Children with Special Health Care Needs
• Classification of disabled children:
Intellectual impairedPhysically impaired
Sensory impairment
Medically compromised
Combination of disabilities
Children who are handicapped for dentistry are those who have a physical and /or mental or emotional condition that may prevent them from treated routinely.
Handicapped Infants’ and young children’s oral health may be affected negatively by:
Medications
Special diets
Decreased saliva flow
Motor problems
Lack of access to preventive care
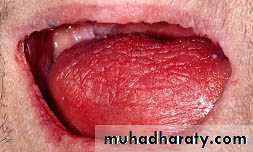
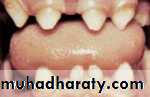
some conditions are associated with increased risk for various oral health problems :
Children with developmental disabilitiesenamel irregularities
gum infections
tooth eruption delays
severe malocclusion
oral infection
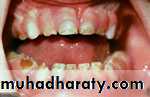
some conditions are associated with increased risk for various oral health problems :
Children with Down syndromeperiodontal disease
Xerostomia
fissuring of the tongue and lips
Malocclusion
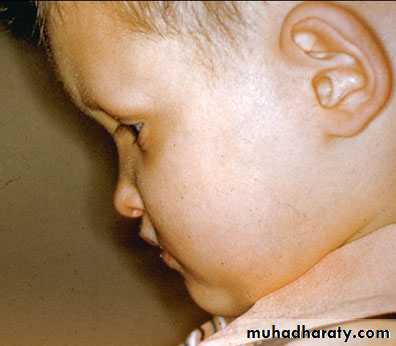
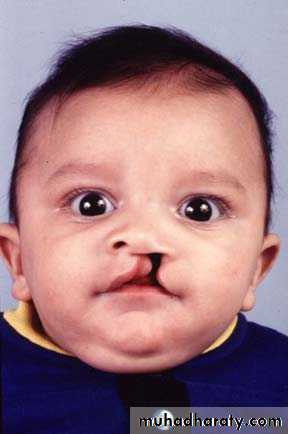
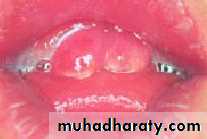
Children with cleft lip or cleft palate
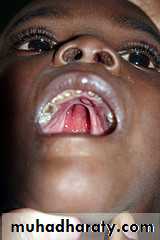
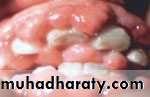
tooth decayGingivitis
malocclusion
some conditions are associated with increased risk for various oral health problems :
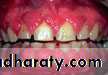
Oral Conditions
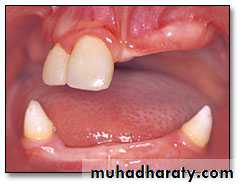
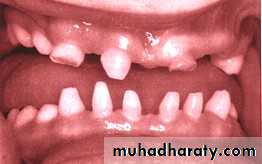
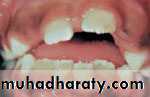
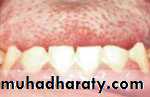
• Delayed Tooth Eruption• Malocclusion
• Dental Anomalies
Oral Conditions
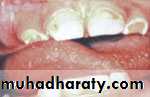
Oral Trauma
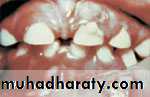
BruxismGingival Overgrowth
Oral Conditions
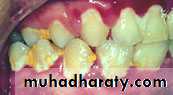
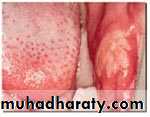
• Oral Infections• caries
• Viral and Fungal Infections
• Gingival Infection
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
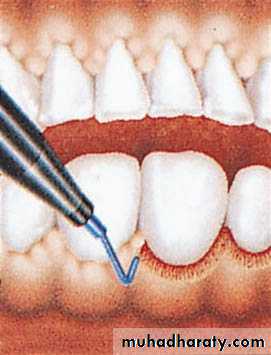
• Periodontal• Gingivectomy
• periodontal packs may not be well tolerated
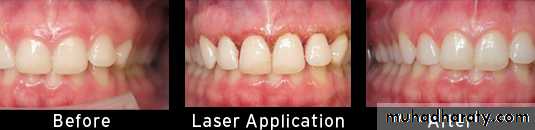
• electrosurgery or laser surgery techniques should be considered
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
• Restorative• Glass ionomer restorations
• Stainless steel crowns
• Maintain even severely worn teeth
• Endodontic treatment
• One visit
• Apex locator
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
• Prosthetic• Fixed prosthodontics are feasible when
• patient can cooperate
• adequate oral hygiene can be maintained
• poorly controlled seizure disorder
• Fixed prosthodontics for anterior teeth contraindicated
• Removable prostheses are contraindicated
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
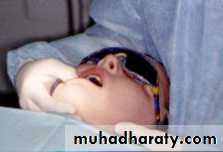
Positioning and Airway Protectionpatients must be properly positioned to prevent aspiration
receive treatment in a sitting or
semi-reclined position.
