• Introduction to Neuroanatomy
• Objectives of lecture• List the anatomical terms used in neuroanatomy and the difference in their use in gross anatomy and neuroanatomy.
• Describe the planes of sections.
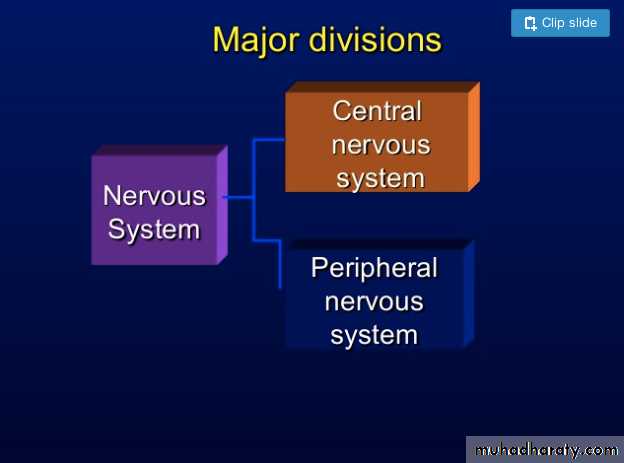
• Describe the anatomical divisions of the nervous system.
• List the neuronal and non-neuronal cells of the nervous system and their major functions.
• The terms: anterior, posterior, superior, and inferior are used in reference with the body axis (which doesn’t bend).
• The terms: dorsal, ventral, rostral, and caudal are used in reference with the long axis of the nervous system (which bends).
• Anatomical Terms in Neuroanatomy:
• The terms: medial, lateral, superficial, and deep have the same use as in gross anatomy.
• The term: ipsilateral means on the same side.
• The term: contralateral means on the opposite side.
• Anatomical Terms in Neuroanatomy
Dorsal
Ventral
Anterior
Posterior
Rostral
CaudalInferior
Superior
Terminology
In reference to the BRAIN
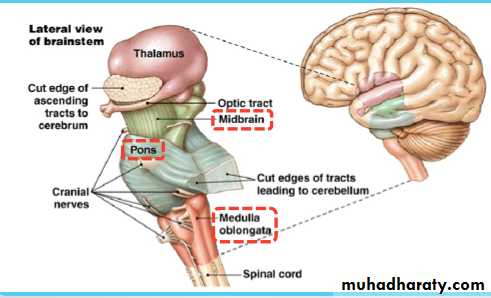
Brainstem & spinal cord
VentralDorsal
RostralCaudal
Anterior
Posterior
Superior
Inferior
Ipsilateral
same side mid-line
Contralateral
opposite side of mid-line
This tract of fibers decussates.
It crosses the midlineTerminology
Afferent - towardEfferent - away from ~
Afferent
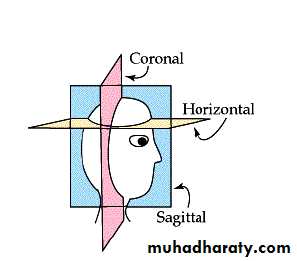
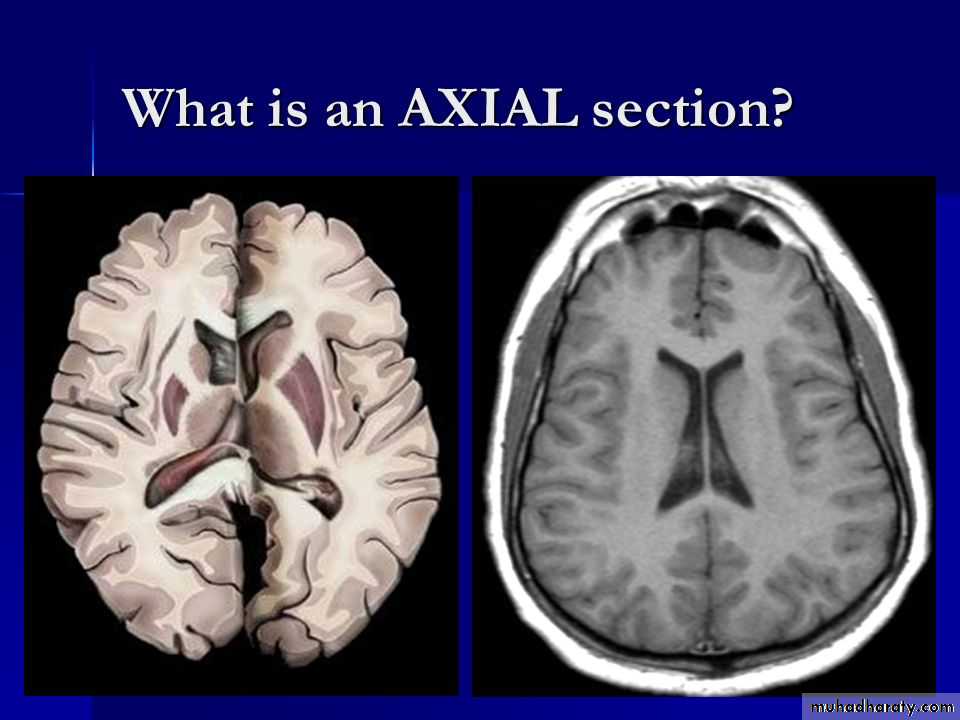
Efferent• Horizontal (axial): divides into above and below.
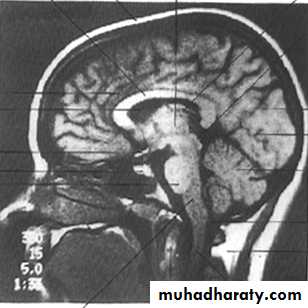
• Coronal (frontal): divides into front and back.• Sagittal: divides into twos sides.
• Planes of Section Neuroanatomy:
Before we can investigate the interior of the brain by cutting it up we need to define the planes of the brain that we will cut (section) in.
Going to a higher horizontal (axial) plane is going rostral. Going down towards the spinal cord and cauda equina is going caudal.
