1
Biochemistry
stage
nd
2
Dr.Lamees Majid Al-Janabi
OXIDATION OF THE FATTY ACIDS
Fatty acids stored in adipose tissue, in the form of neutral TAG, serve
as the body's major fuel storage reserve. TAGs provide concentrated stores
of metabolic energy because they are highly reduced and largely
anhydrous.
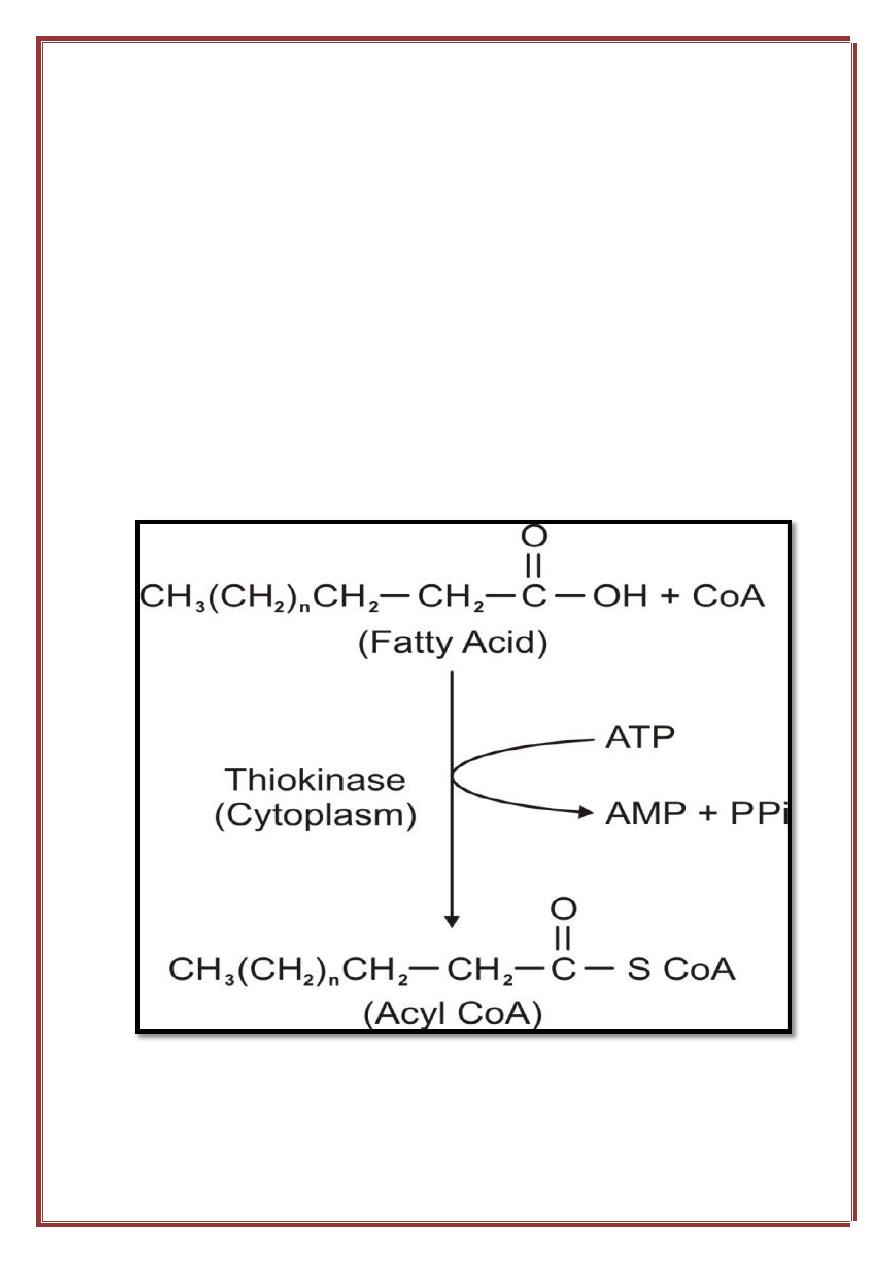
The entry of long chain fatty acids to the cell is mediated by fatty
acid binding proteins. The fatty acids must be converted into active
intermediates by a reaction with ATP before they can undergo any further
metabolism. Long-chain fatty acids are required for energy production
during the fasting state.
