Forth stage
SurgeryUrology
Lec-3
د.أحمد
7/10/2015
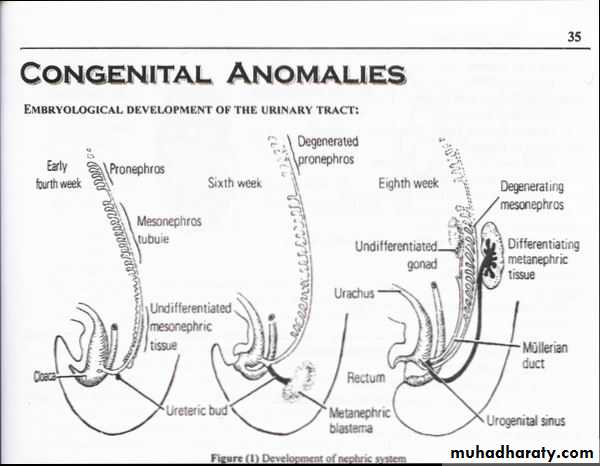
Congenital anomalies of the upper urinary tractCongenital anomalies of the upper urinary tract:
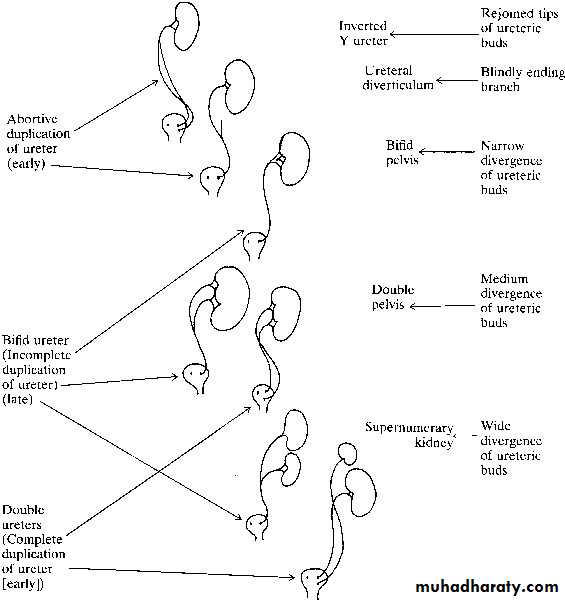
Anomalies of numberAgenesis: Unilateral
Bilateral
Supernumerary kidney
Anomalies of volume and structure
Hypoplasia
Multicystic kidney
Polycystic kidney -Infantile
-Adult -Other cystic disease
-Medullary cystic disease
Anomalies of ascent
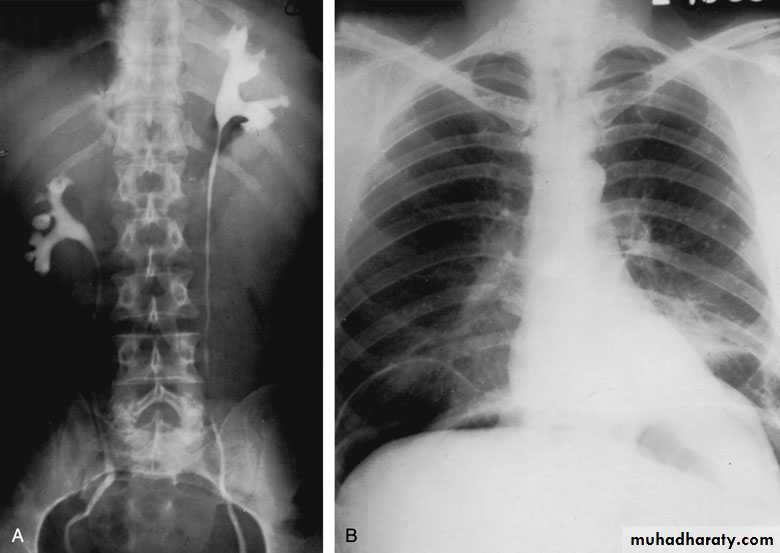
Simple ectopiaCephalad ectopia
Thoracic kidney
Anomalies of form and fusion
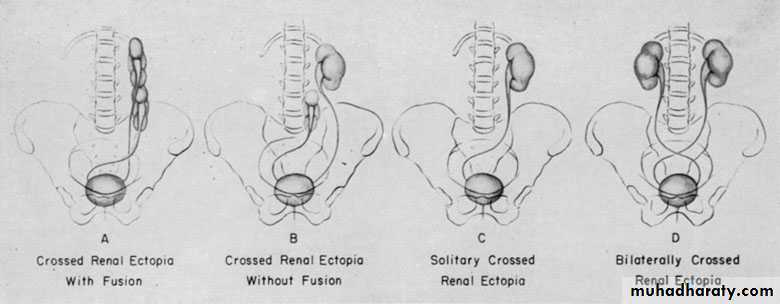
Crossed ectopia with and without fusionUnilateral fused kidney (inferior ectopia)
Sigmoid or S-shaped kidney
Lump kidney
L-shaped kidney
Disc kidney
Unilateral fused kidney (superior ectopia)
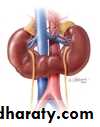
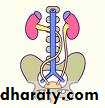
Horseshoe kidney
Anomalies of rotation
Incomplete
Excessive
Reverse
Anomalies of the collecting system
Calyx and infundibulumCalyceal diverticulum
Hydrocalyx
Megacalycosis
Unipapillary kidney
Extrarenal calyces
Anomalous calyx (pseudotumor of the kidney(
Infundibulopelvic dysgenesis
Pelvis
Extrarenal pelvisBifid pelvis
Anomalies of renal vasculature
Aberrant, accessory, or multiple vesselsRenal artery aneurysm
Arteriovenous fistula
In summery
comprise a diversity of abnormalities, ranging from: complete absence kidney, supernumerary Kidney aberrant location, orientation, and shape of the kidney ,aberrations of the collecting system, & blood supply.
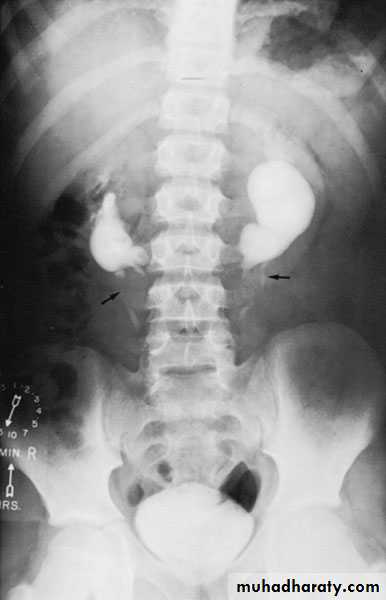
Unilateral Renal Agenesis (URA)
Incidence : 1: 1400 birthsFound accidentally, more frequently on the left side.
