Lecture five
Blood vessels
By Dr.Alaa Al-sahlany
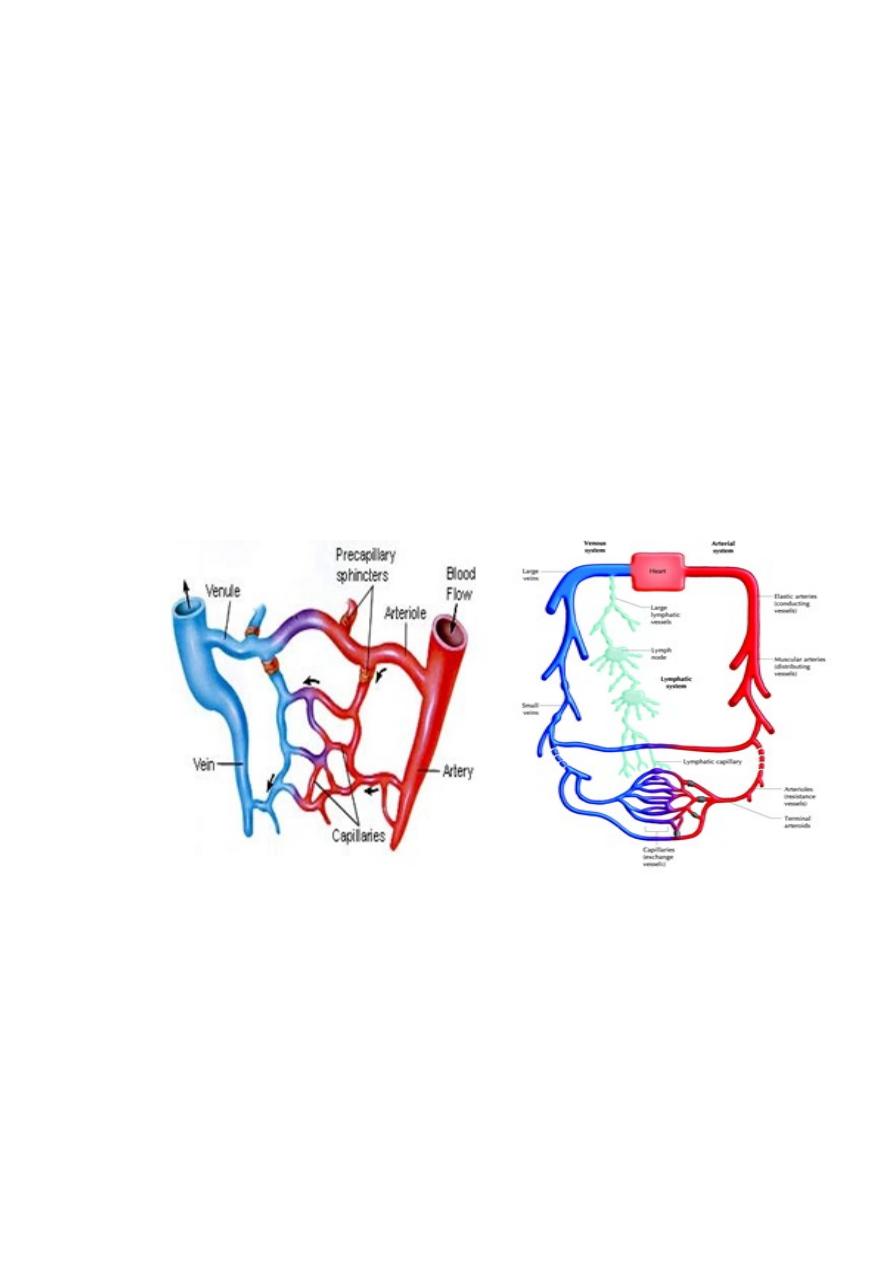
Types of blood vessels
1. Arteries: (a) Large artery (b) Medium sized artery
2. Arterioles
3. Capillaries
4. Venules
5. Veins:(b) Large vein (a) Medium-sized vein
General Structure of blood vessels
(a)
Tunica intima
Is composed of lining endothelium (simple squamous epithelium) and
subendothelial connective tissue.