This is the only step in the fatty acid oxidation that requires ATP and
it is irreversible step because the PPi is hydrolyzed by the pyrophosphatase
enzyme to yield two inorganic phosphates.
2
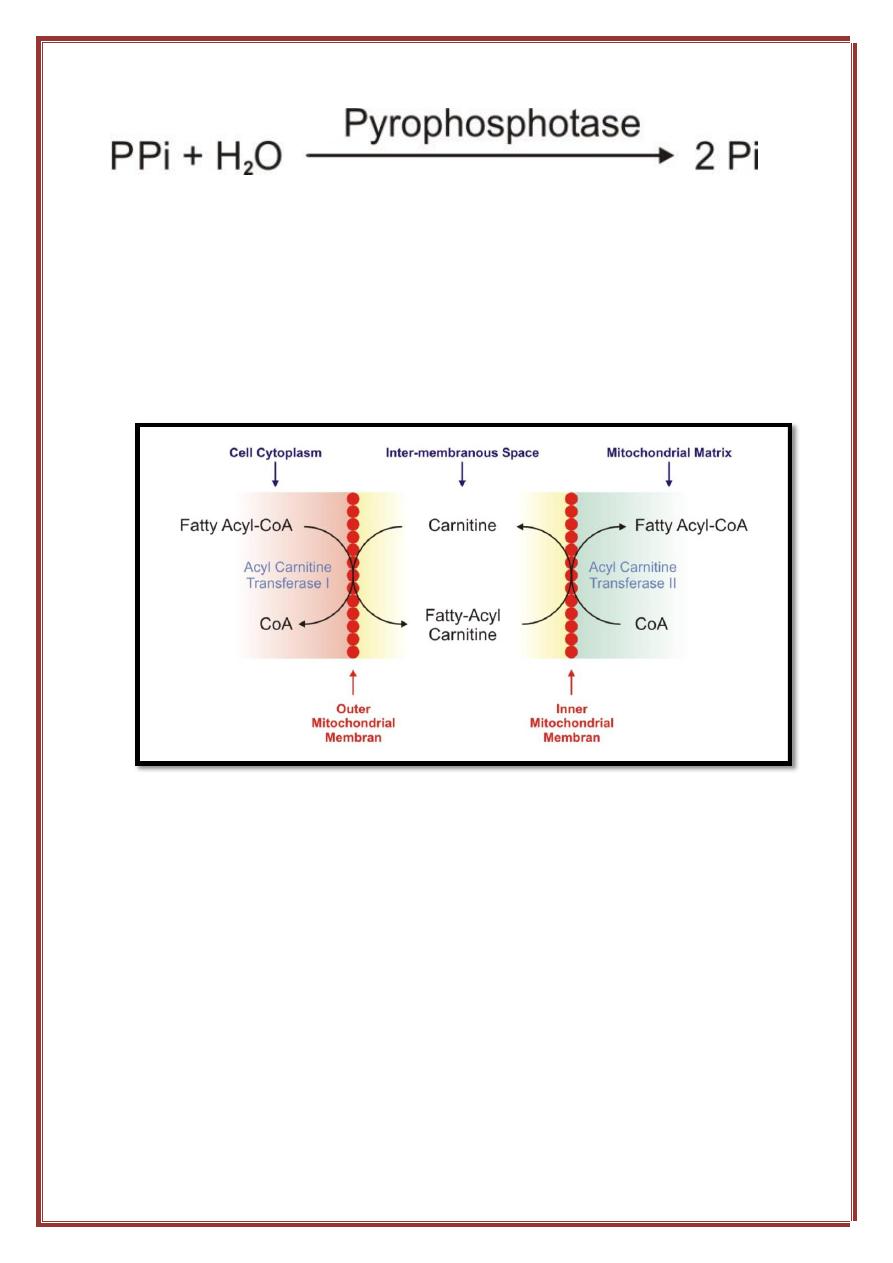
The subsequent steps in the oxidation of the fatty acids occur in the
mitochondrial matrix. Since the mitochondrial membrane is impermeable
to acyl-CoA, therefore a special mechanism is required for the transport of
acyl-CoA from the cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix. This mechanism
involves a compound called
Carnitine
, and the process is known as
carnitine shuttle
.