The use of rubber dam
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
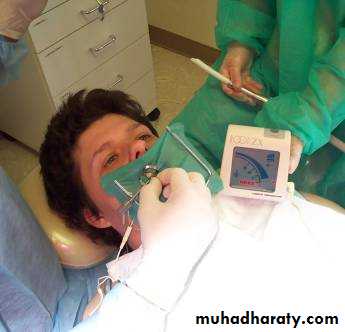
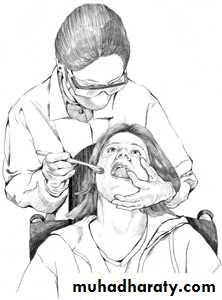
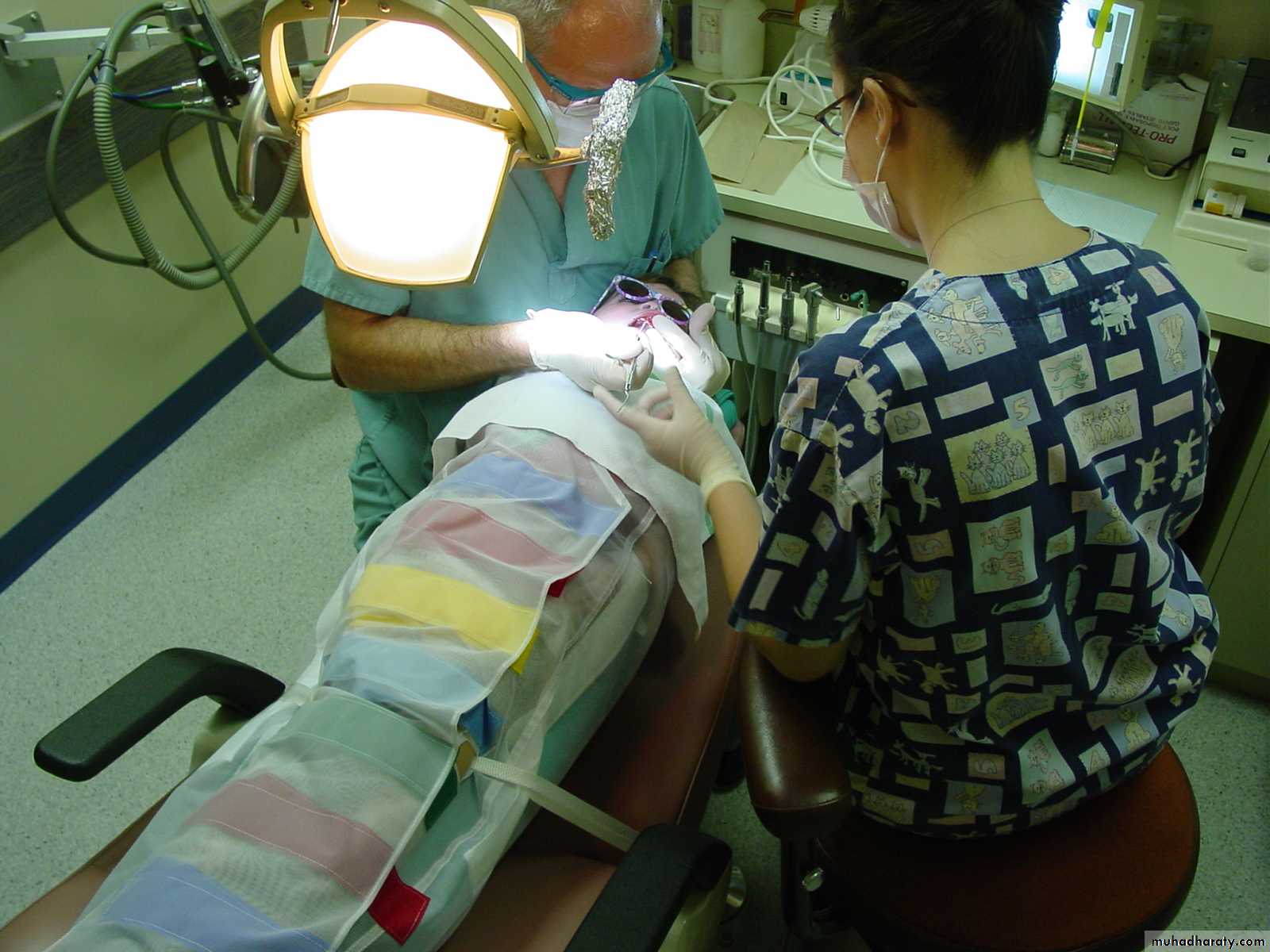
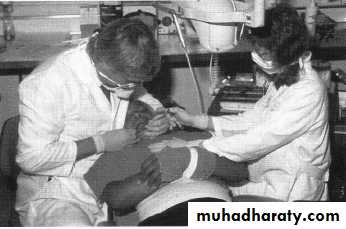
• Behavior Management• creating a caring empathetic relaxed environment
• behavior modification techniques
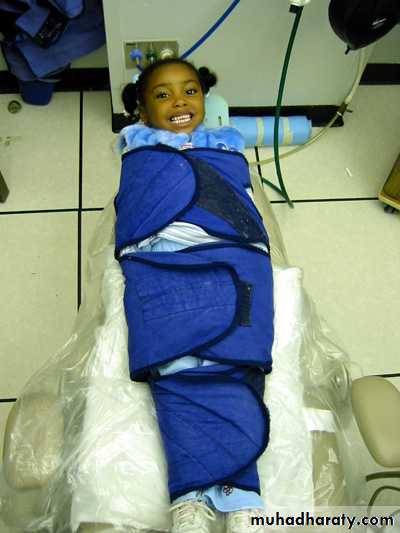
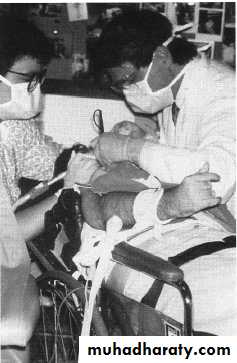
• immobilization with protective devices and restraints
• sedation
• general anesthesia
