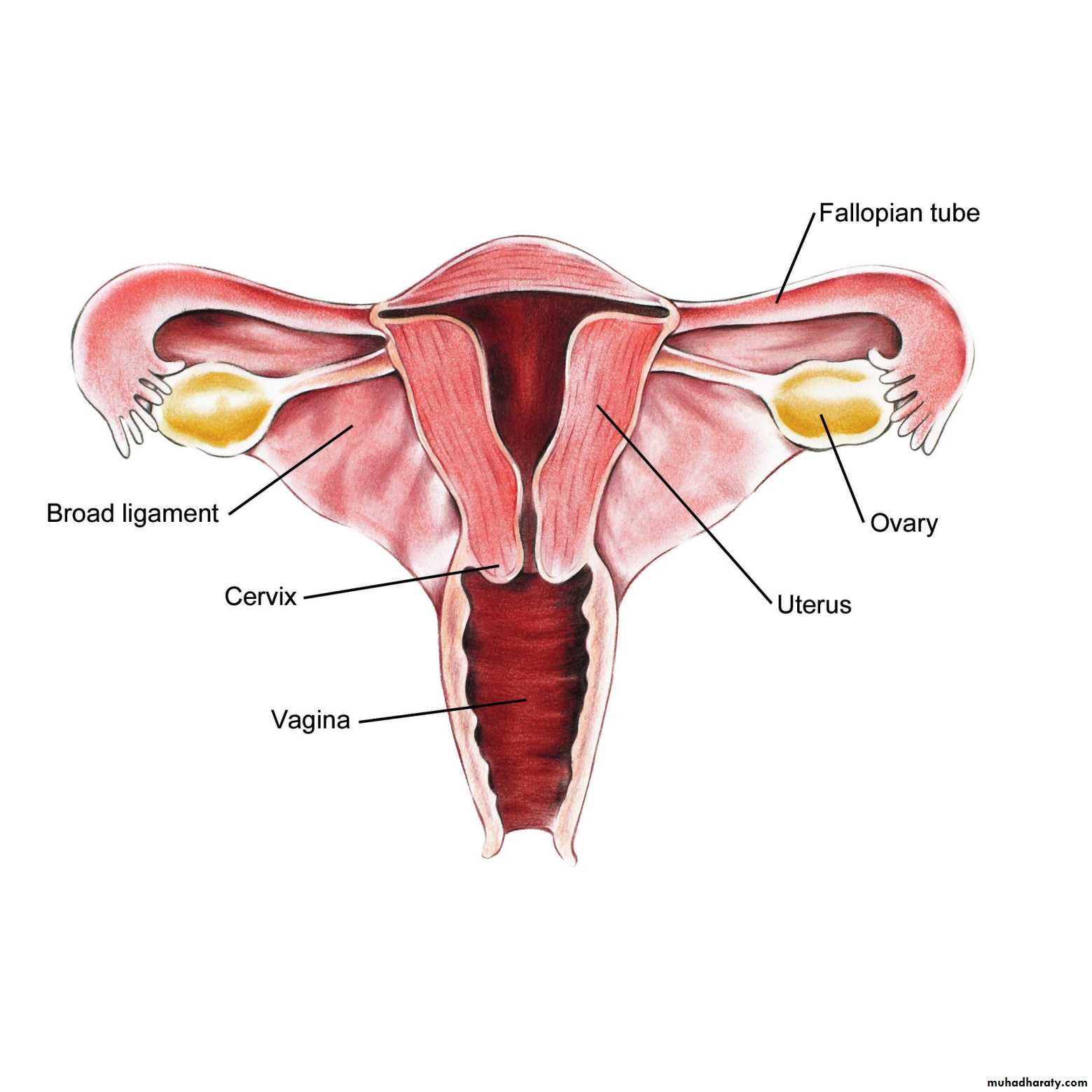
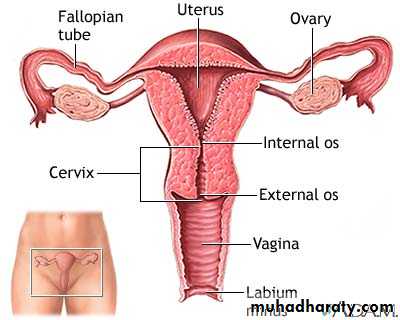
Female genital organs
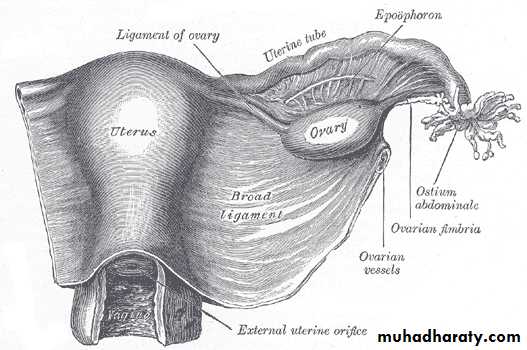
ovaryShape and size; almond shape
Measuring; length 3cmBreadth 2cm
thickness 1cm
Site; in the ovarian fossa in nilliparous women. On the side wall of pelvis
Boundaries of ovarian fossa ;
Infront and above; ext. iliac vessels
Behind; ureter and internal iliac vessels.
Its attach to the superior surface of broad ligament in close relation to the lateral end of the fallopian tube.
The ovaries displaced in pregnancy and never return to the ovarian fossa.
Gereral feature; the ovary has
2 ends; 2 surface &2 borders
2 ends; 1- tubal end ( upper) its directed upward and give attachment to ;
A- the ovarian fimbria of the fallopian tube (uterine tube)
B- the suspensory lig.of the ovary ( infindubulo-pelvic lig)2- uterine end (lower end); directed downward & is attach to the lateral angle of the uterus by the ovarian ligament.
2 surfaces
Medial surface; directed medially & covered by fimbriated end of uterine tubeLateral surface; is directed laterally towards the lateral pelvic wall
Is related to the obturator nerve & vessels in the floor of the fossa.
2 borders
Anterior border; its attached to the sup. Layer of the broad lig. by a short fold of peritoneum called mesovarium.Post. border is a free border directed backwards.
Peritoneum covering of the ovary ;its completely cover with peritoneum except at the line of attachment of the mesovarian
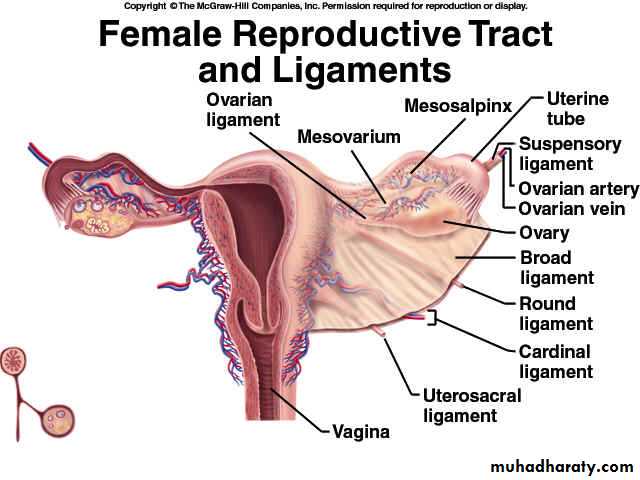
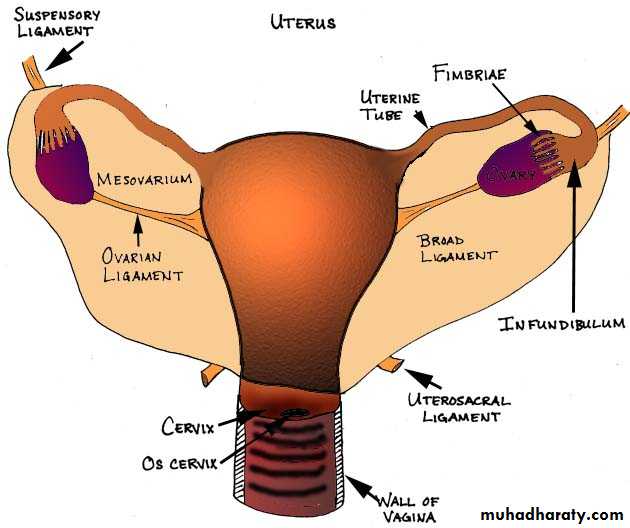
Ligaments of the ovary
1- suspensory ligament; its peritoneum fold transmit the vessels ,nerves,& lymphatics to the broad ligaments .
It extend from the tubal end of the ovary to the side wall of the pelvis at the external iliac vessels.
2- mesovarium; its peritoneum fold extend from the upper layer of broad ligament to the ant. Border of the ovary.