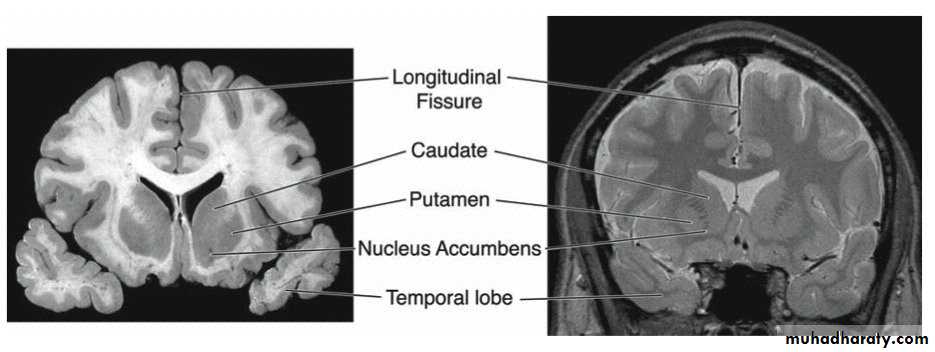
The coronal plane is also known as the frontal plane
Coronal section
Sagittal section
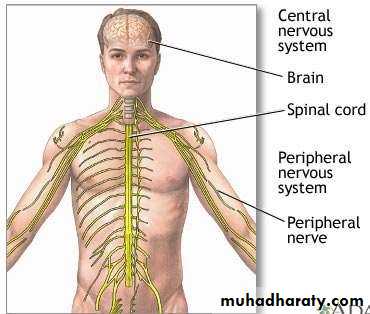
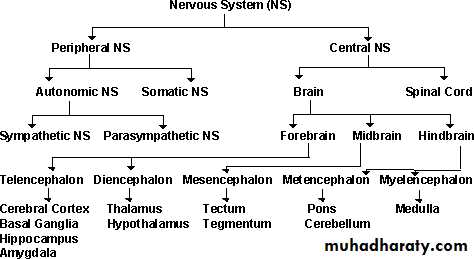
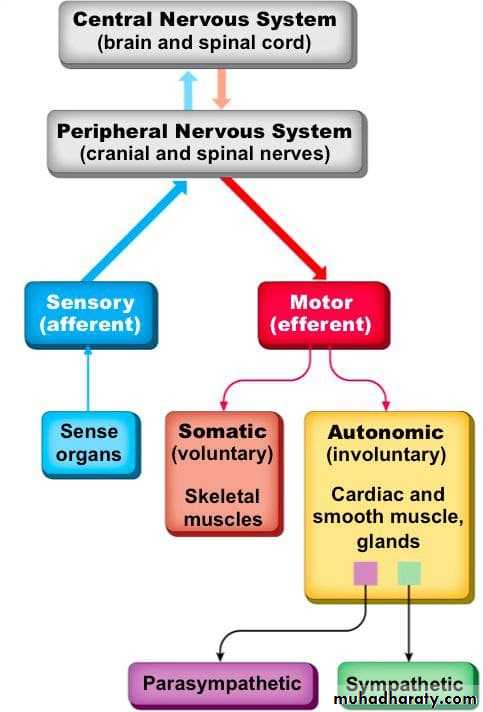
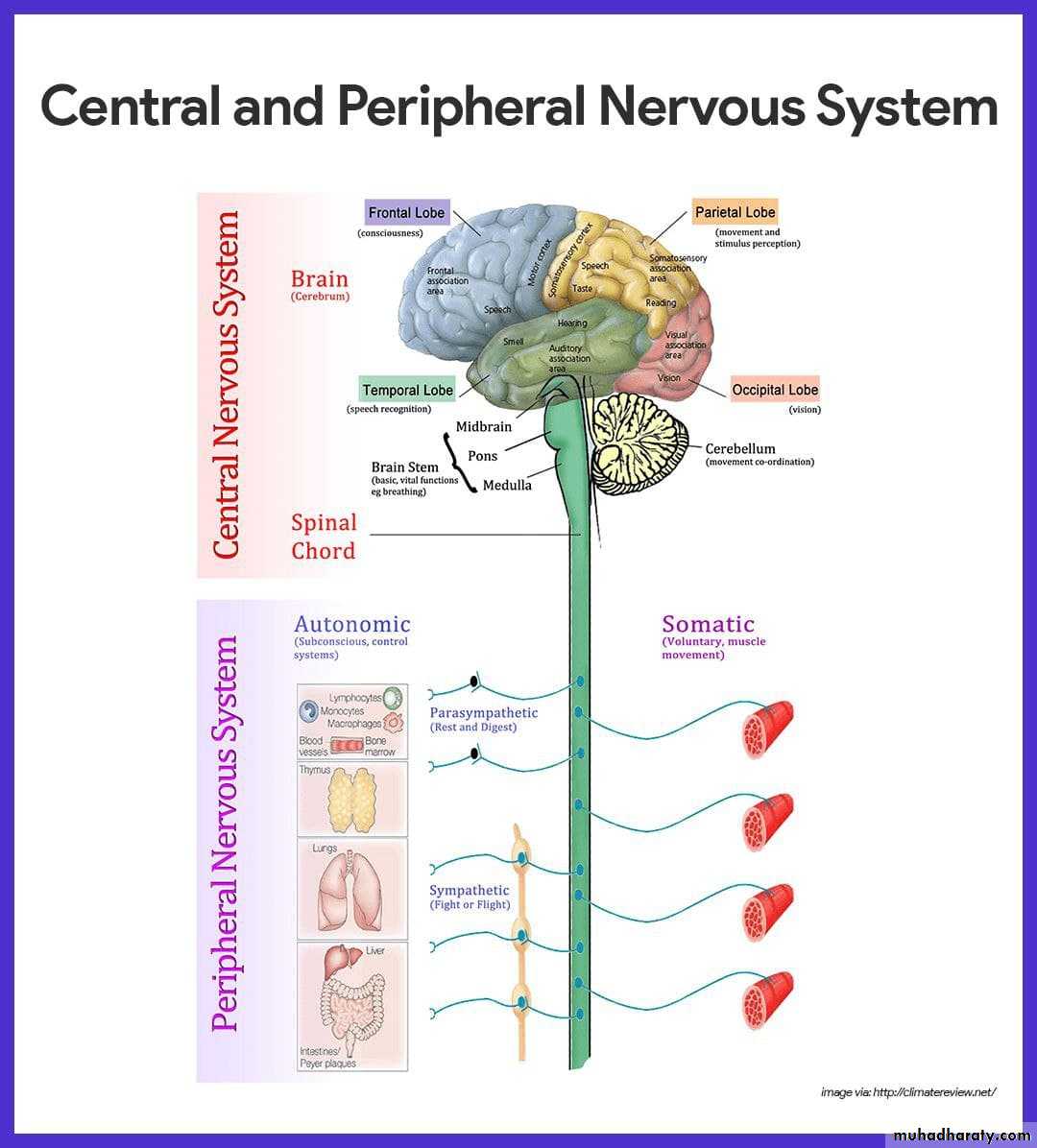
• Anatomical Divisions of the Nervous System• The nervous system is divided anatomically to:
• The central nervous system.• The peripheral nervous system.