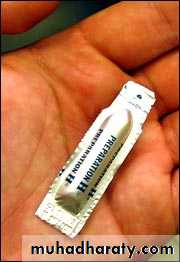
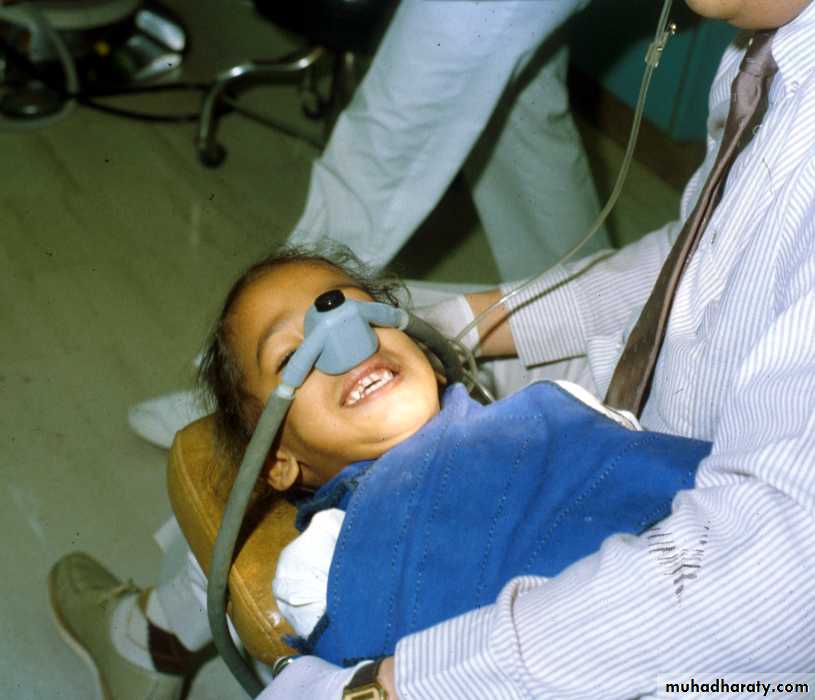
Pharmacotheraputic approaches
Inhalation sedationOral sedation
Rectal sedation
Intravenous sedation
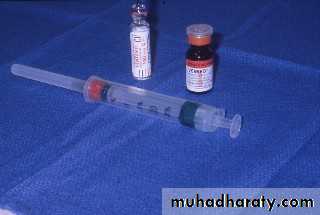
Medication:
Midazolam: 0.2-0.5mg/kgDiazepam: 0.25-0.5mg/kg
Fentanyl: 1-2µg/kg
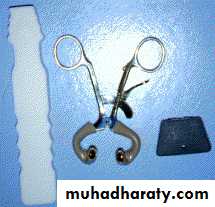
Mouth prop:
Open wide mouth prop:
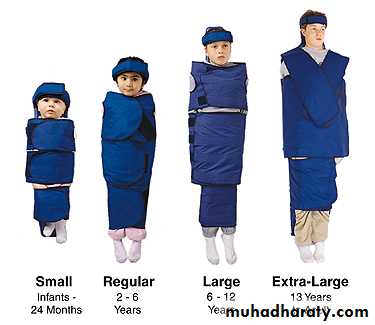
Sterlizable typeRestraints
BodyTriangular sheet
Beanbag dental chair insert
Safety belt
Extra assistant
