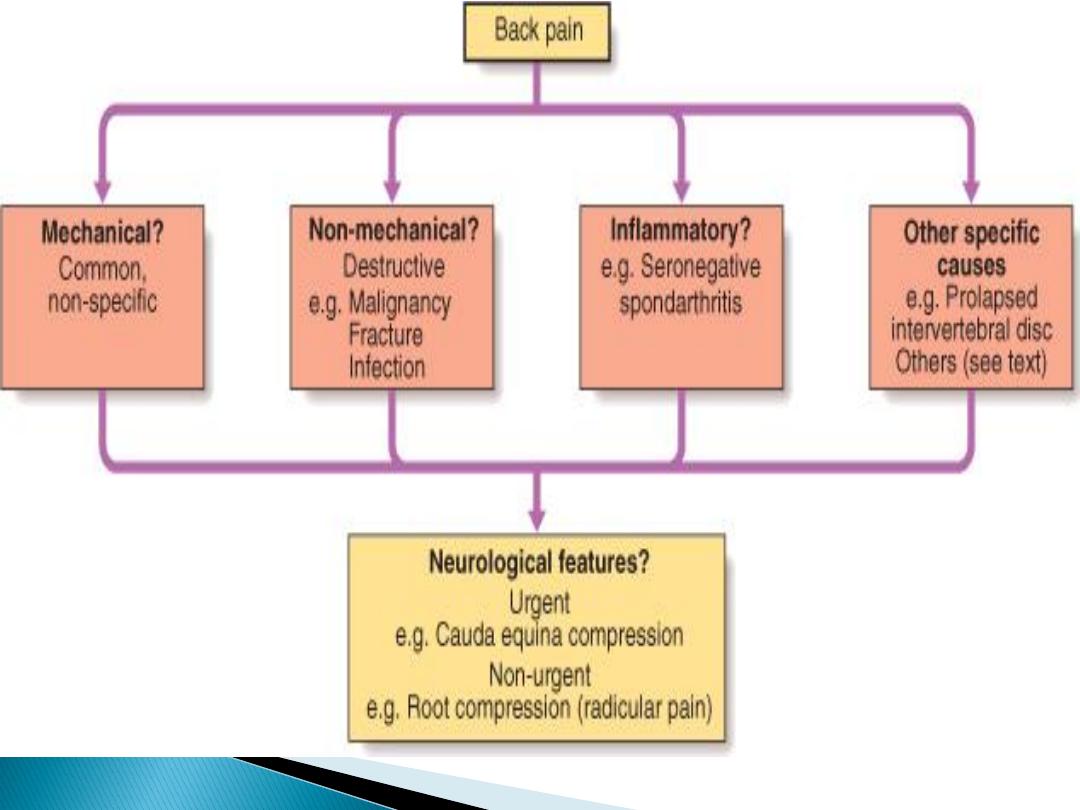
Minority
of patients have a
pathologically
definable
problem
The main role of history and
examination is to identify
the
small number
who have a
serious
or
specific
spinal disorder
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
4
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
5

90%
of back pain,
20-55 years.
Acute,
lifting or bending
Related to
activity,
relieved by
rest
Lumbosacral
, buttock or thigh
Asymmetrical
, and
does not radiate>
knee
Asymmetric
paraspinal spasm
and
tenderness, & painful
restriction of some
but not all movements
Occupations:
heavy lifting and twisting
(e.g. construction, agriculture and nursing)
Psychological
(job, depression, anxiety).
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
6

Constant,
little variation in intensity or
with activity
Anorexia, dyspepsia, change in bowel
habit, prostatism or abnormal per
vaginum bleeding
may indicate gastric,
pancreatic, colonic, prostatic or
gynaecological malignancies
Other
'red flags'
for serious spinal
pathology
If
spinal cord or cauda equina
lesion,
urgent neurosurgical assessment!
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
7

History:
Age
< 20 or >50
Constant,
unrelieved by rest
Thoracic
pain
PMH
- Ca, TB, HIV, corticosteroids
Constitutional
-sweats, malaise, weight loss
Trauma
Examination:
Painful
deformity
Severe/symmetrical
deformity
Saddle anaesthesia-
S3,4,5,
Neurological signs/muscle-wasting
Multiple levels
of root signs
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
8

Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
more gradual
onset and occurs before the age of 30.
Spondylitis: inflammation of the synovial joints
Axial (spine+ shoulder+ hips),
symmetrical and over many segments
Pain from
sacroiliitis
is maximal in the
buttock, radiating down the posterior
thigh.
Marked morning and inactivity stiffness
and improves with activity
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
9
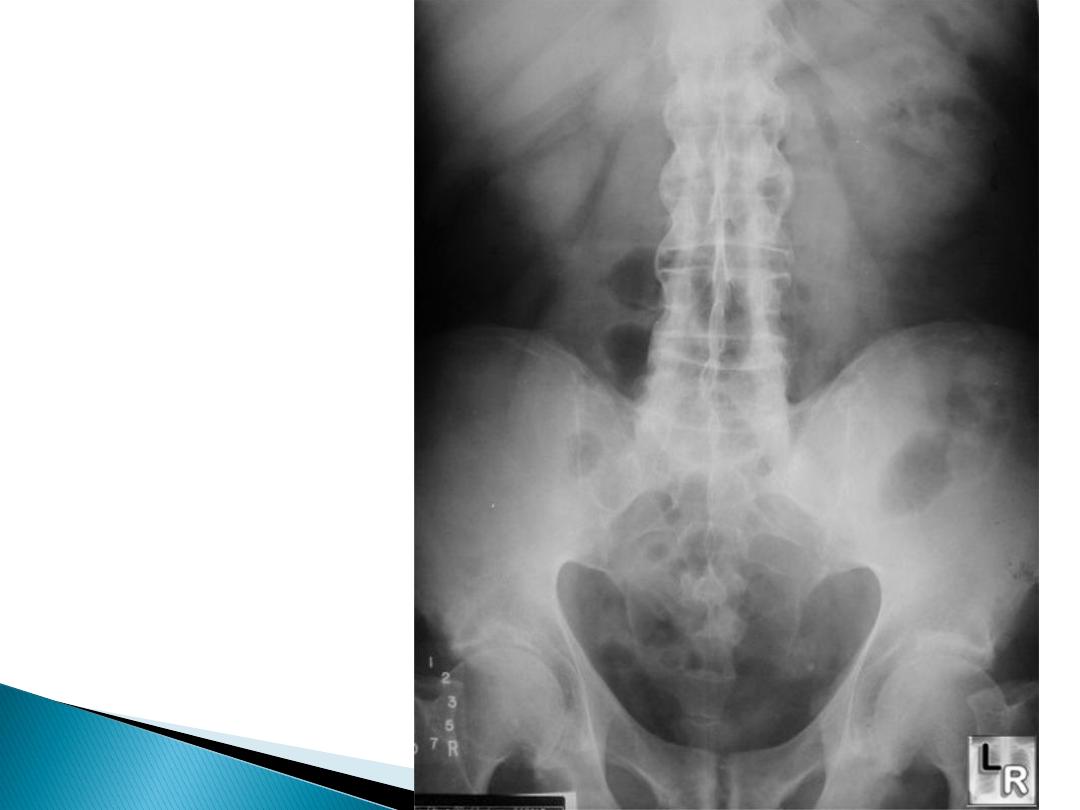
Bamboo spine
(Ankylosing
spondylitis)
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
10
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
11
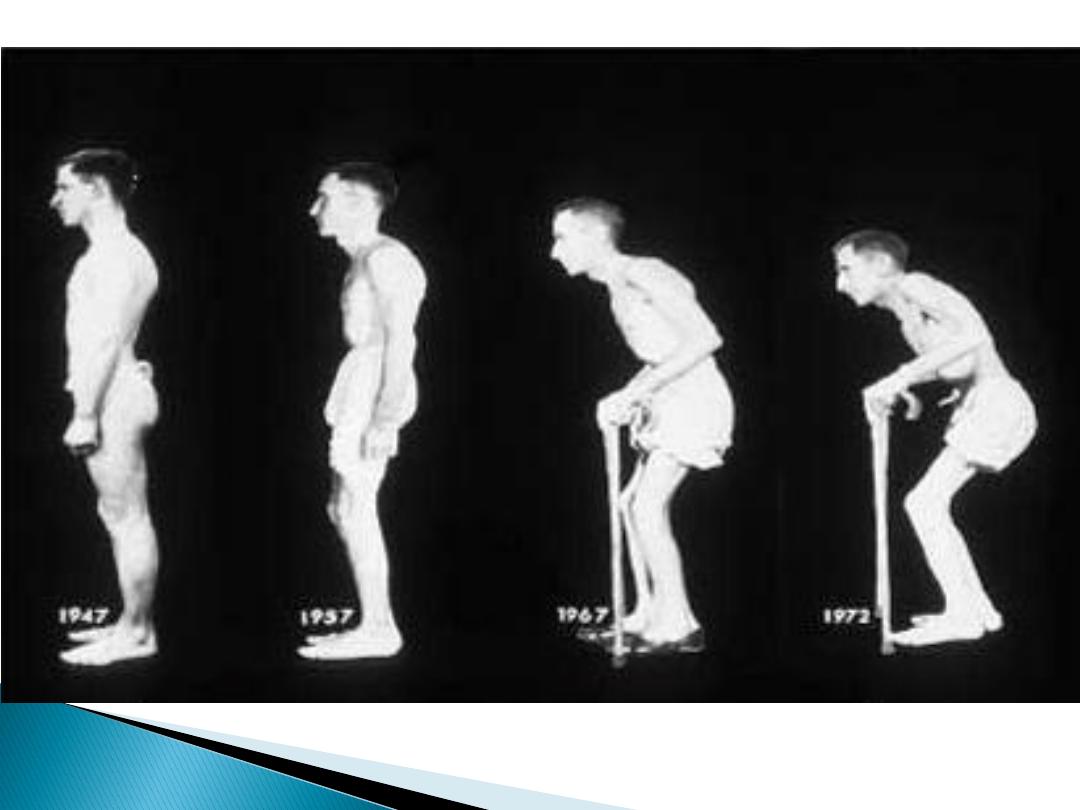
Progress of a patient with ankylosing spondylitis