Nervous System
Brain
NervesGanglia
Peripheral nervous
system (PNS)
Central nervous
system (CNS)
Spinal
cord
• Divisions of the Nervous System
• Enteric nervous system
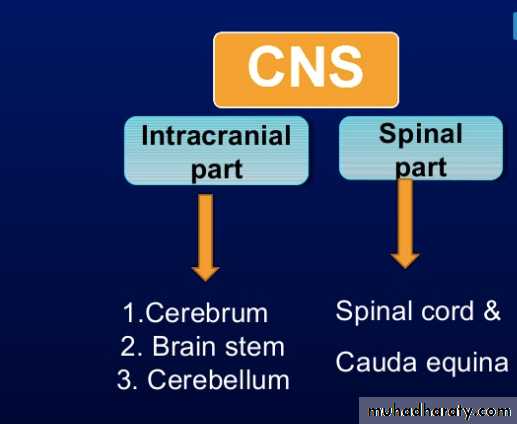
• 3• Main Divisions of the CNS :
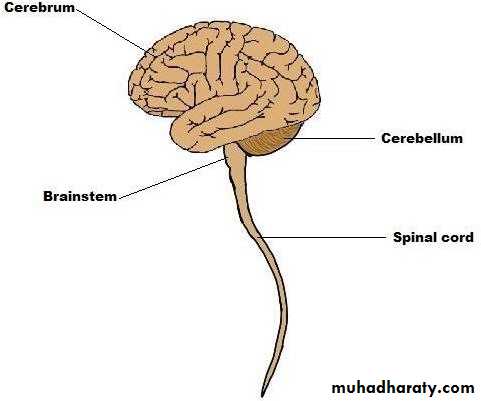
• The CNS is divided mainly to the following:• Brain.
• Spinal cord.
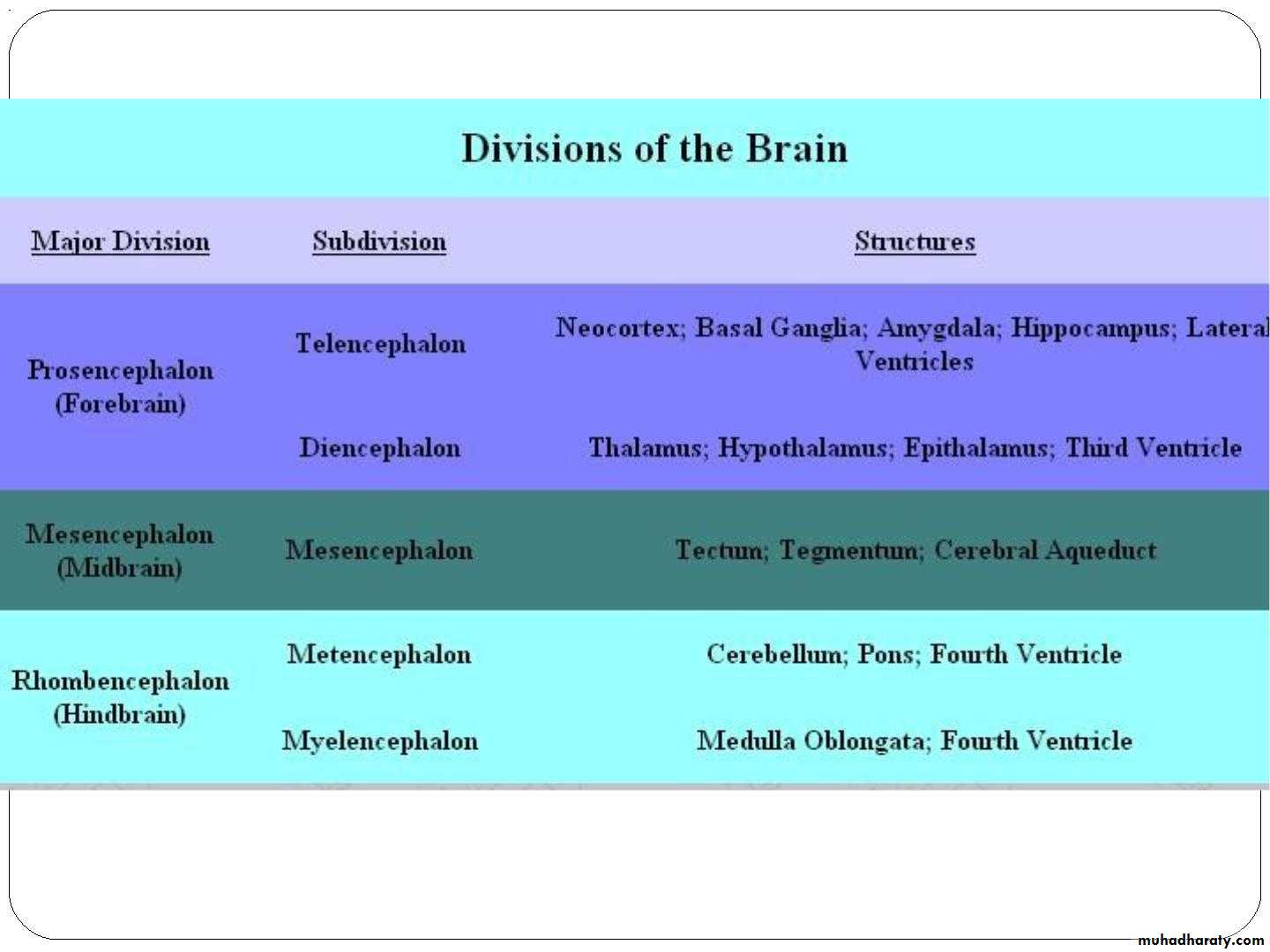
• The Brain is divided to:
• Forebrain.
