
Medicine
Notes…
1
Lecture.3 Clinical manifestations of Cardiovascular diseases
Cardinal Symptoms
• Chest pain
• Palpitation
• Breathlessness (Dyspnea)
• Ankle swelling ( Peripheral oedema)
• Syncope
• Cough and Hemoptysis
• Cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death
• Abnormal heart sounds and murmurs
Chest Pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be
described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may
include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with nausea, sweating,
or shortness of breath.It can be divided into heart-related and non-heart-related pain.
Regarding cardiac chest pain it may be:
• Chest pain on exertion (Stable angina)
• Severe prolonged chest pain (Acute coronary syndromes).
Other cardiac causes include Pericarditis.
non-cardiac cause like disorders of intrathoracic structures
(aorta, pleura, mediastinum, esophagus) , diaphragm, thoracic wall, skin, cervical spine,
breasts, subdiaphragmatic organs stomach, duodenum, pancreas and gallbladder or
could be functional or factitious.
Breathlessness(dyspnoea)
Abnormally uncomfortable awareness of breathing regarded as abnormal only when it
occurs at rest or at level of physical activity not expected to cause it , associated with
diseases of:
• heart
• lungs
• chest wall
• respiratory muscles
• also associated with anxiety
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p?
Medicine
Notes…
2
Causes of cardiac dyspnea:
• Acute left heart failure
• Chronic heart failure