Medium chain fatty acids (shorter than 12 carbon atoms) can cross
the mitochondrial membrane without the aid of carnitine, and even its entry
to the cell does not require fatty acid binding proteins .
Carnitine could be obtained either from the diet (meat and meat
products) or by being synthesized inside the body (from amino acids lysine
and methionine) through an enzymatic system found in the liver and the
kidneys.
The deficiency of carnitine
occurs due to many reasons :
-Could be congenital
-Could occur in newborn babies (especially pre-mature) and this is due to
immaturity of the enzymatic system which will lead to inadequate
synthesis of carnitine.
3
-Malnutrition and those on strictly vegetarian diet
-Liver disease (because it is a main site for the synthesis).
-Increased requirement to carnitine
*Pregnancy.
*Severe Infection.
*Severe Burns.
*Trauma.
*Hemodialysis.
The effect of carnitine deficiency is decrease in the ability of
oxidizing long chain fatty acids and this may lead to weight loss, fatty liver,
and hypoglycemia.
Beta oxidation pathway
The oxidation of the fatty acid will take place on the β carbon atom, so
in each oxidation for (n carbon atoms) fatty acyl CoA the product is acetyl
CoA (two carbon atoms) and (n-2) fatty acyl CoA, and it will also produce
one FADH2 and one NADH.
The new fatty acyl CoA will undergo the same reaction again and again
until all the carbon atoms are converted into acetyl-CoA.

4