Embryology :Complete absence of a ureteric bud or aborted ureteral development prevents maturation of the metanephric blastema into adult kidney tissue.
*Ipsilateral adrenal agenesis is rarely encountered with URA
*Other Genital anomalies are much more frequently observed
Asymptomatic
Diagnosis : U/S or IVU,CT scan: absent kidney on that side + compensatory hypertrophy of the contralateral kidney
Treatment : no specific treatment
Prognosis : no evidence that they have an increased susceptibility to other diseases
Bilateral agenesis: rare, incompatible with life
Supernumerary Kidney truly an accessory organIncidence : very rare
Symptoms : It may not produce symptoms until early adulthood, if at all.
Diagnosis : accidentally by IVU or abdominal U/S
Treatment : no treatment
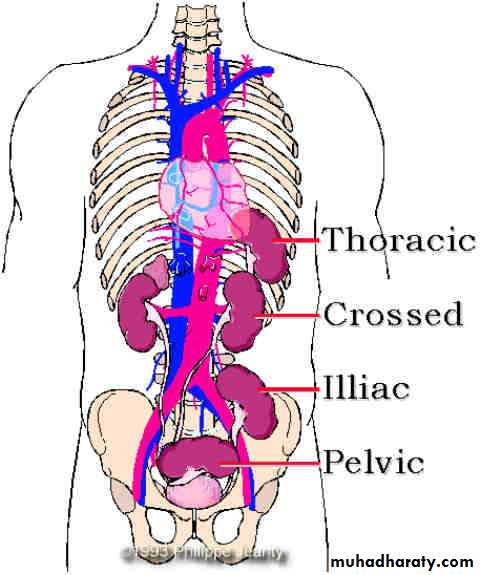
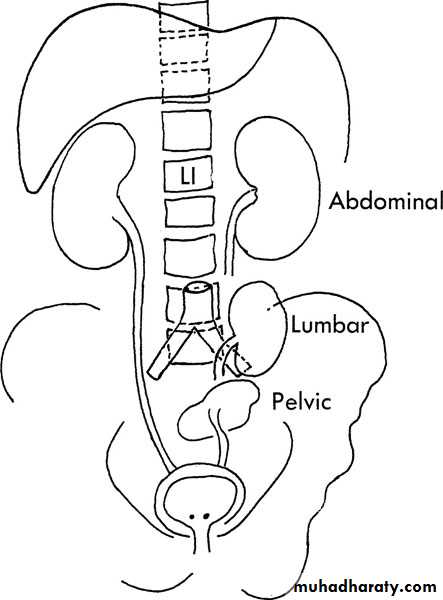
ANOMALIES OF ASCENT
1. Simple Renal Ectopia
When the mature kidney fails to reach its normal location in the " renal fossa "Incidence : The incidence is 1 in 1000
Associated Anomalies : The incidence of contralateral agenesis appears to be rather high
Hydronephrosis secondary to obstruction or reflux may be seen in as many as 25% of none contralateral kidneysClinical features : Most ectopic kidneys are asymptomatic
Diagnosis : U/S, IVU, CT scan
Prognosis : The ectopic kidney is no more susceptible to disease than the normally positioned kidney except for the development of hydronephrosis or urinary calculus formation
