Microbiology
Notes…
1
Immunology Lecture.4 The complement system
• Over 30 proteins produced by the liver and found in circulating blood in inactive form.
• Once activated, the complement works as a cascade system. Cascade is when one
reaction triggers another reaction which trigger others and so on. These types of
systems can grow exponentially very fast.
• Some of which have enzymatic activity, while others are biologically active
substances.
• They constitute about 15% of the total plasma proteins.
Complement System Nomenclature
• Complement proteins are often designated by an upper case letter C and are
inactive until they are split into products.
– Example: C1
• When the products are split, they become active. The active products are usually
designated with a lower case a or b.
– Example: C2a and C2b
Complement System: Three Pathways
The complement system can be activated by either of THREE different pathways.
1. Classical Complement Pathway
part of the specific immunity.
2. Alternative (Properdin) Complement Pathway
part of the non-specific immunity.
3. Mannose- Binding Lectin (MBL) Pathway
A recently discovered system in which C binds to mannose residue of the glycoprotein
or polysaccharides present in bacterial cell wall or viral envelop.
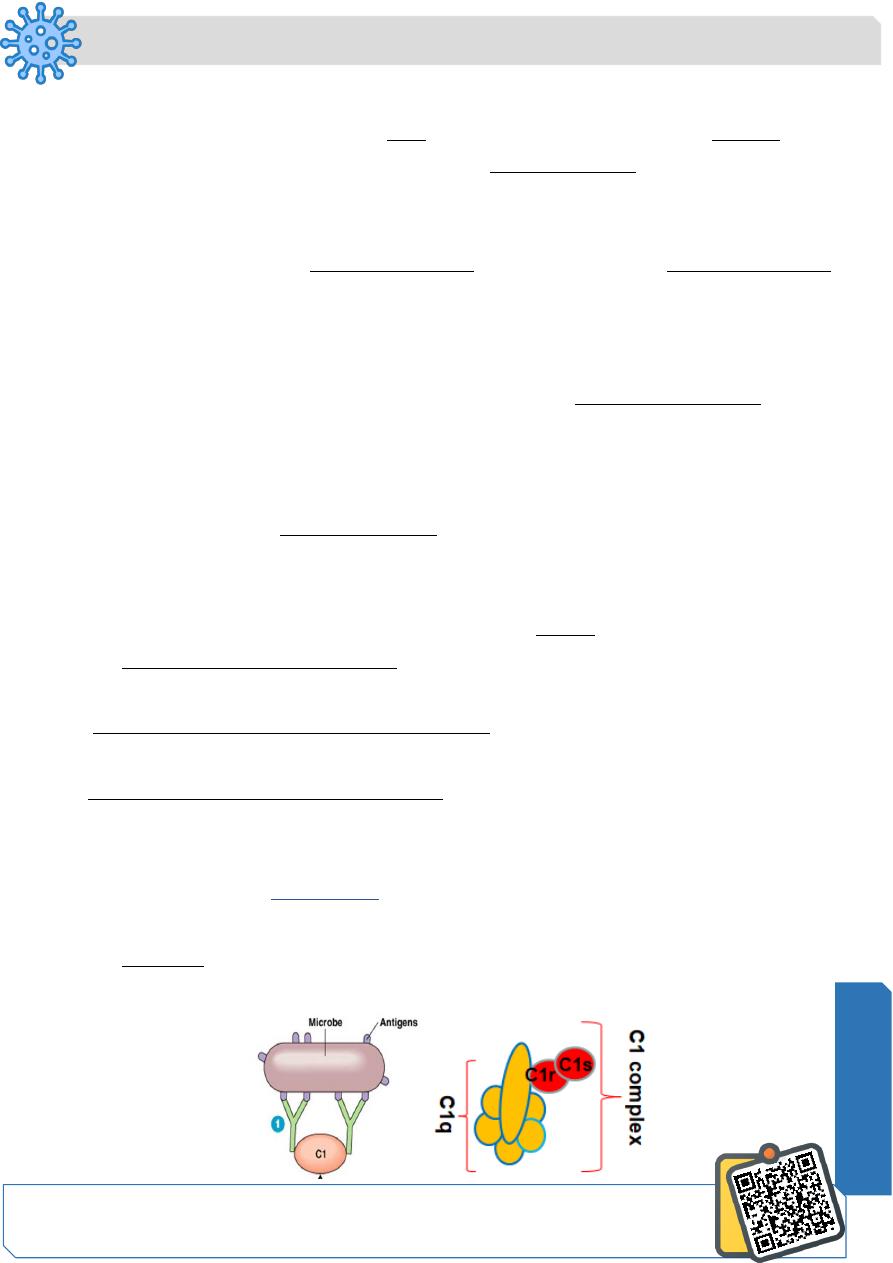
The Classical Pathway:
C1 Complex
• Part of the specific immune response because it relies on antibodies to initiate it.