It transmit the ovarian vessels and nerve to the ovary.
3- ovarian ligament; it’s a fibromascular cord extending from the uterine end of the ovary to the lateral angle of the uterus.
Arterial supply of the ovary
1- ovarian artery; it arise from abdominal aorta at which level ?2- uterine artery; give additional branches
Venous drainage; veins draining the ovary form papiniform plexus which rapidly form ovarian vein which accompany the ovarian artery
Rt drain to the inf. Vena cava and lf to the lf renal vein.
Lymphatic drainage ; to paraortic lymph nodes
Nerve supply ; sympathetic from T10 &11
Parasympathetic from S2,3,4
Ovarian tumour
19 years old female presented with sign and symptoms of acute appendicitis ,at operation the surgeon was found normal appendix.
What due think the surgeon do?
What due think the cause of acute abdomen.?
Why this condition give the same sign and symptoms of appendicitis?
UTERINE TUBE ( FALLOPAIN TUBE)
SIZE; 4 inch 10 cmSite extend from sup.angle of the uterus to the ovary .its lie in the anterior free margin of the brood lig.
Course and relation; it runs in the upper border of broad ligament ,end on the medial surface of ovary by a faunal shaped expansion called infundibulum .
Along its whole course its related to the coil of ileum and sigmoid colon.
Parts of fallopian tube
1- uterine or intramural part 1cm narrowest and shortest part. It penetrates the superior lateral angle of uterus;2- isthmus ; 3 cm lie just lateral to the uterus ,form the lateral 1/3 of the tube. It narrow, rounded, cord like.
3- ampulla 5cm its form lat.1/2 of the tube .its thin wall ,tortuous & widest part of the tube.
4- infindibulum ; (fimbriae end); its faunal shape open to the peritoneal cavity ,its circumference prolonged to NO. of fimbria ,one of which is large and attach to the ovary
Arterial supply of tubes
Medial ¾ by uterine arteryLateral ¼ by ovarian artery
Lymphatic drainage; to the lateral aortic & pre aortic l.n
Lymphatic of isthmus to the superficial ing. L.n
Applied anatomy;
infect ion may spread from tube to the peritoneal cavity ( peritonitis).
Tubal obstruction by fibrosis is a major cause of infertility in female.
HYSTROSALPENGOGRAPH FOR INFERTILE FEMALE
Arterial supply of tubes
39 years female have 6 children she attend the out pt clinic for tubal ligation (T.L) ,WHERE YOU THINK PUT LIGATION ?
uterus
Shape; pear shaped ,thick wall,hallow muscular organ.
Size 3 inch long ,2 width,1 thick
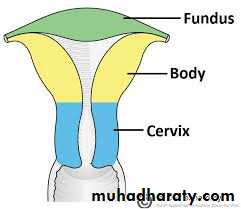
Structure; form by 3 parts ; fundus ,body, cervix.
Fundus; above the entrance of uterine tube ,it convex in all directions
Body; extend from the entrance of uterine tube to the constriction called isthmus
Superior lateral angle of the body and its junction with the tube is called cornu.
Cervix
Is the part below the isthmus ( one inch long) its cylindrical in shape lower half pierces the vagina called vaginal part while upper half lie above the vagina called supravaginal partCavity of uterus;
1- cavity of body; slit-like in sagital section & triangular in coronal section. Its apex of the triangle lying at the internal os of the cervix.
Cavity of the cervix;( cervical canal);is fusiform in shape it communicate with
Above ; uterine cavity through internal osbelow; vaginal cavity through external os ( small and round before childbirth but become slit-shape after child birth.
Normal position of the uterus;
1- the uterus lie between the rectum post. And bladder ant.
2- anatomical position of uterus is anteverted anteflexed
Anteverted means the whole uterus form nearly a right angle with the long axis of the vaginaAnteflexed means long axis of the body form an angle about 170 with the long axis of cervix.
Relation of the uterus
Fundus; covered with peritoneum and related with the coil of ileumBody; has ant and post surface;
Ant. Surface (visceral ) surface ( flattened)
Related to the upper surface of bladder ,its cover with peritoneum which reflected at the isthmus on to the upper surface of the bladder forming uterovesical pouch.
Post. Surface; (intestinal )(convex)
Its related to the coil of ileum and sigmoid colon. Covered with peritoneum which extend to the back of cervix and upper part of the vagina and to the rectum forming Douglas pouchLateral margin ( rounded) ;
It give attachment to the broad ligament.
The uterine art. Ascend along this margin
Uterine tube enters the uterus at this margin
The upper part of lat. Border gives attachments to;
A- the ovarian ligamentB- round lig.of the uterus
Cervix of the uterus ;
It’s a cylindrical in shape and has 2 parts ; vaginal and supra vaginal
25 years old female presented with sever rt renal colic with epigastric pain and repeated vomiting one wk after difficult C/S , on U/S there is moderate hydronephrosis .
What due think the cause of hydronephrosis?
Who you confirm the diagnosis?
Why this happen anatomically?
Relation of supravaginal part of cervix
Lateraly ; its related to 1- uterine artery 2- the ureter run downward and forwards 2 cm lateral to the cervix 3- parameterium; dense C.T between the 2 layers of broad ligament.Posterioly; its covered by peritoneum of douglos pouch and related to coils of ileum and sigmoid colon.
Anterioly; its not covered by peritoeum and is related to the urinary bladder.
Ligaments of the uterus
Round lig. Of uterus; its fibromascular cord extending from the cornu of the uterus to the labium majus .it represents the lower part of the gubernaculum in the fetus.Course and relation; its attach to the upper end of the lateral margin of the body of the uterus in front of the uterine tube
It run between the 2 layer of broad below the uterine tube .
On the lateral pelvic wall it crosses over the ,obtur.n&vessels ,oblitrated umblical art. & ext.iliac vessels( same structure crossed by the vas deference in the male.
It enters the deep inguinal ring just lateral to the inferior epigastric artery ,traverses the inguinal canal (having the same covering as spermatic cord in male)
It emerge from the superficial ring &end in the subcutaneous tissue of the labium majus.
The ovarian ligament
It’s a short fibromascular cord representing the upper part of the gubernaculums.Course; it pass within the broad lig. From then uterine end of the ovary to the cornu of the uterus behind the entrance of the uterine tube.
Broad ligament;
Its double layer sheath of peritoneum extend from the lat.surface of uterus to the side of pelvic wall.Shape; quadrilateral having 4 borders and 2 surfaces.
Relations; the 2 broad lig.together with the uterus dividing the lesser pelvic to anterior compartment containing U.B and posterior compartment containing the rectum and coil of ileum and sigmoid colon.
Surfaces
Upper intestinal surface; its related to the coils of ileum & segmoid colon ,Its upper layer is pierced by the lateral end of uterine tube
Lower vesicle surface; directed downwards toward the U.B
Borders; 4 borders
1- ant.free border; where the 2 layer of lig. Are continuous with each other around the medial 4/5 of the uterine tube .the lateral 1/5 of this border forms the infudibulpelvic lig.
