THE BREAST
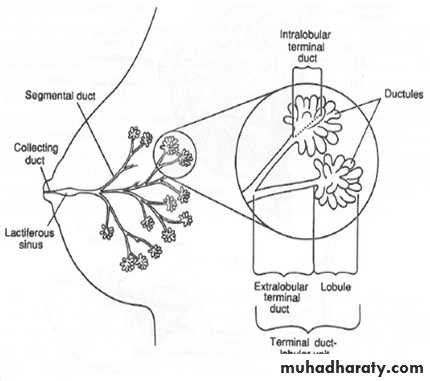
Normal anatomy:-The breast is a modified sweat gland, the morphofunctional unit of the organ is a single gland which's a complex branching structure that's composed of 2 major parts terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) is formed by lobules and terminal ductules and represent the secretory portion of gland, it connect to subsegmental duct which's lead to segmental duct and this to a collecting duct which empties into the nipple.
Diseases of breast:
The predominant symptoms and signs of diseases of the breast are pain, inflammatory changes, nipple discharge, “lumpiness,” or a palpable mass. However, few symptoms are so severe as to require treatment, and the primary reason for investigating their cause is to evaluate the possibility of malignancy. Most symptomatic breast lesions (>90%) are benign, while women with cancer, about 45% have symptoms, whereas the remainder come to attention through screening tests.I. Inflammation:-
1- Acute mastitis:- caused by bacteria which's gain access through fissures of nipple in female during lactation .ex. staphylococcus infections caused breast abscess while streptococcus caused pain, swelling and breast tenderness.
2- Chronic mastitis:-
a- Granulomatous mastitis:- Characterized by presence of non-caseating granuloma confined to breast lobules, it had no microorganisms so it's immunologically mediated.b- Tuberculosis:- is a rare secondary to blood stream dissemination or local extension, microscopically composed of typical caseating granuloma of TB.
.II. Mammary ductectasia:-
The condition occur in female during reproductive life caused by inspissation of breast secretion in main excretory duct, this dilation lead to a reactive changes in the surrounding breast tissue which's infiltrated by inflammatory cells especially lymphocytes, plasma cells and even granuloma, the importance of this condition is causing of skin and nipple retraction similar to seen in carcinoma.
.III. Galactocele:-
This is occurring in lactating female due to cystic dilation of obstructive ducts when ruptured and caused inflammatory reaction in surrounding stroma..IV. Fat necrosis:-
Which's occur due to trauma (accidental or surgical) the importance of this condition in causing breast mass and nipple retraction..V. Fibrocystic disease of breast:-
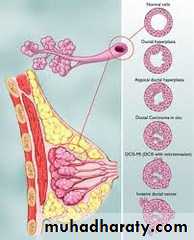
It is a group of changes occur in breast consist of stromal fibrosis with stromal and epithelial hyperplasia inducing micro or macrocysts, there are banal of epithelial hyperplasia the more serious is atypical hyperplasia which's produce palpable lumps and more risky to develop carcinoma, so fibrocystic disease is divided into:-A- Non proliferative lesion:-
This lesion include cysts and/or fibrosis without epithelial cell hyperplasia, it is more common occur in female breast during reproductive life, the disorder is usually multifocal and often bilateral, the breast is consist of ill defined mass and only nodularity.B- Proliferative lesion:-
It is consist of proliferated epithelial cells lined ducts, ductules, or lobules and this proliferation is either mild hyperplasia which's carry little risk of carcinoma, moderate and severe hyperplasia, if the hyperplastic epithelial cells multilayered, disordered and vary in nuclear cell size and shape with nuclear hyperchromasia this approach to carcinoma in situe, but this is usually preserved myoepithelial cell layer.Relationship of Fibrocystic disease to breast cancer.
1. Minimal or no increased risk of breast cancer in fibrosis, cystic changes (micro of macro cystic ) and mild hyperplasia.2. Slightly increased the risk (1.5 to 2 times) in moderate to florid hyperplasia and ductal papillomatosis .
3. Significantly increased risk (5 times) in atypical hyperplasia.
4. proliferative lesions may be multifocal and the risk of carcinoma extends to both breasts.