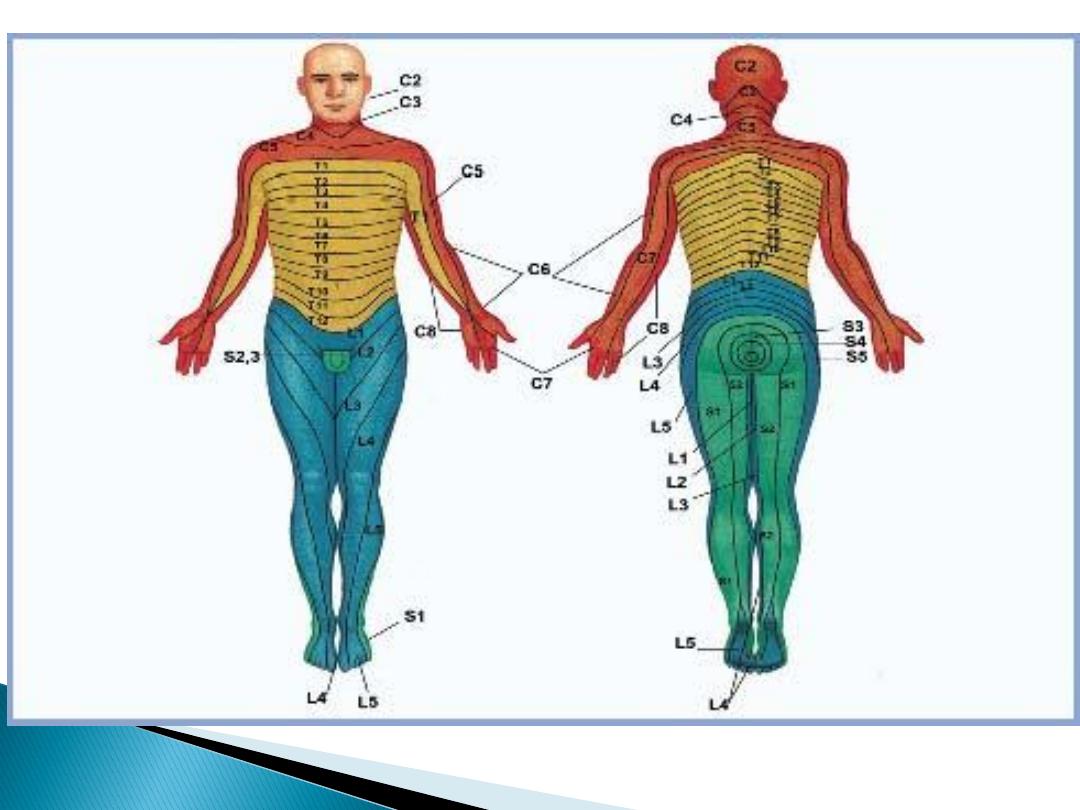
Features of nerve root pain:
Unilateral
leg pain> low back pain
Radiates
beyond knee
Paraesthesia
Nerve irritation
signs (reduced
straight leg raising)
Motor, sensory or
reflex signs
(limited
to one root)
Prognosis reasonable (50% recovery at
6 weeks)
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
12
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
13
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
14
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
15
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
16

17
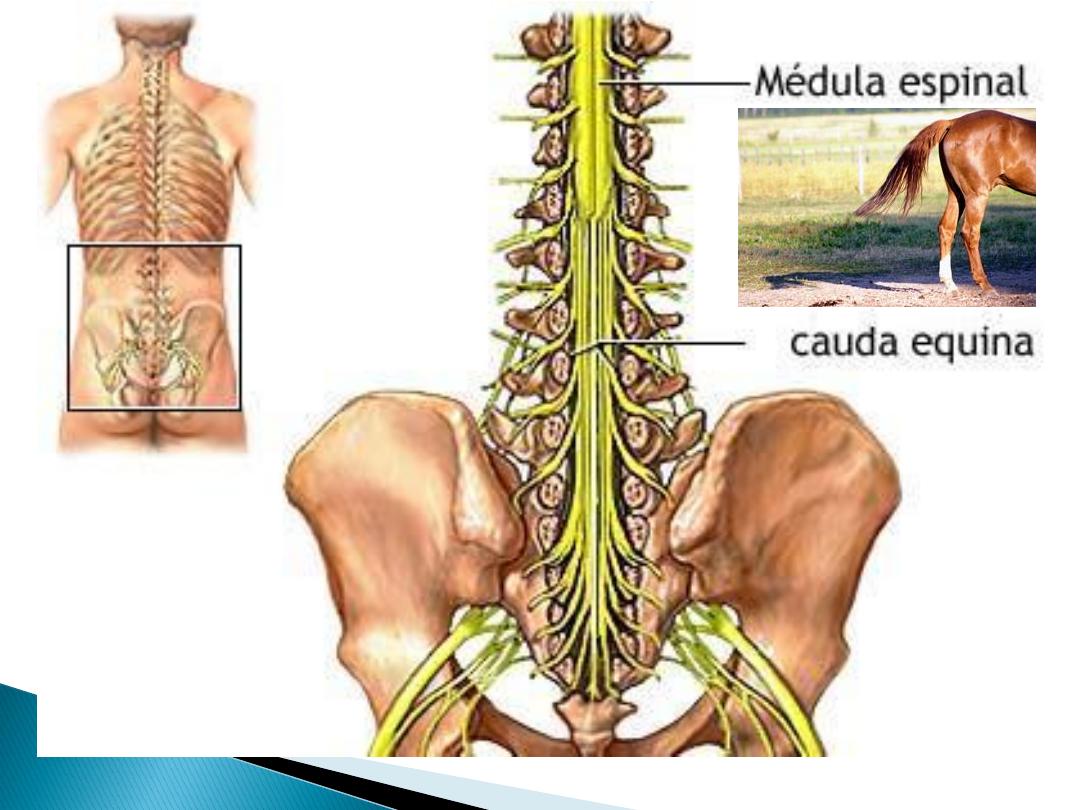
Features of cauda equina syndrome:
1. Difficulty with
micturition
2. Faecal
incontinence
3. Saddle
anaesthesia
4. Motor
weakness
/gait disturbance
5. Sensory
level
Cauda equina compression:
• Lower motor neuron lesion,
• Flaccid paralysis
(drop foot)
• Loss of sensation till the knee and not below!
• Plantars are down
• Retention of urine (emergency)
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman

Plain X-rays:
Rarely helpful, unless
red flags
are present
By the age of 50yrs, 60% of women and 80%
of men have radiographic features of
'spondylosis'
(vertebral sclerosis and
osteophytes, OA of apophyseal facet joints)
No clear correlation between spondylosis
and back pain.
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
18
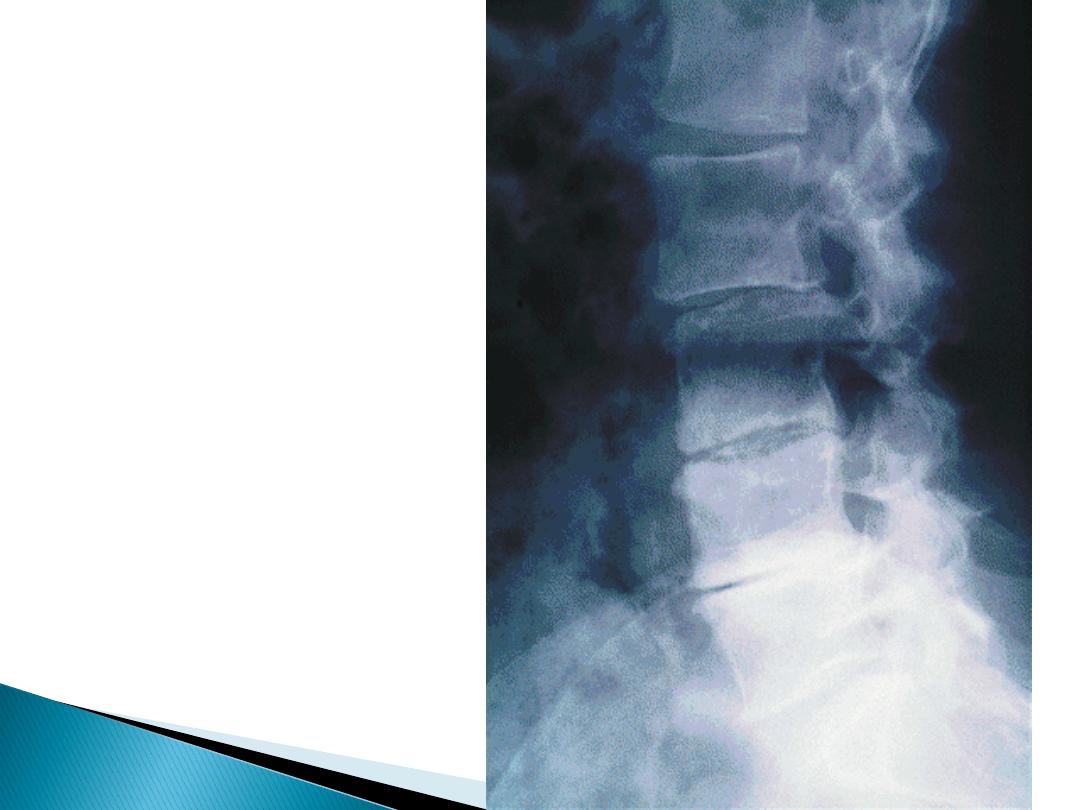
Lumbar
Spondylosis
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
19

