
Microbiology
Notes…
1
Microbial Genetics Lecture.1
Genetics: field of biology that studies genes and their inheritance
Gene
Segment of DNA that encodes a functional product, usually a protein
Gene Vs. Genomes
Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell
Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the nuclear area
Eukaryotic cell has two genomes
▪ Nuclear genome
▪ Mitochondrial genome
If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome
In human beings genes constitute only 1-3 % of the human genome
The remaining 99% of the genome – have yet no known functions! These regions
are called non-coding regions
Genome = Coding regions (genes) + non-coding regions.
Genetics Vs. Genomics
Genetics is the study of single specific, individual genes in isolation and their role
in inheritance
e.g. "monogenic" diseases such as sickle cell anaemia and cystic fibrosis, caused
by an error in a single gene
Genomics is the study of all genes in the genome and,
the interactions among them and their environment (or non-genetic factors such
as a person's lifestyle)
Improve understanding of complex diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and
asthma
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p?
Microbiology
Notes…
2
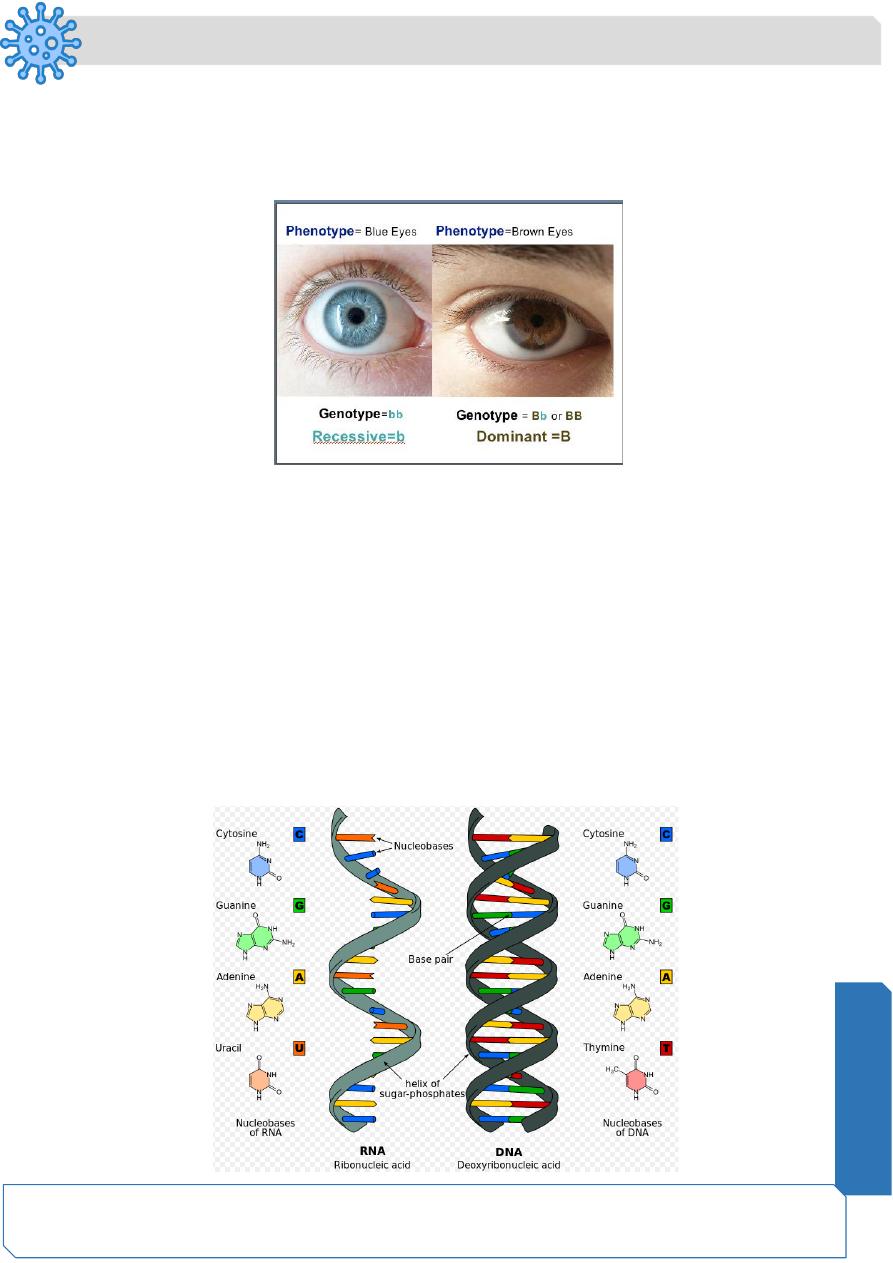
Genotype Vs. Phenotype
"Genotype" is an organism's full hereditary information
"Phenotype" is an organism's actual observed properties, such as morphology,
development, or behavior
Structure and Function of Genetic Material
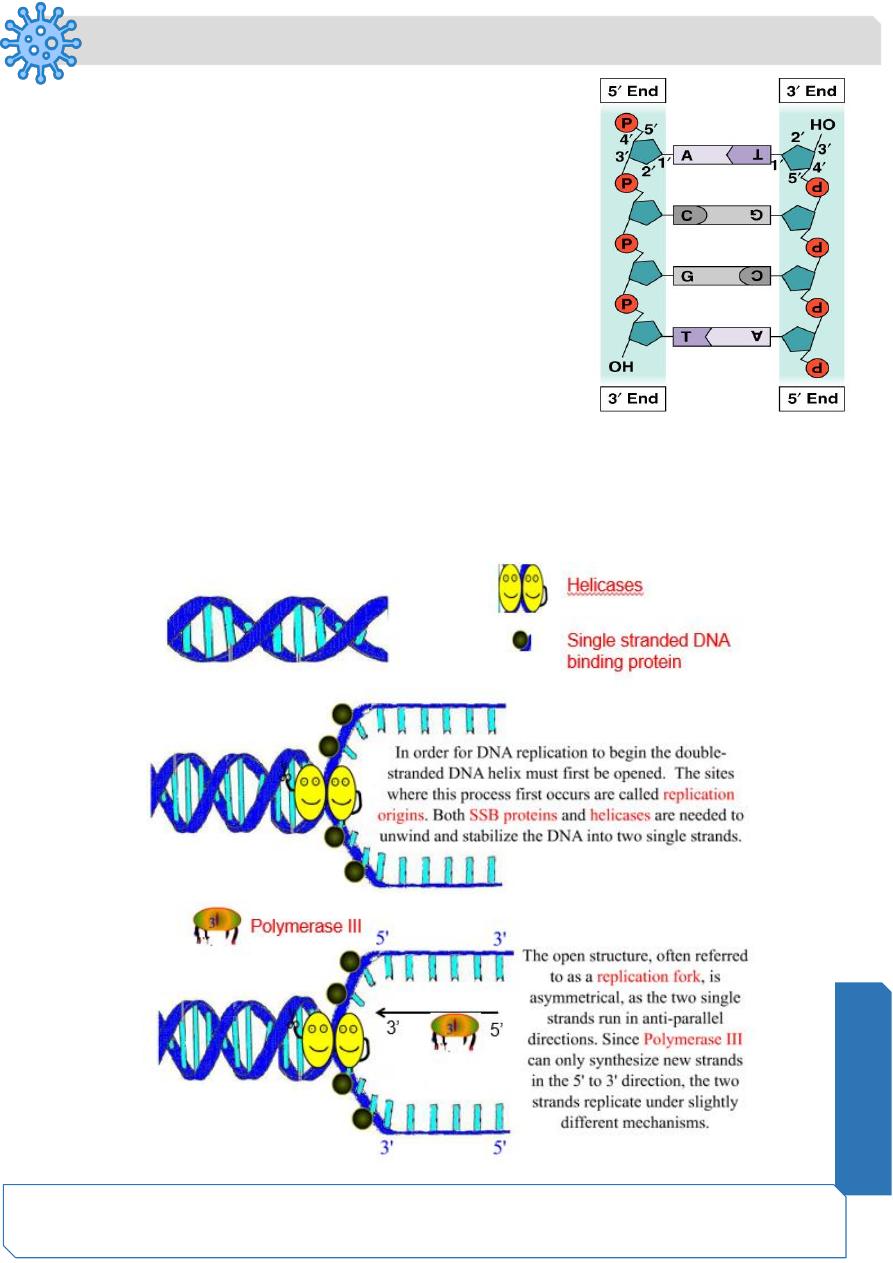
Genetic Material = DNA or RNA