• Arrhythmia
• Angina equivalent
Exertional dyspnoea
Comes on during exertion and subsides with rest.
Commonly due to HF or lung disease COPD
Orthopnoea
breathlessness on lying flat
A symptom of left ventricular failure, due to redistribution of fluid from the lower
extremities to the lungs
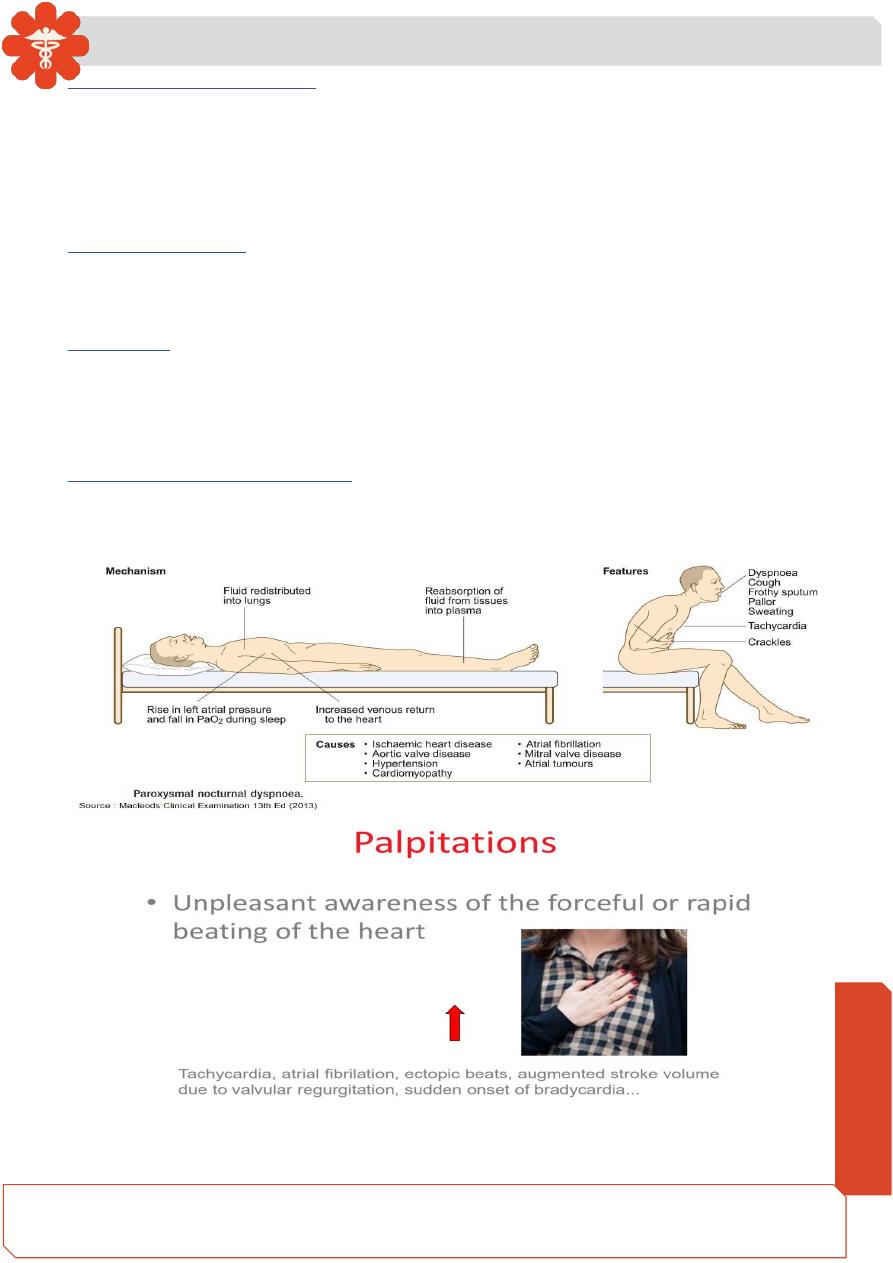
Paroxysmal Nocturnal dyspnoea
A variant of orthopnoea ,patient awakes from sleep severely breathless with persistent
cough, may have white frothy sputum, it is a manifestation of left ventricular failure.
Medicine
Notes…
3
How to evaluate palpitation
• Is the palpitation continuous or intermittent?
• Is the heart beat regular or irregular?
• What is the approximate heart rate?
• Do symptoms occur in discrete attacks?
• Is the onset abrupt? How do attacks terminate?
• Are there any associated symptoms?
• Chest pain, lightheadedness, polyuria (a feature of supraventricular
tachycardia).
• Are there any precipitating factors, such as exercise or alcohol excess?
• Is there a history of structural heart disease, such as coronary artery disease or
valvular heart disease?
Investigation
• The diagnosis should be confirmed by an ECG recording during an episode.
• Using an ambulatory ECG monitor.
• Other investigations include:
Echocardiography
Chest X ray
Thyroid function tests.
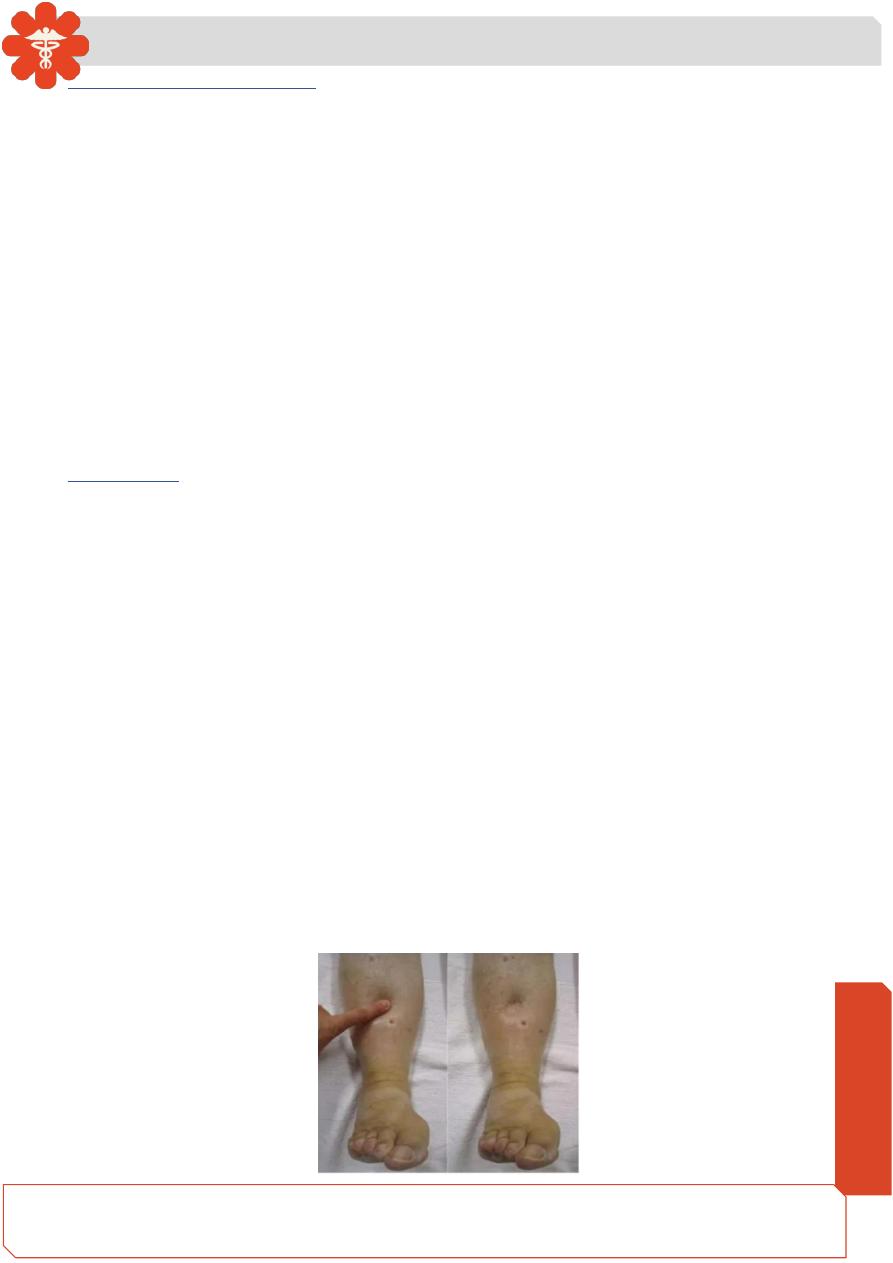
Ankle swelling ( Peripheral odema)
Is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue.
Peripheral Oedema is a feature of chronic heart failure due to excessive salt and water