• First step Binding of complement fixing antibodies (IgG and IgM) to a target antigen
(e.g., cell, bacteria or virus).
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p?
Microbiology
Notes…
2
• C1 complex becomes activated when it binds to the ends of antibodies. The part of
C1 complex which binds antibodies is C1q (6 heads structure). C1 is called
recognition unit. It must attach to at least 2 Fc fragments, requires at least 2
molecules of IgG or one molecule of IgM.
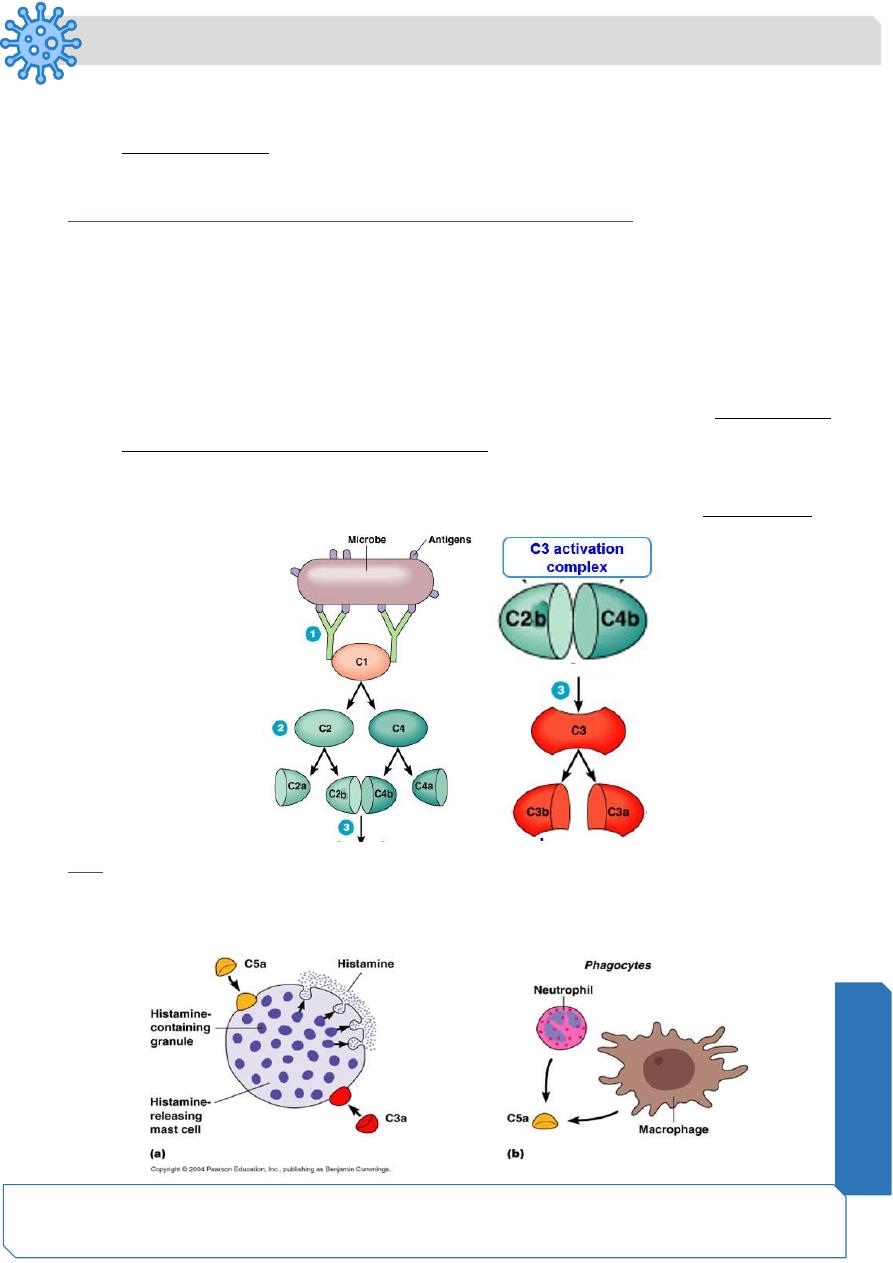
The Classical Pathway: Building up of C3 Activation Complex
• Activated C1 complex acquires enzymatic activity that activate 2 other complement
proteins, C2 and C4 by cutting them into 2 equal halves
• C2 is cleaved into C2a and C2b
• C4 is cleaved into C4a and C4b
• C2a and C4a diffuse away
• C2b and C4b bind together on the surface of bacteria to form a C3 activation
complex (C3 esterase or C3 converstase)
• C3 activation complex has an enzymatic activity . The function of the C3 activation