Plain X-rays
may be helpful in
Persistent pain in a
young
patient to help
confirm a diagnosis of
AS
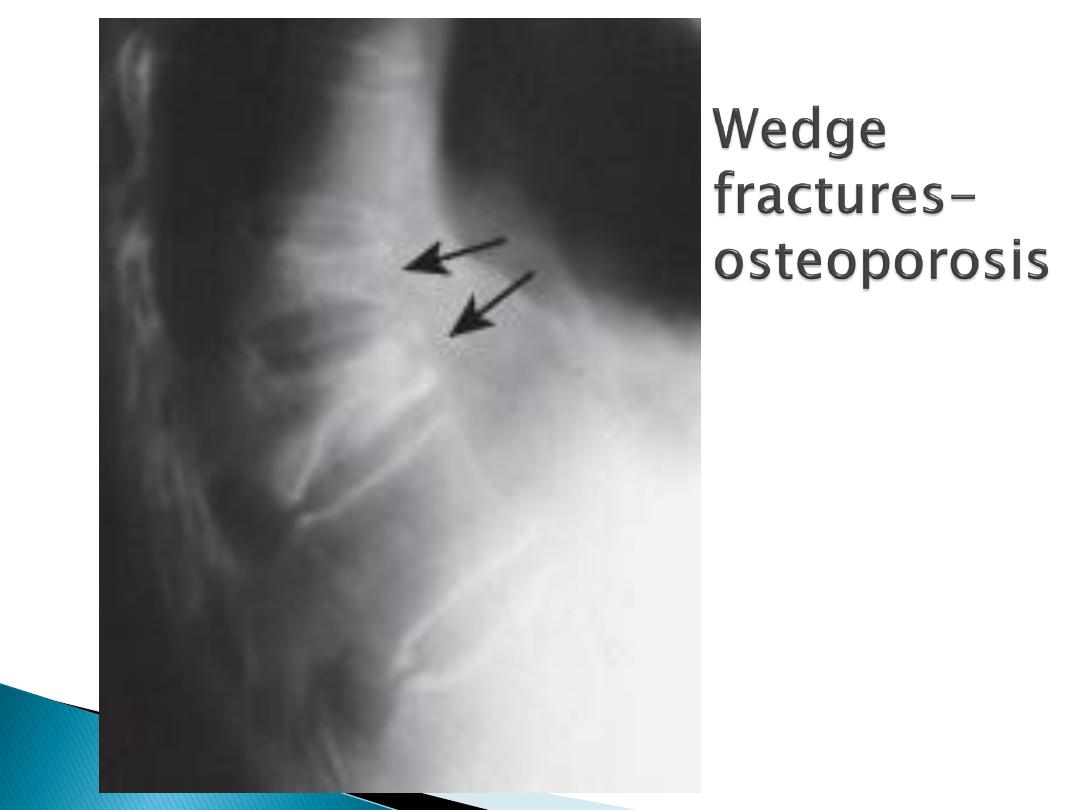
Osteoporotic vertebral fracture
, if H/O
trauma, corticosteroids, height loss or
clinical evidence of kyphosis.
Minor congenital abnormalities, eg
spina
bifida occulta
and
transitional vertebrae
,
are NOT associated with low back pain
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
20
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
21
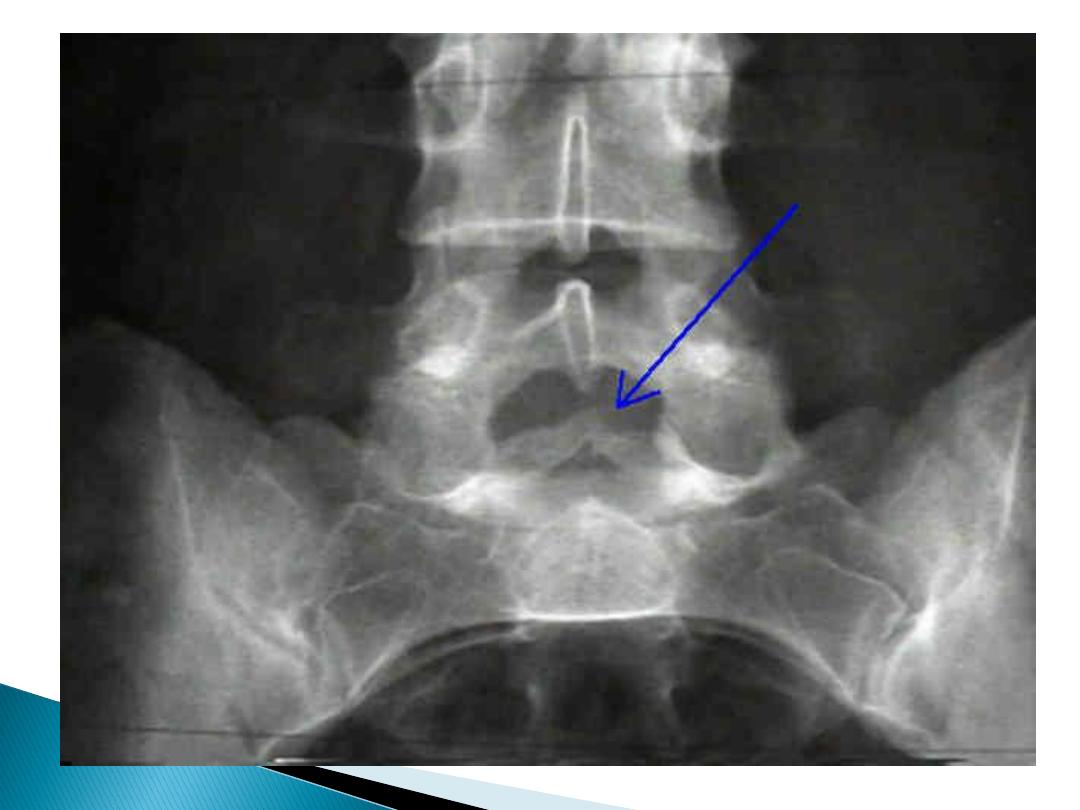
Spina
bifida
occulta
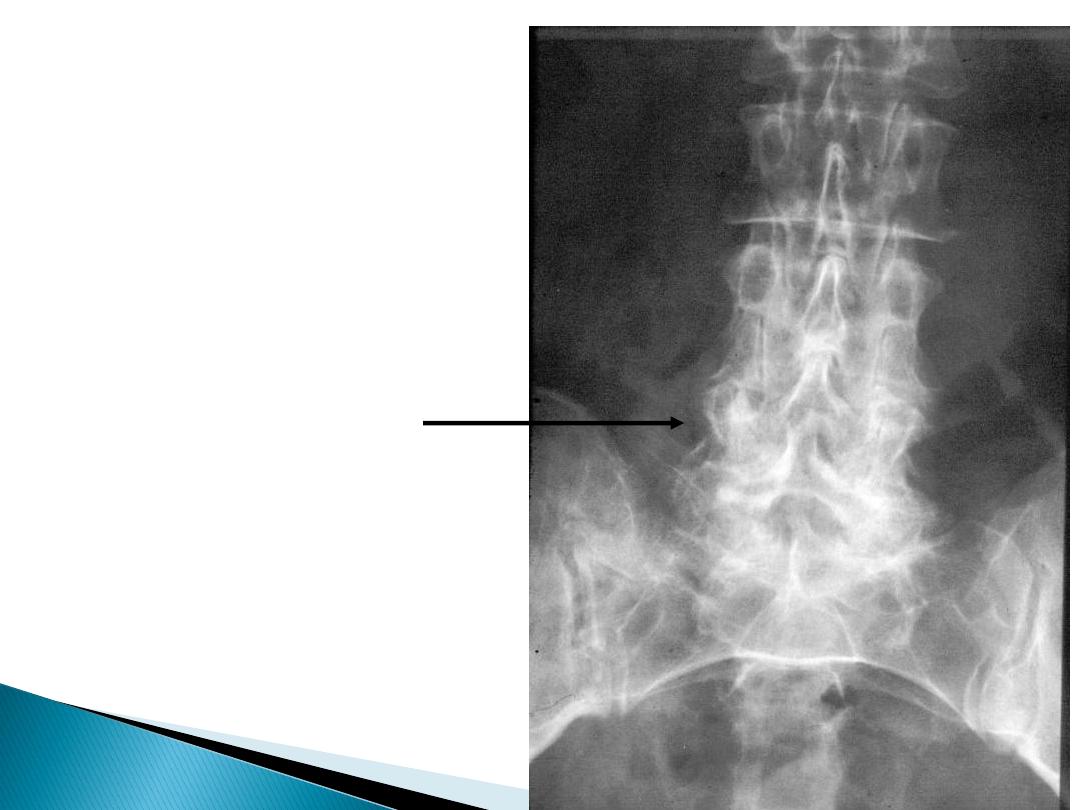
Transitional
Vertebra
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
22
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
23