2.Cephalad Renal Ectopia
3.Thoracic Kidney
ANOMALIES OF FORM AND FUSION
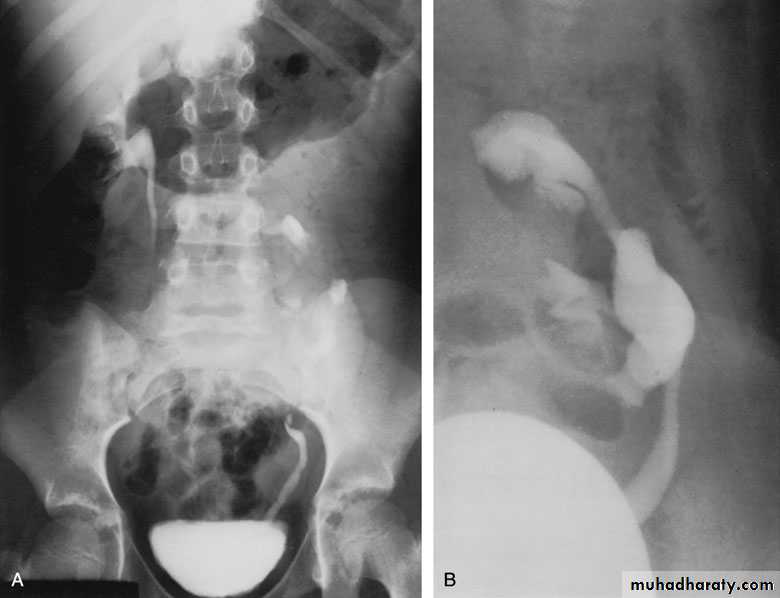
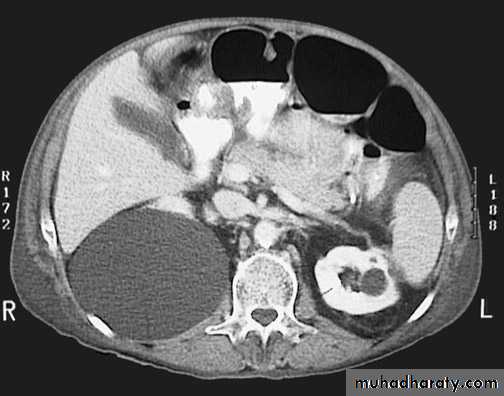
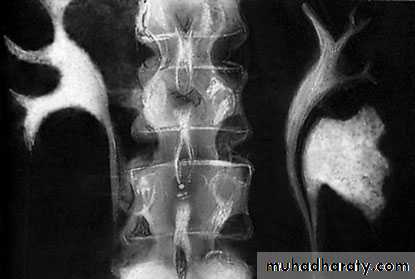
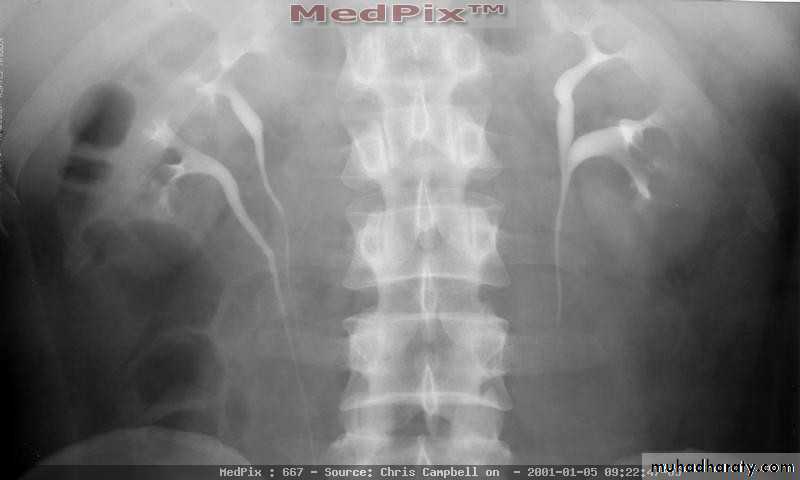
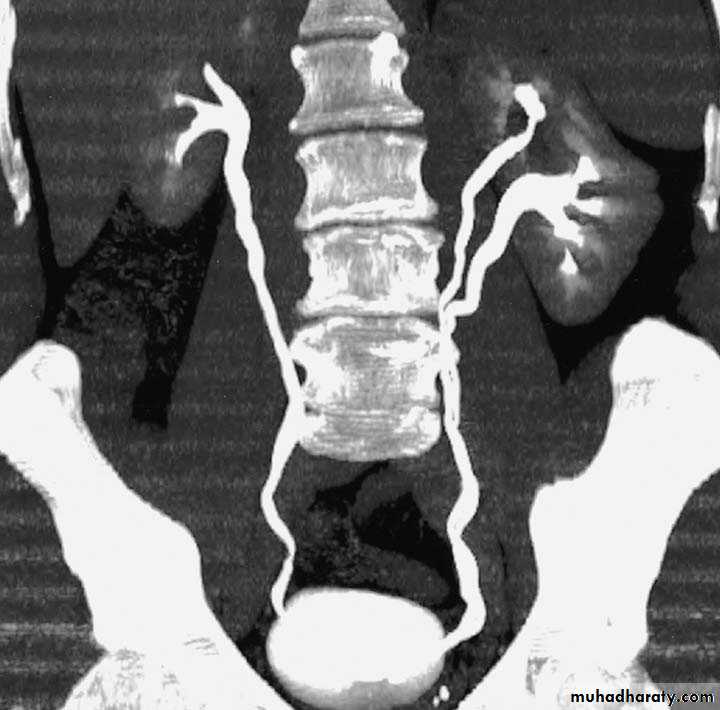
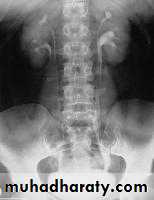
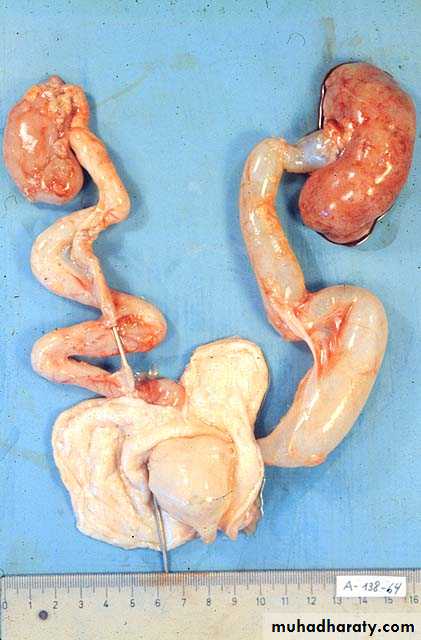
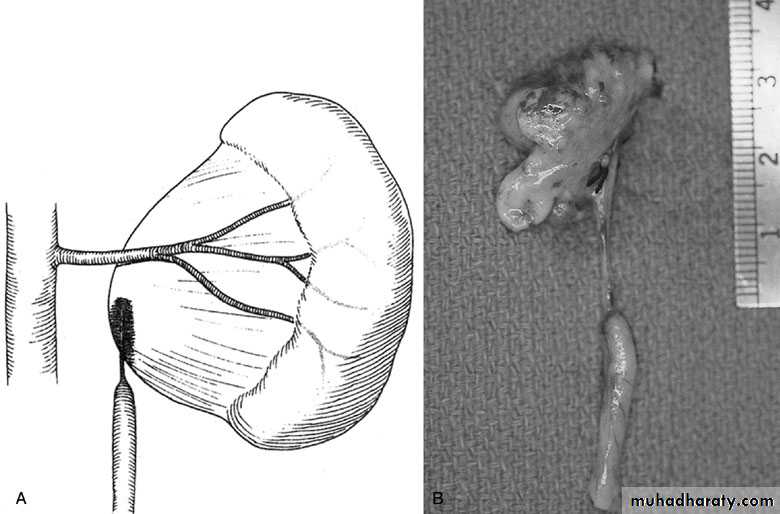
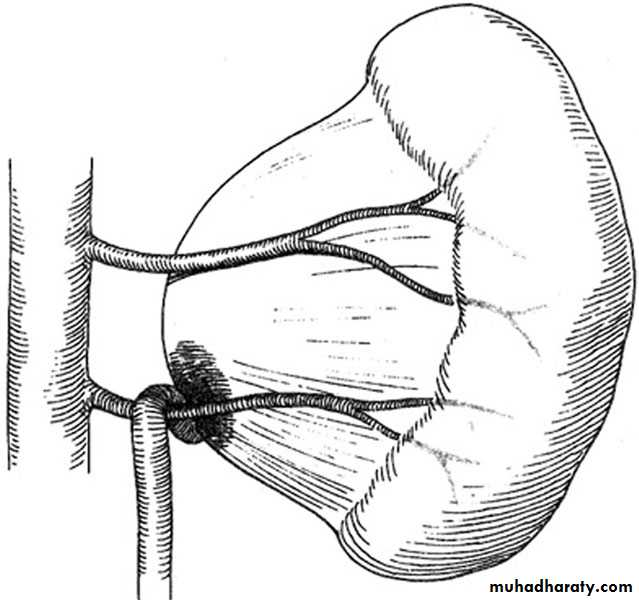
Crossed Renal Ectopia With and Without FusionHorseshoe Kidney
found in 1:1000 necropsies an is commoner in men.probably the most common of all renal fusion anomalies
The anomaly consists of two distinct renal masses lying
vertically on either side of the midline and connected at
their respective lower poles by a parenchymatous or fibrous
isthmus that crosses the midplane of the body.
Fusion of the renal masses early in embryonic life, so its ascent
will be impeded by inferior mesenteric artery.
The kidneys are low located, mal rotated and pelves lie anteriorly
Symptom When present, they are related to complications like hydronephrosis, infection, or calculus formation
Diagnosis ultrasound, IVU, CT scan
Treatment:
-Medical: pain relief and to control infection-Surgical: stone removal, PUJ stenosis correction and isthmus division in cases of
-operations on the aorta
Prognosis usually they have normal life.