• Midbrain.
• Hindbrain.
• Main division of CNS ;
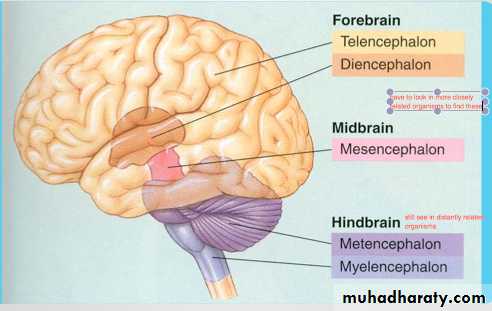
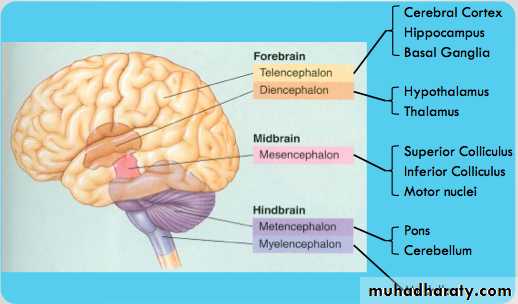
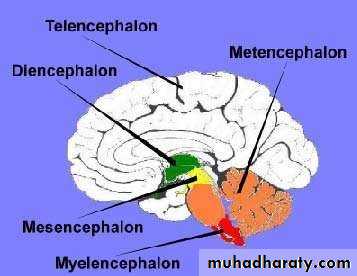
• The forebrain contains:• Telencephalon (cerebral cortex).
• Diencephalon.
• The hindbrain contains:
• Cerebellum.
• Pons.
• Medulla oblongata.
• 9
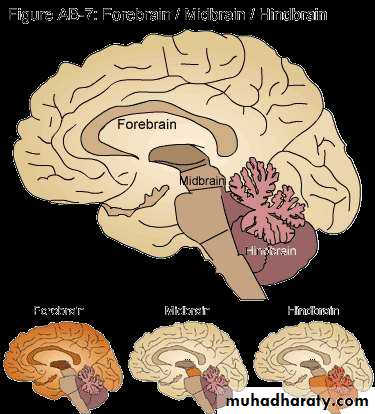
• CNS: Brain, three basic units
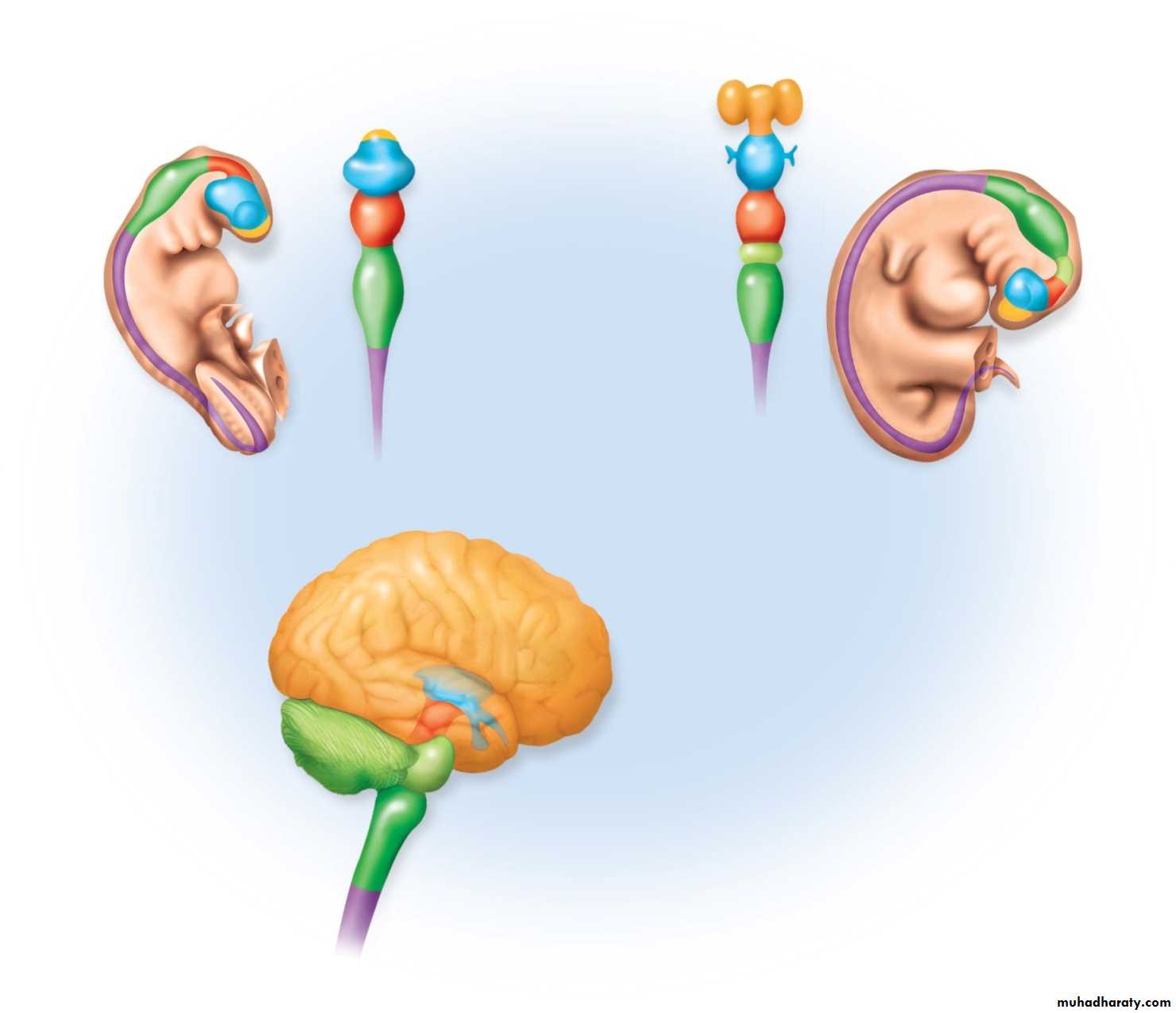
• Illustrative guide to the basic units of the brain: Forebrain/midbrain/ hindbrain
• CNS: Brain, five regions
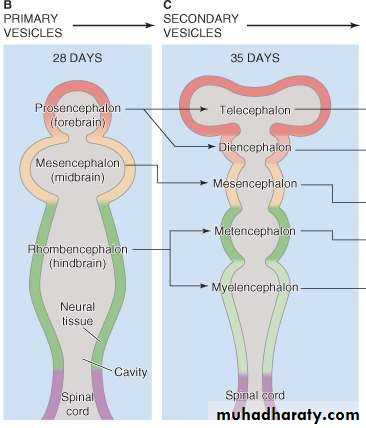
• Regions grouped and named as they develop in the embryo