If red flags
,
MRI,
even if plain X-rays are normal
CT
is inferior to MRI but is useful where MRI is
contraindicated (e.g. pacemaker or metallic clips)
A low Hb and raised CRP or ESR
: inflammation or
malignancy
A raised acid phosphatase or prostate-specific
antigen (PSA)
in metastatic ca of the prostate,
raised alkaline phosphatase
with other bone
metastases
Myeloma is associated with a monoclonal band
on
serum immunoelectrophoresis
and the
presence of urine light chains
(Bence Jones
proteinuria).
EMG and nerve conduction studies
, for nerve
root lesions.
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
24

Most mechanical low back pain
settle
spontaneously with simple analgesics
,
90%
recover
at 6 weeks
10%
Recurrences of pain
Patient education : pain
does not imply
harm
and that
exercise is helpful
not
damaging
.
Regular
analgesia
and/or
NSAIDs
, to
improve mobility and facilitate exercise
Return to work
and normal activity asap
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
25

Simple analgesia
Paracetamol or Paracetamol +Opiates
Muscle relaxants
NSAIDs
Ibuprofen, Naproxen or Diclofenac if
stomach OK
Selective Cox2 inhibitors if GI risk
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
26

Low-dose tricyclic antidepressant
drugs
provide analgesic, sleep and mood
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
27

Bed rest is
NOT
helpful!
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
28
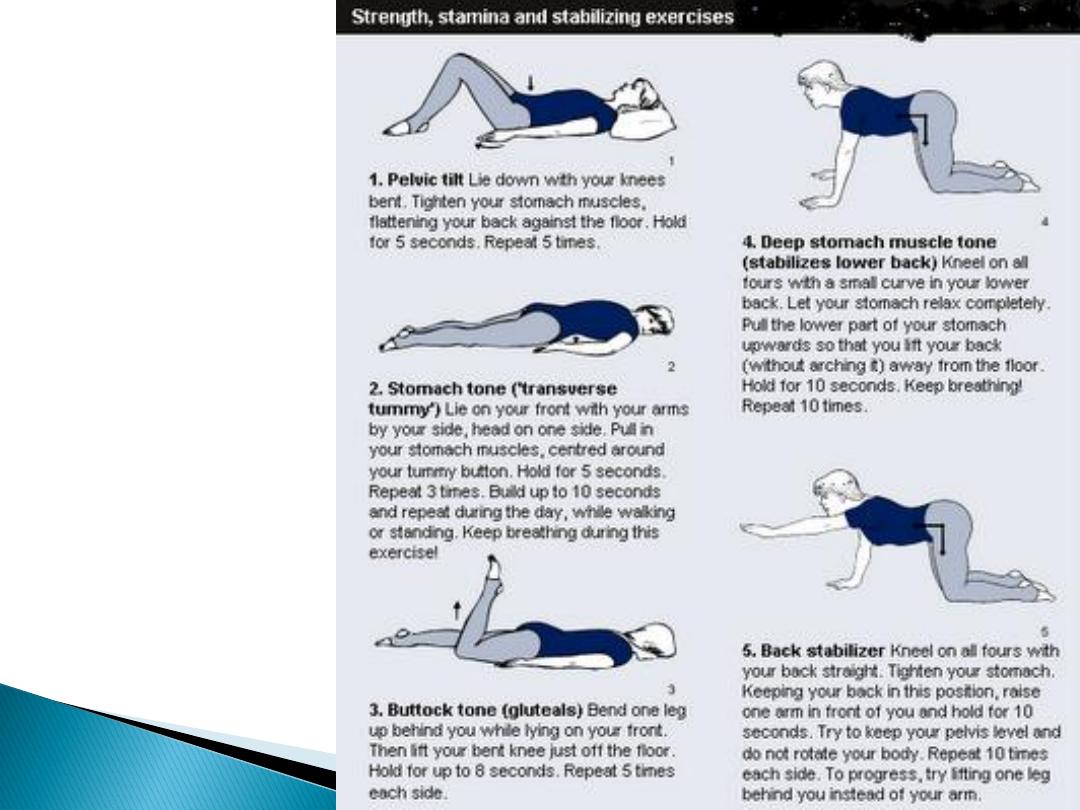
Physiotherapy
(e.g. passive
extension
and postural
correction)
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
29
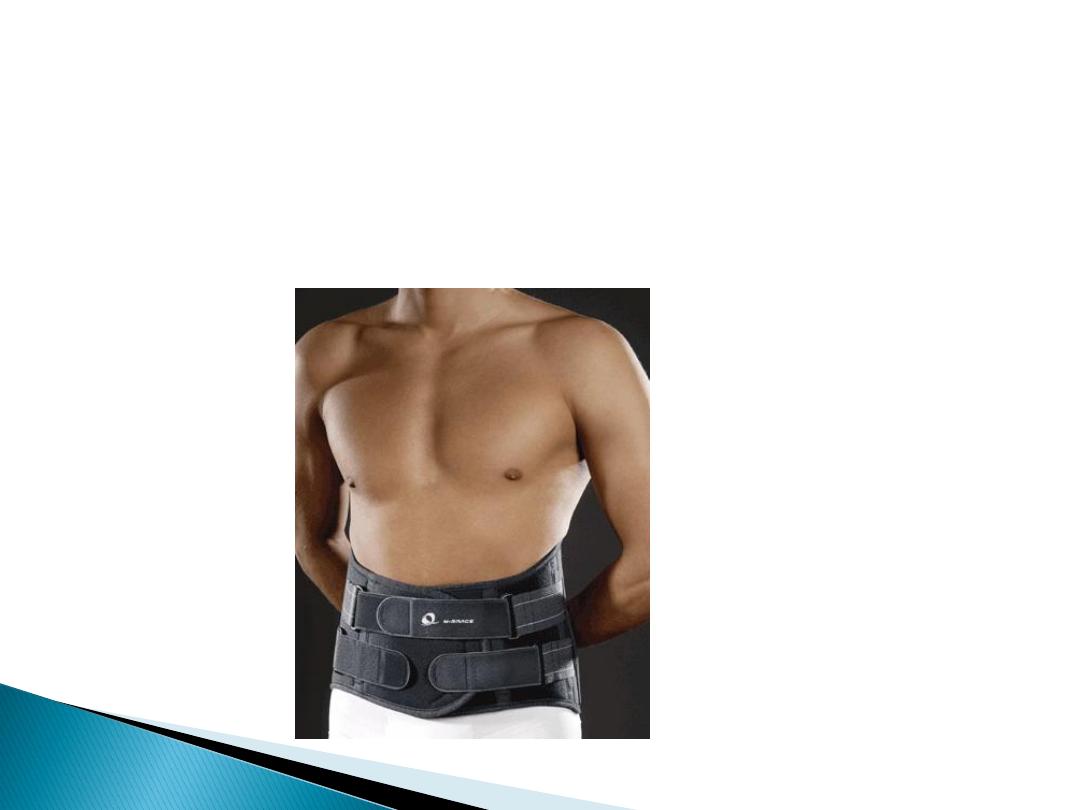

There is NO EVIDENCE from RCTs to
support other treatment modalities:
epidural
and
facet
joint injection,
spinal
manipulation
,
traction
and lumbar
supports
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
30

8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
31

Surgery
is needed in <1% of LBP
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
32