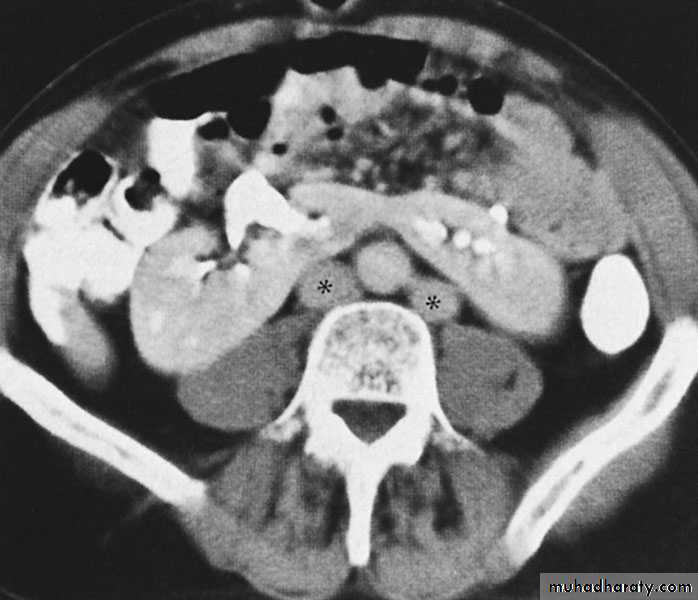
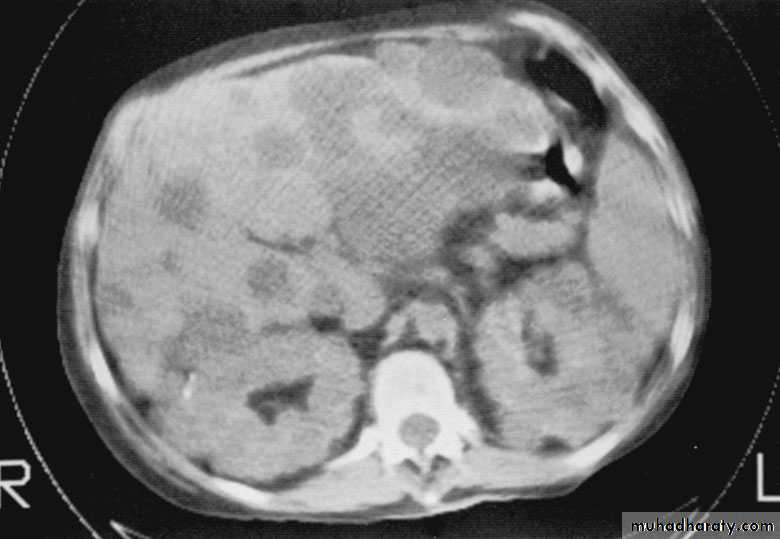
Cystic disease of the kidneysPolycystic kidney disease :
The kidney is one of the most common sites in the body for cysts
Two types:
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE ("INFANTILE") POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT ("ADULT") POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE
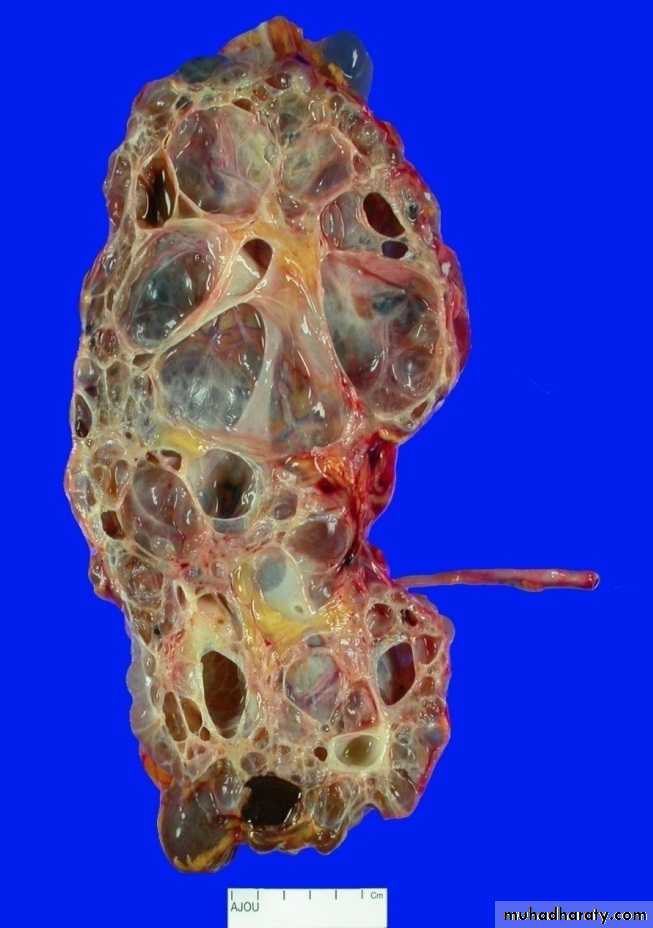
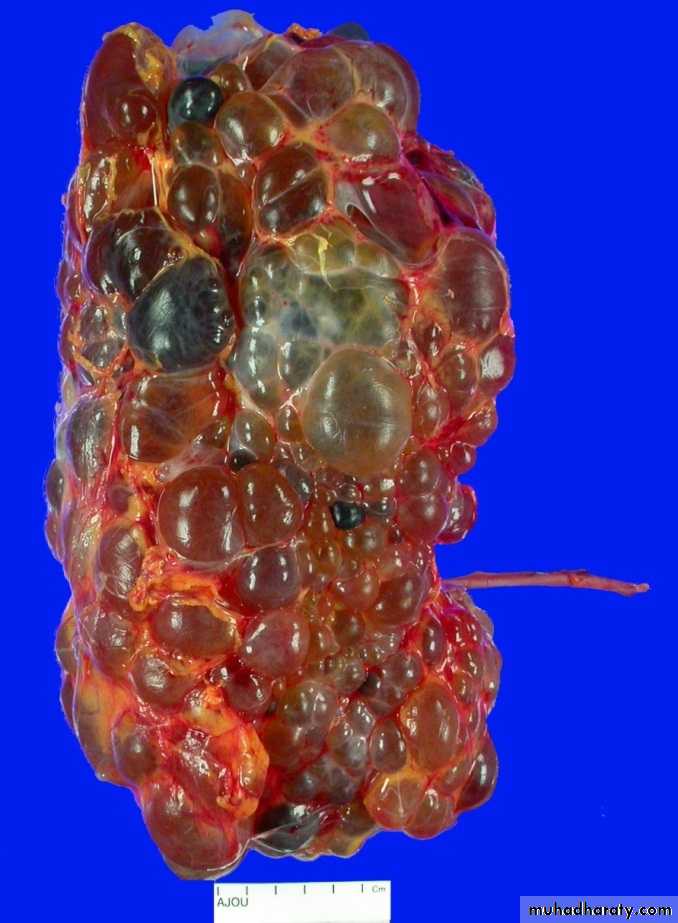
Congenital cystic kidney (polycystic kidney) (Adult cystic renal disease)
Autosomal dominant, transmitted by either parents, 50% of offspring affected.
