Crystals associated diseasesAssistant ProfessorDr Mohammed H AL osamiCABM,FICMS(Med),FICMS(Rheum)consultant rheumatologist
Objectives of the lectures
to:Describe briefly the pathophysiology of Crystals associated diseases.
Define the term hyperurecemia,describe its pathophysiology and diagnostic approach.
List the common causes and clinical features and diagnosis of gout.
Define the terms BONE AND JOINT INFECTION In each case discuss their causes, diagnosis and management.
Define the terms Psoriatic arthritis (PsA)and JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS. In each case an over view of clinical features, diagnosis and treatment is outlined.
Crystals associated diseases
A variety of crystals can deposit in and around the joints and associated with acute inflammations and chronic diseases.Factors influence crystal formation:
1-suffecient concetration of the chemical components
2-the presence or absence of the promoters or inhibitors of crystal nucleation and growth.
Common
Monosodium urate monohydrateAcute gout
Chronic tophaceous gout
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate
Acute 'pseudogout'
Chronic (pyrophosphate) arthropathy
Chondrocalcinosis
Basic calcium phosphates
Calcific periarthritis
Calcinosis
UncommonCholesterolChronic effusions in RACalcium oxalateAcute arthritis in dialysis patients Synthetic crystalsAcute synovitis Plant thorns/sea urchin spinesChronic monoarthritis, tenosynovitis
Crystals may mechanically damage the tissues . Crystals sited deep within tendon or cartilage can cause acute inflammation when they are released from their sites(crystals shedding)
داء الملوك... ...والفقراء gout
Gout is an ancient malady whose incidence continues to rise despite being one of the best understood diseases in all of medicine in terms of pathogenesis and treatment [Roddy et al. 2007].
Gout has increased in frequency in recent decades, affecting about 1–2% of the Western population at some point in their lives. The increase is believed due to increasing risk factors in the population, such as metabolic syndrome, longer life expectancy and changes in diet.
History
The word "gout" was initially used by Randolphus of Bocking, around 1200 AD. It is derived from the Latin word gutta, meaning "a drop" (of liquid).this is derived from "the idea of the 'dropping' of a morbid material from the blood in and around the joints".
The first documentation of the disease is from Egypt in 2,600 BC in a description of arthritis of the big toe.
The Greek physician Hippocrates around 400 BC commented on it in his Aphorisms, noting its absence in eunuchs and premenopausal women:
A. Cornelius Celsus (30 AD) described the linkage with alcohol, later onset in women, and associated kidney problems
In 1683, Thomas Sydenham, an English physician, described its occurrence in the early hours of the morning, and its predilection for older males.
The Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first described the microscopic appearance of urate crystals in 1679. In 1848, English physician Alfred Baring Garrod realized this excess uric acid in the blood was the cause of gout.
A variety of crystals can deposit in and around the joints and associated with acute inflammations and chronic diseases.Monosodium urate monohydrate is the causative crystals of gout.
• Is a true crystal deposit disease (monosodiom urate crystals).
• it may present as acute arthritis, bursitis,tenosynovitis,cellulits or tophaceous deposit .• Prolonged hyperuricemias necessary but alone is not enough to develop gout.
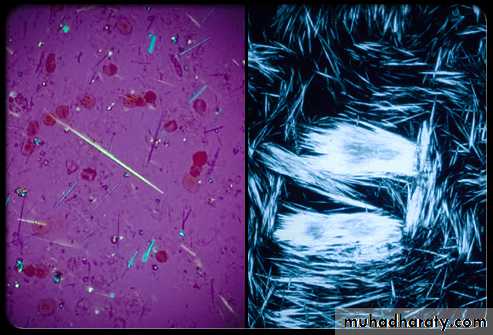
MSU CRYSTALS
Gout occurs in 1% of general population with male predominence (1:10)Primary gout is a male disease while secondery type(secondery to renal disease or drug )mainly affects population over 65 years and seen in famales.
Uric acid in the serum is higher in men than in women and it is affected by the age ,sex ,genetic factors and body bulk.. Hyperuricemia can be defined as (serum uric acid level above the theoretical solubility of MSU crystals in physiological condition (0.42 mmol/L) .or as a serum uric acid level greater than 2 SD above the mean for population(0.4 mmol/L for men) and (0.35mmol/L for women)
95% of hyperuricemic persons never develop gout
Etiology 1/3 of body uric acid pool is derrived from diet . 2/3 of body uric acid pool is from endogenous purine metabolism.Elemination of uric acid by the kidney (2/3) and gut (1/3)
Xanthine oxidase enzyme catalyses the end conversation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and to uric acid .
-in 75% of gouty patients hyperuricemia results from an inherited renal defect in uric acid excretion (under excretors).
