Microbiology
Notes…
1
Immunization Lecture.5
Immunization:
In medicine :
The fact or
the process of becoming immune, as against a disease, usually as a result of
activation of
immune system.
In finance :
The method
of protection against fluctuation in investing rate.
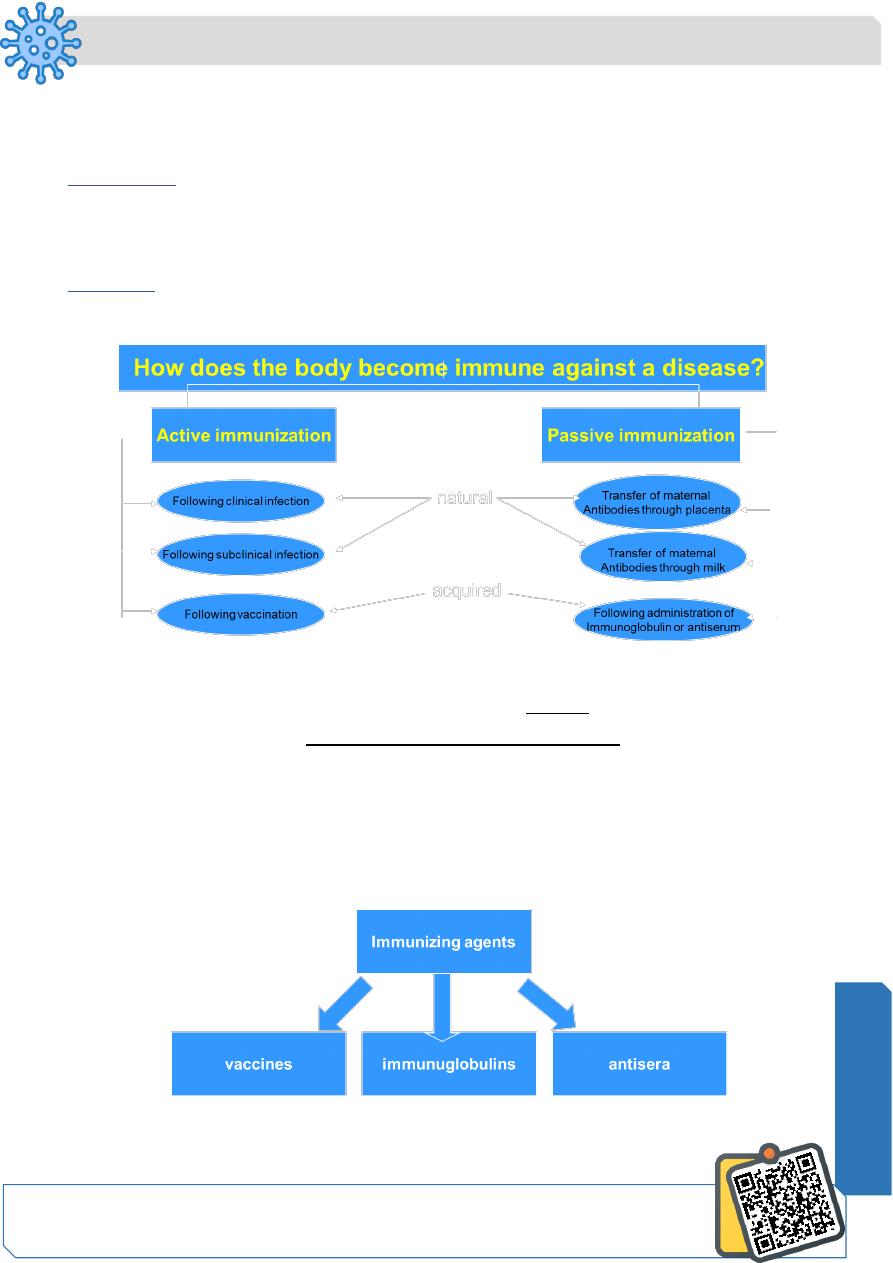
Active immunization:
Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine)
and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host.
Passive immunization:
Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host.
It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-containing preparation).
Immunizing agents:
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p?

Microbiology
Notes…
2
Immunoglobulins: Passive immunization:
❖ There are 5 major classes: IgM, IgA, IgG, IgE, IgD.
❖ Two types of immunoglobulin preparations are available for passive immunization:
– Normal human immunoglobulin
– Specific (hyper-immune) human immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulins: indications...