complex is to activate C3 proteins. This is done by cleaving C3 into C3a and C3b
C3a
C3a increases the inflammatory response by binding to mast cells and causing them to
release histamine
Microbiology
Notes…
3
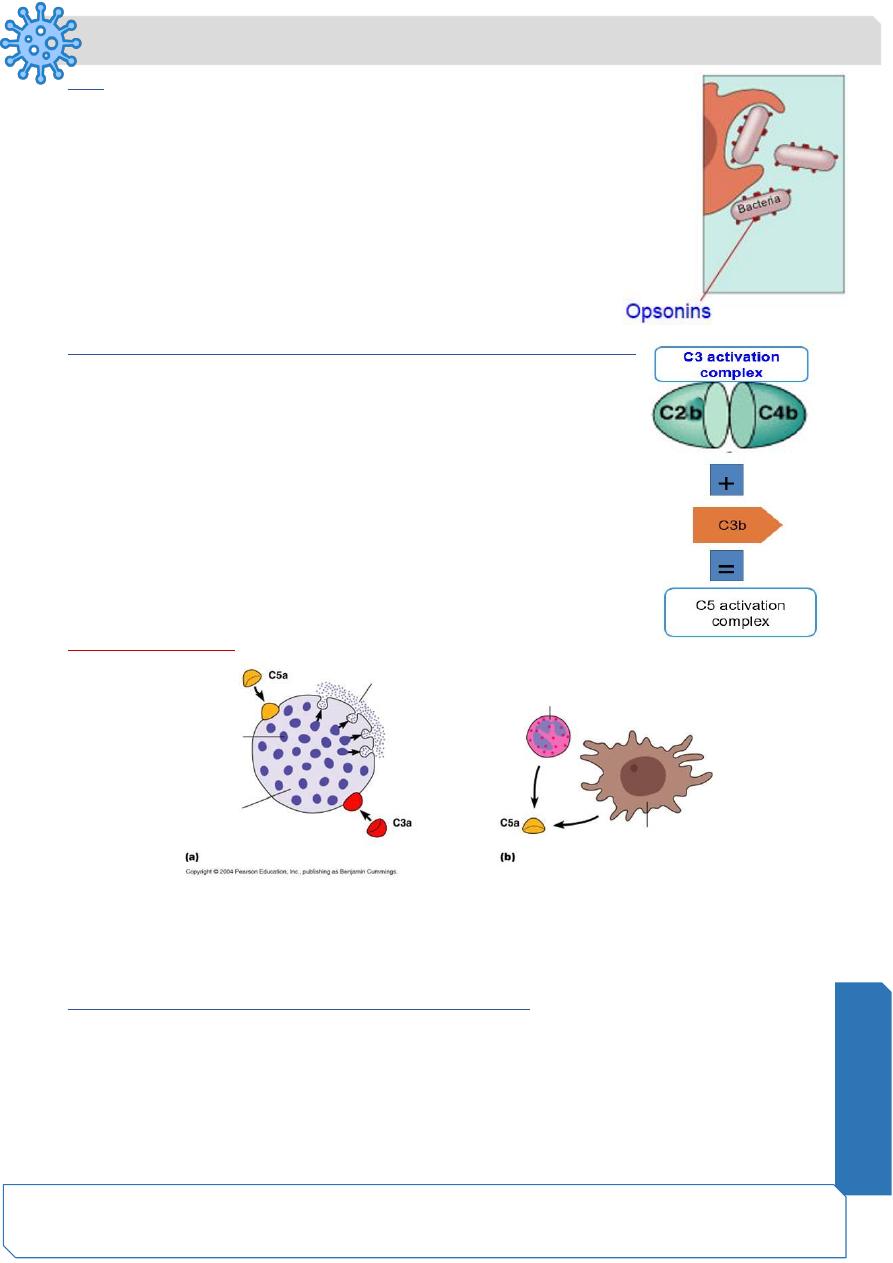
C3b
• The C3b bind to and coat the surface of the bacteria.
• C3b is an opsonin
• Opsonins are molecules that bind both to bacteria
and phagocytes
• Opsonization increases phagocytosis by 1,000 fold.
The Complement System: Building Up C5 Activation Complex
• Eventially enough C3b is cleaved that the surface of the
bacteria begins to become saturated with it.
• C2b and C4b which make up the C3 activation complex
has a slight affinity for C3b and C3b binds to them
• When C3b binds to C2b and C4b it forms a new complex
referred to as the C5 activation complex (C5 convertase)
• The C5 activation complex (C2b, C4b, C3b) activates C5
proteins by cleaving them into C5a and C5b
The function of C5a
• C5a disperses away from the bacteria.