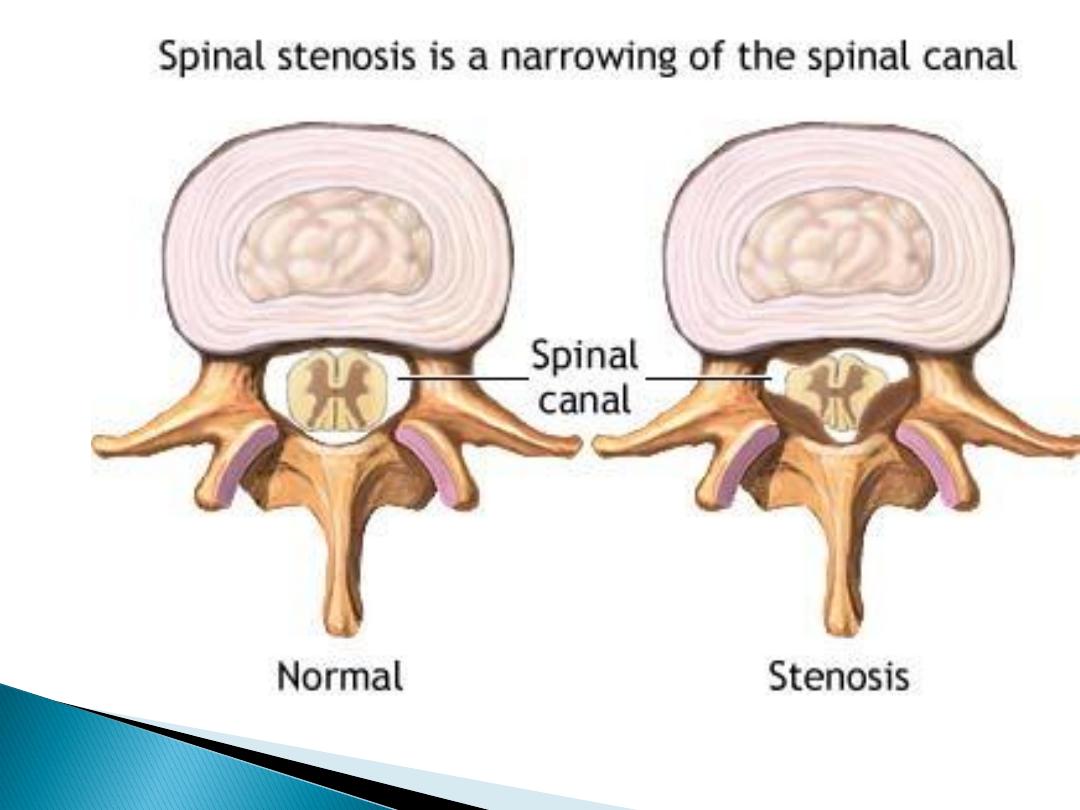
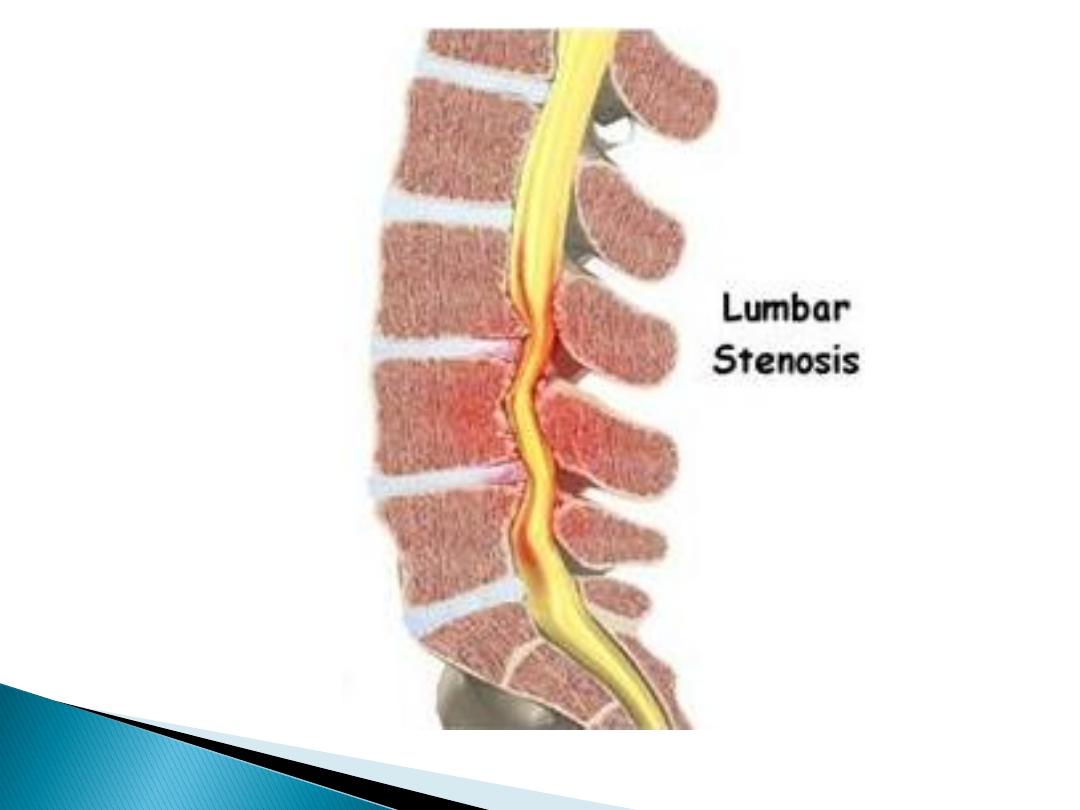
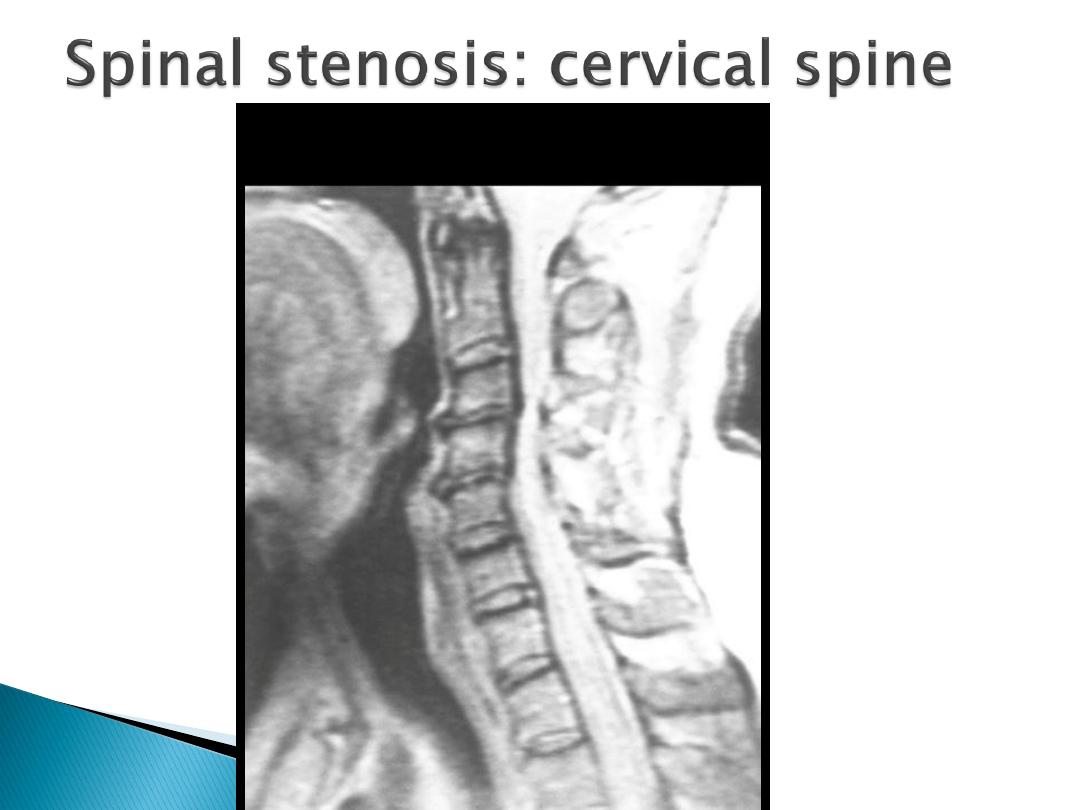
Spinal stenosis:
Symptoms occur due to
limitation of space in
the vertebral canal.
‘Pseudoclaudication' with discomfort in the legs
on walking that is
relieved by rest, bending
forwards (opposite to disc prolapse)
Simian posture,
with a forward stoop and slight
flexion at the hips and knees.
Diagnosis is confirmed by
CT/MRI
Decompression
is indicated if mobility or
quality of life is significantly impaired.
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
33
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
34
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
35
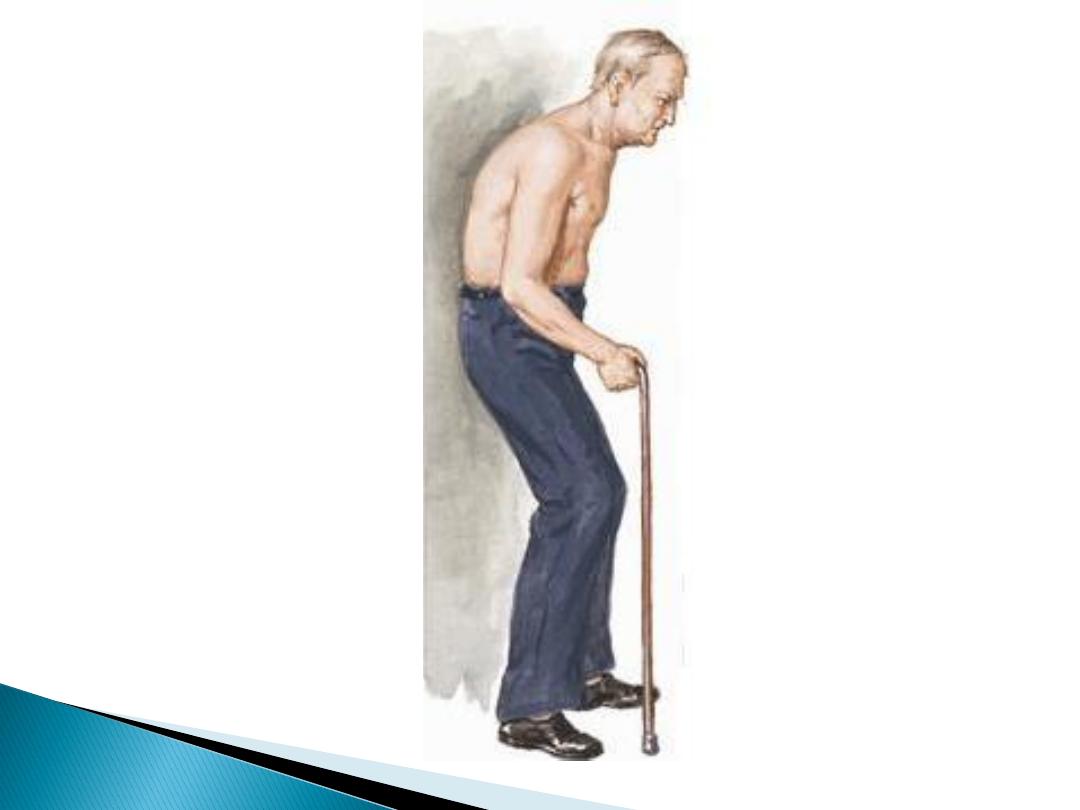