❖ Used
when there is a high risk of infection and insufficient time for the body to develop
its own immune response
,
❖ Or
when people cannot synthesize antibodies, and when they have been exposed to
a
disease that they do not have immunity against it.
❖ Igs
usually given IV or s.c
❖ Usually
temporary ,lasting from few weeks to 3-4 months
Antisera or antitoxins: Passive immunization
These are blood serum containig polyclonal antibodies , or antibodies against specific
toxin prepared in human or non human sources such as horses.
Immunoglobulin and antiserum: examples
Human normal immunoglobulin: Hepatitis A , Measles, Rabies, Tetanus, Mumps
Human specific immunoglobulin: Hepatitis B, Varicella, Diphtheria
Non human Ig (antisera): Diphtheria, Tetanus, Gas gangrene, Botulism, Rabies
Vaccination: Active immunization:
❖ Vaccination is a method of giving antigen to stimulate the immune response through
active immunization.
❖ A vaccine is an immuno-biological substance designed to produce specific protection
against a given disease.
❖
A vaccine is antigenic or immunogic but not “pathogenic”.
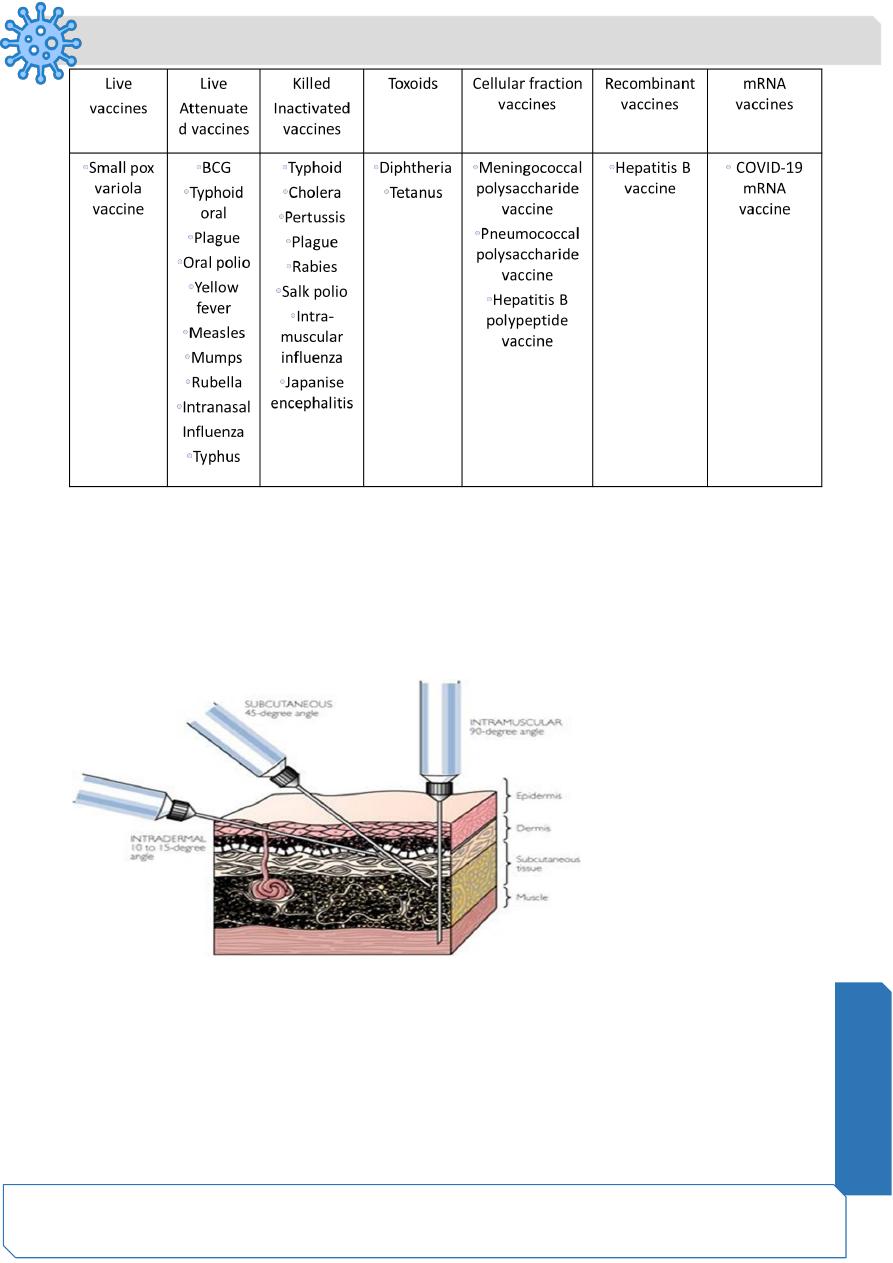
Types of vaccines: 7 Types
Live vaccines, Live attenuated vaccines, Inactivated (killed vaccines), Toxoids
Polysaccharide
and
polypeptide
(cellular
fraction)
vaccines,Surface
antigen
(recombinant) vaccines, mRNA vaccines.