– Binds to mast cells and increases inflammation.
– Most powerful chemotactic factor known for leukocytes
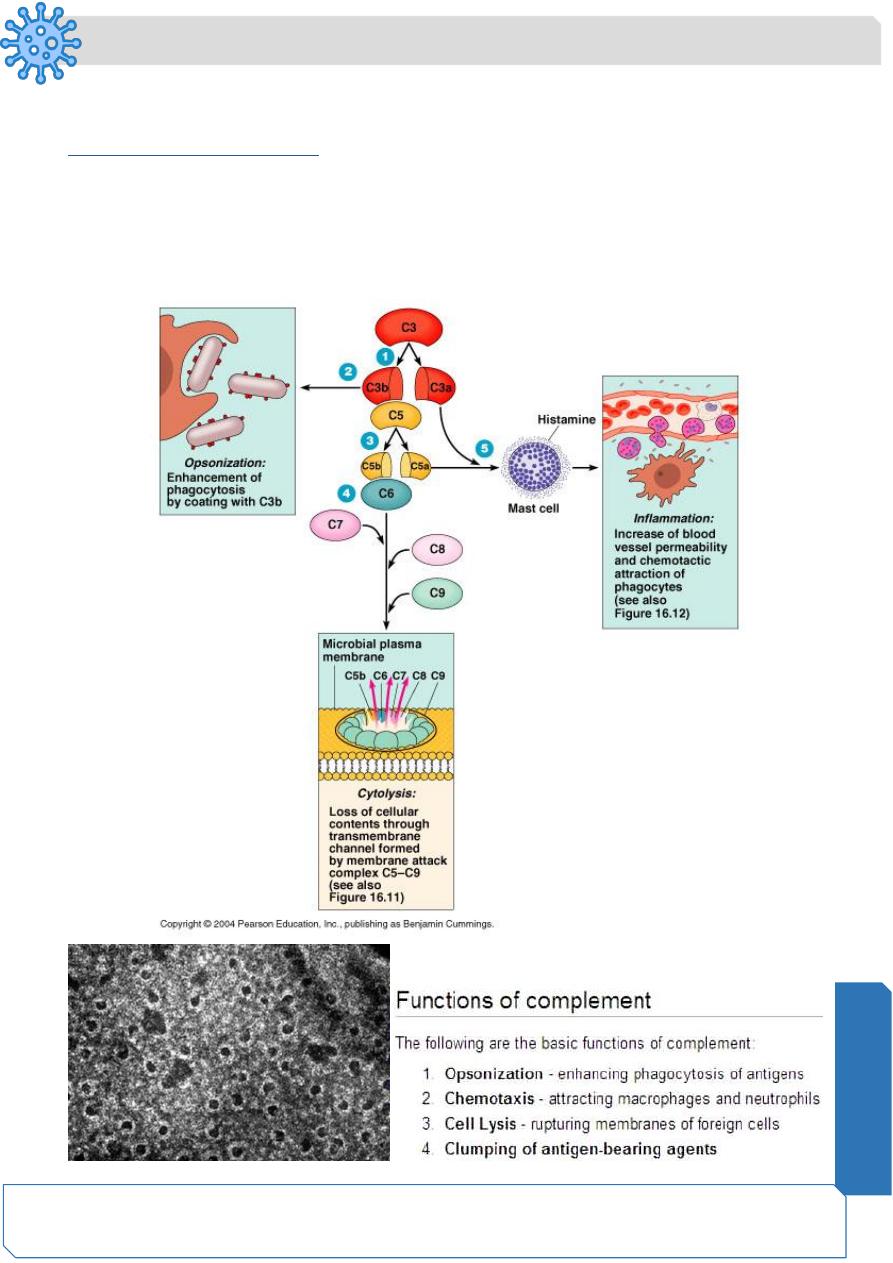
Building up the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
• Many C5b proteins are produced by the C5 activation complex. These C5b begin
to coat the surface of the bacteria
• C5b on the surface of bacteria binds to C6
• The binding of C6 to C5b activates C6 so that it can bind to C7
• C7 binds to C8 which in turn binds to C9’s
Microbiology
Notes…
4
• Together these proteins form a circular complex called the Membrane Attack
Complex (MAC)
Membrane Attack complex
• The MAC causes Cytolysis.
– The circular membrane attack complex acts as a channel in which
cytoplasm can rush out of and water rushes in.
• The cell’s inner integrity is compromised and it dies

Microbiology
Notes…
5
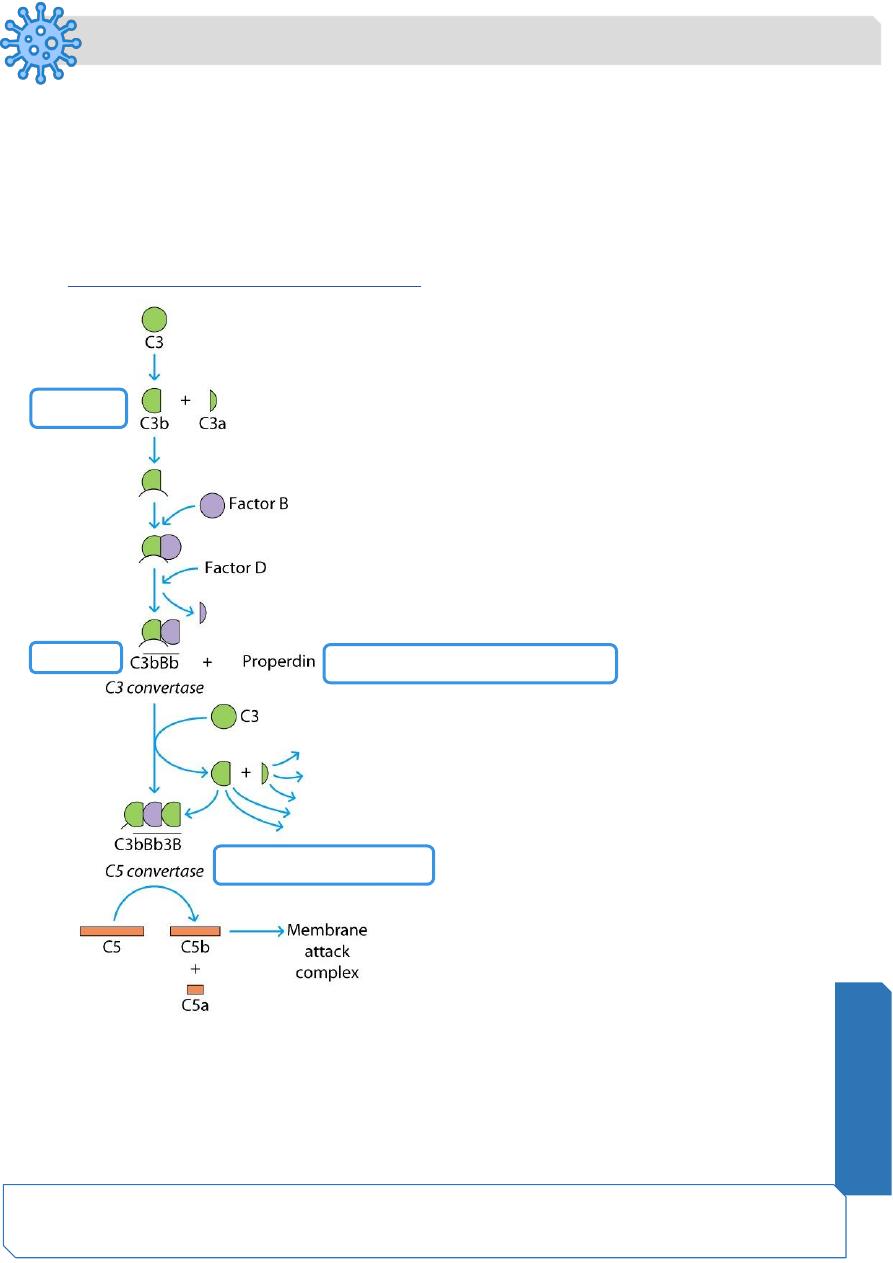
The Complement System: The Alternative Pathway
• The alternative pathway is part of the non-specific defense because it does not
need antibodies to initiate the pathway.