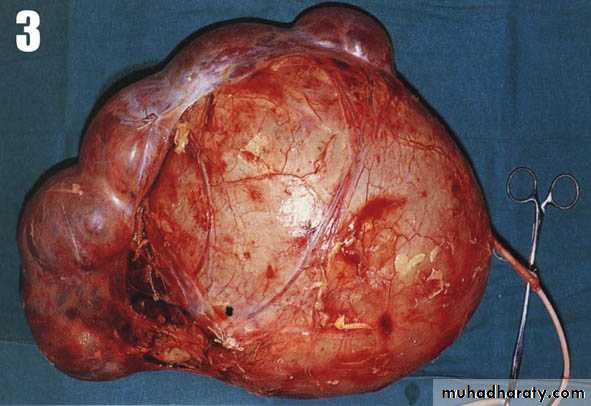
Both kidneys replaced by large no. of cysts of variable size which make the kidney of large size.
The cysts contain clear fluid but sometimes blood.
The cysts progressively increase in size causing pressure atrophy of the renal parenchyma and pressing the ureter.
15% associated with cystic disease of liver, lung, pancreas or spleen.
Etiology & Pathogenesis
The cysts occur because of defects in the development of the collecting and uriniferous tubules and in the mechanism of their joining. Blind secretory tubules that are connected to functioning glomeruli become cystic.Clinical pictures:
Rarely gives clinical manifestation before 4o yearsAsymptomatic: diagnosed accidentally.
Pain: due to pedicle stretching, stone, ureteric obstruction, bleeding inside cyst or infection.Hematuria: cyst distention and rupture to the collecting system.
Infection: renal or cyst infection causes fever, rigor and loin pain.
Hypertension: in 70%, Unknown cause.
Renal impairment: anorexia, headache, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness and coma.
Renal enlargement: large knobby palpable kidney
Diagnosis: Family history of polycystic disease.
U/S, IVU, CT scan, MRI
Treatment:
Medical: (Expectant)
To control infection, hypertension, pain and anemia.
Renal impairment: by low protein diet and dialysis.
Surgical:
Rovsing’s operation (deroofing) for large cysts causing symptoms or obstruction.
Stone removal.
Renal failure: Renal transplantation.
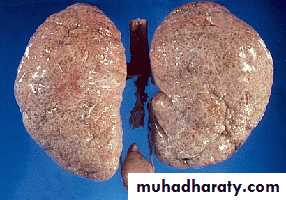
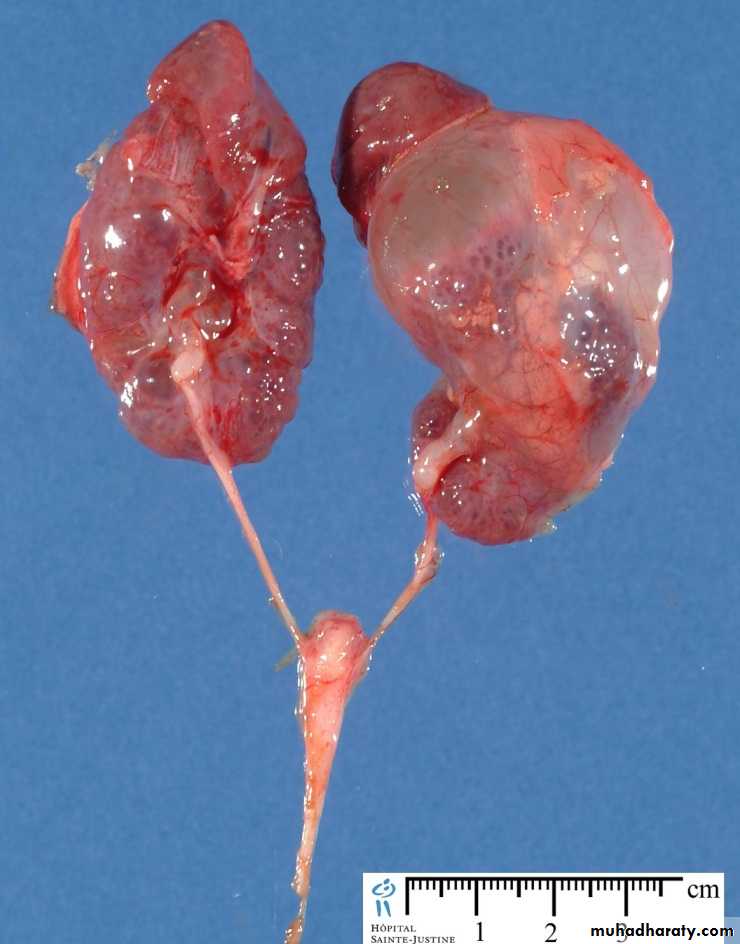
Infantile polycystic disease of the kidney
Rare autosomal recessive, incompatible with life.Both kidneys are large in size and replaced by large number of cysts which may obstruct labor.
The condition is due to failure of ureteric bud to fuse with metanephrose.
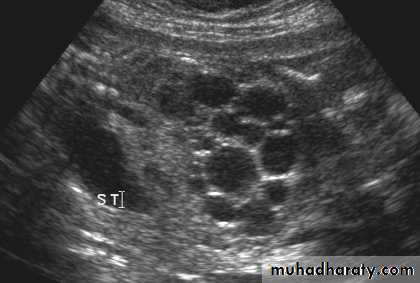
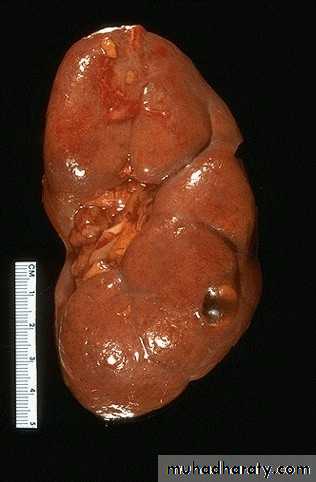
Simple (solitary) renal cyst
Common condition.
single or multiple.
uni or bilateral.
Congenital or acquired.
Usually asymptomatic.
In 10% symptomatic: pain, heaviness, infection, bleeding inside the cyst or
pressure effect on the ureter causing hydronephrosis.
Diagnosis
Examination: usually –ve, big cyst cause painless loin mass, & painful if complicated by bleeding or infectionU/S: echo free area (cystic lesion)
KUB: soft tissue shadow.
IVU: stretched calyx, filling defect or hydronephrosis.
CT scan &MRI: are diagnostic.
Treatment: usually no treatment needed
Symptomatic cases:Aspiration and injection of sclerosing agent.
Rovsing’s operation (deroofing)
Partial or total nephrectomy in destructed kidney.