retention .
In ambulant patients found in the ankles, legs, thighs and lower abdomen. While in
patients who are recumbent , it is found over the sacrum associated with other features
of heart failure .
Usually pitting except if it has been long standing.

Medicine
Notes…
4
Causes of oedema
➢ Bilateral oedema: Heart failure, kidney disease (nephrotic syndrome,
glomerulonephritis), liver disease (liver cirrhosis) ,idiopathic oedema, pregnancy,
continuous sitting with the legs bent (elderly patients who sit for prolonged
periods and paralysed patients), hypoalbuminemia, severe hypothyroidism. Drugs
retaining sodium (fludrocortisone, NSAID) increasing capillary permeability
(nifedipine).
➢ Unilateral oedema: Deep vein thrombosis(DVT) , lymphoedema, cellulitis ruptured
Baker’s cyst .
Syncope
Definition:
Sudden temporary loss of consciousness with spontaneous recovery commonly due to
reduced brain perfusion.
Cardiac causes :
Cardiac conditions to consider in patients with suspected syncope include :
Brady dysrhythmias, Tachydysrhythmias
Cardiac myxoma
Aortic stenosis
Noncardiac causes:
Vasovagal sycope
Carotid sinus syncope
Cough (posttussive) syncope
Micturition syncope
Postprandial syncope
Medicine
Notes…
5
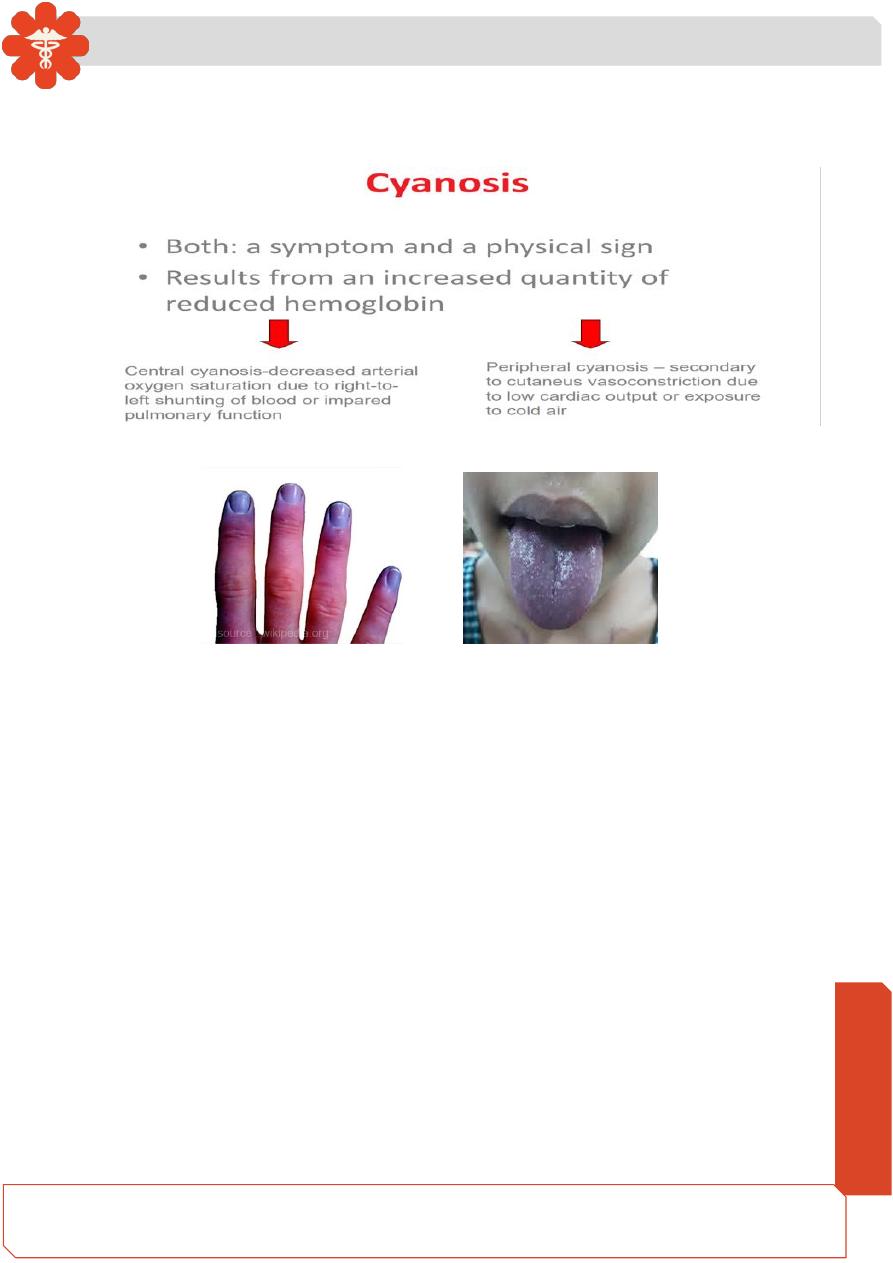
Cyanosis
Defined as a bluish discoloration, especially of the skin and mucous membranes, due to
excessive concentration of deoxyhemoglobin in the blood .
Peripheral Cyanosis Central Cyanosis
Cough
