1st lecture
Important note:
The lectures of immunology as part of microbiology are based on
authors :
Kathleen Talaro and Arthur Talaro 2002(Foundations in Microbiology –basic principles ) book.
Dr. Abdullrazaq al mashhadni ( how to learn immunology by ten lectures)
Kuby, immunology 6 ed.
Introduction
Immunology, the study of the body’s immune response, is responsible for protection the body against diseases.The term immunity means protection from diseases e.g. resistance to re-infection.
Immune system: is a defense system that has evolved to protect animals from invading pathogenic microorganisms and cancers.Our environment contains large numbers of microbes. These can cause disease, and if they multiply unchecked they will eventually kill their host. So, the primary function of the immune system is to eliminate infectious agents and to minimize the damage they cause.
Environment
HostMicrobes
Immune system
Antigens
Immune responseTumor
AgI.R.
Functionally, an immune response can be divided into two related activities:
1. The immune system is able to recognize subtle chemical differences that distinguish one foreign pathogen from another. Furthermore, the system is able to discriminate between foreign molecules and the body’s own cells and proteins.The different types of the immune response fall into two categories:
Innate (non-specific) immune response: which is the first line of defense against infection and it does not alter on repeated exposure to a given infectious agent and it react in the same manner with each pathogen.
Adaptive (specific) immune response: it is a highly specific for a particular pathogen and the immune response improves with each successive encounter with the same antigen. Thus, the two key feature of the adaptive immune response are the specificity and the memory. The major agent of adaptive immunity are lymphocyte and the antibodies and other molecules they produce.
Immune response
N.
Characteristics
Innate Immunity
Adaptive immunity
1.
Presence
Innate immunity is something already present in the body.
Adaptive immunity is created in response to exposure to a foreign substance.
2.
Specificity
Non-Specific
Specific
3.
Response
Fights any foreign invader
Fight only specific infection
4.
Response
Rapid
Slow (1-2 weeks)
6.
Time span
Once activated against a specific type of antigen, the immunity remains throughout the life.
The span of developed immunity can be lifelong or short.
7.
Inheritance
Innate type of immunity is generally inherited from parents and passed to offspring.
Adaptive immunity is not passed from the parents to offspring, hence it cannot be inherited.
8.
Memory
Cannot react with equal potency upon repeated exposure to the same pathogen.
Adaptive system can remember the specific pathogens which have encountered before.
9.
Presence
Present at birth
Develops during a person’s lifetime and can be short-lived.
10
Used Against
For microbes
Microbes and non-microbial substances called antigens
11.
Memory
No memory
Long term memory
12.
Speed
Faster response
Slower response
13.
Anatomic and physiological barriers
Skin, Mucous membranes, Temp, pH, chemicals, etc.
Lymph nodes, spleen, mucosal associated lymphoid tissue.
14.
Composition
The innate immune system is composed of physical and chemical barriers, phagocytic leukocytes, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and plasma proteins.
Adaptive immune system is composed of B cells and T cells.
15.
Example
White blood cells fighting bacteria, causing redness and swelling, when you have a cut.
Chickenpox vaccination so that we don’t get chickenpox because adaptive immunity system has remembered the foreign body.