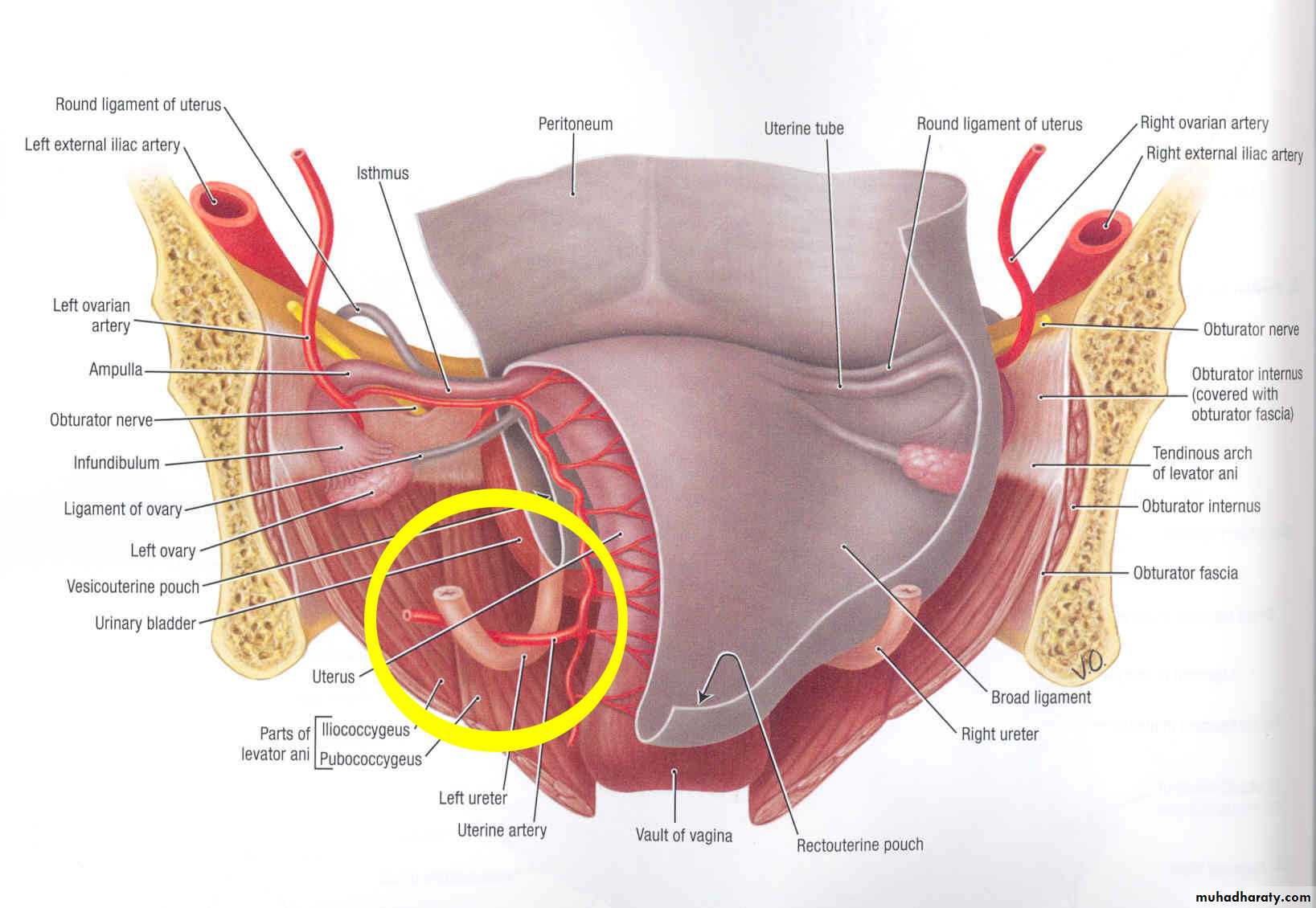
2- post.attached border; its attached to the pelvic floor .the uterine vessels run along this border ( between the 2 layer) the ureter crosses below the attached border 2 cm lat .to the cervix.
3-medial border ; attach to the lateral border of the uterus where the 2 layers separate too enclose the uterus ,the uterine vessels ascend along this border ( between the 2 layer)
4- lateral border; attach to the side wall of true pelvis where it crosses the fallowing structure from above downwards;
A- external iliac v. b- obliterated umbilical A.
C- obturator N. & V.
Parts of broad ligaments
1- mesovaium; it’s a peritoneal fold connecting the ovary to the sup.layer of broad the lig. it transmit ovarian vessels and nerves to the ovary.2- mesosalpinx; is the part between the uterine tube and the attachment of mesovarium
3- infundibulopelvic lig. (suspensory lig.of the ovary); is the upper lat.part of the broad lig. Extending from the infundibulum of the uterine tube to the lat.pelvic wall . It transmit ovarian vessels and nerves to the mesovarium.
4- mesometerium; is the remaining greater part of the broad lig. Closed to uterus.
Contents of the broad ligament;Between 2 layers contain 2 tubes .2 ligaments.2 arteries. 2 embriological remnant ¶meterium.
A. Tubes ;1- uterine tube ; on ant. Free border of the broad lig.
2-Ureter; below the root of broad lig. 2 cm lat to the cervix.
B. Ligaments; 1- ovarian ligament.
2- round lig. Of the uterus
C. Arteries
1- ovarian artery ;pass through suspensory lig. Of ovary
2- uterine artery; pass first medially in the post attached border (root)of the broad lig. Crossing above the ureter 2 cm lateral to the cervix. then ascends in the medial border of the lig.and finally turn laterally in the mesosalpinx below the uterine tube.(THIS COURSE IMPORTANT)
D-Embryological remnants;
1- epoophoron; about 15 -20 rudimentary tubules present in the lat. Part of the broad lig.2- paroophoron ; few scattered tubules lying in the broad lig. medial to the attachment of the mesovaium.
N.B; both epoophron and paraophron are the embryological remnant of the mesophrenic duct & tubules of the embryo.
E-parametrium
It’s a dense fibro fatty C.T between the 2 layer of broad ligament and contain;1-uterovaginal and ovarian plexuses of nerves
2- lymphatic and lymph nodes.
Ligaments of cervix
There are condensation of the endopelvic fascia and include;1- pubocevical ligaments; they extend from the cervix and upper part of the vagina around the sides of the urethra to the post. Surface of the pubis. they correspond to puboprostatic lig.in male
2- uterosacral ligs; they extend from the cervix around the sides of the rectum to the periosteum of the front of the sacrum (2nd & 3rd segmens).
they are enclosed within the rectouterine fold of peritonium
3- transverse cervical ( cardinal or Mackenrodt’s )ligaments; extend from the side of cervix and lat. Fornix of vagina to be attached to the side wall of the pelvis.
They are strong fan shaped condensations of the pelvic fascia above levetor ani muscle and are very important factor in the support of the uterus
Peritoneal ligaments of the uterus
1- post. Ligament; its recto uterine fold of peritoneum extending from the front of the rectum to post . Fornix of vagina and supravaginal cervix2- anterior ligament; it’s the utervesical fold of peritoneum extending from the front of the cervix to the upper surface of the bladder.
Factors maintaining the position of the uterus
1- uterine axis ;the antiverted position of the uterus pervent it from sagging down through the vagina, this antiverted is maintained by uterosacral and round ligaments.2- ligaments of the body and cervix which connect the uterus to the pelvic wall
3- pelvic floor muscles( pelvic diaphragm)
4- uro-genital diaphragm muscles of deep perineal pouch
5-perineal body ; it’s a fibromascular node between the vagina and anal canal, receiving the insertion of all perineal muscles.
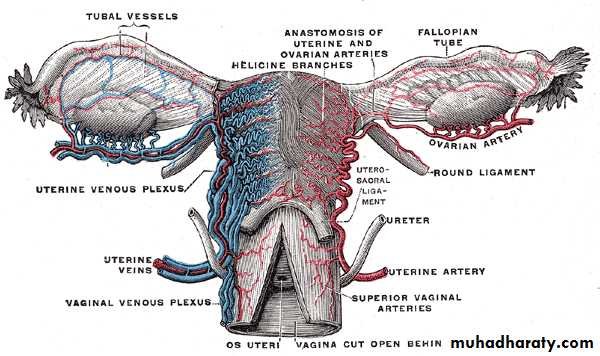
Blood supply of the uterus
Arterial supply; the uterine arteryArise from ant division of internal iliac artery
It crosses above the ureter about 2 cm lateral to the cervix
Then it ascends along the side of the body of uterus in a wavy course
Finally it turns laterally below the uterine tube to end by anastemosing with ovarian artery
It supplies the uterus,med.2/3 of the uterine tube and give branch to the vagina
Venous drainage
The veins drain through 2 venous plexuses along the 2 lateral border of uterus then to the internal iliac veins
Lymphatic drainge;
Upper part of the body +fundus +uterine tube to the paraortic l.n
Lower part of the body to the ext.iliac l.n
Cornu of the uterus to superfascial ing.l.n
Cervix; to 3 group of l.n
a- internal iliac l.n
B- ext.iliac l.n
C- sacral l.n infront of sacrum
Nerve supply of uterus
Sympathetic; from T12 & L1 produce uterine contraction and vasoconstriction.Parasympathetic from S 2,3,4 causing uterine relaxation and vasodilatation.
The vagina
Its fibromascular tube lined by non keratazed stratified squamous epithelium .Long axis of vagina is nearly perpendicular with that of uterus
It has 2 wall ant & post.
relation of Ant. Wall;
Upper 1/3 is pierced by cervix
Middle 1/3 attach to the base of bladder
Lower 1/3 related to the urethra which imbedded in ant. Wall of vagina
posterioly
Upper ¼; its cover with pertoneium of douglos pouch and related to the coil of ileum and sigmoid colon
Middle ½ related to the lower 1/3 of rectum
Lower ¼ related to the perineal body which separate vagina from anal canal
Laterally;
Upper part (lat.fornix) related to the ureter& to the uterine artery as it crosses above the ureter
Middle part; related to the leveter ani (sphincter vaginali)
Lower part; traverses the deep perineal pouch & is related to the bulb of vestibule ,bulbospongiosus m & to the greater vestibular gland.Fornices of the vagina
the interior of the upper end of vagina ( vaginal vault) is converted by the protruding cervix ( vaginal part) into a circular grooveThe ant part of that groove is shallow & called ant. Fornix
The post part of that groove is deep and called post fornix
On each side of the cervix there is a lateral fornix.