Microbiology
Notes…
3
Live vaccines:
❖ Live vaccines are made from live infectious agents without any amendment.
❖
The only live vaccine is “Variola” small pox vaccine, made of live vaccinia cow-pox
virus (not variola virus) which is not pathogenic but antigenic, giving cross immunity
for variola.
Live attenuated (avirulent) vaccines:
❖ Virulent pathogenic organisms are treated to become attenuated and avirulent but
antigenic.
❖ Live attenuated vaccines should not be administered to persons with suppressed
immune response :
Leukemia and lymphoma ,Other malignancies, Receiving corticosteroids and anti-
metabolic agents, Radiation,pregnancy.
Inactivated (killed) vaccines:
❖ Organisms are killed or inactivated by heat or chemicals but remain antigenic.
❖ They are usually safe but less effective than live attenuated vaccines.
❖ The only absolute contraindication to their administration is a severe local or general
reaction to a previous dose.
Toxoids: detoxyfied toxin:
❖ They are prepared by detoxifying the exotoxins of some bacteria rendering them
antigenic but not pathogenic.
❖ The antibodies produces in the body as a consequence of toxoid administration
neutralize the toxic moiety produced during infection rather than act upon the organism
itself.
❖ In general toxoids are highly effective and safe immunizing agents.
Polysaccharide and polypeptide (cellular fraction) vaccines:
❖ They are prepared from extracted cellular fractions e.g.
❖ meningococcal vaccine from the polysaccharide antigen of the cell wall,
❖ pneumococcal vaccine from the polysaccharide contained in the capsule of the
organism,
❖ hepatitis B polypeptide vaccine.
Their efficacy and safety appear to be high.
Microbiology
Notes…
4
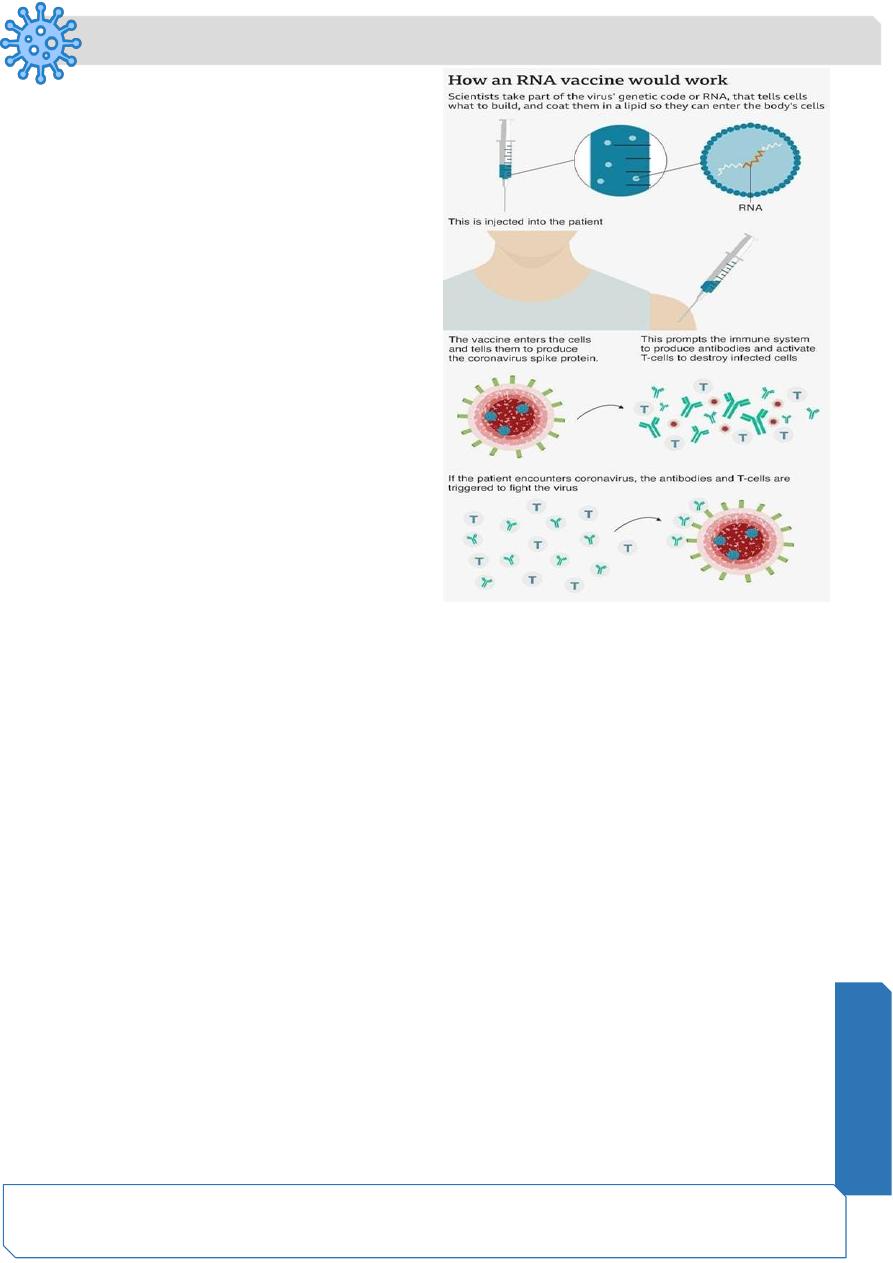
mRNA vaccines:
❖ An mRNA vaccine consists of a
synthetic mRNA strand that codes for a
disease-specific antigen.
❖ mRNA molecule is then delivered into
the cells in lipid nanoparticles,
❖ the cells use them to make the protein
piece which is then displayed on their
surfaces.
❖ Our immune systems recognize that
the protein doesn’t belong there and