N.B. Malignant cyst: radical nephrectomy.
N.B. Hydatid cyst aspiration is contraindicated because of anaphylaxis and dissemination.
Congenital Anomalies of Renal pelvis & Ureter
Duplication of Renal Pelvis
Incidence: 4 %
More common on left side
Renorenal reflux may occur from one pelvis to the other
Duplication of the ureter
Incidence : 3 %
Usually the ureters fuse & have common orifice in the bladder although they
may open independently in which case the ureters cross each other so that the
ureter that drain the upper pelvis open below (more distally) in the bladder &
vise versa.
Clinical features : usually asymptomatic
More prone to infections, calculus disease & hydronephrosis
Treatment: expectant
Ureteral duplication: partial and complete
-Partial duplication:
Is more common. Two ureters draining single
kidney for variable length, then unite together
before entering the bladder in one ureteric
orifice.
Rarely the lower part is duplicated as inverted Y
ureter.
-Complete duplication:
Less frequent,The whole ureter is duplicated, and each one
opens in separate orifice in the bladder.
The ureter draining the upper part opens more
distally in the bladder.
Ectopic Ureters
80% are associated with a duplicated collecting system
In the male, the posterior urethra is the most common site of termination, also to semenal vesicle
In the female, the urethra and vestibule are the most common sites
Clinical features: According to the site of orifice
In females: continuous dribbling
In males: urinary tract infection
Diagnosis: IVU, U/S, CT scan, cystoscopy
Treatment: Ureteric reimplantation or implantation of one ureter to the other ureter isused
Ectopic ureters may drain renal moieties (either an upper pole or a single-system kidney) that have minimal function. Therefore, upper pole partial nephrectomy (or nephrectomy of single system) is sometimes recommended