▪ In the vast majority of organisms, genetic material is DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid)
▪ In some viruses , genetic material is RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Genetic Material: Basic Building Units
• Nucleotides
• Phosphate group
• Pentose sugar
• Nitrogenous base
Microbiology
Notes…
3
Structure of DNA
Double stranded (double helix)
Adenine (A), thymine(T),cytosine(C) and guanine(G)
"Backbone" is deoxyribose-phosphate
Strands held together by hydrogen bonds between
AT and CG
5’ to 3’ (strands are anti-parallel)
Complimentary base pairing
▪ A-T • G-C
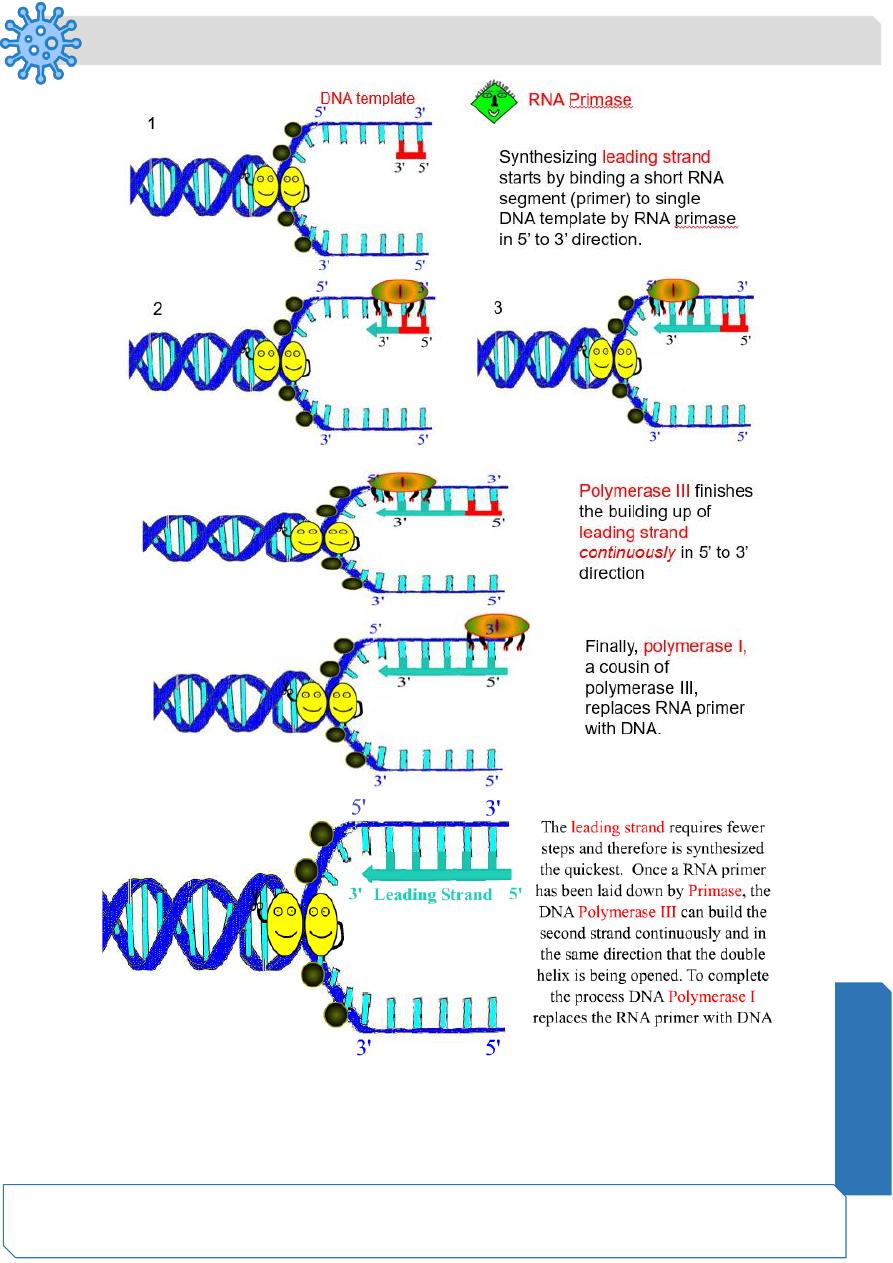
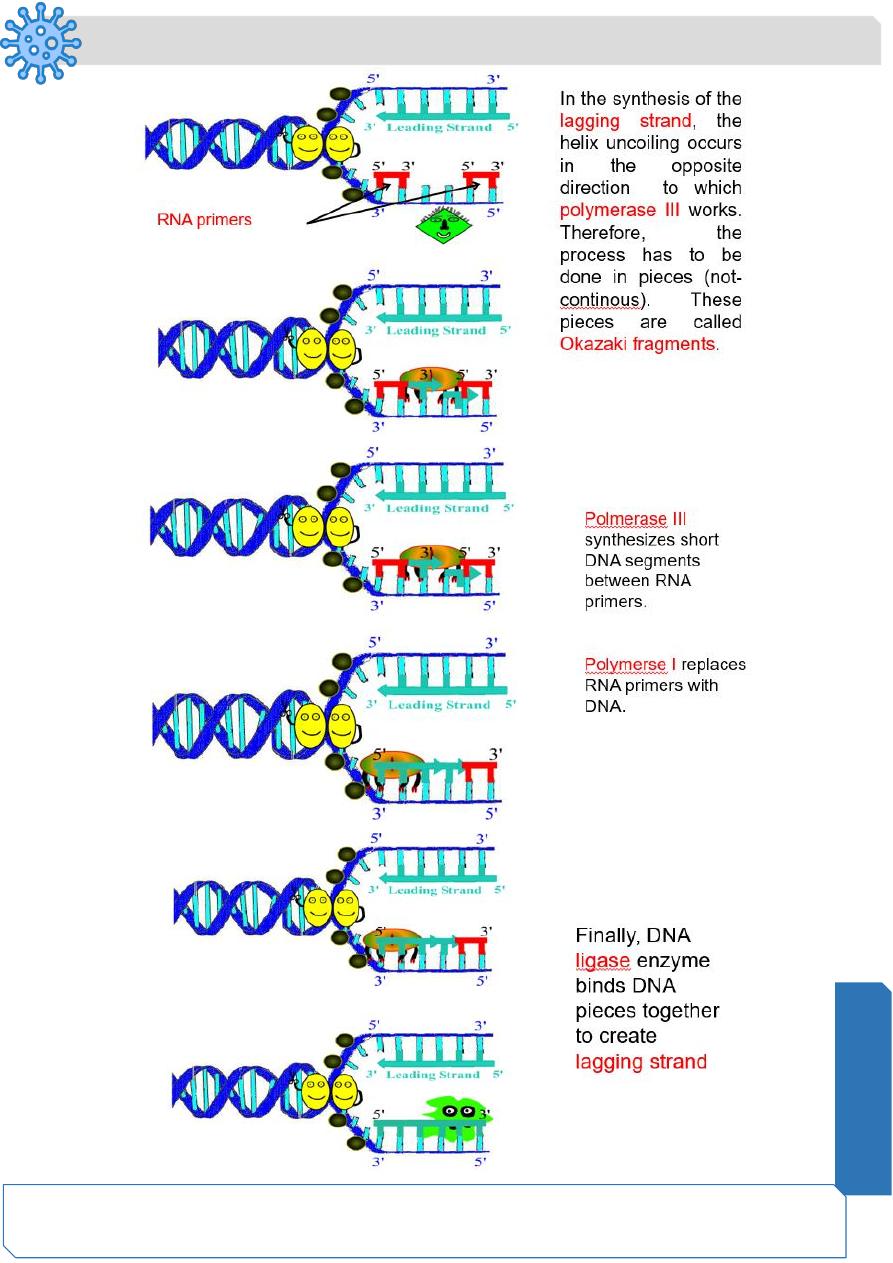
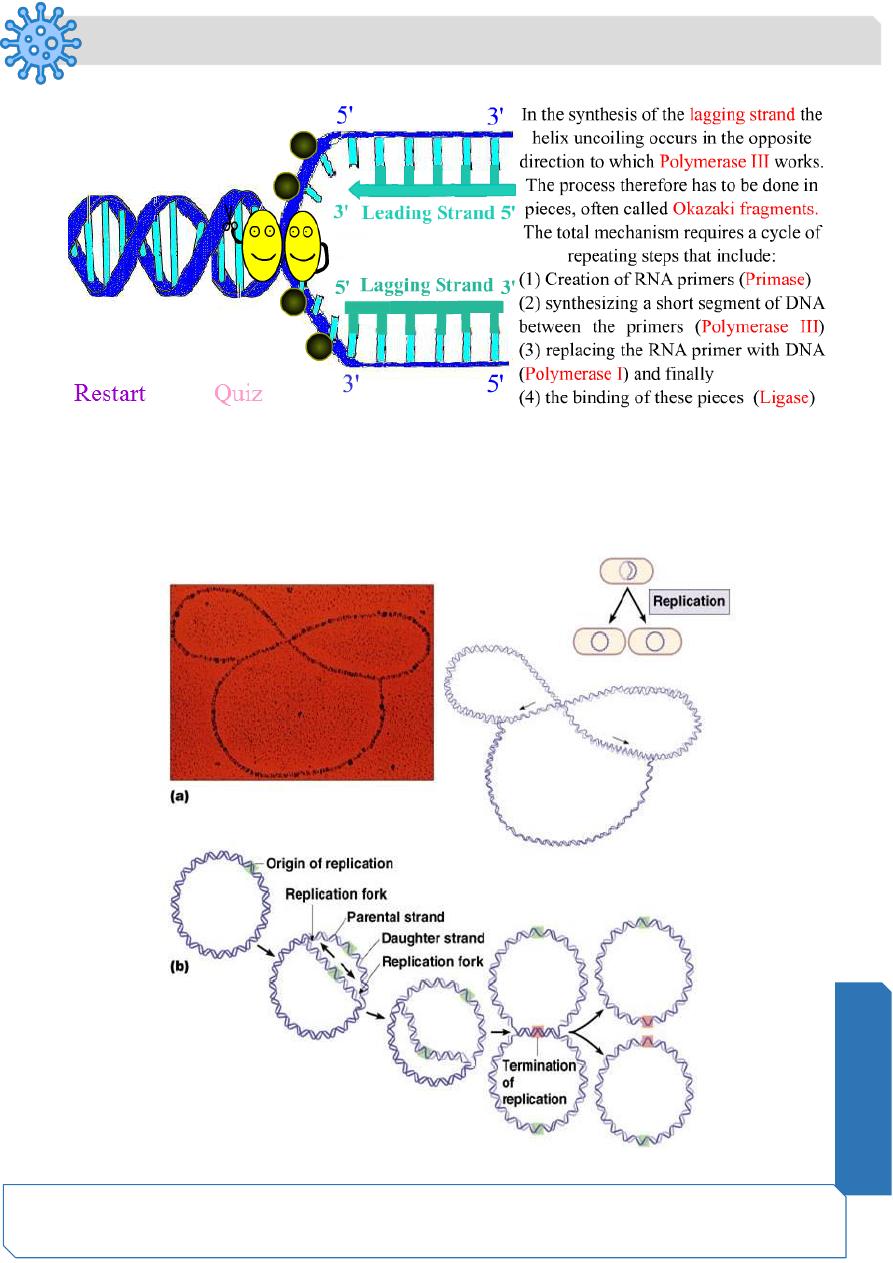
DNA Replication
Bacteria have closed, circular DNA
E. coli
▪ 4 million base pairs
▪ 1 mm long (over 1000 times longer that actual bacterial cell)
▪ DNA takes up around 10% of cell volume
Microbiology
Notes…
4
Microbiology
Notes…
5
Microbiology
Notes…
6
DNA replication is semi-conservative:
What does it mean?
During cell division, each daughter cell inherits 2 DNA strands, One is old and one is new.
Microbiology
Notes…
7