Arterial supply
Supply by branches from1- vaginal a. 2- uterine a. 3- middle rectal a.
4- internal pudendal a.
All anastemose togather forming vaginal azygos arteries
lymphatic drainge; upper 1/3 ext.iliac l.n
Middle 1/3 internal iliac l.n
Lower 1/3 superfacial ing. L.n
Nerve supply
Upper 2/3 is pain insensitive and supply by autonomic fiber sympathetic L1&2parasympathetic S2,3
Lower 1/3 is pain sensitive and supply by pudendal n.
PERINEUM
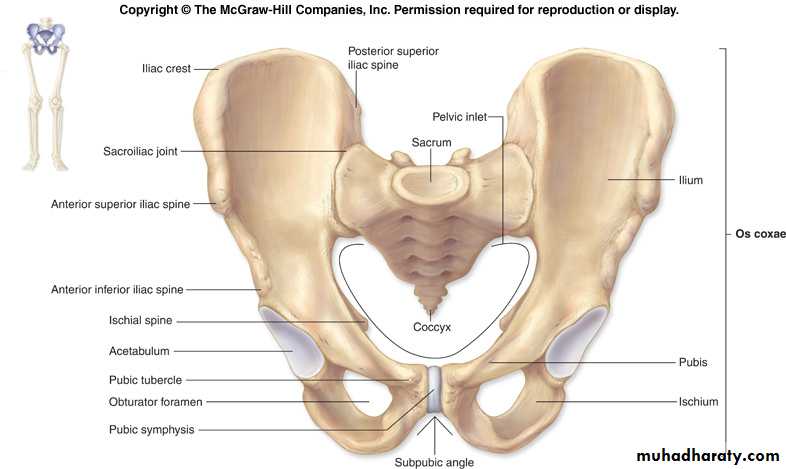
It’s the region which overlies the pelvic outletShape ;it has diamond shape out line
Boundreies; has 4 border and 4 angles
A- angles; ant. Angle formed by ; lower border of sym. Pubis& inf. Pubic lig.
Post angle; formed by the tip of coccyx.
2 lateral angles formed by ischial trubutaries
Borders;
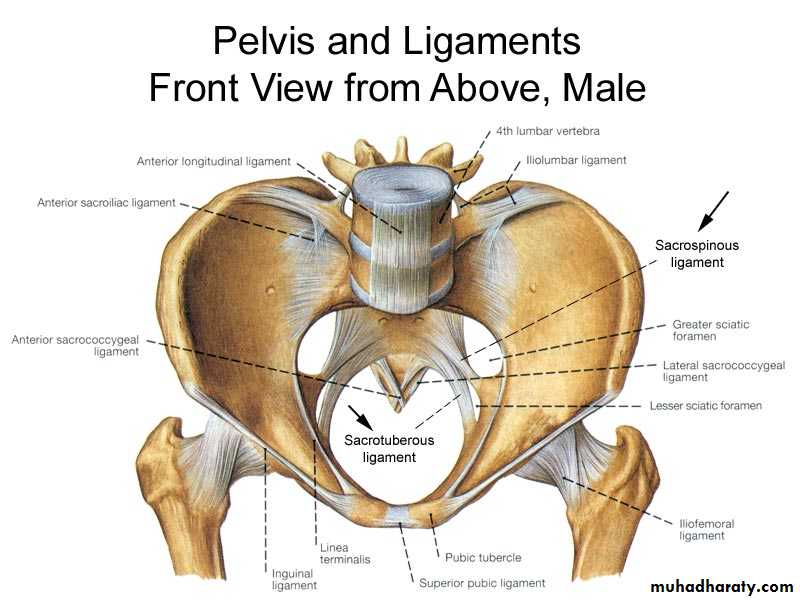
2 anteriolateral borders; formed by pubic arches.2 post lateral borders; formed by sacrotuberous ligaments
Divisions of the perineum
Divided to 2 traingle if an imaginary line joining the 2 ischial tuberosities and passing just infront of anus.ant. Urogental triangle and post. Anal traingle
Anal traingle;
Site; behind the line joining the 2 ischial tuberosities
Contents;
1- The ana canal in the median plane ( surrounded by external anal sphincter
2- 2 ischiorectal fossa on each side of anal canal
Urogental traingle
Site ; infront of the line joining the 2 ischial tuberosities
Contents;
1- deep perineal pouch
2- superfascial perineal pouch
3- the urethra
4-The external genital organs
ISHIOREctal FOSSA
Shape & position:*it is wedge – shaped space situated one on each side of the anal canal*it has an apex ( directed upwards), abase(directed downwards & 4 walls ( ant , post ,med & lateral)
Dimensions :
1- anteroposterior (length) 2 inches
2-side to side ( width) 1 inch
3-vertically ( depth) 2 ½ inches
Boundaries:
1) the base : is directed downwards & formed by the perineal skin & fascia on the side of anal orifice2) the Apex : directed upword ( forming the edge of the wedge). It is formed by the meeting of the medial & lateral walls of the fossa i.e at the origin of levator ani m . from the obturator fascia
3) Ant. Wall: formed by the post . Border of the perineal membrane and superficial & deep transverse perineal muscles ( superficial& deep to the perineal membrane
4) post Wall : formed by sacrotuberous lig. & the lower border of the gluteus maximums
5) Lateral Wall ; ( vertical ) formed by obturator internus m. & its covering fascia including the pudendal canal
6) Media Wall : (sloping ) & formed by:
a) levator ani muscle …..( in the upper 2/3)
b) external anal sphincter .. ( in the lower 1/3)
Contents OF The ischiorectal fossa
(1) Semiliquid pad of fat : allows distension of the anal canal during defecation.(2) inf. Rectral neves:
* arises from the pudendal nerve in the post . Part of the pudendal canal
* traverses the fossa from lat to med where it enters the ext. anal sphincter to supply it
(3) inf. Rectal vessels ( artery & vein)
* arise from the internal pudendal vessels in the pudendal canal*accompany the inf. Rectal n. across the fossa to reach the anal canal & the skin around the anus (4) Post. Scrotal ( labial ) nerve & vessels:* arise in the pudendal canal & pass forwards in the ant. Part of the fossa to reach the superficial perineal pouch
(5) Perineal br.of S4 : pierces the coccygeus m. to enter the post part of the fossa where it supplies the ext-anal sphincter & the skin around the anus.
(6) Pudendal canal & its contents :
Pudendal canal
Its fascial tunnal in the lateral wall of ischiorectal fossa transmitting the pudendal nerve and internal pudendal vessels.It lie just above the sacrotuberous ligament extending from the lesser schiatic foramen to the post. Border of the perineal membrane.
Its formed by the splitting of the fascia covering the obturater internus m. below the tendenous arch into 2 layers that envelope the pudendal nerve and internal pudendal vessels.
Contents;
1-Pudendal nerve.; in the post. Part of the canal ,pudendal nerve give the inf, rectal nerve.
And then soon divides into a larger perineal nerve and smaller dorsal nerve of penis(or clitoris)
2- internal pudendal vessels; internal pudendal artery gives off its inf.rectal branch in the post part of the canal .in the ant part of the canal the artery give its scrotal or labial branch.
The internal pudendal veins. receives tributaries corresponding to the branches of the artery.