Simian
posture of
spinal
stenosis
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
36

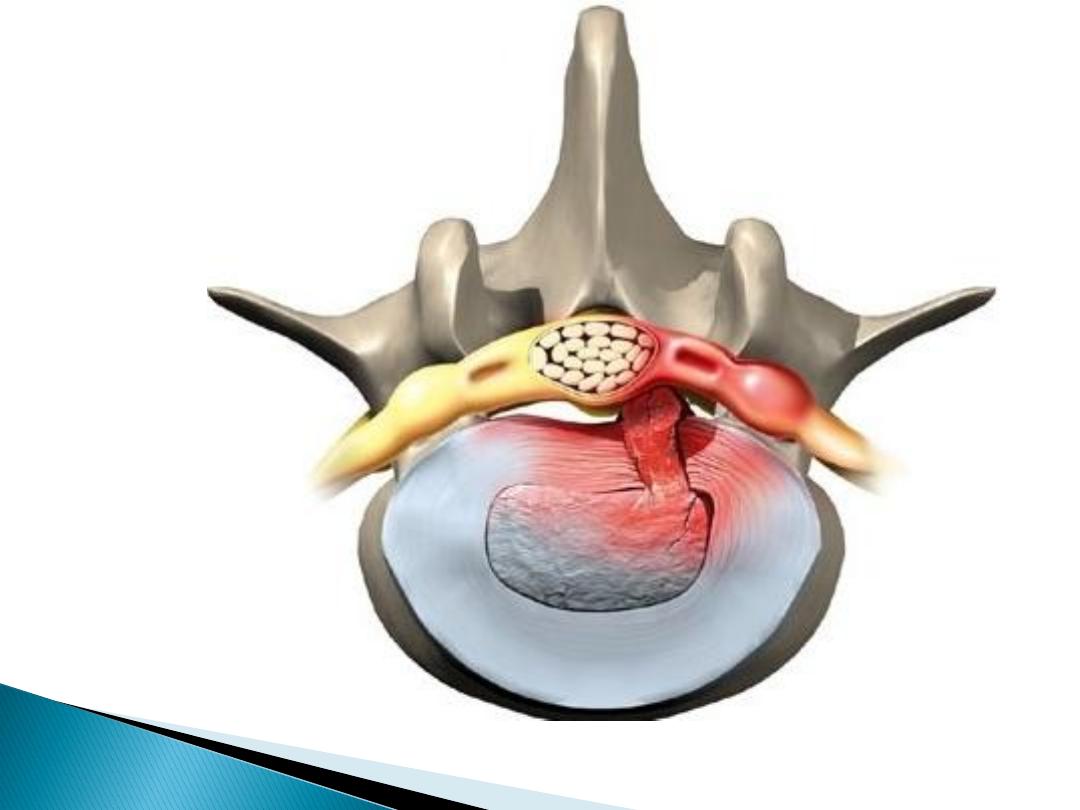
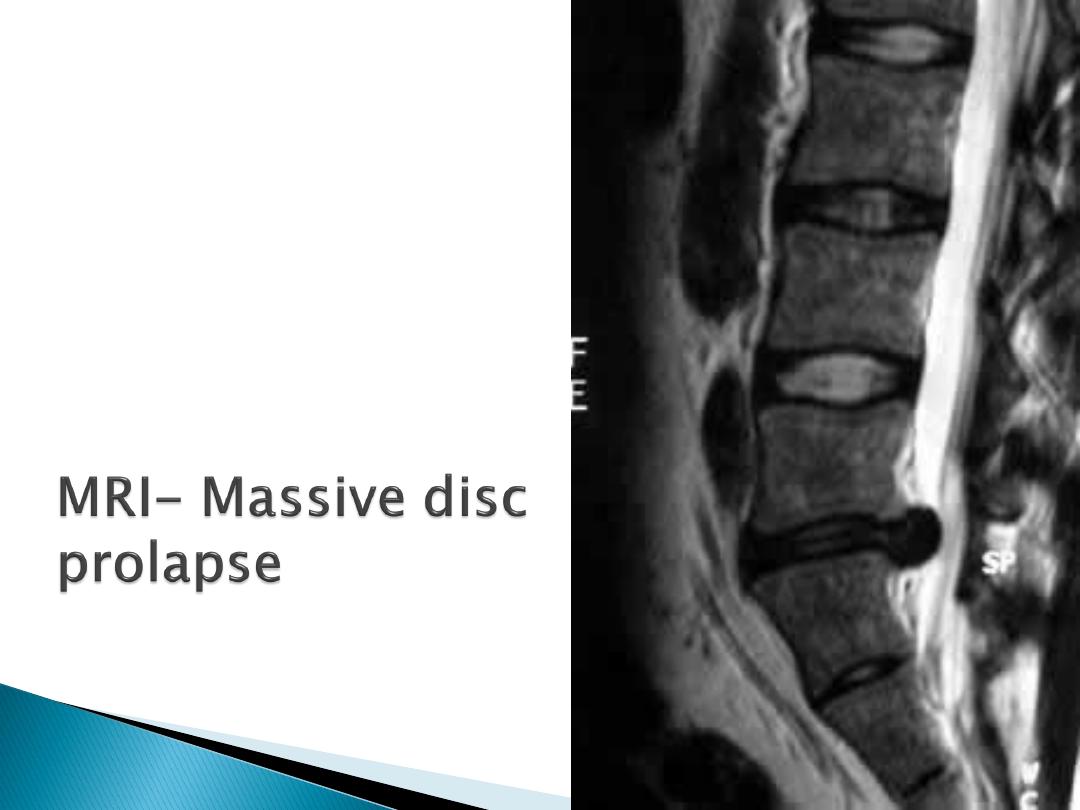
3- Prolapsed intervertebral disc :
Most frequently at
L4 and L5
Most first episode ages
20-30
yrs
Radicular pain
(invariably felt below the
knee) + evidence of
root involvement
(sensory deficit, motor weakness,
asymmetrical reflexes) and a
positive
sciatic or femoral stretch test.
About
70%
improve by 4 weeks
Persistent neurological deficit >6 weeks
is an indication to consider surgery..
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
37
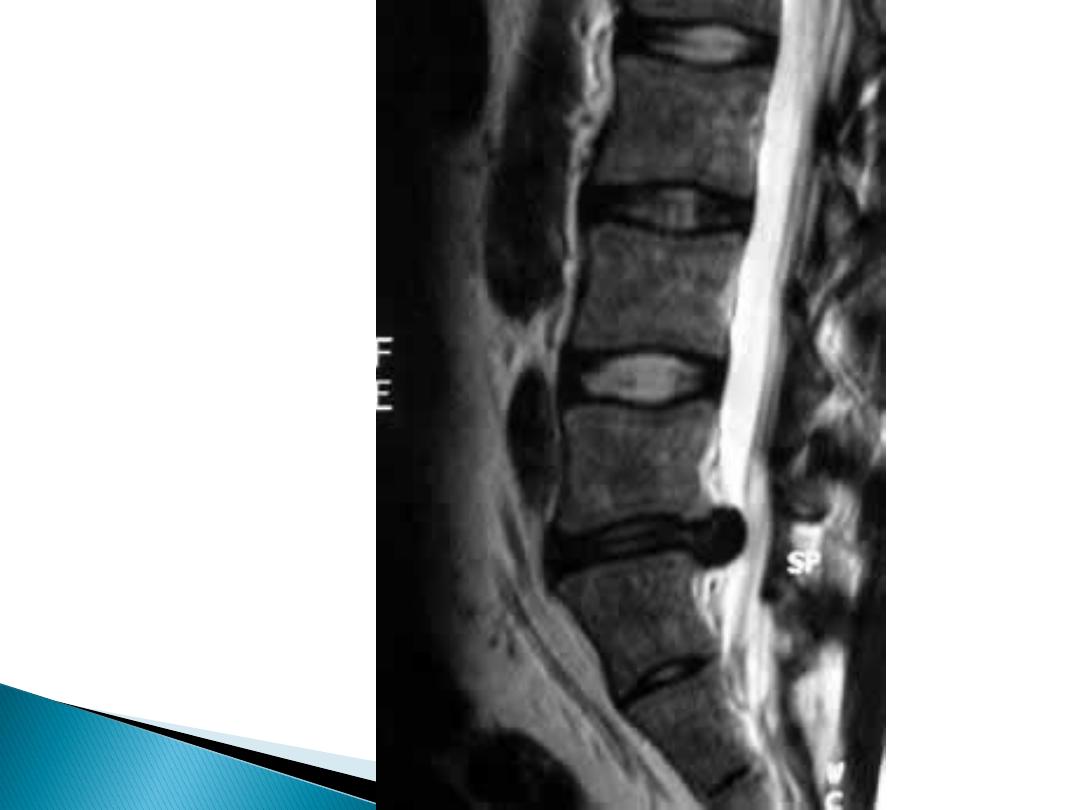
Specific causes of low back pain
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
38

