Microbiology
MicrobiologyIs a science that deals with study of organisms which unable to be seen by naked eye such as bacteria , viruses etc.
Medical microbiology
Is a branch of microbiology deals with micro-organism that causes the diseases for human & other organisms and its divided to several branch e.g. :-
1 – bacteriology .
2 – virology .
3 – parasitology .
4 – mycology .
5 – immunology .
Chapter 4
Microorganisms
belong to the Protista biologic kingdom include some eukaryotes and prokaryotes, viruses, viroids, and prions , these are classified according to their structure, chemical composition, biosynthetic and genetic organization.Chapter 4
Prokaryotic cells
have no organelles, no membrane-enclosed nucleus, and no histones; in rare cases, they contain complex phospholipids, sphingolipids, and sterols.
have 70S ribosomes.
have a cell wall composed from peptidoglycan-containing muramic acid.
are haploid with a single chromosome.
have short-lived, unprocessed mRNA.
have coupled transcription and translation.
Chapter 4
BacteriaTypical bacteriaMycoplasmasRickettsia organismsChlamydiaKoch's postulates (modified)
1. The organism must always be found in humans with the infectious disease but not found in healthy ones.2. The organism must be isolated from humans with the infectious disease and grown in pure culture.
3. The organism isolated in pure culture must initiate disease when re-inoculated into susceptible animals.
4. The organism should be re-isolated from the experimentally infected animals.
Chapter 4
Structure of BacteriaSize of Bacteria
Average bacteria 0.5 - 2.0 um in diameter.
They havent organelles , no nuclear envelope , have a single chromosome and distinct cell wall .
Chapter 4
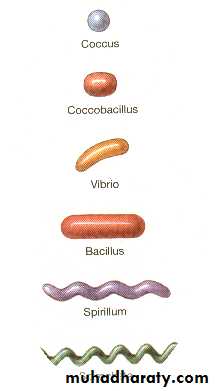
Shapes of BacteriaCoccus
Chain = Streptococcus
Cluster = Staphylococcus
Bacillus
Single = enteric bacteria
Chain = Lactobacillus
Cocco-bacillus = enteric bacteria
Vibrio = curved
Spirillum =Spirochete
Chapter 4
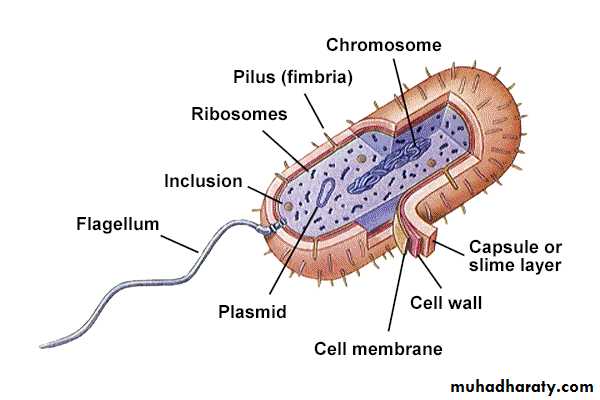
Bacterial Structures
Flagella
Pili
Capsule
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm
Cell Wall
Lipopolysaccharides
Teichoic Acids
Inclusions
Spores
Chapter 4
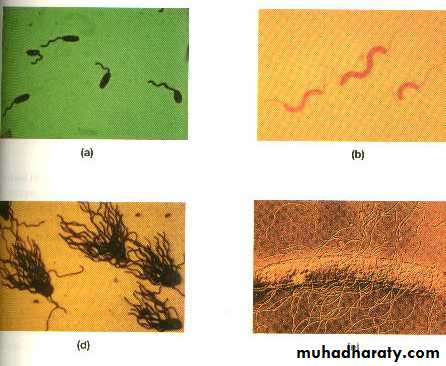
FlagellaMotility - movement
Swarming occurs with some bacteria spread to entire petridish like : Proteus spp.Arrangement basis for classification
Monotrichous; 1 flagella
Lophotrichous; tuft at one end
Amphitrichous; both ends
Peritrichous; all around bacteria
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Pili
Short protein appendages smaller than flagella Adhere bacteria to surfaces . Antibodies will block adhesion .F-pilus; used in conjugation to Exchange of genetic information
Chapter 4
Capsule or Slime Layer
Glycocalyx - Polysaccharide on external surfaceAdhere bacteria to surface . Prevents Phagocytosis . Complement can’t penetrate sugars
Chapter 4
Cytoplasm
80% Water {20% Salts-Proteins)Osmotic Shock important
DNA is circular, Haploid
Plasmids; extra circular DNA may associated with Antibiotic Resistance
No organelles (Mitochondria, Golgi, etc.)
Chapter 4
Bacterial genome
is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane, nor does it contain a mitotic apparatus.
is generally called a nucleoid or nuclear body.
consists of polyamine and magnesium ions bound to negatively charged, circular, supercoiled, double-stranded DNA; small amounts of RNA; RNA polymerase; and other proteins.
Chapter 4
Bacterial ribosomes
have a sedimentation coefficient of 70S and are composed of 30S and 50S subunits containing 5S, 16S, and 23S rRNA, respectively.ribosomes are the sites of action of many antibiotics that inhibit protein biosynthesis.