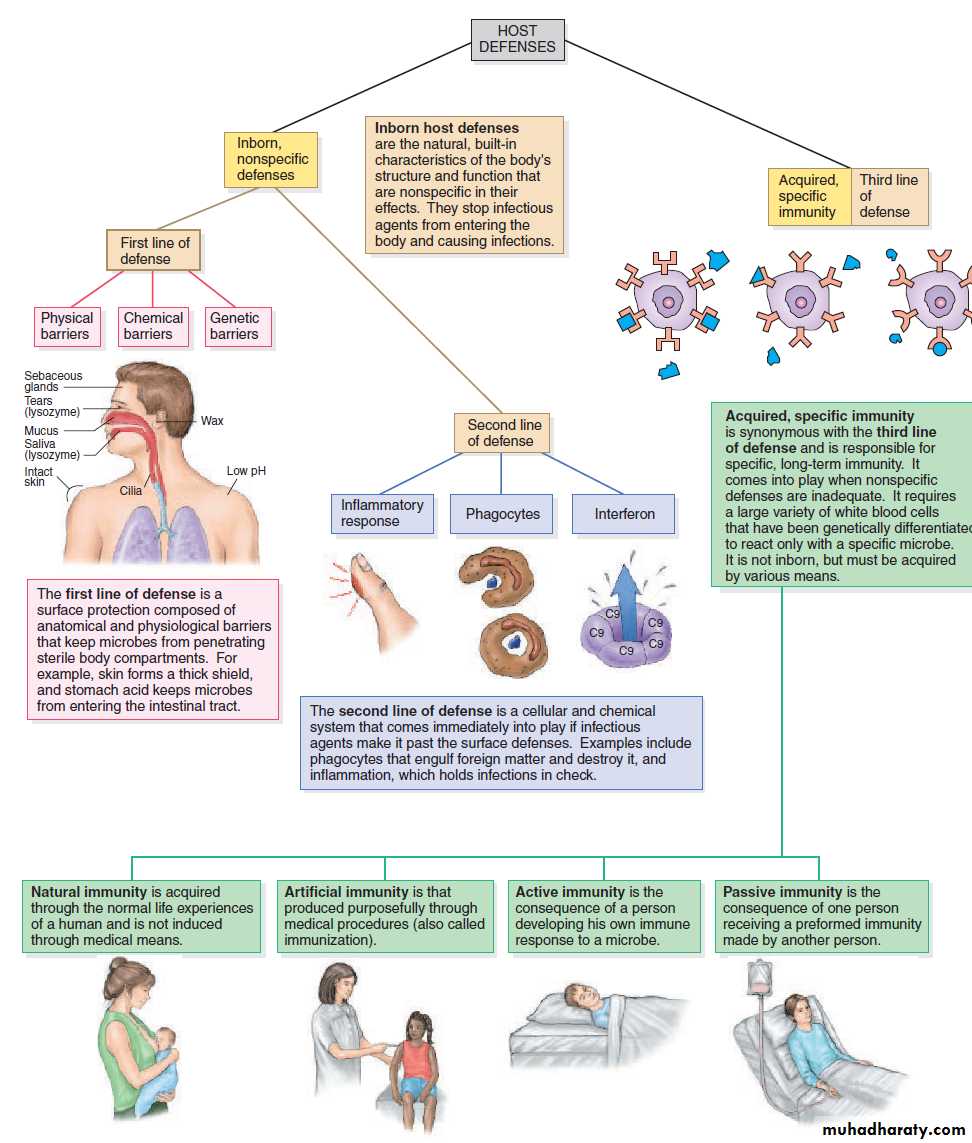
Defenses exist at several levels of development and specificity.
First line defenses are inborn physical barriers such as skin, and second line defenses are non-specific, protective reactions in the fluid compartments such as phagocytosis.
Third line defenses are aimed at a specific pathogen and give a long term form of protection that will come into play if that pathogen is ever encountered again.
1st lecture
inborn
acquired and specificInnate Immunity
• Anatomical barriers• physiological barriers
• phagocytic barriers
• Inflammatory barriers.
The natural, inborn, nonspecific defenses that can be divided into physical, chemical, and genetic barriers that impede the entry of microbes at the site of first contact
1st lecture
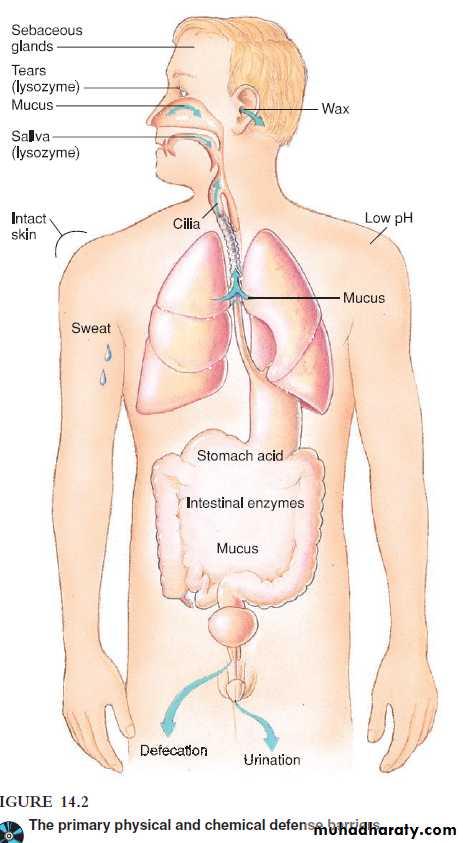
Barriers at the Body’s Surface
In the skinStratum corneum of the skin is composed of epithelial cells that have become compacted, cemented together, and impregnated with an insoluble protein, keratin.