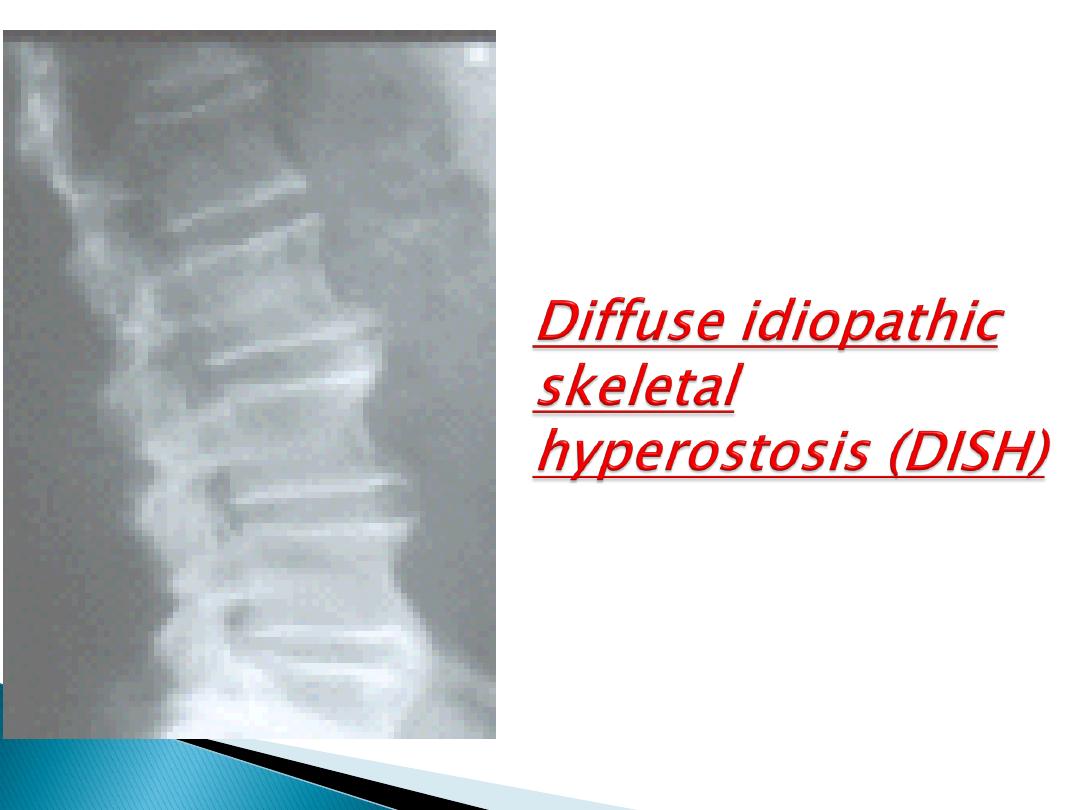
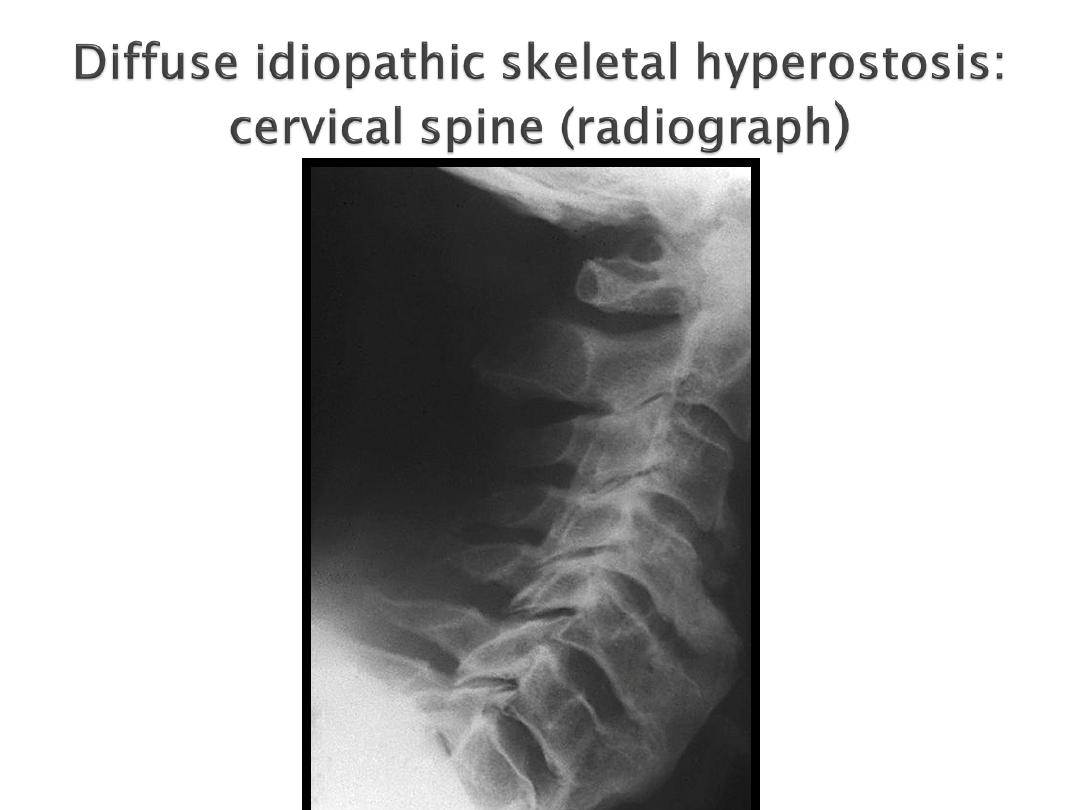
4- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH):
('Forrestier's disease')
Associated w
obesity, hypertension and
type 2 diabetes
Florid new bone formation
along the
antero-lateral
aspect of at
least 4
contiguous vertebrae
Distinguished from lumbar spondylosis by
the absence of disc space narrowing and
marginal vertebral body sclerosis
, and
from spondylitis by the
absence of
sacroiliitis or apophyseal joint fusion.
Usually an
asymptomatic
radiographic
finding
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
39
Specific causes of low back pain
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
40

Mechanical or degenerative problems
Serious spinal disease needs to be
excluded using the same principles as
for low back pain.
Most transient mechanical neck pain is
not associated with demonstrable
spinal pathology..
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
41