5. A family history of breast cancer increases the risk in all categories.
VI: Tumors of breast:
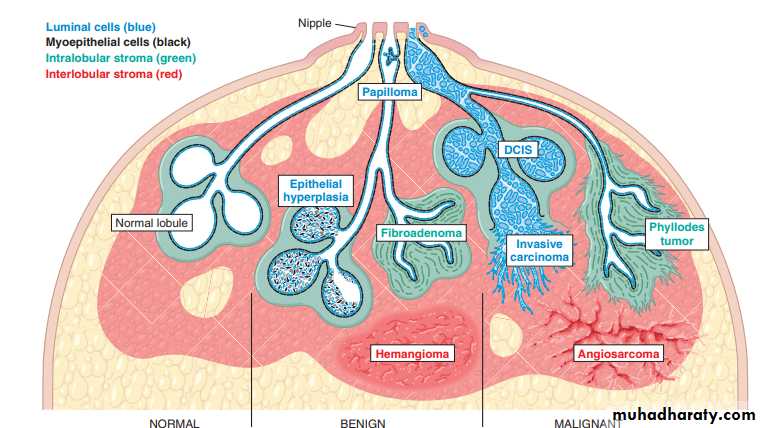
STROMAL NEOPLASMS
The two types of stroma in the breast, intralobular and interlobular, give rise to different types of neoplasm, tumors derived from intralobular stroma have been divided into benign fibroadenomas and more cellular phyllodes tumors, which sometimes recur following excision and rarely pursue a malignant course. It is now appreciated that these tumors share driver mutations in the same genes and appear to be part of a spectrum of related neoplasms, Lesions of interlobular stroma are monophasic (only comprised of mesenchymal cells) and include benign soft tissue tumors found elsewhere in the body, such as hemangiomas and lipomas. The only malignancy derived from interlobular stromal cells of note is angiosarcoma .
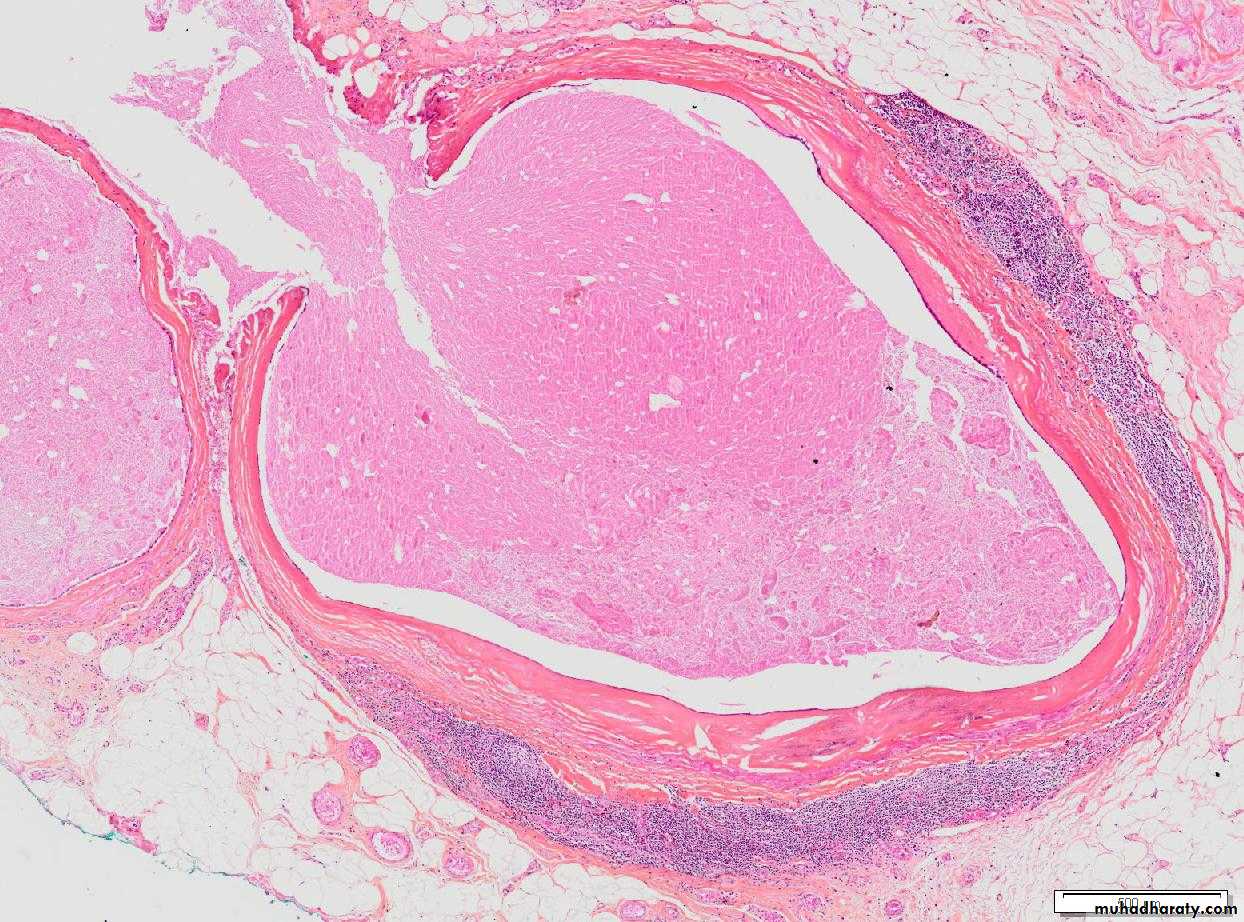
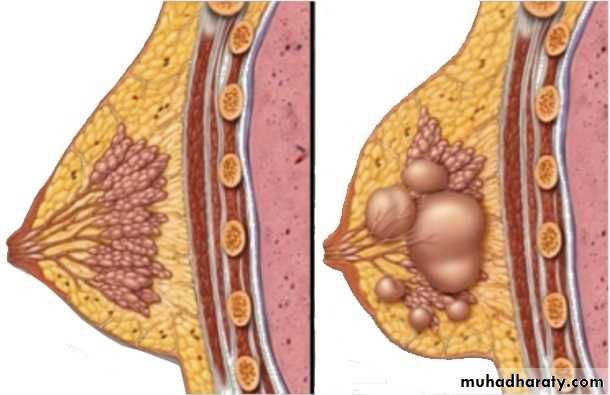
Fibroadenoma:-
It is a common benign tumor occur in female breast in young age group, the peak incidence usually in ages 20-35 years, the estrogen is play important role in it's development, the tumor usually well capsulated, freely movable hard mass.Grossly : appear as hard, firm mass white in colour.