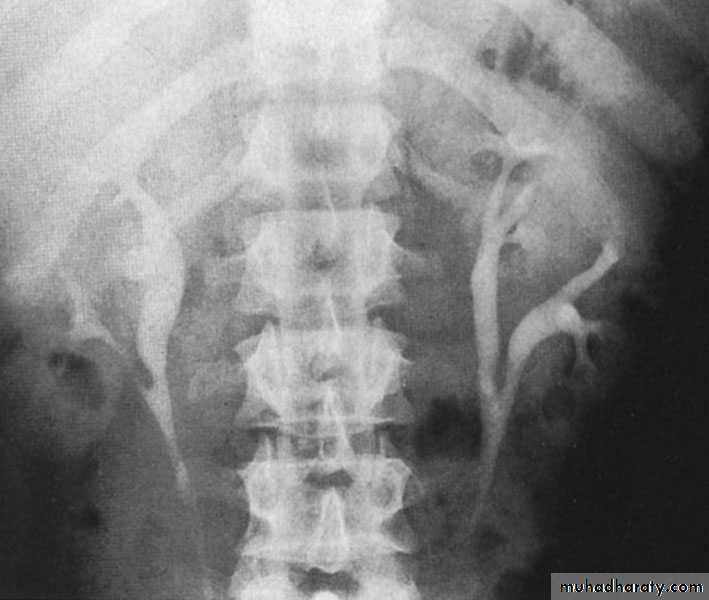
Complete ureteral duplication and ectopic ureteric orifice
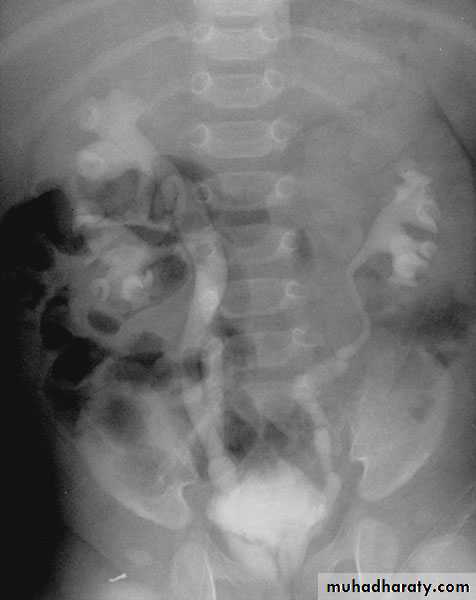
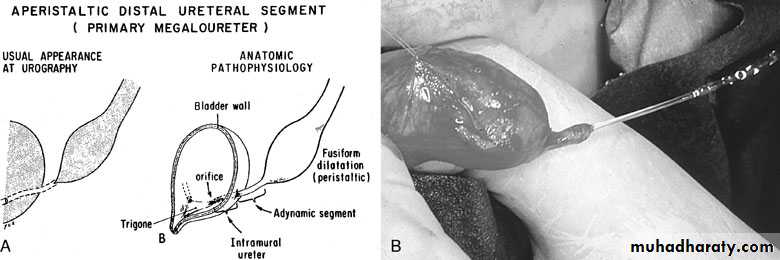
Congenital Megaureter
Grossly dilated ureter
Unilateral or bilateral
More common in male
Clinical features:
Asymptomatic, pain, repeated UTIs
Lower ureter might be obstructed
Sometimes associated with
vesicoureteral reflux
Diagnosis: IVU
Treatment
Infection should be controlledExcision of the lower stenotic segment
(if present)
Ureteric tapering & reimplantation in to the
bladder
Nephroureterectomy for non functioning
kidney
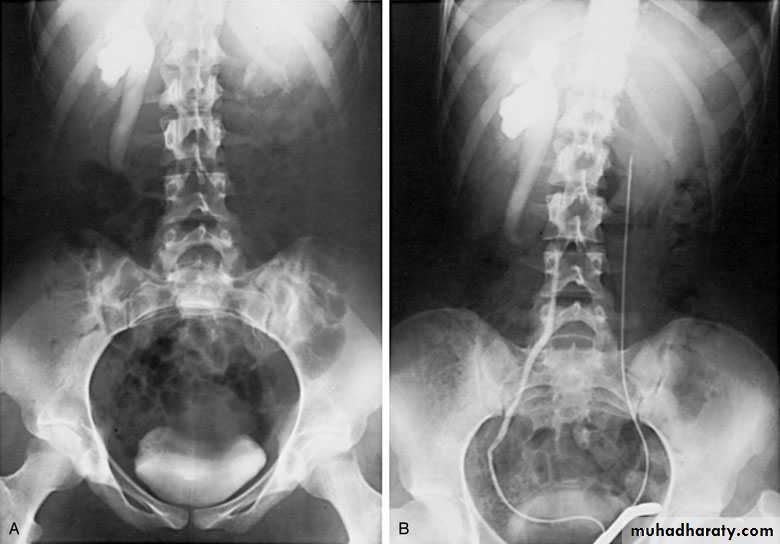
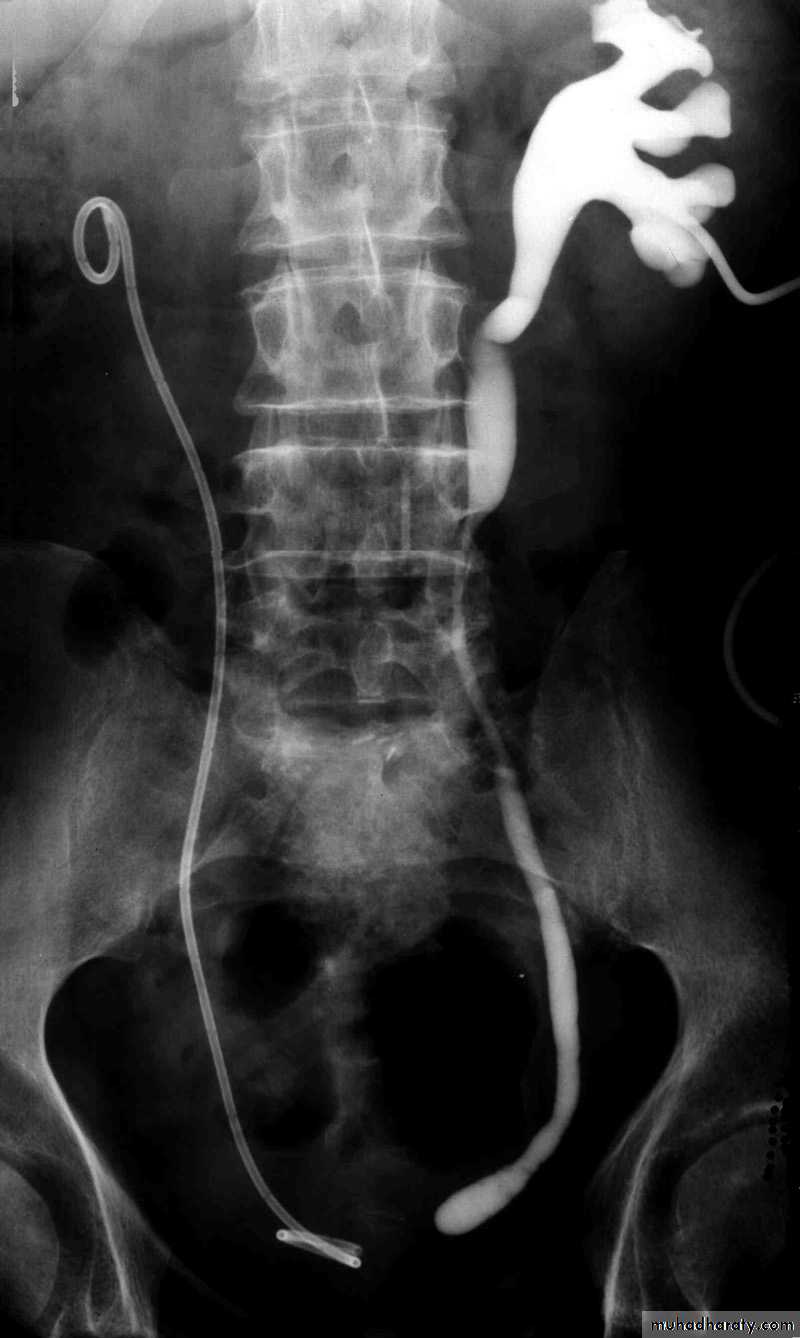
Postcaval (Retrocaval) ureter (Preureteral Vena Cava )
The right ureter pass behind the inferior vena cava
This might causes obstruction
Vascular abnormality
Incidence: about 1 in 1500Although it is congenital, most patients present at 3rd or 4th decade.
Diagnosis: IVU
Treatment:
surgical correction involves ureteral division, with relocation and ureteroureteral or ureteropelvic reanastomosis,
usually with excision or bypass of the retrocaval segment, which can
be aperistaltic
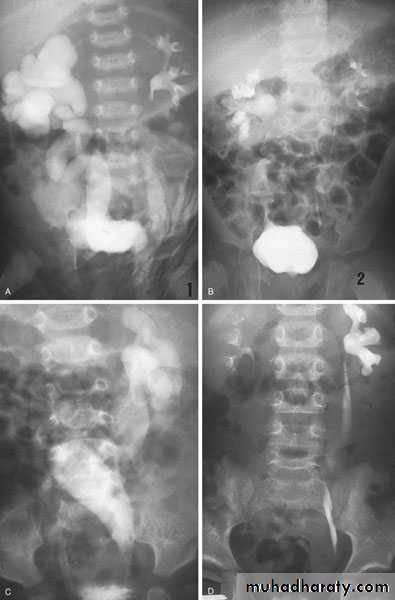
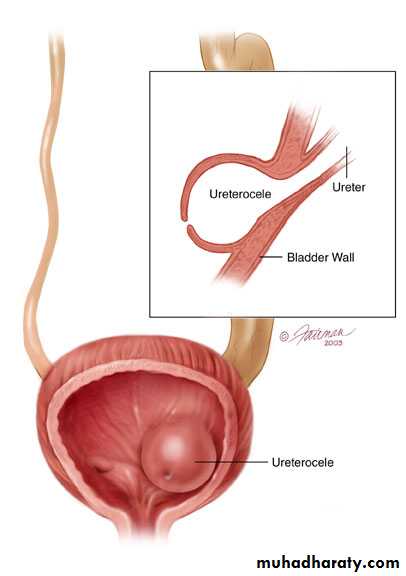
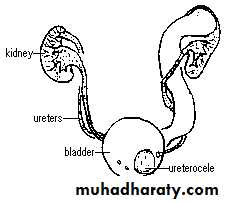
Ureteroceles
Is due to congenital atresia of the ureteric orifice which causes a cystic dilatation of the intramural portion of the ureter
Women > men
Sometimes involves with ectopic ureter
More prone to stone disease & UTIs
Clinical Features : Asymptomatic
Repeated UTIs, Hematuria
Diagnosis:
IVU, cystoscopy, cystogram
The ‘adder head’ on excretory urography is typical.