Applied anatomy
1-I.R.fossa act as a cushion like support to the rectum and anal canal …..so prolapsed rectum
2-I.R. abscess
3-Ano rectal fistula if burst in anal canal
4-If burst out side cause ext. fistula
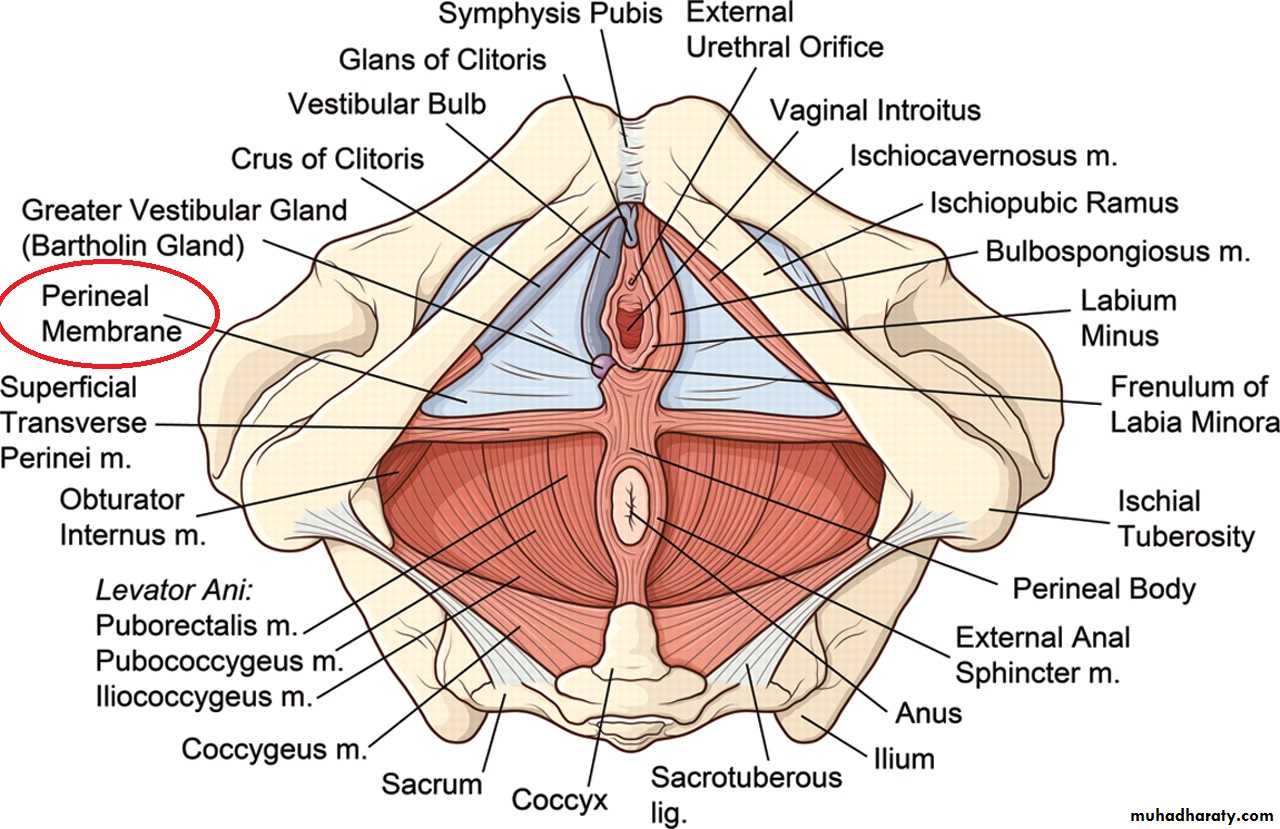
Urogital traingle 1- superficial perineal pouch
It’s a facial space in the urogeital triangle lying between the perineal membrane and the membranous layer of superficial fascia of the perineum ( colles fascia)Boundreis
Roof (superiorly); perineal membrane
Floor ( inferiorly) membranous layer of superfascial fascia of perineum ( colles fascia)
Posteriorly the pouch is closed by the fusion of the roof and floor along the post. Border of the perineal membrane.
On each side (laterally); the pouch is closed by attachment of the roof & floor to the sides of the pubic arch.
Interiorly ; the pouch is open & is continuous with the space deep to the membranous layer of the superficial fascia of the anterior abdominal wall ( scarpo’s fascia)
Contents of superfascial perineal pouch in male
Contents in the maleA. 3 stractures forming the root of the penis
1- bulb of the penis ; its covered by pair of bulbospongiosus m.
2- crura of the penis 2 in no.
Each crus is the proximal part of corpus cavernosus
Each crus is firmly attach to the pubic arch
Each crus is covered superficially by the ischiocavernosus m.
Each crus is pierce by deep artery of the penisB. 3pair of superficial perineal M.
1- ischiocavenosus m rt & lf
2- bulbospongeosus m rt &lf
3- sperfascial transvesus perinei m rt&lf
All perineal M are supplied by the perineal br. Of pud. N
Origin , insertion and function of these M. important in lacture.
c. Vessels and nerves
1- 4 arteries on each side ( branch of internal pud. Art.)
1- dorsal artery of penis
2- deep artery of the penis
3- artery of the bulp of penis
All these 3 arteries peirse the perineal mem. To enter the superfascial pouch.
4-Post. Scrotal artery arise in the pudendal canal
2 nerves
1- post. Scrotal n. arise from arise from perineal branch of pudendal n.2- dorsal n. of the penis its one of 2 terminal branch of pudendal n
1 vein ; the deep dorsal vein of the penis it enter the pelvis to join prostatic plexus of veins
Contents of the superficial perineal pouch in the female
A. the structures forming the root of clitoris1- 2 pulb of vestibule
2- 2 crura of clitoris
B. 3 pairs of the muscles as in the male
C.Vessels and nerves;
1- 4 arteries ; brs. Of int. pud. Art. A-Dorsal art. Of clitoris
B- deep art. Of clitoris
C- art. Of the bulb of vestibule
D- post labil art.
C- 2 nerves
Post. Labial N. & dorsal N.of clitoris
D. greater vestibular glands
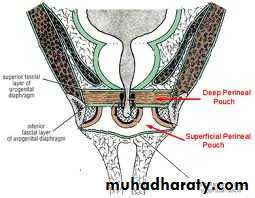
2. Deep perineal pouchDefinition: it is a completely closed fascial space situated in the urogenital triangle above (deep to) the superfiscial pouch. It is also called urogenital diaphragm
Boundaries:
1. Superiorly: sup. Fascia of urogenital diaphragm2. Inferiorly: perineal membrane.3. On each side (laterally): the space is closed by fusion of the roof & floor to the sides of pubic arch.
Ant. & Post. => the space is closed by fusion of roof & floor.
* Contents of Deep perineal pouch (in male):1. Membranous urethra
2. Pair of bulbo-urethral glands3. Dorsal n. of penis (from pudendal n.)
4. Termination of int. pudendal a.
5. Sphincter of urethrae muscle
6. Deep transversus perinei m. (Rt&Lt) in the post. Part if deep pouch.
7. Plexus of veins
• Its contents in females:
• 1-Urethra
• 2-Vagina
• 3-Dorsal n. of clitoris
• 4-Termination of internal pudendal artery
• 5-Sphincter urethrae muscle
• 6-Deep transversus perinei (Rt&Lt)
• 7-Plexus of veins
Perineal Membran
Definition: It is a strong triangular fibrous membrane which fills the space between the pubic arches.Attachments:1. Apex (ant. Border): is directed forward towards the symphysis pubis where it is thickened to form perineal lig.2. Base (Post. Border): stretches be the 2 ischial tuberosities where it fuses with both pelvic fascia & Colle’s fascia
3. On each side => attached to pubic arch.
Structures piercing the perineal membrane:
• (A) In MALE• 1-Urethra
• 2-Ducts of bulbo-urethral glands: one on each side.
• 2-Artery of the bulb: one on each side close to the opening.
• 3-Deep artery of penis
• 4-Dorsal artery of penis
• 5-Dorsal nerve of penis
Structures piercing the perineal membrane:
:(B) In FEMALE
• 1-Urethra
• 2-Vagina
• 3-Artery of bulb
• 4-Deep artery of clitoris
• 5-Dorsal artery of clitoris
• 6-Dorsal nerve of clitoris
Perineal Body
Definition: It is a pyramidal fibromusclar mass lying in the middle line of the perineum at the junction between the urogenital triangle & anal triangle.Site:Male => it is between the bulb of penis & anal canal
Female => it lies between the lower 1/3 of vagina & anal canal
Function: it acts as tendnous centre for the attachment of several muscles:1. ant. Fibers of levator ani (pubococcygeus part) of both sides
2. Fibers of sphincter of urethra muscle
3. The deep transverses perinea muscles
4. Superficial transverses perinea muscles
5. Bulbospongiosus muscle
6. Fibers of the external anal sphincter
Applied Anatomy
The perineal body is essential for the integrity of the pelvic floor (particularly in females). Its rupture during delivery leads to widening of the gap between the anterior borders of levator ani muscle of both sides thus predisposing to the prolapsed of the uterus, rectum or even urinary bladder.
Main differences between male & female perineum
• 1-The deep perineal pouch (urogenital diaphragm) is split, in females into 2 halves by vagina.• 2-The muscles of the deep perineal pouch are not well developed in female & sphincter urethral muscle does not encircle the female urethra completely. (One cause of urine incontinence)
• 3-The muscles of the superficial perineal pouch are also smaller in female & the bulbospongiosus muscle is divided into 2 halves by the vagina.