Embryonic Brain DevelopmentCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Telencephalon
Forebrain
Pons
Cerebellum
Metencephalon
Spinal cord
Hindbrain
Telencephalon
Optic vesicleDiencephalon
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Spinal cord
Rhombencephalon
Mesencephalon
Prosencephalon
(a) 4 weeks
(b) 5 weeks
(c) Fully developed
Midbrain
Myelencephalon
(medulla oblongata)
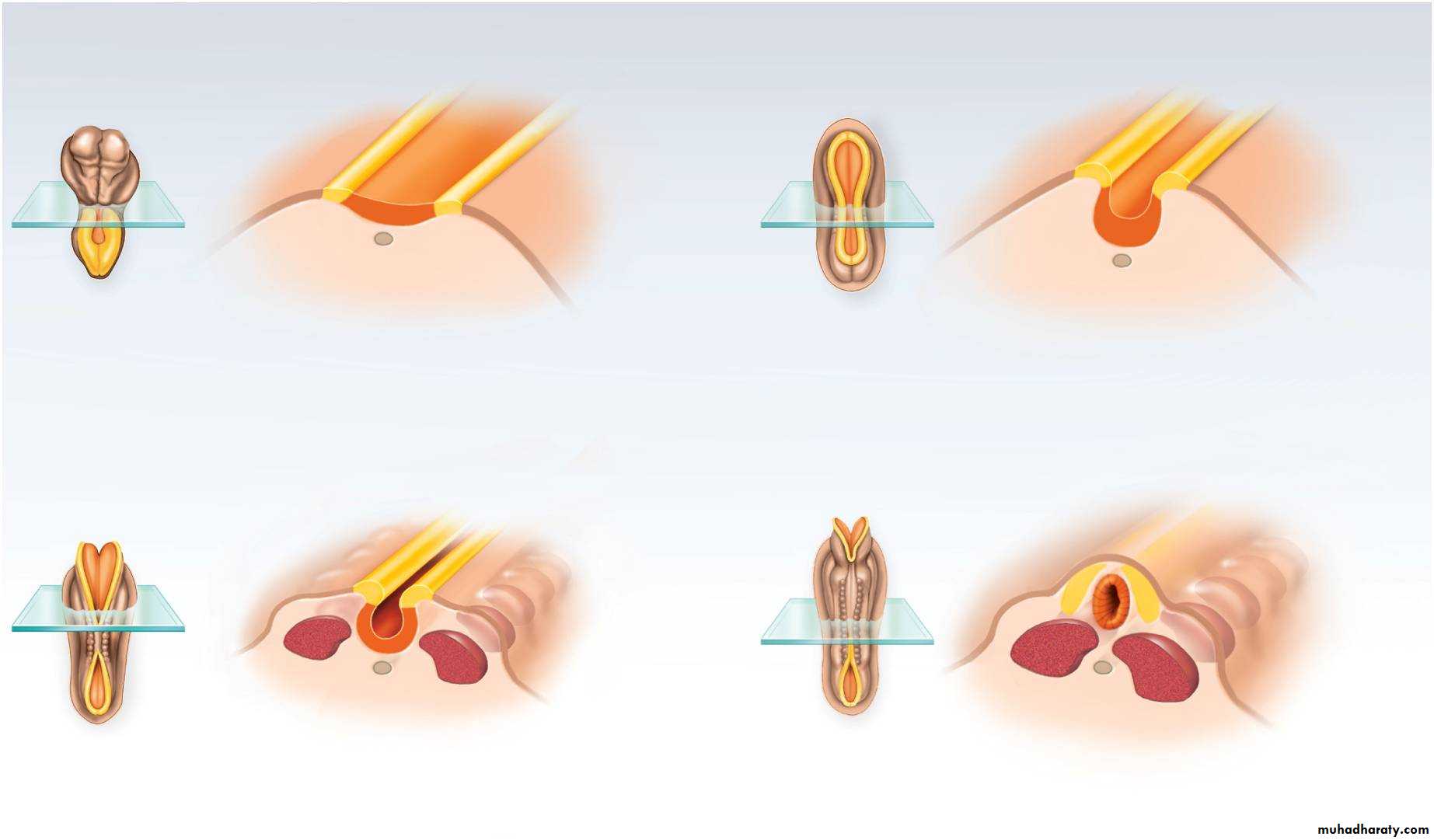
leaves
Neural groove
Neural fold(b) 20 days
(d) 26 days
Neural crest
Neural
crestNeural
tube
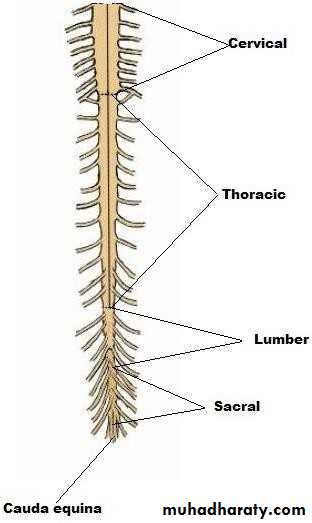
• The spinal cord is divided to
• Cervical spinal cord 8 pairs of nerves.
