Hemoglobinopathies
(Genetic abnormalities of Hb)1- Polypeptide chain with abnormal sequence of amino acids Abnormal Hb.
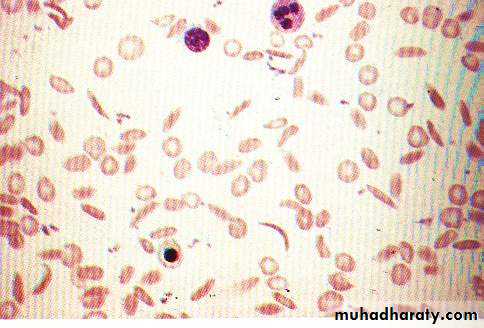
Exp: Hb S (in Sickle cell anemia)
2- polypeptide chain production is impaired or absent.
Exp: alpha or beta Thalassaemia
Destruction of red blood cells and catabolism of hemoglobin:
Anemia
Reduction in blood Hb level and/or in RBC count below the normal range for the patient’s age and sexClassification; according to the cause:
a. Inadequate production of normal RBCs.
Deficiency of iron, B12, folic acid or Aplastic anemia .
b. Excessive destruction of RBCs (hemolysis).
c. Hemorrhage: acute or chronic.
Anemia
Reduction in blood Hb level and/or in RBC count below the normal range for the patient’s age and sex
Classification; according to the blood indices:
MCV, MCH, MCHC.
• MCV (80 – 95 ft), >95 fl Macrocytes
• < 80 fl Microcytes
• MCHC (32-36%), > 36% Hyperchromic
• < 32% Hypochromic
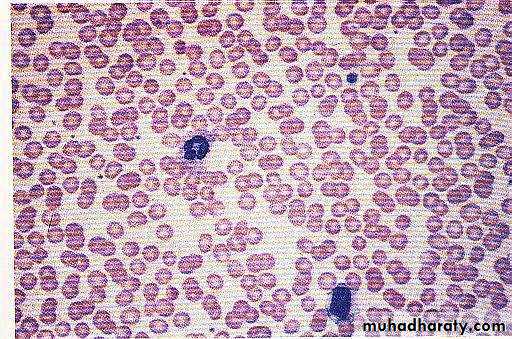
Fe deficiency anemia Microcytic hypochromic RBC
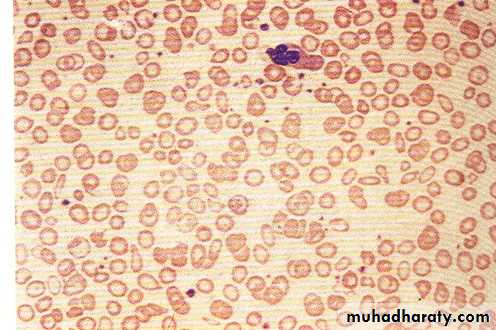
B12 & folic acid deficiency Macrocytic hypochromic RBC
Iron deficiency anaemia
Megaloblastic anaemia
Sickle cell anaemia
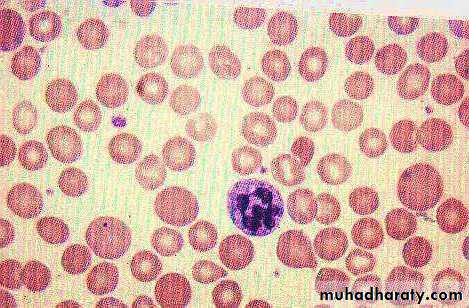
Normal
Polycythemia
Increased concentration of RBCs.1. Relative polycythemia plasma volume
2. Absolute (true) polycythemia;a- secondary polycythemia;
b- primary polycythemia (polycythemia vera).