Histologically: consist of loose fibroblastic stroma with duct like epithelium lined spaces of various forms and sizes.
Malignant transformation in fibroadenoma found in 0.1% of the cases.
Phyllodes tumor:-
They are much less common than fibroadenoma and are arising from intralobular stroma, most of these tumor usually benign but some become malignant which there are increased in stroma cellularity with anaplasia, high mitotic activity and rapid increase in size.EPITHELIAL NEOPLASM:
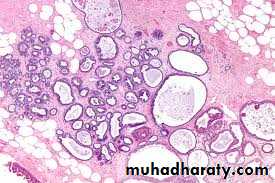
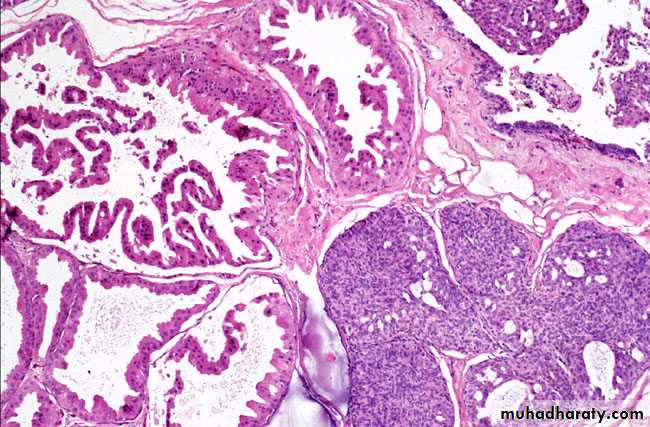
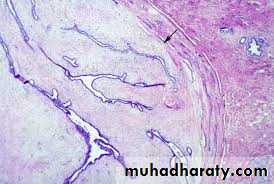
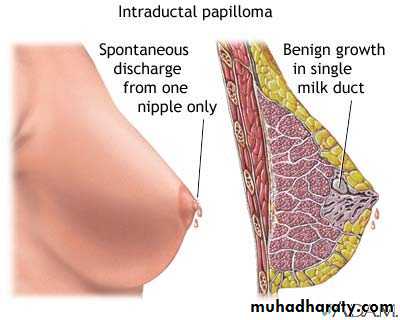
Intraductal papilloma:-It's a benign papillary growth within a duct, most lesion are solitary occur in common ducts the presentation are usually characteristic by:-
1- Serous or bloody nipple discharge.
2- Presence of small subareolar tumor.
3- Rarely nipple retraction.
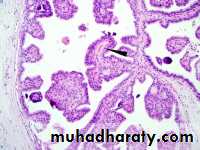
Microscopically: seen as multiple papillae having fibrovascular core and lined by cuboidal to columnar epithelial cells usually double layer epithelial and myoepithelial cells.