• Thoracic spinal cord 12 pairs of nerves.
• Lumbar spinal cord 5 pairs of nerves.
• Sacral spinal cord 5 pairs of nerves.
• Coccygeal spinal cord 1 pair of nerves.
15
• CNS: Spinal cord
• Functions• Conducts afferent stimuli from sensory receptors to the brain
• Conducts efferent stimuli from brain to effectors/muscles
• Site of reflex integration and houses certain central pattern
• Peripheral Nervous System
• Autonomic• Somatic
• Parasympathetic
• Sympathetic• Sensory
• Motor
• Afferent neurons carrying information from
• Efferent neurons carrying information from the CNS to
• All parts of nervous system outside the dura mater
• Includes sensory receptors, peripheral portions of spinal and cranial nerves (including those of the ANS), and sensory ganglia
• Sensory ganglia are aggregates of nerve cells located
• outside the CNS
• Neuronal and Non-neuronal Cells of the Nervous System
• Microanatomy: Neurons and Glial cells
• Neurons• Convey electrical signals within CNS and PNS
• Glial cells
• regulate neuron environment & form the myelin sheath around neurons
• Astrocytes: regulate
• Oligodendrocytes: form myelin sheath in CNS
• Schwann cells: form myelin sheath in PNS
• Ependymal cells: line the
• Microglia: monocytes of the brain
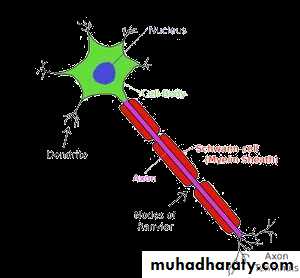
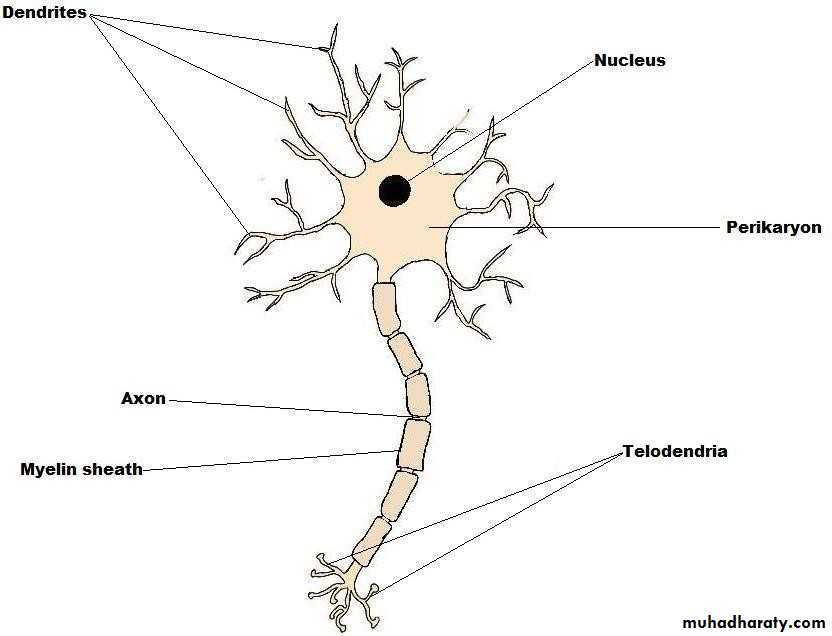
• Definition and parts of neuron..
• Neuron is the main functional unit of the nervous system.
• Neurons are composed of:
• Cell body.
• Dendrites.
• Axons
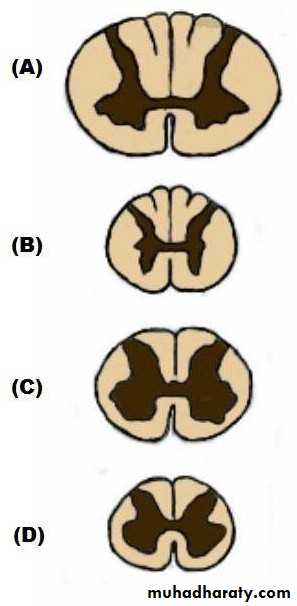
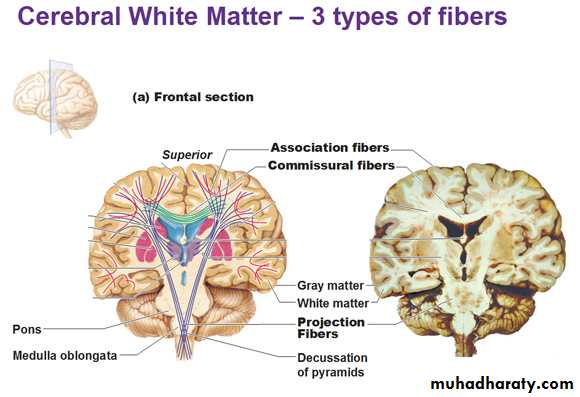
• Collection of cell bodies constitute grey matter, while collection of axons constitute white matter.
• Cell bodies are concentrated mainly in:
• Cerebral and cerebellar cortex.
• Spinal cord grey matter.
• Various nuclei in the CNS.