The FADH2 and NADH formed from oxidation of the fatty acid that has
even number of carbon atoms equal :
( The number of Carbon atoms / 2 ) – 1
ex. Palmatic acid(16C)→ 8 acetyl CoA+ 7 FADH2+ 7NADH
5
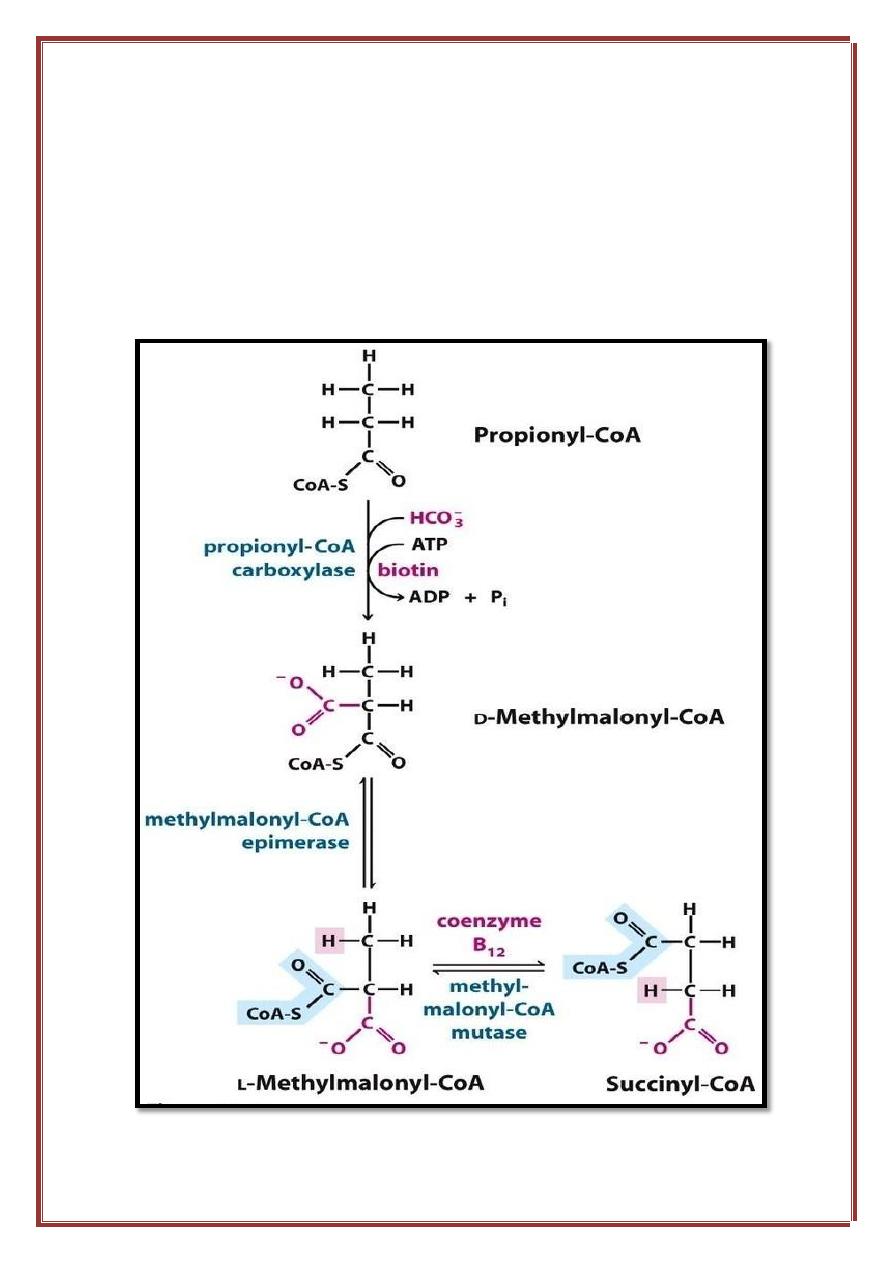
Oxidation of the Fatty Acids with Odd Number of C atoms:
The β oxidation of the fatty acid chains that have odd number of carbon
atoms will use the same reaction steps until the final three carbon acids are
reached and they are called here propionyl-CoA. The propionyl-CoA will
be converted into methyl-malonyl-CoA by a step that requires the use of
one ATP. Then the methyl-malonyl-CoA will be converted into the final
product which is the succinyl-CoA.
6
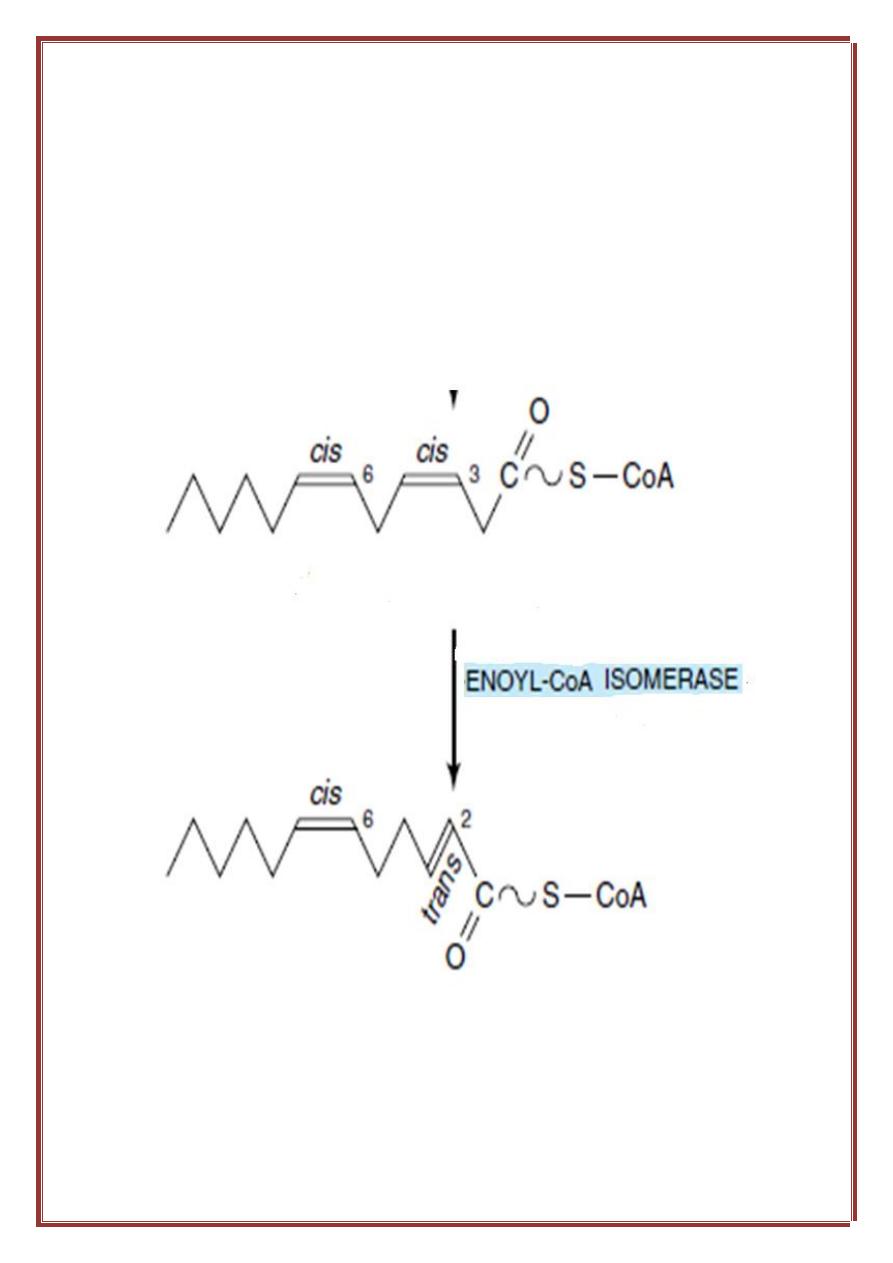
OXIDATION OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS:
Undergo the same sequence of reaction as saturated fatty acid until we
reach to the double bond between carbon 3 & 4.Usually the configuration
around the double bond is cis. In the saturated fatty acid we make a double
bond between C2 & C3 but in the unsaturated fatty acid the last double
bond is found between C3 & C4 so we will transfer the double bond to put
it between the C2 & C3 by the enzyme Enoyl CoA isomerase. This
enzyme transfer the double bond and change the configuration from cis to
trans.
7
After the transforming of the double bond to C2-C3 position now
the fatty acid will undergo the same reaction of β oxidation but it will not