Sometimes Tunica intima is demarcated from tunica media by
internal elastic
lamina
(b)
Tunica media
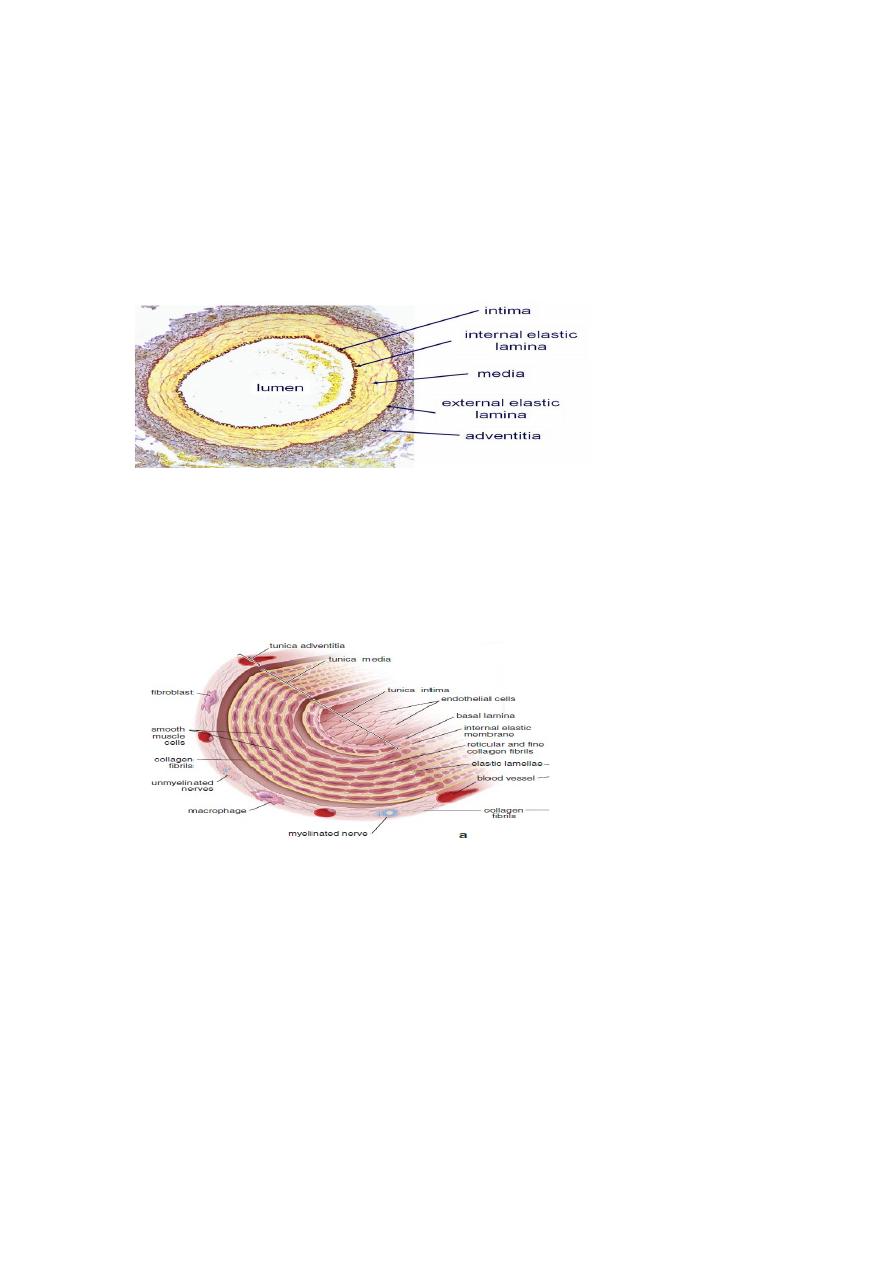
Is made of smooth muscle and connective tissue
.
Sometimes it is thickened and demarcated from adventitia by
external elastic
lamina
(c)
Tunica adventitia
It is composed of elastic connective tissue
.
It carry small blood vessels (vasa vasorum) and sympathetic fibers
.
