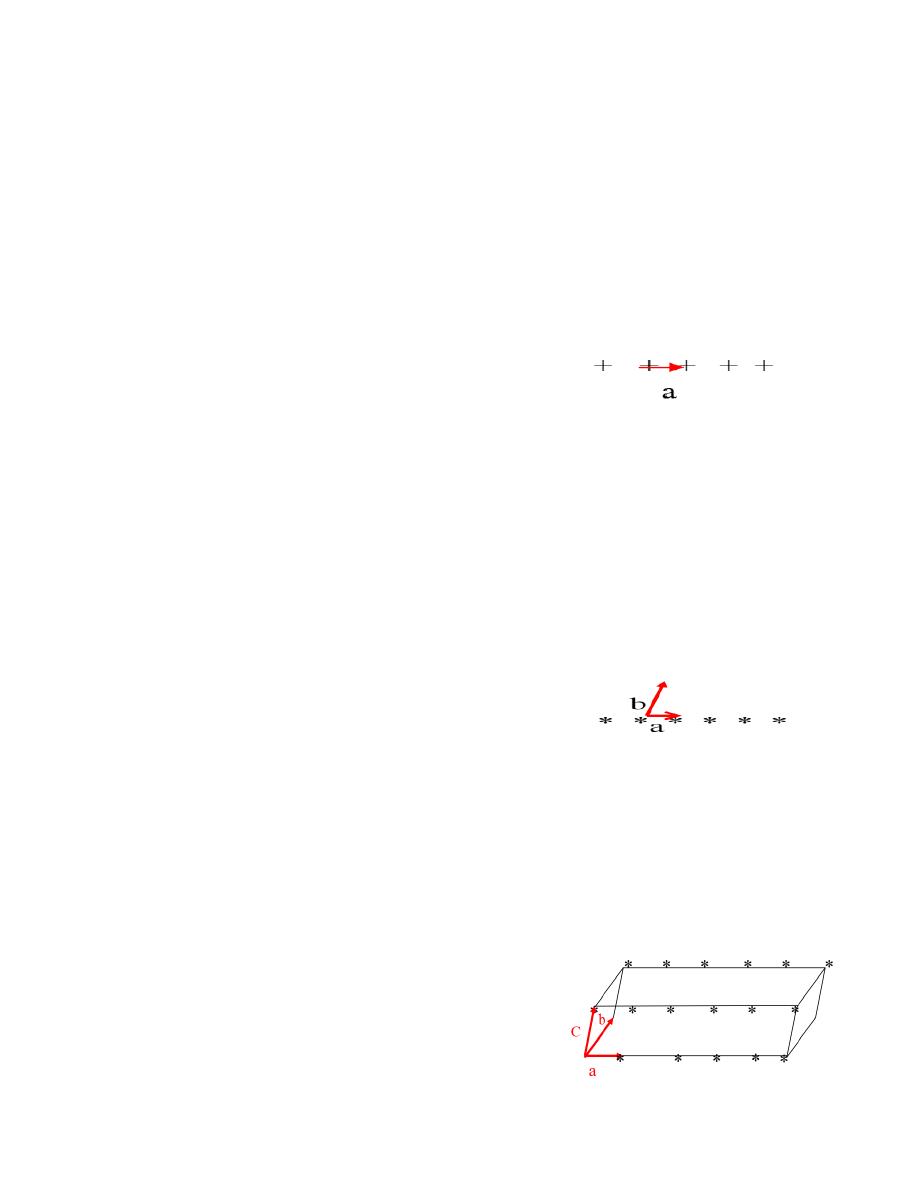
Lattice Translation Vectors :
The relative locations of the lattice points are determined by the
primitive transition vectors (a) on the axis (x) and (b) on the (y) axis and
finally the (c) axis, which is located on the (z) axis.
1. Translation vector in linear lattice :
The locations of the one-dimensional lattice points are
determined by a single primitive transitional vector called (a) and
drawn between any two points Adjacent symmetries as shown below:
The lattice transition vector (R) for any symmetric point in the
linear lattice
R = na
2. Translation vector in planer lattice :
The two-dimensional plane lattice is defined by two primitive
transposition vectors, which are (a) and (b). the lattice transition
vector (R) for any symmetric point in the planar lattice must start from
the intersection of the two transmission vectors which is the point the
original as shown below and can be written in the following
mathematical form :
R = n
1
a + n
2
b
Which (n
1
) and (n
2
) are two integer numbers, the value of each
of them depends on the choice of the location of the origin.
3. Translation vector in space lattice :
The primitive vectors a, b, and c define the space lattice in three
dimension. Thus, the lattice transition vector (R) for any symmetrical
point in this network must start from the intersection of the three
vectors which is the origin point as shown below :
R = n
1
a + n
2
b + n
3
c
Which (n
1
),(n
2
) and (n
3
) are integer numbers.