Treatment:
Asymptomatic : no treatment
Cystoscopy with diathermy cauterization of the hole
Nephrectomy in non functioning kidney
In complicated cases, ureteral reimplantation and vesical reconstruction
Cobra (Adder) head appearance of ureterocele
Ureterocele involving single system Ureterocele involving duplicated ureter
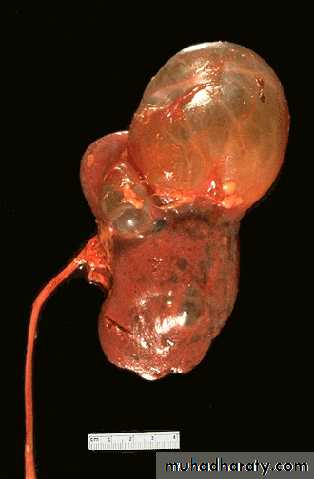
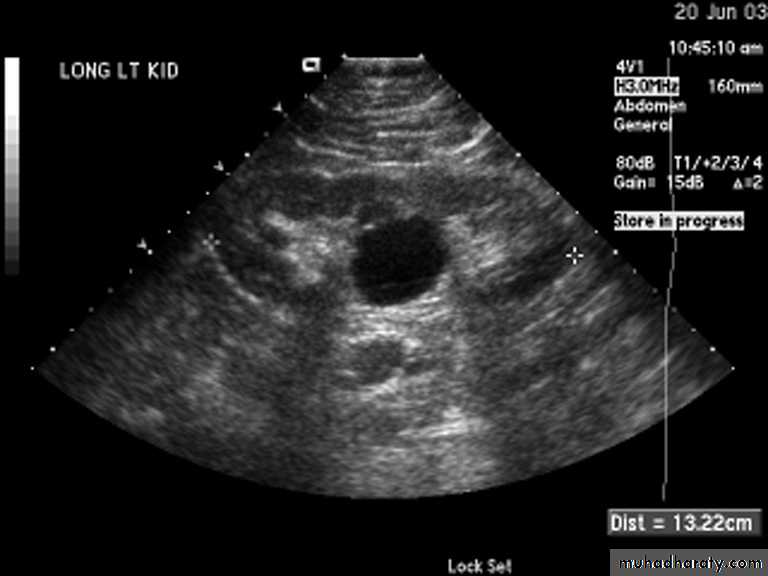
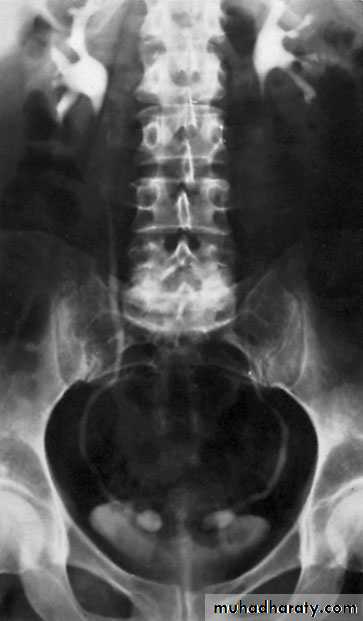
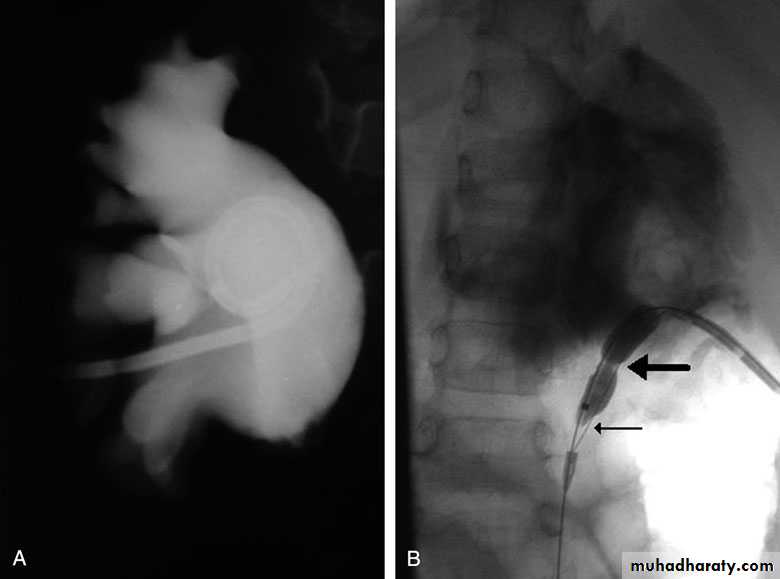
Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ)(PUJ) Obstruction (stenosis)
The most common cause of significant dilation of the collecting system in the fetal kidney
Boys > Girls
Left-sided lesions predominate
15% bilateral
ETIOLOGY
Intraluminal : mucosal fold that causes valvelike effect.
Intrinsic (intramural) interruption in the
development of the circular musculature of the UPJ
Extrinsic An aberrant, accessory, or early-branching
lower-pole renal artery
PUJ Obstruction – gross pathology
SYMPTOMS/PRESENTATION
Most infants are asymptomatic and most children are discovered because of their symptomsEpisodic flank or upper abdominal pain, sometimes associated with nausea and vomiting
DIAGNOSIS
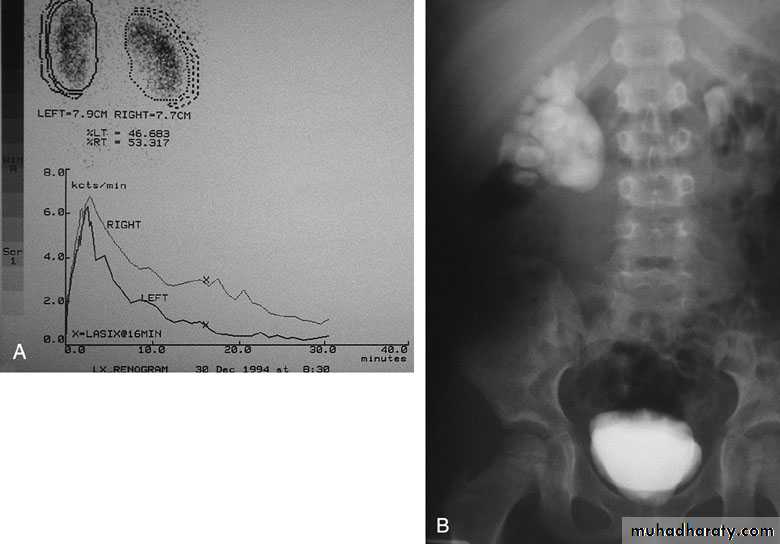
U/S: hydronephrosis
IVU: diagnostic , hydronephrosis with
fixed stenotic segment or complete
obstruction
CT scan: hydronephrosis that ends
abruptly
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Radionuclide Renography: to see the
split function of each kidney
Pressure-Flow Studies: Whitaker test
Treatment:
Medical: control infection and pain.
Surgical:
Indications for surgery:
1-progressive hydronephrosis.
2- UTI, and symptomatic patients.
3- Severe hydronephrotic non functioning kidney.
Treatment
SURGICAL REPAIR including open surgical techniques, laparoscopic, & endoscopic approaches
Open & laparoscopic surgical techniques Anderson-Hynes dismembered pyeloplasty:
excision of the pathologic UPJ & appropriate
reanastamosis or flap technique or flap
operation
Endoscopic Approaches
balloon dilatation
Antegrade endopyelotomy
Nephrectomy
for non functioning kidney
Bilateral PUJO