Types of blood vessels
Arteries
1
.
Large (Elastic )artery
Aorta and its branches are examples
Presence of elastic fibers in the wall allows it to expand during contraction (systole)
and to recoil during relaxation (diastole) of heart.
Tunica media mainly made of elastic lamellae, therefore, it is named elastic artery
2
.
Medium-sized(Muscular )artery
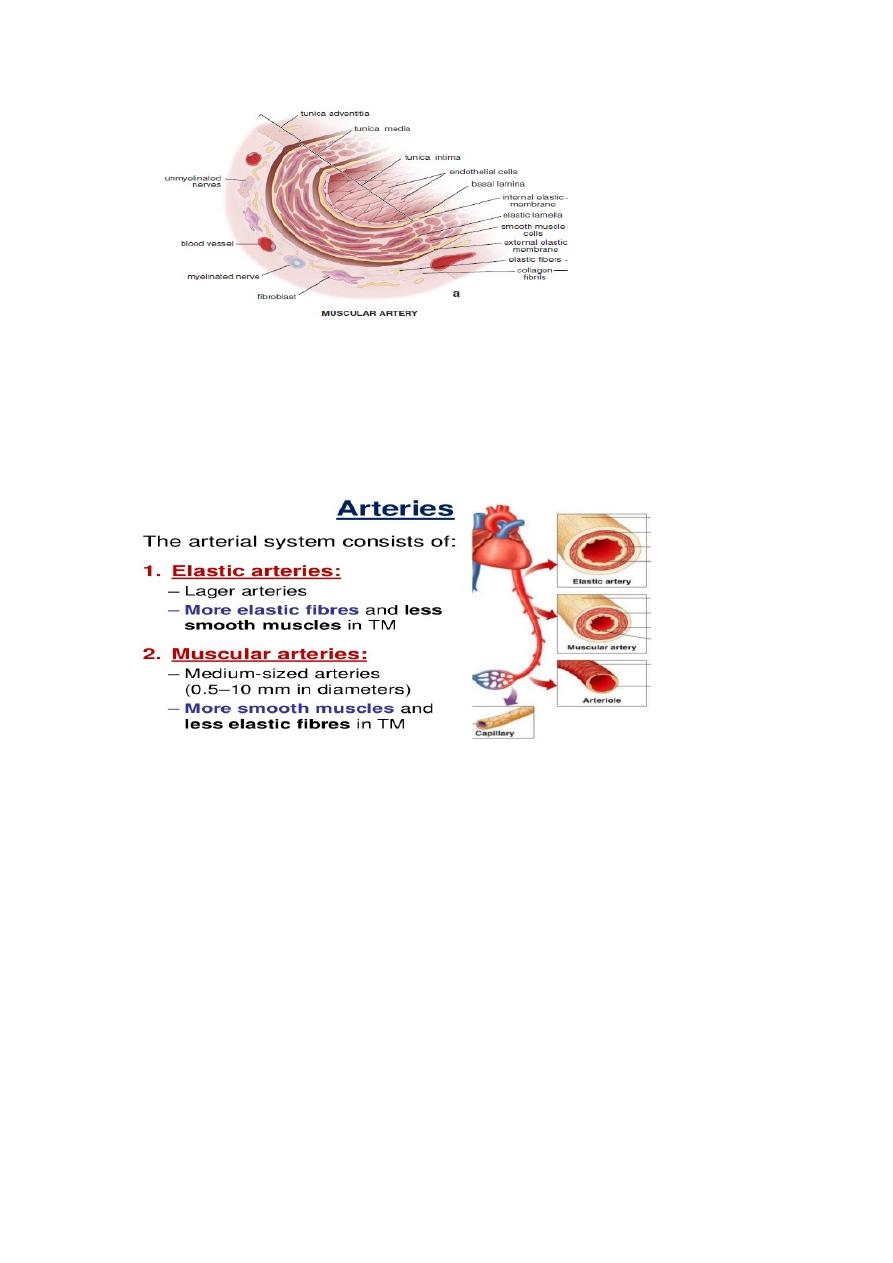
Radial and ulnar arteries are examples
Presence of smooth muscle in its wall helps to control pressure of blood through
vasoconstriction or vasodilatation.