Sebaceous secretions have an antimicrobial effects
The high lactic acid and electrolyte concentrations of sweat and the skin’s acidic pH and fatty acid content
1st lecture
Skin is an example of physical barrier
Combat microbes at dermis levelLangerhans and other immune cells
Compete with pathogenic
Normal microbiota
Protect hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands
Toxic lipids, lysozyme
Remove adherent pathogens
Sloughing of surface cells
Prevent colonization, keratin hard to degrade
Dead, keratinized
Prevent microbes growth
Dry, acidic (pH 5.0)
Function
Defense
Eye
Blinking and (lacrimation) flush the eye’s surface with tears and rid it of irritants.Specialized glands such as the meibomian glands of the eyelids lubricate the conjunctiva with an antimicrobial secretion (lysozyme)
1st lecture
The digestive tract
The mucocutaneous membranes of the free surface of digestive tract.
Saliva
HCl
the intestine’s digestive juices and bile.
Vomiting and defecation
1st lecture
The genitourinary tract
The mucocutaneous membranes.
periodic bladder emptying and continuous trickle of urine through the ureters that flushes the urethra.
Semen contains an antimicrobial chemical that inhibits bacteria.
the vagina has a protective acidic pH maintained by normal flora.
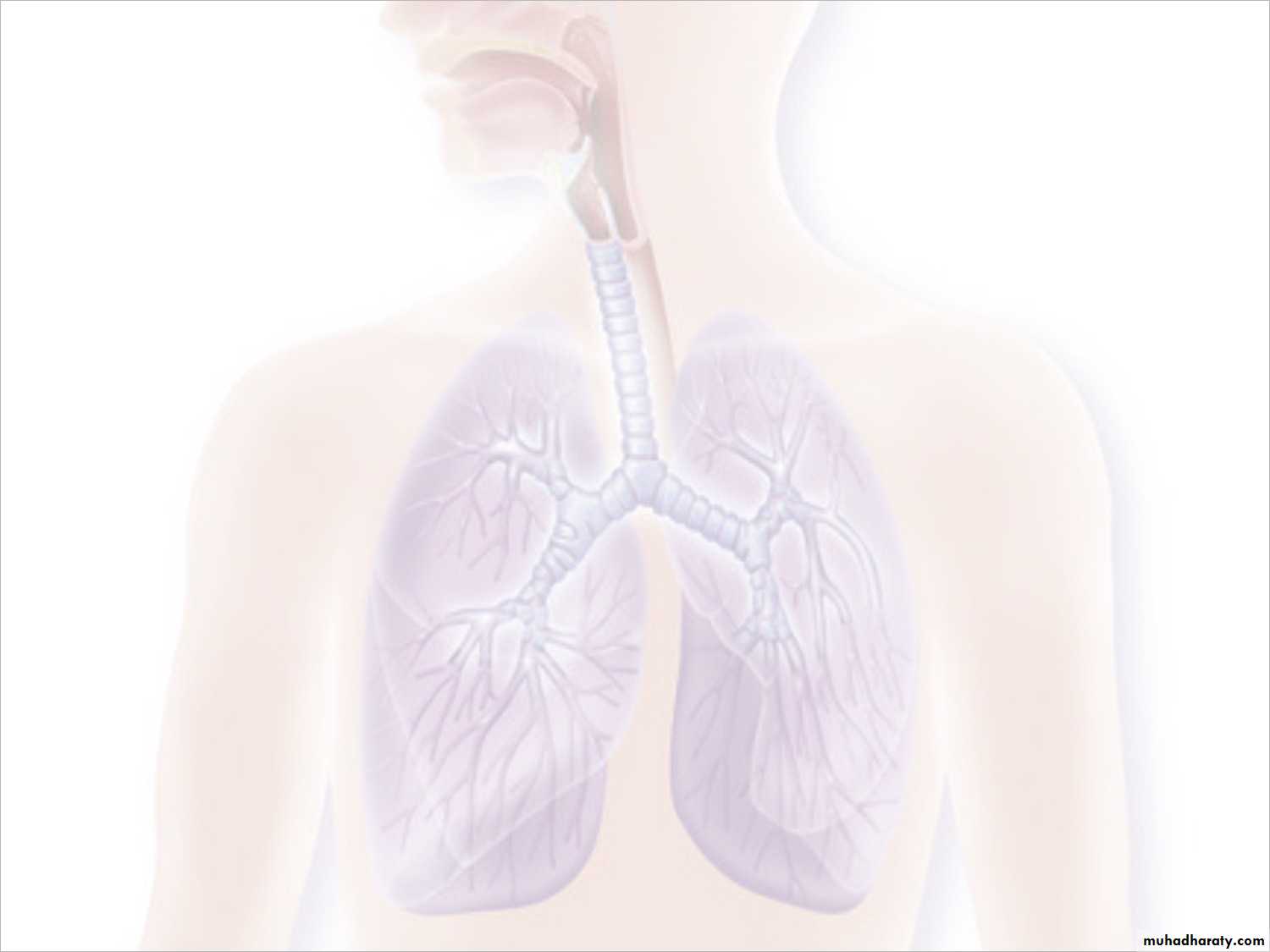
Respiratory tract effective adaptations
Nasal hair
Flushing action and copious flow of mucus and fluids that occurs in allergy and colds.
The ciliated epithelium
Irritation of the nasal passage reflexly initiates a sneeze, which expels a large volume of air at high velocity.
The acute sensitivity of the bronchi, trachea, and larynx to foreign matter triggers coughing, which ejects irritants
1st lecture
Some pathogens have a great specificity to infect one host species that they are incapable of infecting other species ( e.g. Humans can’t acquire distemper from cats, and cats can’t get mumps from humans)
Genetic differences in susceptibility can also exist within members of one species.
2. Physiologic barriersThe physiologic barriers that contribute to innate immunity include temperature, pH, and various soluble and cell associated molecules.