Defined as explosive expiration for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and
foreign bodies.
cardiovascular causes include pulmonary venous congestion, interstitial and alveolar
oedema.
The nature of the sputum is often helpful in diagnosis
❑ pink frothy sputum - pulmonary oedema
❑ clear white mucoid sputum viral infection or longstanding bronchial irritation
❑ thick, yellowish sputum infection
❑ rusty sputum pneumococcal pneumonia
❑ blood streaked sputum tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, Ca lung or pulmonary
infarction

Medicine
Notes…
6
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of tiredness. It may be sudden or gradual in onset. It is a normal
phenomenon if it follows prolonged physical or mental activity, and resolves completely
with rest. However, it may be a symptom of a medical condition if it is prolonged, severe,
progressive, or occurs without provocation. Common in patients with impaired
cardiovascular function consequent to a reduced cardiac output associated with
muscular weakness
❑ May be caused by drugs e.g. ß-blockers
❑ May also result for excessive blood pressure reduction in patients with
hypertension or heart failure
❑ May be caused by excessive diuresis or diuretic induced hypokalemia
Other symptoms
• Nocturia a condition characterized by the need to awaken ≥ 1 times per night to
void. common in early heart failure.
• Anorexia.
• Abdominal fullness.
• Right upper quadrant abdominal discomfort.
• Weight loss and cachexia.