• The alternative pathway is slower than the classical pathway.
Factors of Activation
1. Bacterial cell wall polysaccharides.
2. Bacterial Endotoxin.
3. Cobra venom factor.
4. Trypsin & plasmin.
• This system starts from C3b which is always available in the body. The activation
passes into the following steps:
The Alternative pathway : C3b
• C3 contains unstable thioester bond.
• This unstable bond makes C3 subject to slow spontaneous hydrolysis to C3b
(Factor A) and C3a.
• The C3b is able to bind to foreign surface antigens.
• Mammalian cells contain sialic acid which inactivates C3b and prevent over-
activation of pathway
Alternative Pathway: Factor B
• C3b on the surface of a foreign cells binds to another plasma protein called factor
B (C3-Proactivator) forming C3bFactor B
Alternative Pathway: Factor D
• The binding of C3b to factor B allows a protein enzyme called Factor D to cleave
Factor B to Ba and Bb.
• Factor Bb remains bound to C3b while Ba and Factor D disperse away.
• C3b Factor Bb (enzyme) has a catalytic enzymatic activity in its B moiety. However,
this enzyme is unstable it may dissociate into C3b + Bb.
Alternative Pathway: The C3 Activation Complex
• Properdin (220 KDa glycoprotein , also called factor P, binds to the C3bBb complex
to stabilize it (C3bFactorBbP)
• C3bBbP make up the C3 activation complex (C3 convertase) for the alternative
pathway. The latter breaks C3 into C3a (small) and C3b (large)
• The C3 activation complex causes the production of more C3b.
Microbiology
Notes…
6
• This allows the initial steps of this pathway to be repeated and amplified
• 2X10
6
molecules can be generated in 5 minutes
• When an additional C3b binds to the C3 activation complex it converts it into a C5
activation complex (C5 convertase).
• The C5 activation complex cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b.
• C5b begins the production of the MAC.
The Alternative Complement Pathway
C3b BbP (C3 activation complex)
(C5 activation complex
(
Unstable
Factor 1