4. The labia majora in female are the homologues of the scrotum in male
5. The clitoris in female is homologues of penis & its vessels and nerves correspond to those of penis6. In female, the 2 greater vestibular glands are homologous with the bulbourethral glands lying in Deep p. pouch in male.
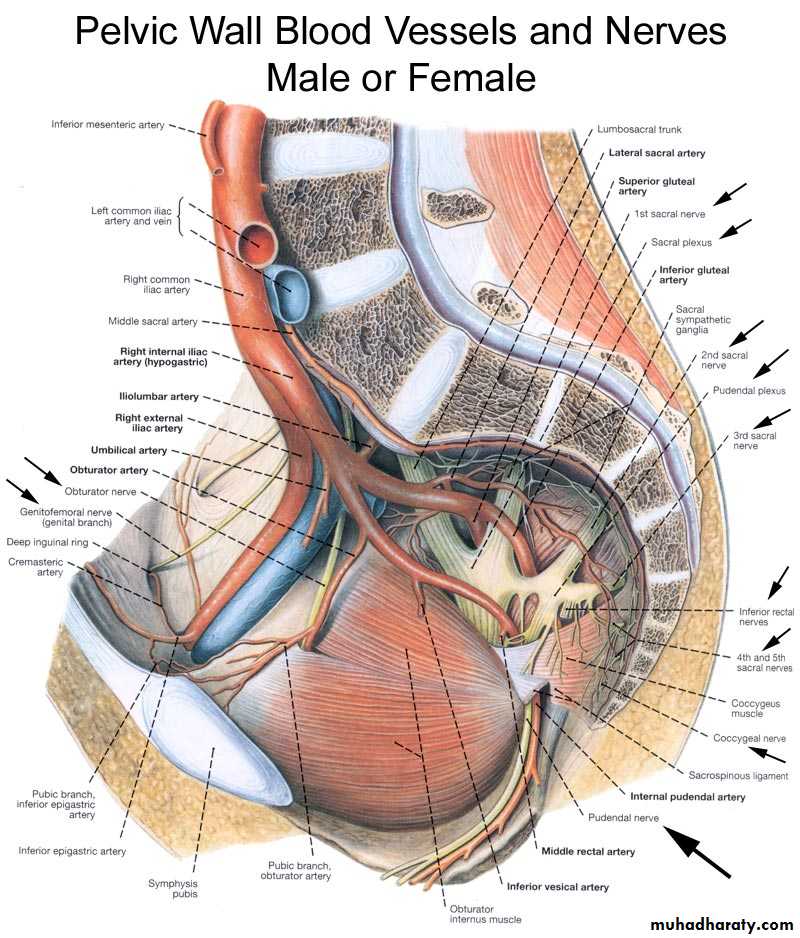
Internal Pudendal Artery
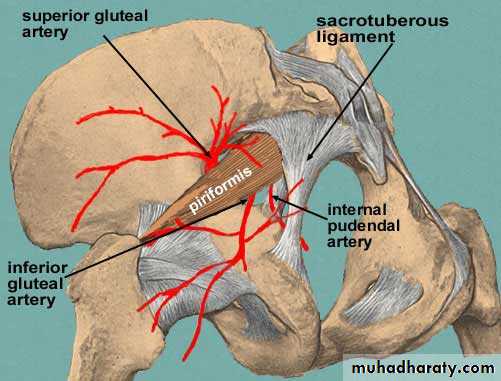
Origin: it arises inside the pelvis as one of the 2 terminal branches of ant. Division of internal iliac artery.Course & Relations:1. It leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen (below piriformis muscle) to reach the gluteal region.
2. In Gluteal region it crosses the back of ischial spine (between Pudend. N. medially & Obturator internus N. laterally.
3. It leaves the gluteal region & enters the lesser sciatic foramen to reach the PERINEUM accompanied by the pudendal n
4. It enters the pudendal canal
5. It enters the deep perineal pouch, where it ascends along the side of the pubic arch accompanied by dorsal nerve of penis.
Termination: In DEEP perineal pouch, a short distance below the symphysis pubis & dividing into (DEEP & Dorsal arteries of penis)
Its Branches
1. Inf. Rectal a. : arises in the pos. part of the pudendal canal. It tansverses the ischio-rectal fossa from lateral to medial to reach the analcanal (supplying it).
2. Perineal a. : from int. pud. A. near the ant. End of pudendal canal then pierces the perineal membrane to enter the superficial perineal pouch where it gives 2 branches Transvers perineal artery & Post. Scrotal (labial) artery,
3. Artery of the bulb: arises in deep perineal pouch then pierces the perineal membrane to supply the bulb of penis4. Urethral .5. Deep a. of penis (on of terminal 2 branches)
6. Dorsal a. of penis ( other terminal branch)
Pudendal nerve
Its arise as one of terminal branch of sacral plexus.It terminte in pudendal canal by dividing to 2 terminal branch dorsal nerve of penis and perineal nerve
Course and relation; it accompaies the internal pudendal artery as far as the pudendal canal and having the same course
It leave the pelvis through greater sciatic foramen ,crosses the sacrospinous ligament then enter the lesser sciatic foramen then enter the pudendal canal
Branchesall arise in the pudendal canal
1- inferior rectal nerve ; arise in the post part of pudendal canal it supply ;
A- levetor ani m. ( lower surface);
B- external anal sphinctor
C-anal canal below the pectinate line
2- perineal nerve ; the larger of the 2 terminal brs. It divided in to
A- post. Secrotal ( labial) nerve it supply post. Part of secrotum ( labium majus in femal)
B- muscular br. To supply all perineal m.
3- dorsal n. of the penis ( clitoris) the smaller br.
Course; it run first in pudendal canal then in deep perineal pouch between the pubic arch and internal pudendal art.Then it pierces the perineal mem. To reach the dorsum of penis where it runs lat to the dorsal art. Of penis to end in the glans penis
It supply the skin of penis and glans penis.
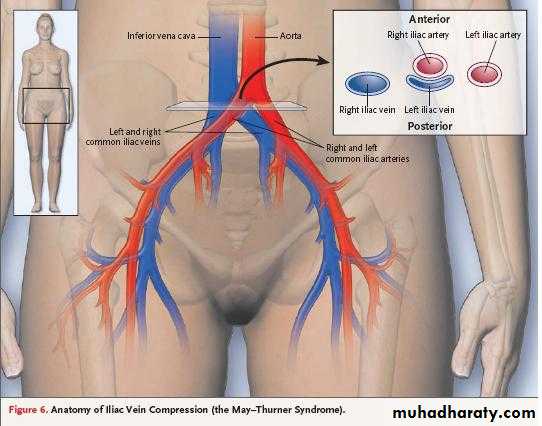
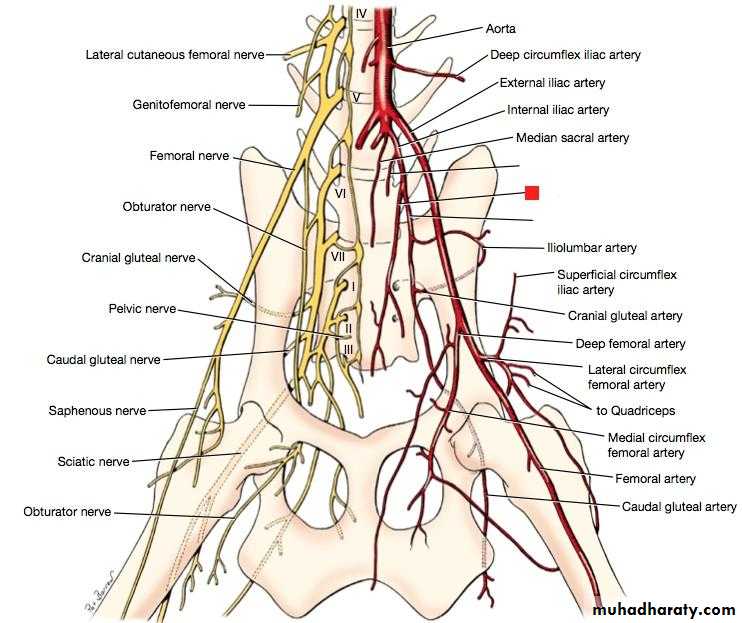
Arteries of the pelvis1- common iliac artery
Beginning; at lower border of 4th L.V. as one of terminal br. Of abdominal aorta.Course; it descend downward and laterally along the medial border of psoas major m.
It terminate opposite to the sacroiliac joint by dividing to internal and external iliac art.
Relation of rt & lf common iliac art
RT common iliacAnt. ;1- pariatal perto.