• Chickens, for example, have innate immunity to anthrax because their high body temperature inhibits the growth of the bacteria.
• Gastric acidity is an innate physiologic barrier to infection because very few ingested microorganisms can survive the low pH of the stomach contents.
• A variety of soluble factors contribute to innate immunity, among them the soluble proteins lysozyme, interferon, and complement.
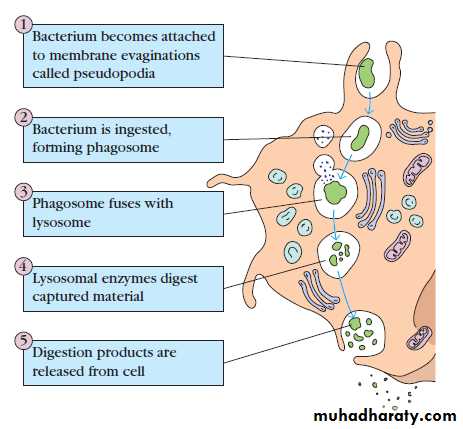
3. Phagocytic barrier
The ingestion of extracellular particulate material by phagocytosis. Phagocytosis is one type of endocytosis, the general term for the uptake by a cell of material from its environment.
4. Inflammation represents a complex sequence of events that stimulates Immune responses
Tissue damage caused by a wound or by an invading pathogenic microorganism induces a complex sequence of events collectively known as the inflammatory response.a molecular component of a microbe, such as LPS, may trigger an inflammatory response via interaction with cell surface receptors. The end result of inflammation may be the marshalling of a specific immune response to the invasion or clearance of the invader by components of the innate immune system.
Why the first line of defense alone is not sufficient to protect against infection ?
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity is capable of recognizing and selectively eliminating specific foreign microorganisms and molecules (i.e., foreign antigens).Adaptive immunity displays four characteristic attributes:
• Antigenic specificity of the immune system permits it to distinguish subtle differences among antigens. Antibodies can distinguish between two protein molecules that differ in only a single amino acid.
• Diversity: The immune system is capable of generating tremendous diversity in its recognition molecules, allowing it to recognize billions of unique structures on foreign antigens.
3. Immunologic memory: a second encounter with the same antigen induces a heightened state of immune reactivity.
4. Self/non self recognition: the immune system normally responds only to foreign antigens, indicating that it is capable of self/nonself recognition.