begin building an immune response
against it.
❖ The mRNA is delivered by a co-
formulation of the RNA encapsulated in
lipid nanoparticles that protect the RNA
strands and help their absorption into the cells.
Surface antigen (recombinant) vaccines:
❖ It is prepared by cloning HBsAg gene in yeast cells where it is expressed.
❖ HbsAg produced is then used for vaccine preparations.
❖ Their efficacy and safety also appear to be high.
Facts about COVID-19 mRNA vaccines:
❖ mRNA vaccines do not use the live virus that causes COVID-19 and cannot cause
infection with the virus that causes COVID-19 or other viruses.
❖ mRNA never enters the nucleus of the cell where our DNA (genetic material) is located,
so it cannot change or influence our genes.
❖ Our cells break down mRNA and get rid of it within a few days after vaccination.
Microbiology
Notes…
5
Routes of administration:
Oral route (Polio vaccine, oral BCG vaccine,Intradermal route (BCG vaccine),Deep
subcutaneous or intramuscular route (most vaccines,Scarification (small pox vaccine)
Intranasal route (live attenuated influenza vaccine)
Differences among Intradermal, S.C and IM injections:
Periods of maintained immunity due to vaccines:
Short period (months): cholera vaccine,Two years: TAB vaccine,Three to five years: DPT
vaccine (triple),Five or more years: BCG vaccine,Ten years: yellow fever vaccine
Solid immunity: measles, mumps, and rubella vaccines.
Microbiology
Notes…
6
Immunization Schedule In Iraq:
❖
*First 24hr : hepatitis B vacc .(HBV)
❖
*
72
hr. : BCG , OPV
.
❖
*
2 m. : DPT , OPV , HBV , Hib , Rota virus vacc
.
❖
*
4 m. : DPT , Hib , OPV , Rota virus vacc
.
❖
*
6 m. : DPT , HBV , Hib
, Opv
, Rota virus vacc .
❖
*
9 m. : Measles vacc + , .Vitamine A 100,000 I.u .
❖
*
15 m. : MMR
❖
*
18 m. : DPT , Hib
, Opv
, Vitamine A 200.000 I.u .
❖
4
–
6
y. : DPT
, Opv
, MMR
.
Complications of vaccination:
local
skin reaction
. . Fever. Renal complications . .Neurological complications ..Paralytic
complications
. .Encephalitic complication
. . Joint involvement
. Lymphadenopathy
.
.Teratogenic effect
. Skeletal complications . .Hematological complication
.