Tunica media consists mainly of smooth muscle cells. Hence the name muscular
artery
ARTERIOLES
It has a thick wall relative to the size of its small lumen
Serve as flow regulators for the capillary beds
CAPILLARIES
Arterioles break up into small blood vessels called capillaries which are the
smallest diameter blood vessels
They are involved in exchange of gases, nutrients and metabolites between blood
and tissue
.
Tissues with high metabolic rates have abundant capillary network (e.g. liver,
cardiac muscle)
.
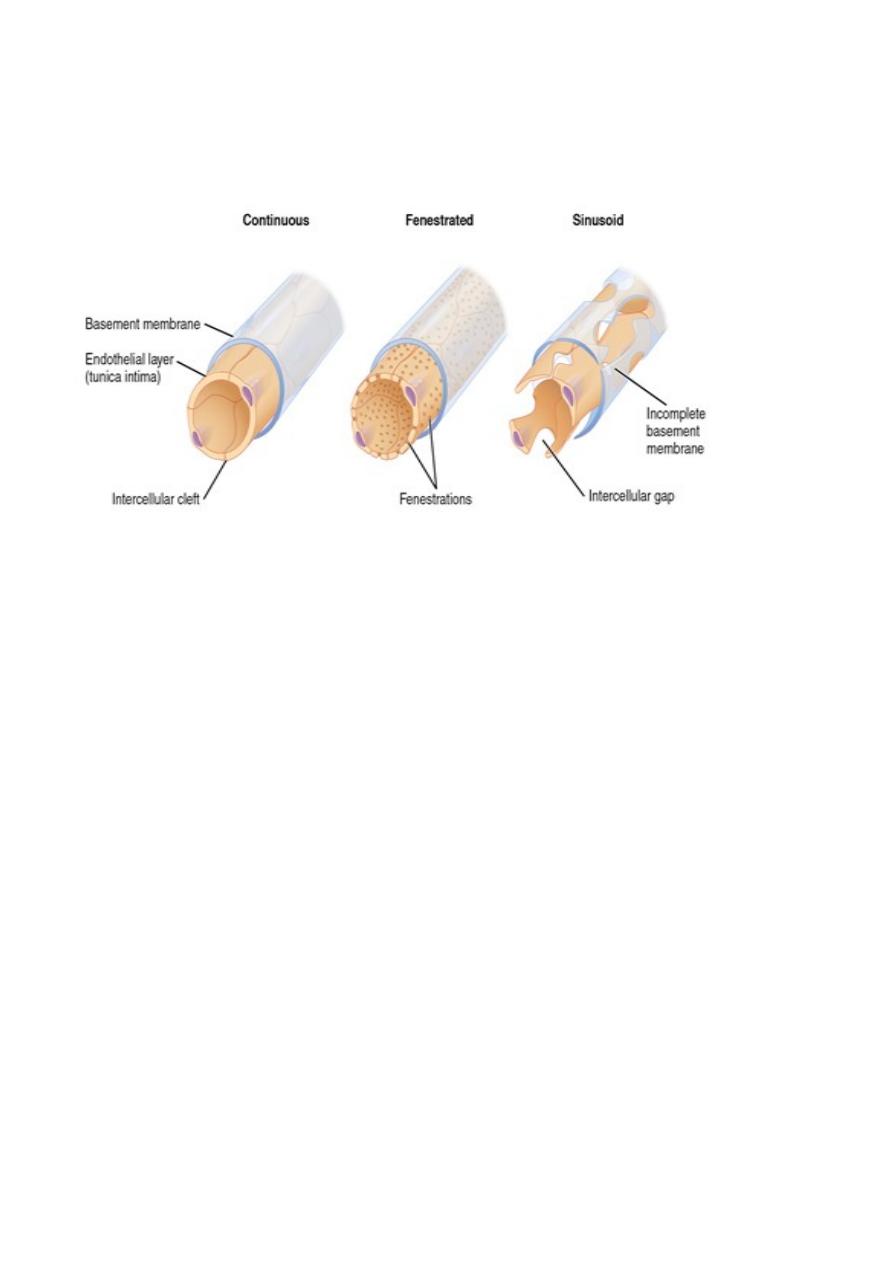
Types of capillaries
1
.
