-
:
Personality
*Group of triats that are dynamically organized and differentiating each person from others in
behaviors, emotion
-
:
personality
that explain
Theories
*
1-Freud's psychoanalytic theory.
●Most of our behaviors are unconscious.
●Part of our personality that contain memories, beliefs, feeling, urges, instincts that in which
individual not aware.
●Since the unconsciousness is unobservable directly, so it is necessary to interpret.
Clues to unconscious
●Some of information are at pre conscious state which are easily brought to mind like 2+2=4.
●But deeper in the unconscious are instinctual derives, wishes, desire are hidden from conscious
awareness, because conflict and pain if they aware every day.
-
:
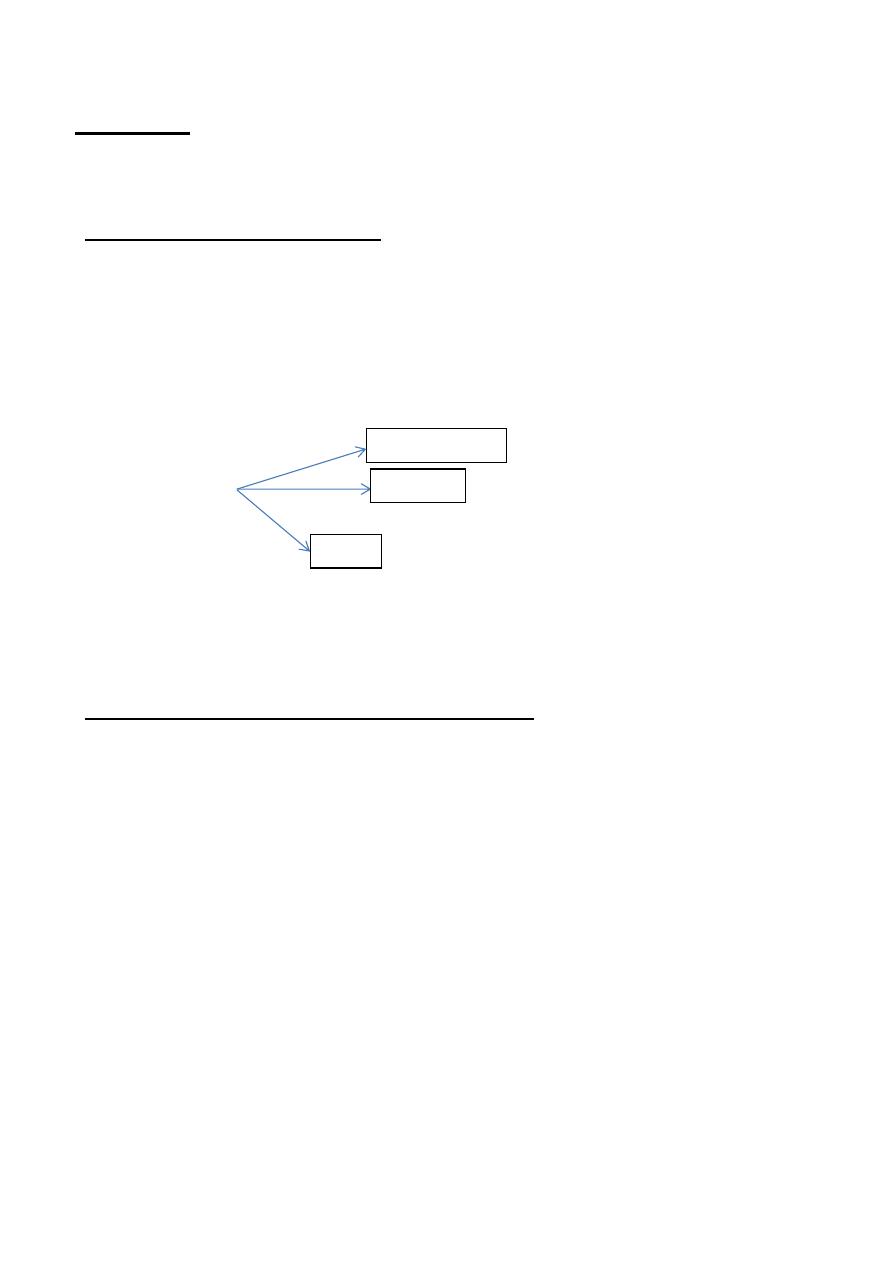
, SUPEREGO
1D, EGO
-
lity :
Structuring persona
*
1-1D:-It operates according to (pleasure principle)
-Immediate gratification and desire.