Mechanical
Postural
Whiplash injury
Disc prolapse
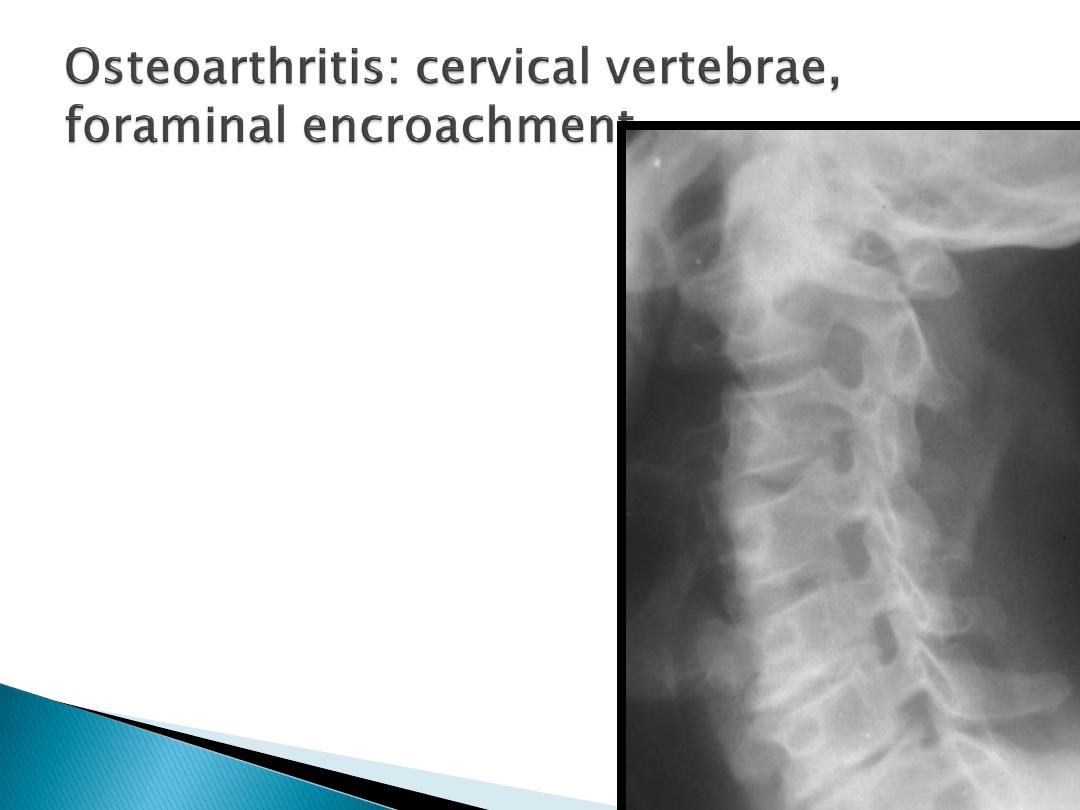
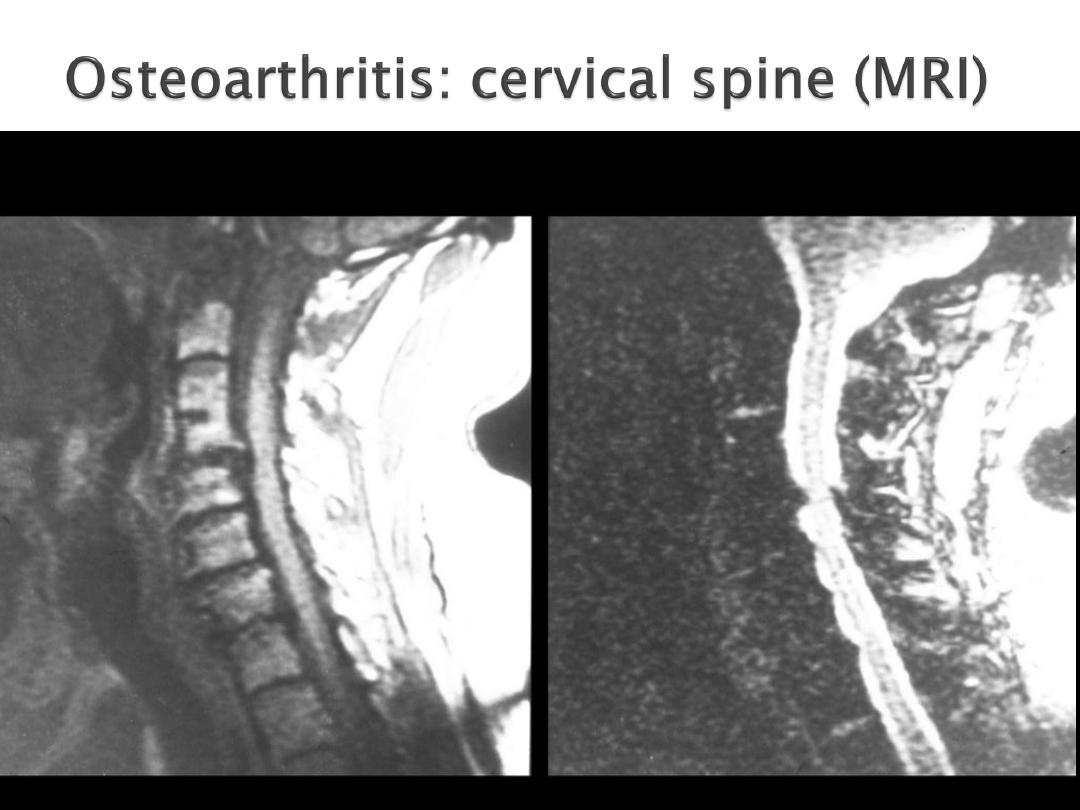
Cervical spondylosis
Inflammatory
Infections
Spondylitis
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
RA
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Metabolic
Osteoporosis
Osteomalacia
Paget's disease
Neoplastic
Metastases
Myeloma
Lymphoma
Intrathecal tumours
Other
Fibromyalgia
Torticollis
Referred Pain
Pharynx
Cervical lymph nodes
Teeth
Angina pectoris
Aortic aneurysm
Pancoast tumour
Diaphragm
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
42

Often poorly localised.
Pain from upper segments may radiate
to the occiput, temple or face
Pain from lower segments radiates to
the scapula, shoulder, arm and
occasionally chest wall.
Mechanical neck pain is often acute in
onset and associated with asymmetrical
restriction of neck movements
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
43

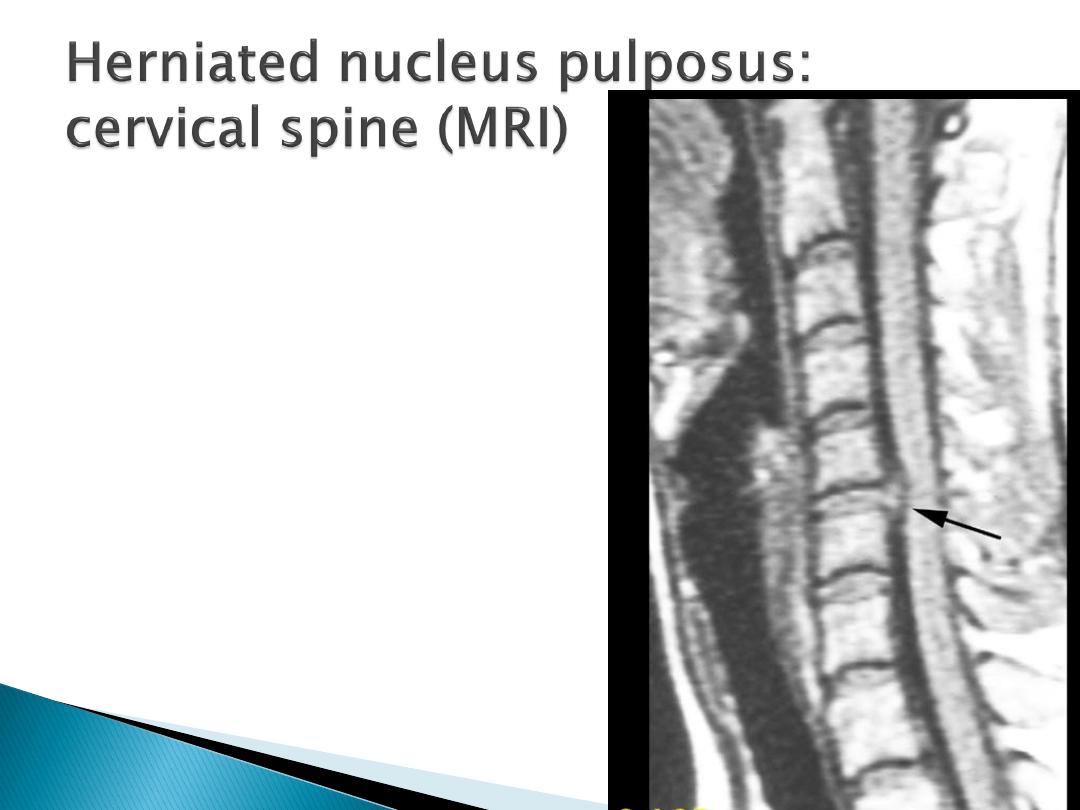
Radicular pain may arise from
compression by osteophyte or disc
prolapse.
70% C6 disc, compressing the C7 root,
20% C5 and compress the C6 root.
Massive cervical osteophytes or DISH
May cause dysphagia due to
oesophageal indentation.
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
44

The principles of investigation and
management are identical to those for
low back pain
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
45

Surgery is only required when there
are neurological signs of
radiculopathy or progressive cervical
myelopathy
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
46
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
48

8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
52

DR SAMI SALMAN, FRCP, MRCP, DMR, CES, MB,ChB
PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE & RHEUMATOLOGY
http://www.samisalman.comyr.com

Challenge 1: A 45 year old has sharp or burning pain radiating down
the lateral or posterior aspect of the leg to the ankle. There's a little
bit of numbness and tingling. What's the diagnosis?
Challenge 2: A 70 year old man presents with urinary retention with
overflow incontinence, bilateral shooting pain down the back of his
legs, and leg weakness. You note perianal anesthesia. What's the
diagnosis?
Challenge 3: A 16 year old IV drug user presents with low back pain
after a day of heavy lifting. He has no other symptoms and no other
medical problems. Do you image his back?
Challenge 4: A 30 year old woman who is a smoker presents with
low back pain after sleeping funny for a week. She has no other
symptoms and no other medical problems. Do you image her back?
8 October 2015
back&neck pain SSalman
54