Continuous capillary
It is the commonest type of capillary present in muscle, brain, etc
.
The endothelial cells form a continuous lining of the capillary
2
.
Fenestrated capillary
Characterized by the presence of pores (fenestrations) in the endothelial cells
.
These pores are allows substances and molecules to pass through
.
The permeability of fenestrated capillary is much greater than that of continuous
capillary therefore found in tissues in which rapid exchange of substances occur
3
.
Sinusoidal capillary
Found in haemopoietic organs like bone marrow and spleen and liver
.
Lumen is lined by discontinuous endothelium (the basal lamina is discontinuous)
forming gaps that permit the passage of blood cells and large molecules
Venules
Venules receive blood from capillaries
Only
postcapillary venules
take part in exchange of metabolites between blood and
tissue besides capillaries
.
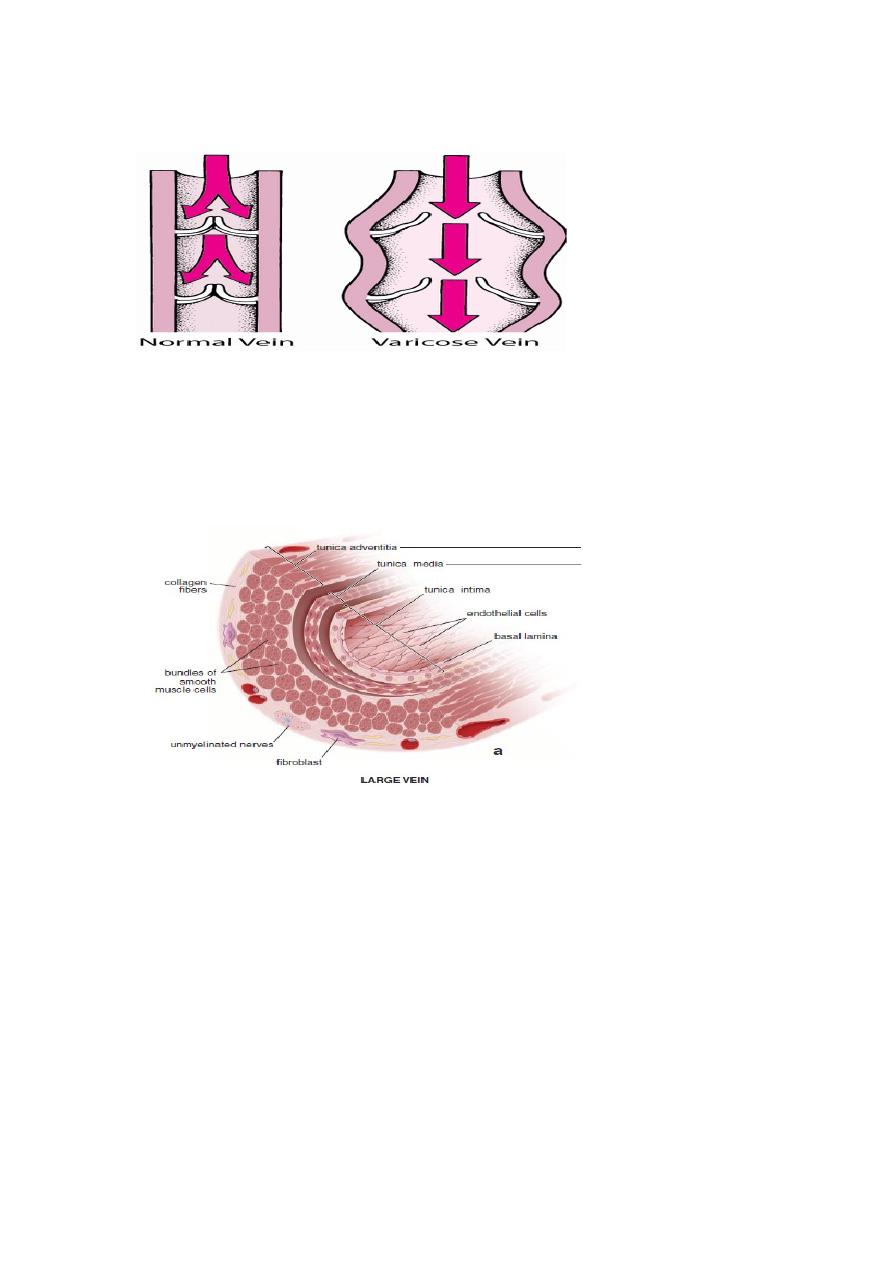
VEINS
Veins are thin-walled blood vessels that carry blood from capillaries to heart
.
