Lect..3,,,,4
Dr. Methaq A.M. HusseinAssist.prof. of internal medicine
MRCP(UK)…. Endocrine, D.M (UK)
Causes of Hyperkalaemia
Decreased or impaired potassium excretion – renal failure, potassium-sparing diuretics, urinary obstruction, sickle cell disease, Addison disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)Additions of potassium into extracellular space - potassium supplements (eg, PO/IV potassium, salt substitutes), rhabdomyolysis, and hemolysis (eg, blood transfusions, burns, tumor lysis)
Transmembrane shifts (ie, shifting potassium from the intracellular to extracellular space) - acidosis and medication effects (eg, acute digitalis toxicity, beta-blockers, succinylcholine)
Factitious or pseudohyperkalemia - improper blood collection (eg, ischemic blood draw from venipuncture technique), laboratory error, leukocytosis, and thrombocytosis
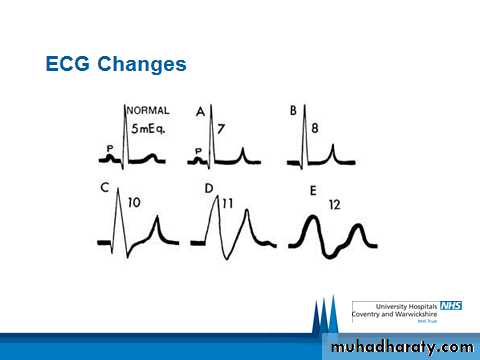
ECG Changes
From reduction of P wave amplitude and prolongation of PR interval to absence of P waves altogether.Increase of QRS duration.
Increase of QT duration.
Slowing of heart rate.
T waves become tall and spiked.
Decreased R wave amplitude
3 Principles of Treatment
Stabilise myocardium
Move it into cells
Increase elimination
1.Calcium Gluconate…..to counteract the effect of K on the heart
Dextrose – Insulin 2.Sodium Bicarbonate 3.
Calcium Resonium 4.
Salbutamol 5.
6.Furosemide
7.haemodialysis
HYPOKALEMIA
Causes of Hypokalemia
I. Decreased intake
A. Starvation
B. Clay Ingestion
II. Redistribution into Cells
A. Acid-Base (Metabolic Alkalosis)
B. Hormonal (Insulin, Beta agonist, Alpha )
C. Anabolic State (folic acid)
D. Other (Hypothermia, Pseudohypokalemia
III. Increased Loss
A. Nonrenal1. Gastrointestinal Los
2. Integumentary Loss (sweat)
B. Renal
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
FatigueMyalgia
Muscular weakness & paralysis
Hyporeflexia
Dyspnea
Arrhythmia
Predispose to digitalis toxicity
Constipation
ECG changes
Due to delayed ventricular repolarizationEarly changes: flattening or inversion of T wave, prominent U wave, ST-segment depression, prolonged QU interval
Severe K+ depletion: prolonged PR interval, decreased voltage and widening of QRS complex
Periodic limb hypokalaemic paralysis
Patient coplain from recuurent attacks of palalysis……monitored as inpatient due to risk of resp. failure
Ppt. factors
1.heavy meals of CHO
2.straneuos excersize
3.standing from prolond sitting
4.awake from prolong sleeping
Causes
1.idiopathic channalopathy2.thyroid disease
3.other causes of recurrent hupokalaemia
Treatment
1.monitor of repiratory sys……FVC2.correction of hypokalaemia by oral KCL…if patient sever symptoms or cannot take orally ,,,so infusion wth fluid???????
Mannitol infusion with KCL
NO NO ….GW OR NORMAL SALINE ?????
3.treatment of the cause like thyroid problem