• Various ganglia in the PNS
• White matter is present mainly in:
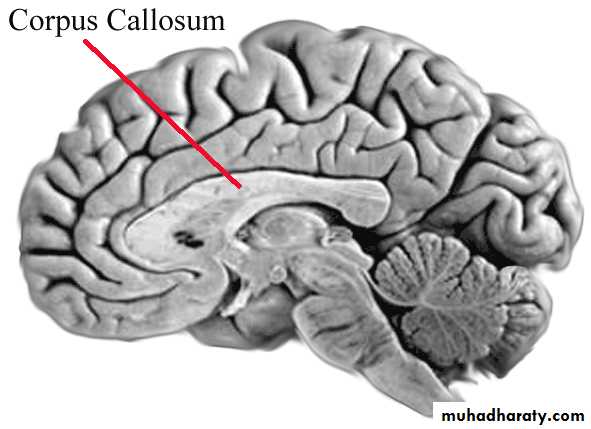
• Various sensory and motor tracts in the CNS and projection fibers.• Commissural fibers (connecting the two cerebral hemisphere), mainly:
• Corpus callosum.
• Anterior and posterior commissures.
• Associational fibers connecting various parts of the same cerebral hemisphere
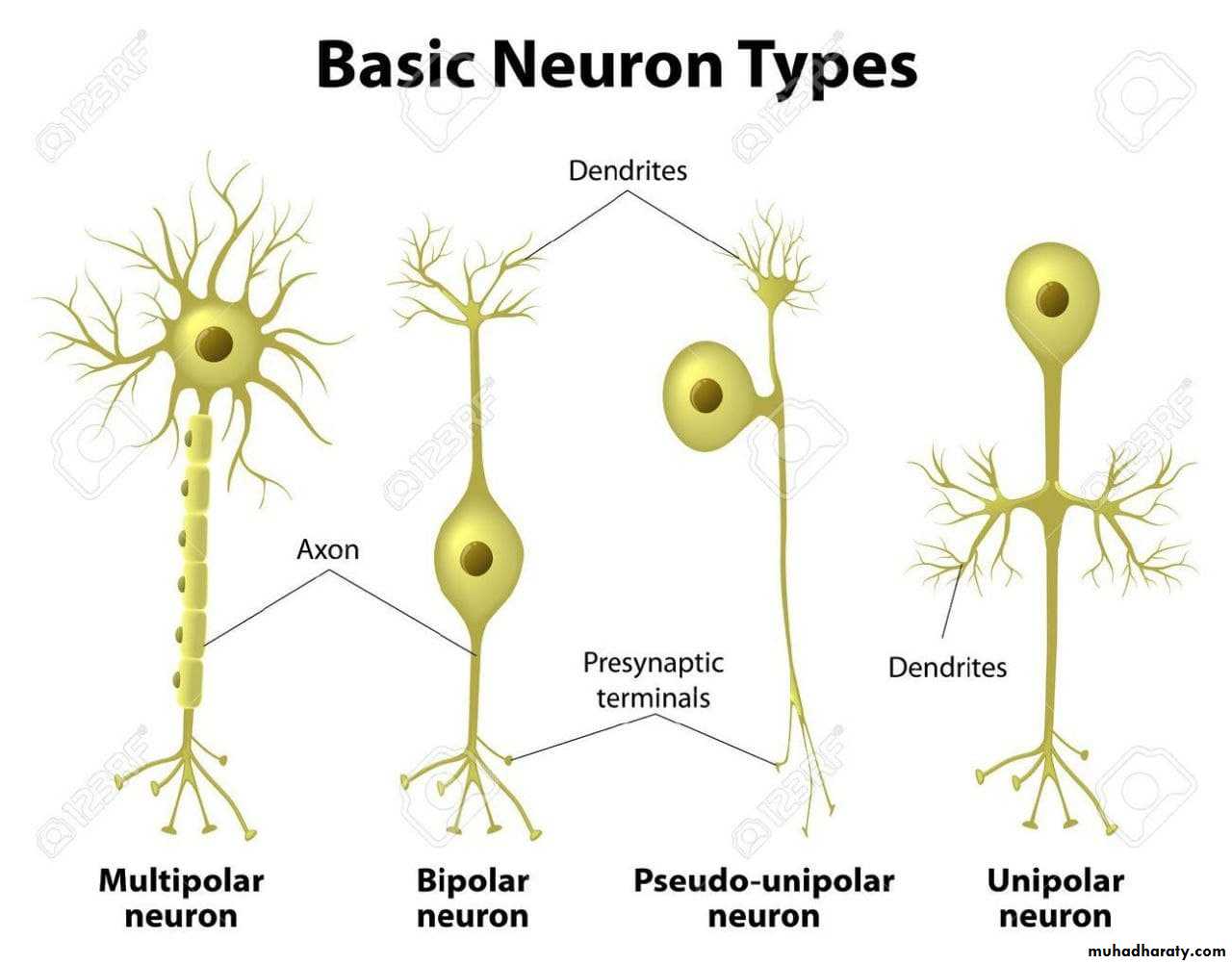
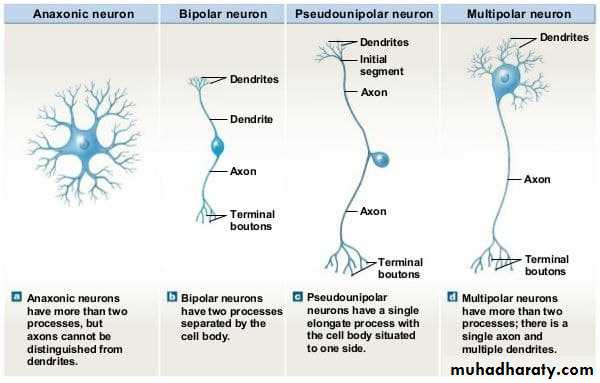
• Types of neuron ;
• Morphological classification of neurons:• Multipolar neurons.
• Bipolar neurons.
• Unipolar (or pseudounipolar) neurons.