They are often provided with valves (especially in lower limbs) which serve to
prevent the reflux of the blood
1
.
Large vein
Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava are examples
Tunica media: It is thin or absent.
Tunica adventitia: It is the thickest coat.
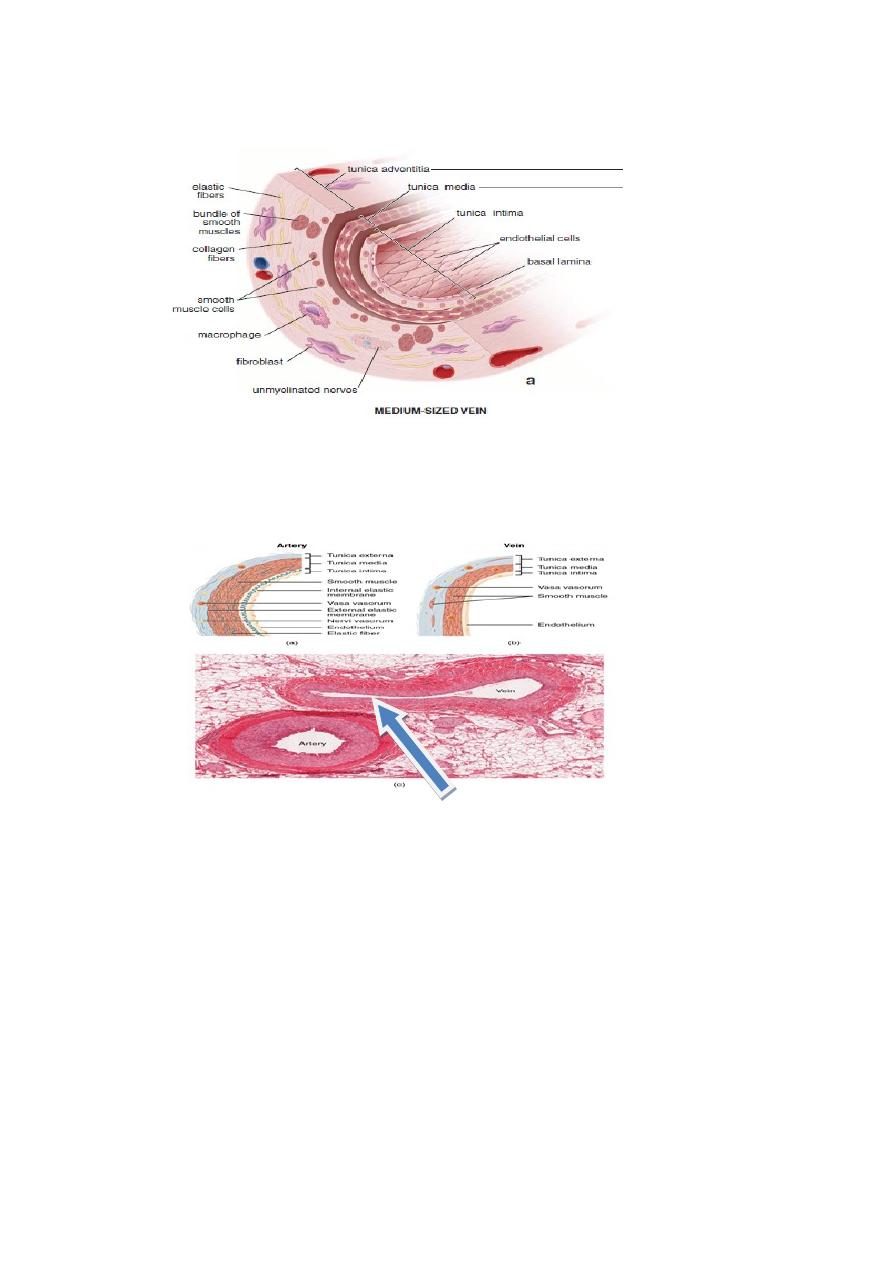
2
.
