
(1)
Subject: Medical physics
قسم الفسلجة والفيزياء
الطبية
Energy, Work, and Power of the Body
Energy is a basic concept of physics. All activities of the body, including
thinking, involve energy changes. The conversion of energy into work
represents only a small fraction of the total energy conversions of the body.
25% is being used by the skeletal muscles and the heart.
19% is being used by the brain.
10% is being used by the kidneys.
27% is being used by the liver and spleen.
The body's basic energy source is food.
The uses the food energy to:-
1) Operate its various organs,
2) Maintain a constant body temperature,
3) Do external work.
A small percentage (~5%) of the food energy is excreted in the feces and
urine.
Conservation of energy in the body:-
We can write the first law of thermodynamics as
(1)
is the change in stored energy
is the heat lost or gained
is the work done by the body in some interval of time
this equation assumes that no food or drink is taken in and no feces or
urine is excreted during the interval of time. A body doing no work (
=0)
and at a constant temperature continues to lose heat to its surroundings,

(2)
is negative. Therefore,
is also negative, indicating a decrease in stored
energy. It is useful to consider the change of
, , and in a short
interval of time
. Equation(1) then becomes
(2)
⁄
is the rate of change of stored energy
⁄
is the rate of heat loss or gain
⁄
is the rate of doing work (chemical power)
Eq.(2) is merely another form of the first law of thermodynamics. It tell us
that energy is conserved in all processes, but it does not tell us whether or
not a process can occur.
Energy change in the body:-
Physiologist usually use kilocalories (kcal) for food energy and
kilocalories per minute for the rate of heat production. In physics the unit for
energy is the newton – meter or joule (N . m =J) ; power is given in joule per
second or watts(W). The unit in the cgs system is the erg, and that in the
English system is the foot – pound(ft –lb).
A convenient unit for expressing the rate of energy consumption of the
body is the ( met).
1met=50 kcal/m
2
of body surface area per hour.
A typical man has about 1.85m
2
of surface area and a woman has about
1.4m
2
and thus for a typical man 1met=92 kcal/hour=107W.
Oxidation occurs in the cells of the body. In oxidation by combustion heat
is released. In the oxidation process within the body heat is released as
energy of metabolism. The rate of oxidation is called the metabolic rate. The
oxidation equation for 1mole of glucose(C
6
H
12
O
6
) is
This is, 1 mole of glucose(180g) combines with 6 mole of O
2
(192g) to
produce 6 mole of each of H
2
O(108g) and CO
2
(264g), releasing 686 kcal of
(3)
heat energy in the reaction. Similar calculation can be done for fats, protein,
and other carbohydrates. Typical caloric values of these food types and of
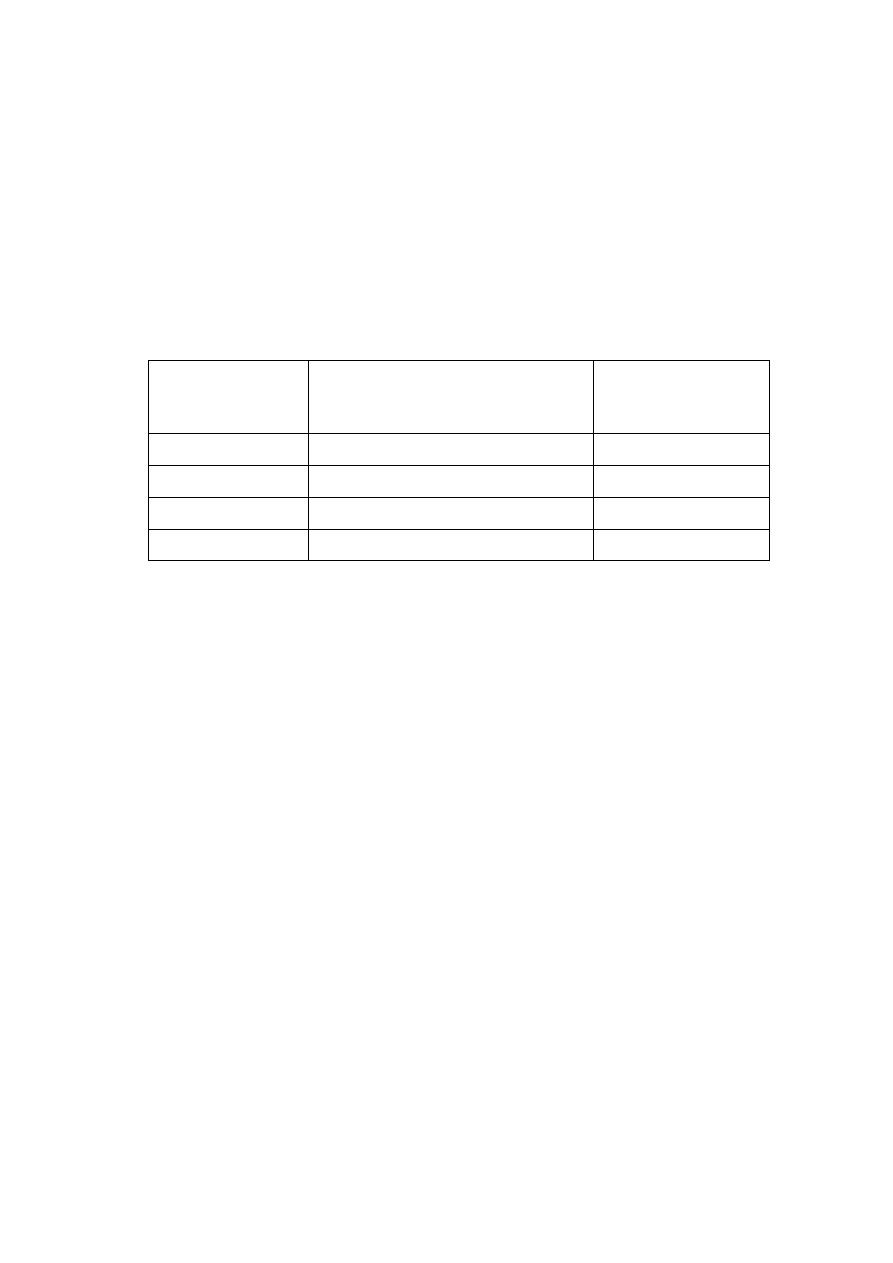
common fuel are given in Table(1). This table also lists for the various types
of food the energy released per liter of oxygen consumed; thus by measuring
the oxygen consumed by the body, we can get a good estimate of the energy
released.
Table(1)
Food or Fuel
Energy Released per Liter
of O
2
Used (kcal/liter)
Caloric
Value(kcal/g)
Carbohydrates
5.3
4.1
Proteins
4.3
4.1
Fat
4.7
9.3
Typical diet
4.8 – 5.0
_
Not all of this energy is available to the body because part is lost in
incomplete combustion. The unburned products are released in feces, urine,
and flatus (intestinal gas). What remains is metabolizable energy. The body
is usually quite efficient at extracting energy from food. For example, the
energy remaining in normal feces is only about 5% of the total energy
contained in the consumed food. When the body is at constant temperature
the energy that is extracted from food plus the body fat make up the
available stored energy.
When completely at rest, the typical person consumes energy at a rate of
about 92 kcal/hr, or 107W, or about 1 met. This lowest rate of energy
consumption, called the basal metabolic rate (BMR), is the amount of energy
needed to perform minimal body functions (such as breathing and pumping
the blood through the arteries) under resting conditions. The BMR depends
primarily upon thyroid function. A person with an overactive thyroid has a
higher BMR than a person with normal thyroid function.