2-Rt ureter ( crosses the end of the artery)
3-Sympathetic fiber passing to the sup.hypogastric plexus
Post.; 1-) 4th & 5th lumber vertebra
2-) rt sympathetic chain , obtur. N, & lumbosacral trunk
3-) begning of I.V.C.
Medially; lf common iliac vein
Laterally; 1- rt psoas 2- rt common iliac veinLf common iliac artery
Ant. 1- parietal peritoneum.
2- lf ureter
3- symp. Fiber passing to sup. Hypo.gast.
4- sup.rectal vessels crossing the meddle of the art.
Post; 1-) 4th & 5th L.V
2-) lf symp.chain & obtur. Nerve & lubosacral plexusMedially ; lf common iliac vein
Laterally; lf psoas major muscle
External iliac artery
It arise at the level of sacro iliac joint as a larger br. Of C.I.A
It terminate when enter the thigh by passing deep to inguinal lig. At the mid ing. Point
Course; it runs along the medial border of psoas major. m. on the pelvic brim
Relations
Ant. Medially; a- its covered by peritoneum which separate the artery from the terminal part of the ileum on the rt side and sigmoid colon and ileum on the lf side
B- it crossed by 1- the ureter ( crosses the artery at its beginning)
2- vas deferens ( in the male)Ovarian vessels and round lig. Of uterus in female
Laterally; psoas major muscle
Posteriorly; ext. iliac vein
Branches;
1- inf. Epigastric a.
2- deep circumflex iliac a.
It arise from EIA just above the ing. Lig
It pass toward the ant. Sup .iliac spine
Then it pierces the transversus abdomenis m. and pass between it & internal abdominal obl. M. (so in app)
Branches;
1- muscular br. To ms of ant. Abdominal wall
2- ascending br. Ascend between the trans. Abd. & int. obl. M. to anastemose with the lumber arteries and musculophrenic art.
3- anastomotic br. Share in anastemosis around the ant sup. Iliac spine.
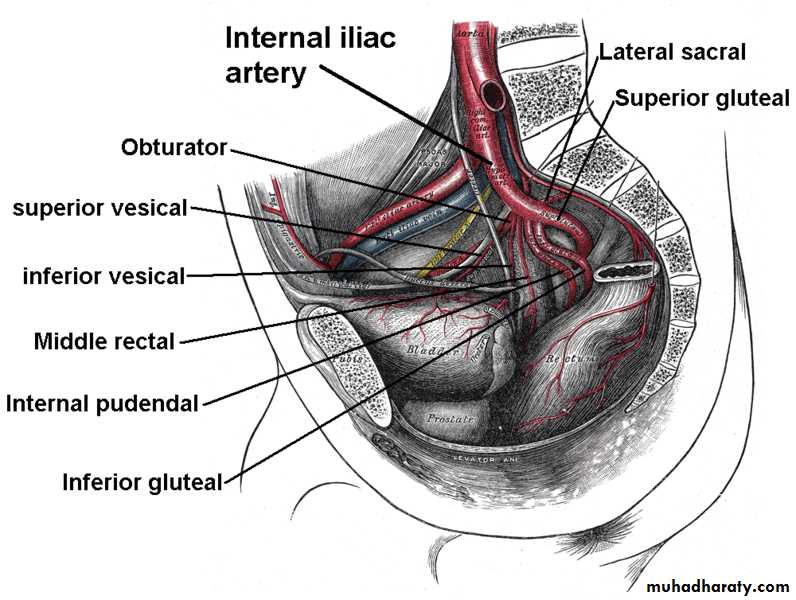
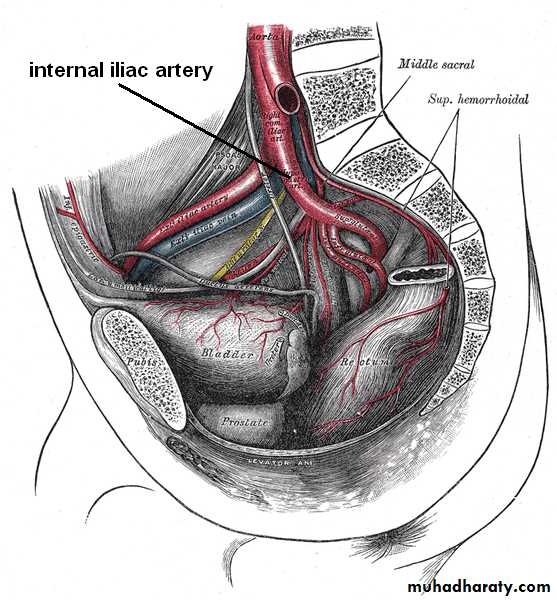
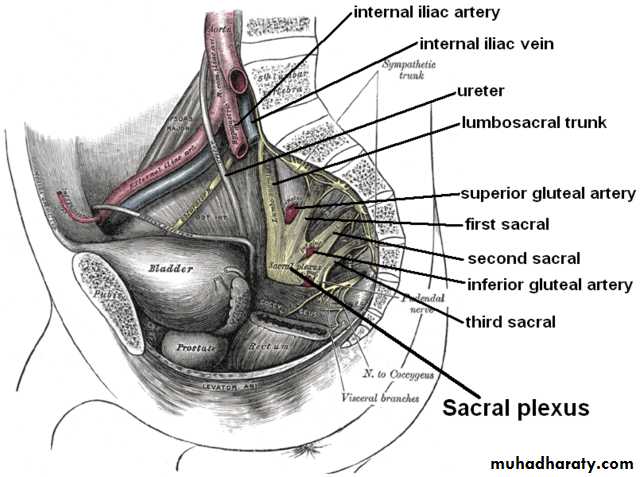
Internal iliac artery
It arise as a smaller terminal br.of CIE opposite to sacroiliac joint at the level of lumbosacral JOINT.It terminate at upper margin of greater sciatic foramen by dividing to ant& post, divisions.
Course;it descend on lateral pelvic wall for 4 cm then divided to ant. Division continue to ischial spine and post. Division which run back words toward the greater sciatic foramen
relations
Infront; 1- ureter parallel to the artery (both sex)2- ovary and lateral end of uterin tube ( in female)
Behind; 1-internal iliac vein} parallel to artery
2- lumbosacral trunk} parallel to artery
3- sacroiliac joint
Laterally; 1- external iliac vein –separate the artery from paoas major m.
2- obturator nerve; seperat the artery from pelvic wall
Medially; peritoneum, seperating the artery from
1- terminal part of the ileum on the rt side
Sigmoid colon on the lf side
Branches of internal iliac artery
From post, division;1- iliolumber art.
2- lat. Sacral art.
3- sup. Glueteal art.
From ant. Division;
1- obturator art.2- internal pud, art.
3- inf. Gluteal art. 4- sup. Vesical art
5-inf. Vesical art.
6- middle rectal art.
(A) Branches of post. Division
1. Iliolumbar a.- Passes upward & laterally infront of sacro iliac joint.
- It gives to 2 branches:a) ilica br. Runs laterally deep to iliacus muscle. It anastomeses with iliac br. Of obturator a. around the ant. Sup. Ilica spine
b) Lumbar br. Ascends between psoas major and quadratus lumborum (supplying both)
2. Lateral sacral arteries:they are 2 arteries and each artery divides into 2 branches, the resulting 4 arteries enter the ant . Sacral foramina, then emerge from post. Sacral foramina to supply muscles & skin on the back of sacram.
3. Superior gluteal artery: is the continuation of post. Division of int. iliac a (largest branch), it passes between the lumbosacral trunk and 1st sacral nerve OR between the 1st and 2nd sacral nerves.
The Superior Gluteal artery ends in gluteal region by dividing into:
a. Superficial br. To the deep surface of gluteas maximus.b. Deep br. Laterally deep to gluteus medius and supplies (gluteus medius & minimus.(B) Branches of ant. Division1. Obturator artery
It runs forwards on the lat. Pelvic wall, accompanied by obturator n. (above the artery) & obturator vein (below the artery){NAV}- It gives the following branches in the pelvis:a. iliac brs. To the iliac fossa.b. Pubic br.: arises just before the artery reaches the obt. Canal.
- It ascends behind the sup. Pubic ramus to anastomose with the pubic br. Of inf. Epigastric artery.
N.B. in 20-30% of people, the pubic br. Of inf. Epigastric artery is large & replaces the Obturator artery. & is called the Abnormal obturator artery. It crosses the base of the lacunar lig. To reach the Obt. Canal ..(femoral hernia)
C- Vesical br. To the urinary bladder (may replace the inf. Vesical artery).
2. Inferior gluteal artery
- It is the larges of 2 terminal brs. Of ant. Division on int. iliac artery- It passes between the 1st & 2nd (or between the 3rd & 4th) sacral nerves.