Medium-sized vein
Medium-sized vein differs from medium-sized artery in having a collapsed lumen
Tunica adventitia is the thickest coat unlike arteries.
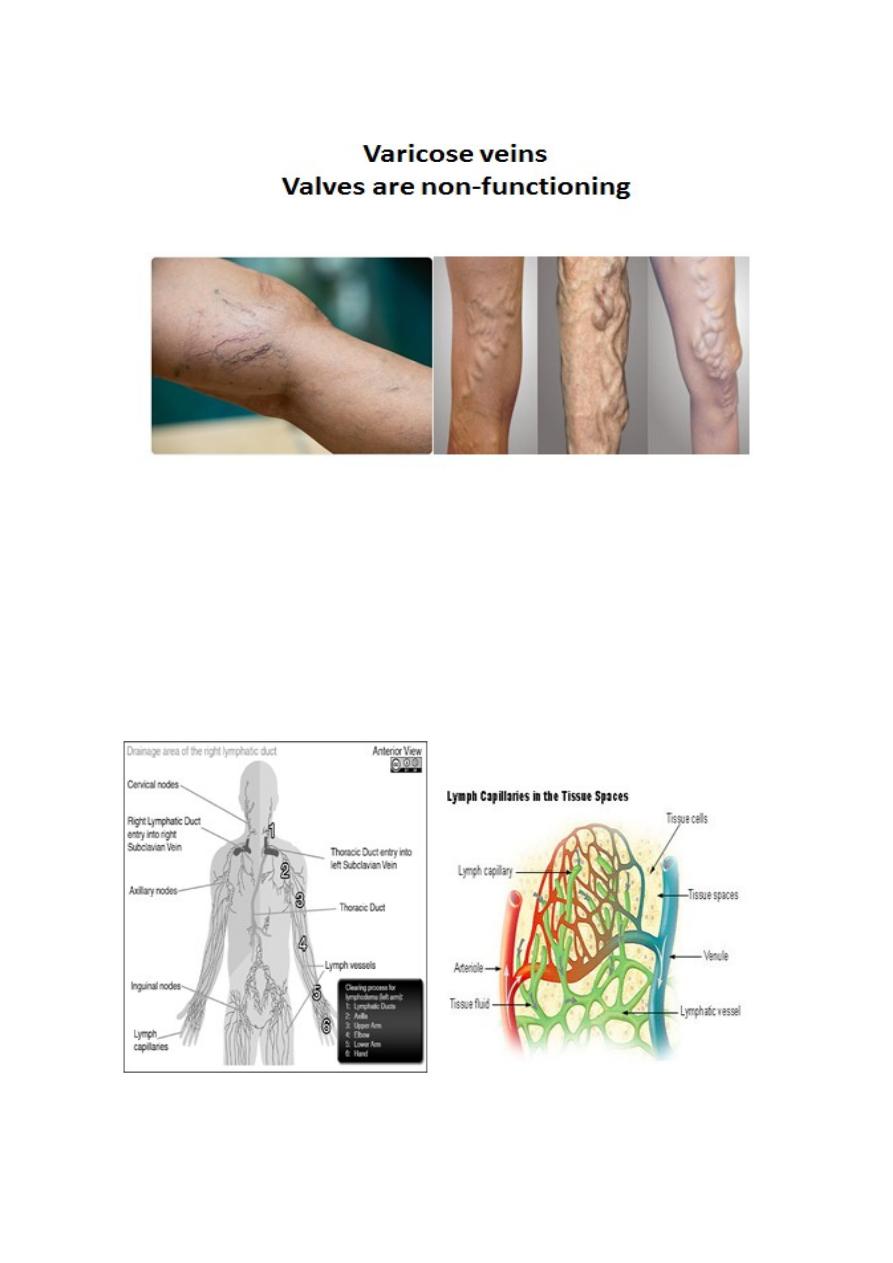
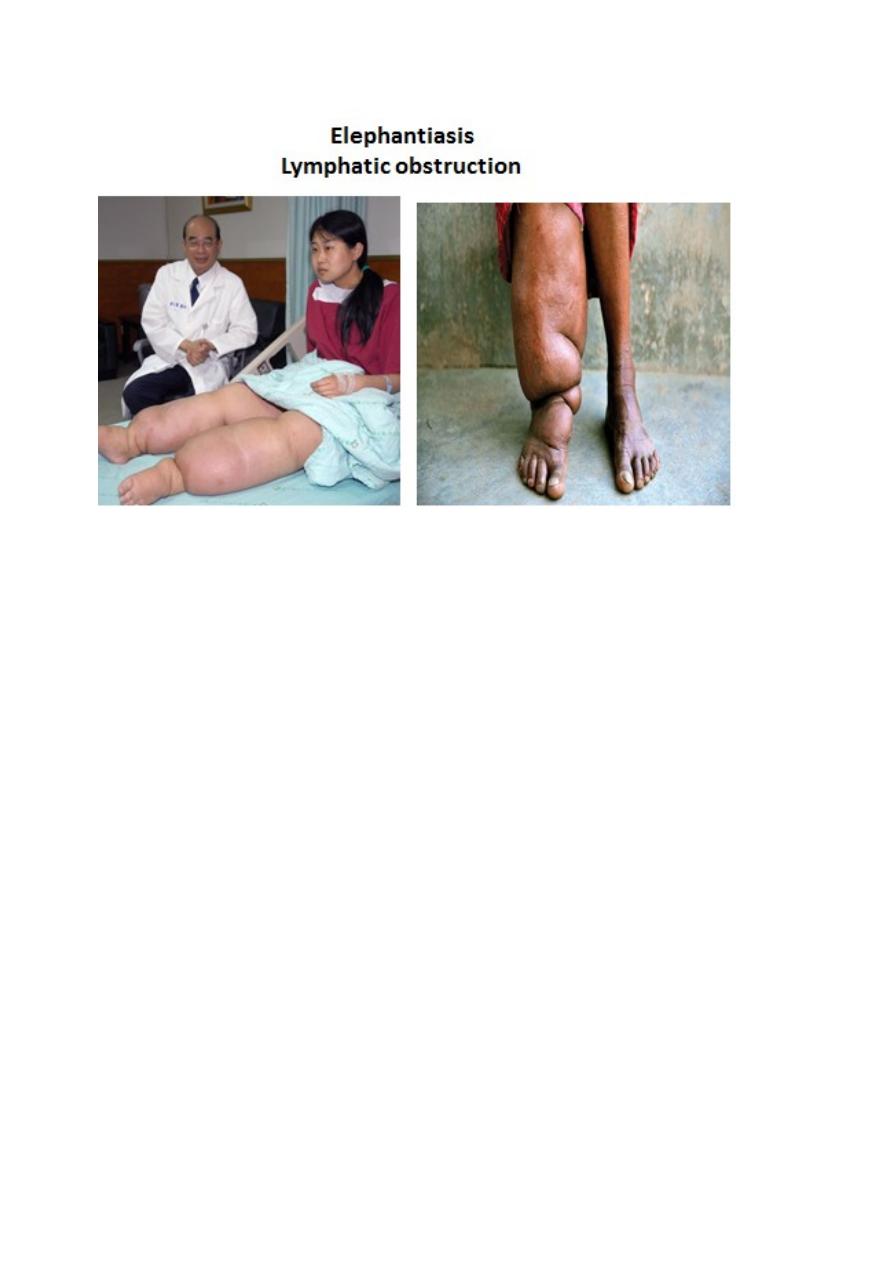
Lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic vessels are unidirectional (have valves), conveying fluid only from
tissues
Because of their greater permeability, lymphatic capillaries are more effective than
blood capillaries in removing protein-rich fluid from the extracellular spaces