Chapter 4
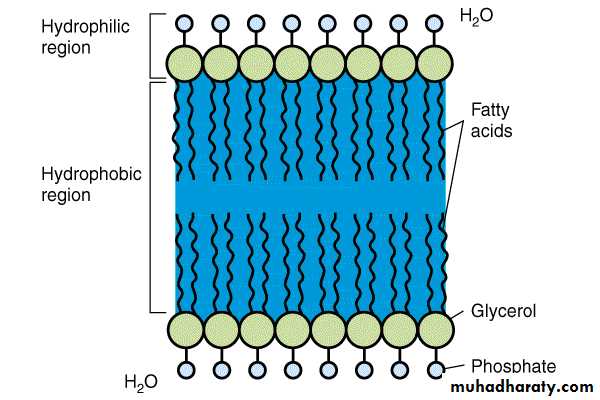
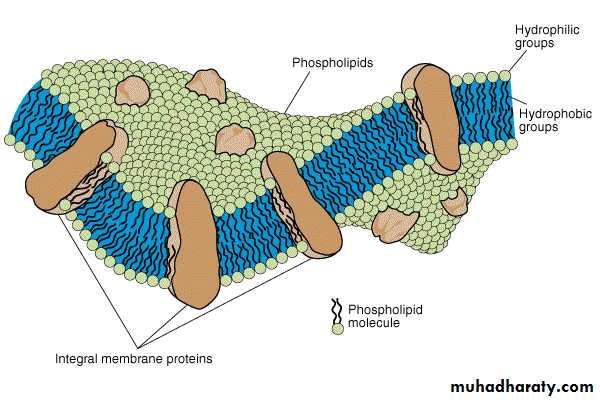
Cell MembraneBilayer Phospholipid
Water can penetrate
Flexible
Not strong, ruptures easily
Osmotic Pressure created by cytoplasm
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
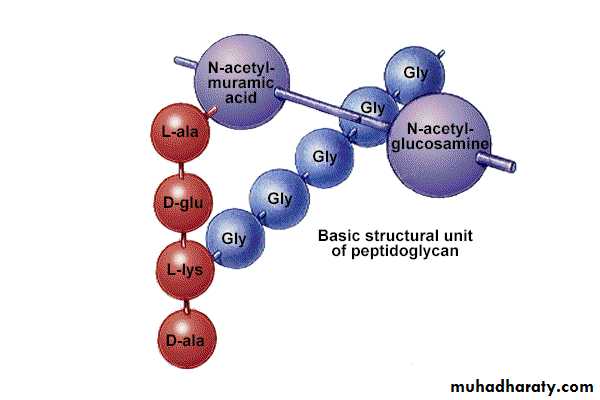
Cell WallPeptido-glycan Polymer (amino acids + sugars) , Unique to bacteria
Sugars : containing N-acetylglucosamine
N-acetymuramic acid
D form of Amino acids used not L form
Hard to break down D form
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Cell Wall
Determine shape of bacteriaStrength prevents osmotic rupture
20-40% of bacteria
Unique to bacteria
Some antibiotics effect directly
Penicillin
Chapter 4
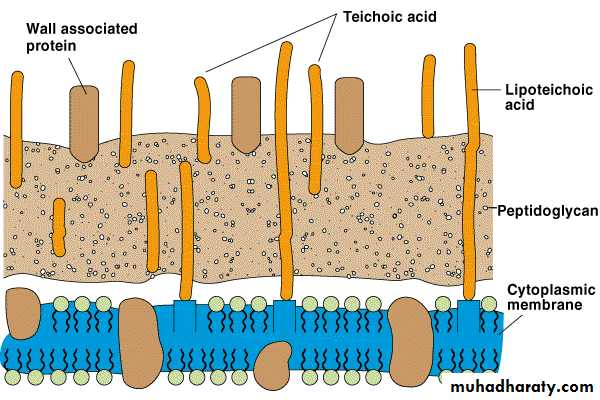
Teichoic Acids
Gram + onlyGlycerol, Phosphates, & Ribitol
Attachment for Phages
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
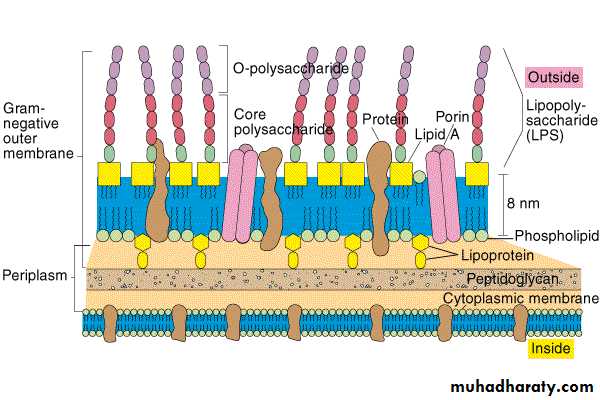
LPS
FunctionsToxic; kills mice, pigs, humans
G- septicemia; death due to LPS
Pyrogen; causes fever
DPT vaccination always causes fevers
Adjuvant; stimulates immunity
Heat Resistant; hard to remove
Chapter 4
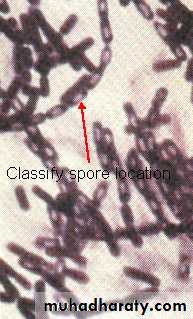
Endospores
Resistant to heat, radiation, cold , Boiling >1 hr still viable .
Location important in classification , Central, Sub terminal, TerminalBacillus stearothermophilus –spores Used for quality control of heat sterilization equipment ( autoclaving )
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Cell WallTeichoic Acids
LPS
Endospores
Circular DNA
Plasmids
Chapter 4