-Reduction of tension.
2-Ego :-
-Strive to (balance) the desires of ids.
-Dealing with (reality principle).
-Restrain the (immediate instinctual energy).
-It is (executive) of personality, it makes decision,
control of action, solving high order.
Slips of tongue
Fantasies
Dream

3-Super ego:-
-Develop in childhood in response to (right and
wrong) as society or parent modeled.
-It compose of (conscience) which prevent us from immoral behaviors
-Help to control impulsive behaviors.
-Searching for (perfectionist).
psychosexual stages
-
Developing of personality :
*
●Freud proposed five psychosexual stages.
●Conflict between demand of society and sexual urges of person.
●Fixation :- failure to resolve such conflict person develop fixation, like oral fixation :- interest in
drinking, smoking anal fixation :- lead to state of obsession.
-
:
5 stage are
1-Oral stage :- (0-1 year)
●Child focus on mouth as focal pleasure.
●Weaning of breast feeding lead to oral fixation.
2-Anal stage :- (1-3 year).
●Major source of pleasure is anal area.
●Child have pleasure from both retention and expulsion of feces,
●Fixation during anal stage might result in rigidity, orderliness.
3-Phalic stage :- (3-5 year)
●Interest and pleasure in gentelia by fondling them.
●(Oedipal complex) :- (5-6 year)
*As child focus on gentelia, according to Freud at this time male unconsciously developed sexual
interest in his mother.
*Child begin to see his father as rival, and harber wish to kill him.
*Child fear of father as powerful he develop complexity of (castration anxiety) (loss of penis)
is process of imitating father behavior, developing of beliefs, Morales by
-
:
dentification
I
identifying father and seeking woman like his unattainable mother. All steps lead to resolution of
(oedipal complex) for female, she started to develop sexual arousal toward father and begin to develop
envy. blaming mother for absence of penis (missing) in girl charing mother with their castration.
Feeling lead to (inferior feeling of woman to man).
4-5year-adolescent
●Which last until puberty,
●Sexual interest became dormant, even unconscious, until adolescent stage sexual arousal start to
reemerge again.
5-Gential stage (adolescent-adulthood)-
-Reemergence of sexual interest and establishment of mature sexual relationship.
Freudian Psychoanalysts : building on Freud
-
The Neo
*Group of successors who were trained on traditional Freudian theory,
*Later on they rejected some of its major point, these theories are known as
Neo-Freudian psychoanalyst.
*Theory focus more on the social environment and minimizing the importance of sexual deriving force
in people's lives.
*They also pay greater attention on the effect of society and culture on development of personality.
Jung's collective unconscious
-
1
-One of influential Neo-Freudian, Carl Jung.
-He reject the Freud primary importance of unconscious sex urge.
-Collective unconscious
:- Jung suggest universal
●idea, feeling, image, symbols, that we inherit from our relatives, the whole human races, and even
nonhuman animal ancestor from the distance past.
●example (fear of snake, dark media, full from high).
●archetype:- like publicity of (star war) movies due their use broad of good (Luke Skywalker).
●Jung approached personality below area of psychology.
Freudian perspective
-
orny's Neo
H
-
2
-Karen Horney sometime feminist psychologist.
-She suggested (personality) development progress in content (social relationship) and
-depend basically on relation between parent and child and how needs met.
-She stress on (cultural factors) :-
●Society rigid gender role for women lead them to experience of (ambivalence) about success.
●Fearing of making enemies, if they are too successful (1930,1940) which leaded to
●idea of (femminizim), that emerged decade later.
Fredian
-
Adler and Others Neo
-
3
-Alfred Alder, also misplaced of Freudian sexual need.
-He focus on primary human motivation is striving for (superiority) over others.
-(inferiority complex) :-
●Situation on which adult have not been overcome the inferiority feeling that developed during
childhood when they were small with limited knowledge.
Erikson Erikson
-
4
-Who developed psychosocial.
-Focus less on sexual and aggressive drives and more focusing on cultural factor behind personality.