(4)
Since the energy used for basal metabolism becomes heat which is
primarily dissipated from the skin, one might guess that the basal that the
basal rate is related to the surface area or to the mass of the body and is
proportional to mass
3/4
.
The metabolic rate depends to a large extent on the temperature of the
body. Chemical processes are very temperature dependent, and a small
change in the temperature can produce a large change in the rate of chemical
reactions. If the body temperature changes by 1
0
C, there is a change of about
10% in the metabolic rate. For example, if a patient has a temperature of
40
0
C, or 3
0
C above normal, the metabolic rate is about 30% greater than
normal. Similarly, if the body temperature drops 3
0
C below normal, the
metabolic rate( and oxygen consumption) decreases by about 30%. You can
see why hibernating at a low body temperature is advantageous to an animal
and why a patient's temperature is sometimes lowered during heart surgery.
Obviously, in order to keep a constant weight an individual must consume
just enough food to provide for basal metabolism plus physical activities.
Eating too little results in weight loss; continued too long it results in
starvation. However, a diet in excess of body needs will cause an increase in
weight. Weight loss through dieting and physical exercise as in the following
example:-
Example(1) suppose you wish to lose 4.54 kg either through physical
activity or by dieting.
a – How long would you have to work at an activity of 15 kcal/min to lose
4.54 kg of fat?(of course, you could not maintain this activity rate very long)
From table, you can expect a maximum of 9.3 kcal/g. If you worked for
T minutes, then
( ) (
) (
) (
)
T =2810 min
47 hr

(5)
Not that a great deal of exercise is needed to lose a few pounds.
b – It is usually much easier to lose weight by reducing your diet intake. If
you normally use 2500 kcal/day, how long must you diet at 2000 kcal/day to
lose 4.54 kg of fat?
⁄
The BMR is sometimes determined from the oxygen consumption when
resting. We can also estimate the food energy used in various physical
activities by measuring the oxygen consumption. Oxygen consumption for
various organs has been measured, some of the organs use rather large
amounts of energy and that the kidney uses more energy per kilogram than
the heart.