• Anaxonic neurons.
23
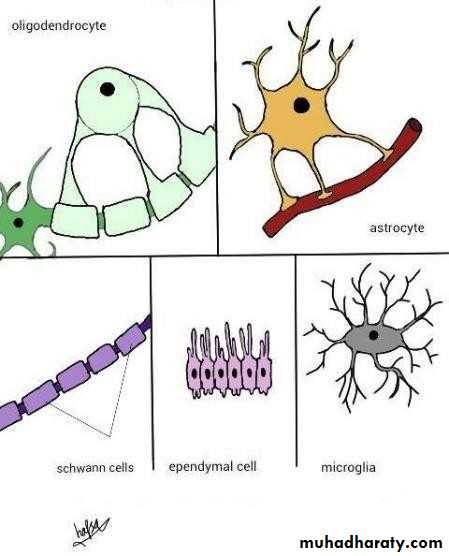
• They have various roles and functions to support neurons.
• Major types of glial cells:
• Astrocytes.
• Oligodendrocytes.
• Microglia.
• Ependymal cells.
• Schwann cells.
• Satellite cells of ganglia.
• Non neuronal cells ..
• They are called neuroglia or glial cells.
• Astrocytes have the following main functions:
• regulate the extracellular ionic concentration.• support the neurons physically.
• contribute to the blood-brain barrier.
• Oligodendrocytes are found in the CNS white matter, they produce the myelin sheath.
• Microglia are the main immune defence in the CNS, they originate from monocytes.• Ependymal cells line the brain ventricles and the spinal canal, they assist in the movement of CSF.
• Schwann cells produce myelin sheath in the PNS.
• Satellite cells of ganglia support the neuronal cell bodies in the ganglia.
29
Summary
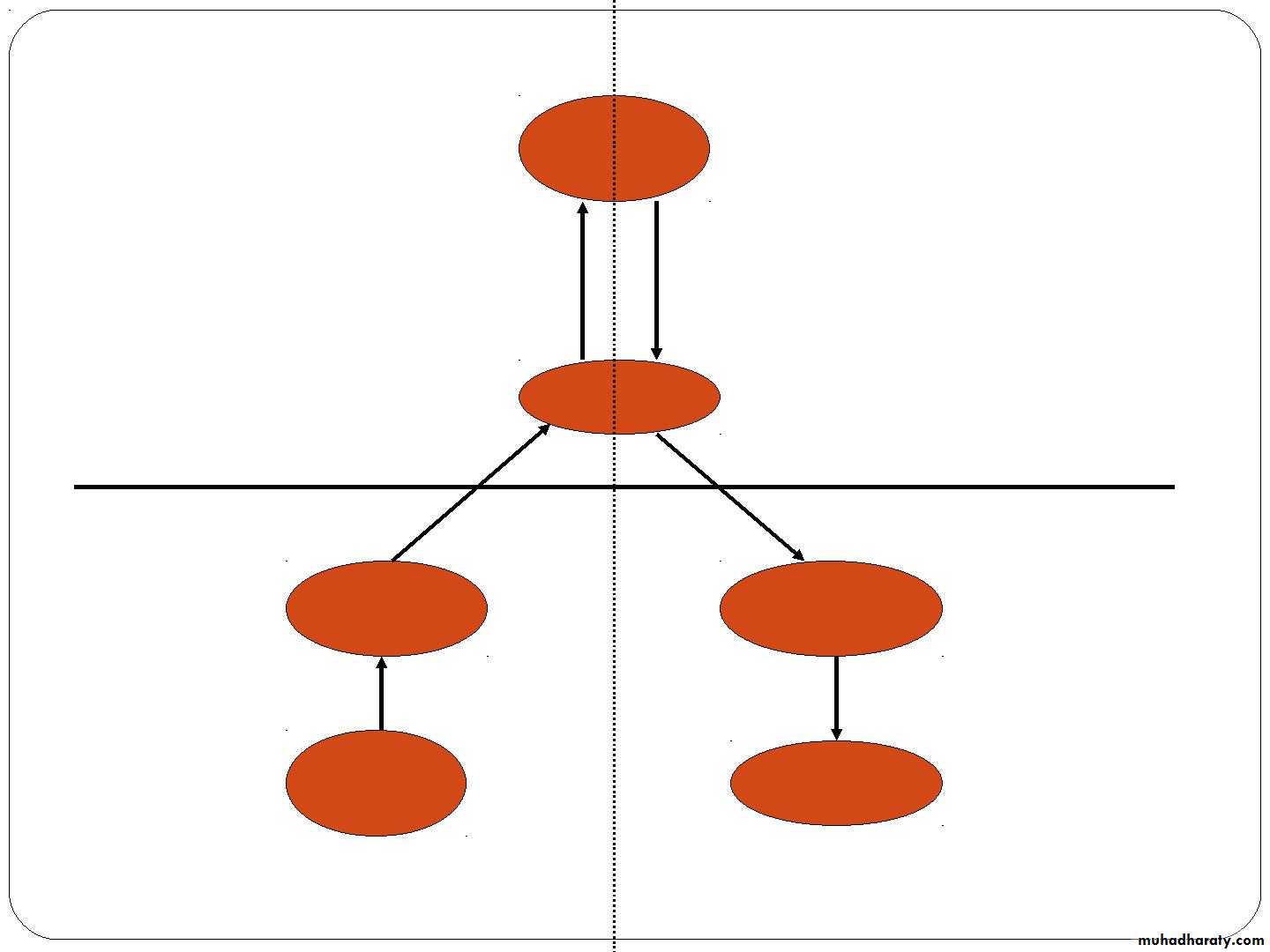
• Divisions of the Nervous SystemCentral nervous system
• BRAINAscending
tracts
Descending
tracts
Spinal cord
Aff
Eff
Sensory
nerve
Motor nerve
• effector
Receptor
Peripheral Nervous System
Peripheral NS
Central NSCranial Nerves
• Spinal Nerves
Bundle of axons
Tract
Group of cell bodies
Ganglion
Nucleus