- It leaves the pelvis by passing through the greater sciatic foramen, below piriformis m.
- It enters the gluteal region where it supplies the gluteal muscles & shares in the iliac, cruciate & trochantric anastomoses.
3. Internal pudendal artery:
It is the smaller terminal br. Of the ant. Division.4. Obliterated umbilical artery
- It passes forwards on the side wall of the pelvis then ascends on the back of the ant. Abdominal wall as far up as the umbilicus.
- Its proximal part (1-2 inches) is patent & gives of 2-3 sup. Vesical arteries to supply the urinary bladder & the artrey of vas defrens
- Its distal part is obliterated & called the lat. Umbilical lig.
5. Inferior vesical artery
- It supplies the base of urinary bladder, lower part of the ureter, seminal vesicles & prostate.
In female, this artery is replaced by the vaginal artery.
6. Vaginal artery: runs forward & medially in levator ani m.
7. Uterine artery8. Middle rectal artery gives brs to prostate & seminal vesicle (in male) & to vagina (in female).
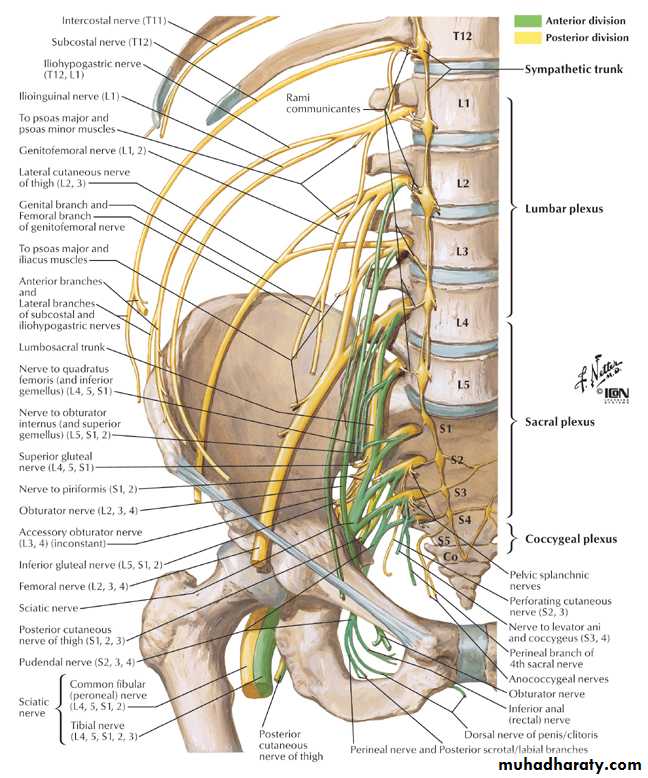
Nerves of the Pelvis
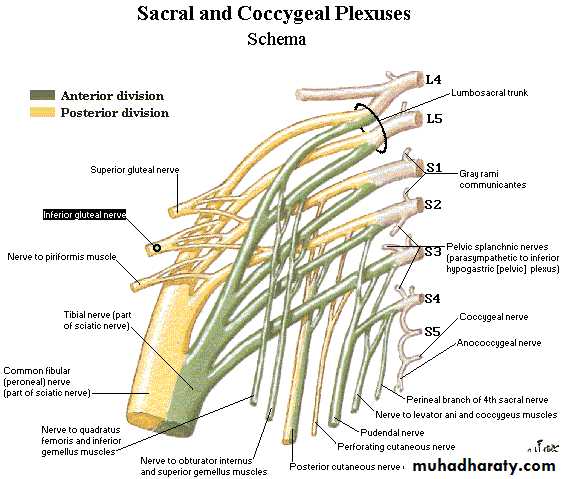
• Sacral plexus*Formation: it is formed by the lumbosacral trunk & the ventral rami of S1,2,3 & upper part of S4 nerves. (the roots have ant. & post. Divisions).
*Site & Relations:it lies on the post. Pelvic wall infront of piriformis M. and behind the internal iliac vessels & ureter.- the roots converge towards the lower part of greater sciatic foramen.
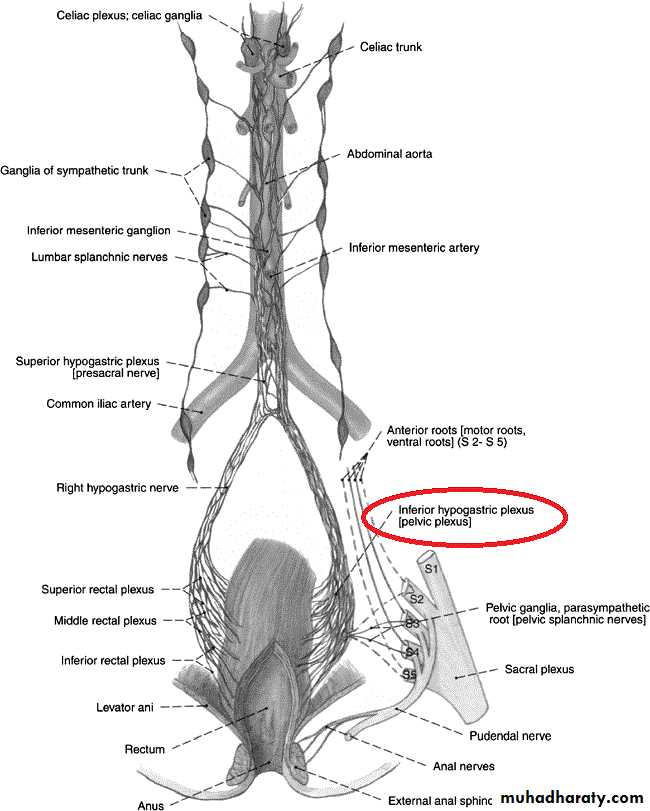
Then they unite and form a triangular band ends by dividing into: A. Larger terminal band (Sciatic N.) B. Smaller terminal band (Pudendal N.)
Branches of the plexus:
A. From roots only:1. Nerve to piriformis (S1,2)2. Perforating cutaneous n. of thigh (S2,3)3. Pelvic splanchnic n. [Parasympathetic S2,3,4]
4. Perineal branch of 4th sacral n.
5. Pudendal n.
B. Branches from anterior divisions:
• Nerve to quadratus femoris [L4,5,S1]
• Nerve to obturator internus [L5,S1,2]
C. Branches from posterior divisions:
• Superior gluteal n. [L4,5&S1]• Inferior gluteal n. [L5,S1&2]
D. Branches from both ant. & Post. Divisions:
1. Post. Cutaneous nerve of thigh [post. Div. of S1,2 & ant. Div. of S2,3]2. sciatic nerve: common pereneal portion [ post. Div. of L4,5, S1,2] & tibial portion [ant. Div. of L4,5].
2. Coccygeal plexus
3. Pelvic part of sympathetic chain
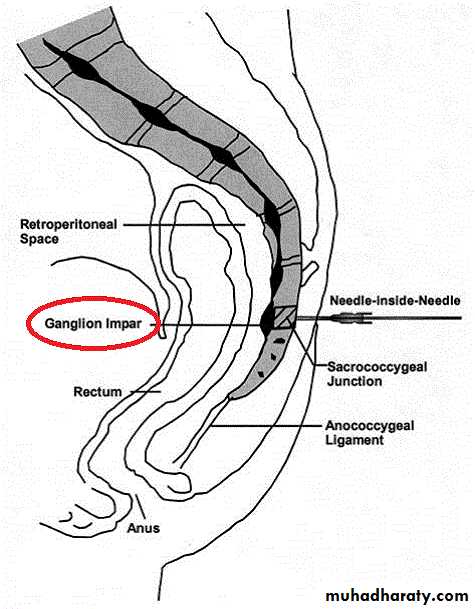
The sympathetic chain (one on each side) enters the pelvis by crossing infront of the ala of sacrum & deep to common iliac vessels. It contains 4 ganglia.Course & Relations:
it decsends on the pelvic surface of the sacrum (just med. To ant. Sacral foramina) & behind the sigmoid colon & rectum.
The Rt. & Lt. chains converge & unite together infront of coccyx ending in a small ganglion called ganglion impar
Branches
Grey rami communicates [post. Ganglion fibers] to all the sacral nerves & coccygeal nerve.Branches from upper 2 ganglia to the inferior hypogastric plexus.
Vascular branches to:
The arteries of the perineum reaching them via pudendal n.
Popliteal artery of the lower limb (reaching it via femoral nerve)
N.B. : the sym. Vascular brs. To femoral artery arise from the lumbar part of symp. Chain.
4. Inferior Hypogastric plexuses