pass in the first step that yield the FADH2.{so the oxidation of unsaturated
fatty acid with 16 carbon atom will give only 6 FADH2 and not 7 FADH2).
So removal of acetyl CoA in this step will produce only 3ATP not 5ATP.
PROBLEMS
Q.1. saturated fatty acid contain 16 carbon atom {palmatic acid} how
many the ATP produced after the oxidation of it ?
Answer: by β oxidation pathway it will give:
7 FADH2 and each FADH2 will give 2 ATP (so 7*2=14 ATP).
7 NADH2 and each NADH2 will give 3ATP (so 7*3=21 ATP).
8 acetyl CoA and each one will enter the citric acid cycle and give 12 ATP
(so 8*12=96 ATP).
14+21+96= 131 ATP.
But we need 2ATP IN THIOKINASE REACTION thus the no. Of ATP
131-2= 129 ATP produced from palmatic acid
Q.2. unsaturated fatty acid contain 16 carbon atom how many the ATP
produced
after
the
oxidation
of
it?
Answer: by β oxidation
6 FADH2 (so 6*2= 12 ATP).
7 NADH2 (so 7*3=21 ATP).
8 Acetyl CoA (so 8*12=96 ATP).
12+21+96=129 ATP.
129-2= 127 ATP.
8
Q.3. saturated fatty acid contain 17 carbon atom how many the ATP
produced after the oxidation of it?
7 FADH2 ( 7x2=14 ATP).
7 NADH2 ( 7x3= 21 ATP).
7 Acetyl CoA ( 7x12= 84 ATP).
14+21+84= 119 ATP.
119-2 = 117 ATP.
5 ATP from succinyl-CoA
117+ 5= 122 ATP
Q.4. unsaturated fatty acid contain 17 carbon atom how many ATP
produced after its oxidation ?
6 FADH2 (6x2=12 ATP).
7 NADH2 (7x3=21 ATP).
7 Acetyl CoA (7x12=84 ATP).
12+21+84= 117 ATP.
117-2= 115 ATP.
5 ATP from succinyl-CoA
115+ 5= 120 ATP