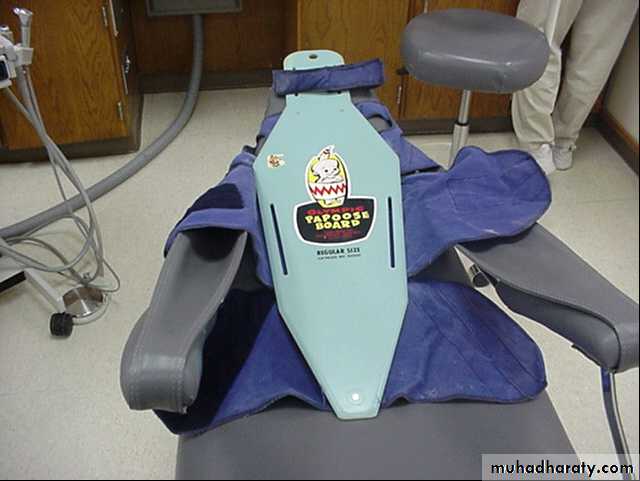
Papoose Board:
Pedi Wrap:Restraints
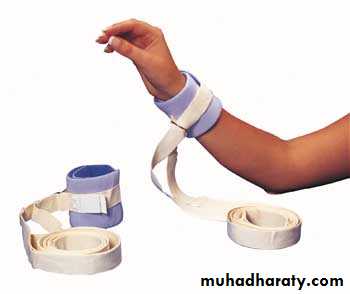
ExtremitiesPosey straps
Velcro straps
Towel and tape
Extra assistant
Restraints
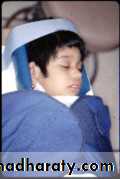
HeadForearm-body support
Head positioner
Plastic bowl
Extra assistant
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
Preventionbrushing
Treatment Modifications of the handicapped patients
PreventionFlossing
Fluoride (IFRD)
Chlorohexidine
Xerostomia
Dietary counseling