20% of primary gouty patients are intrinsic overproducers of uric acid & <1% of primary gout patients have inherited enzyme of purine synthesis and they have :
1-very early onset of gout(<25)2-urolithiasis is the presenting features.3-strong family history of early onset gout
Risk factors for gout
1- hyperuricemia2-obesity
3-high alcohol intake
4-hypertension
5- IHD
6-inhereted alteration of tissue factors
Obesity IS A RISK FACTOR
Secondary gout
results from chronic hyperuricemia due to;1- chronic renal impairment
2-chronic diuretic users, and in these patients nodal OA is a risk factorThe first metatarsophalangeal joint is the classical site
The classical 1st MTP involvement in gout
Clinical features
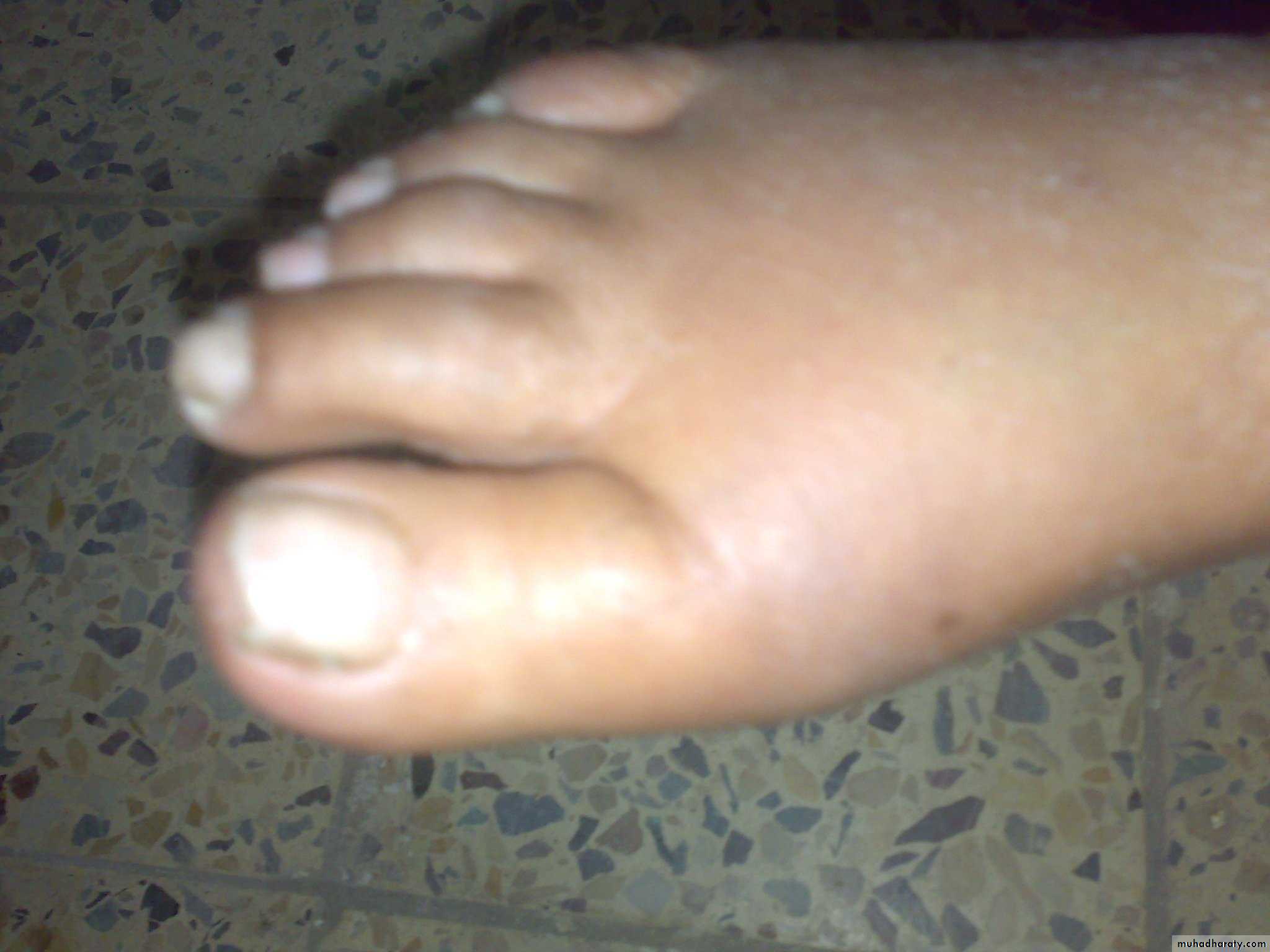
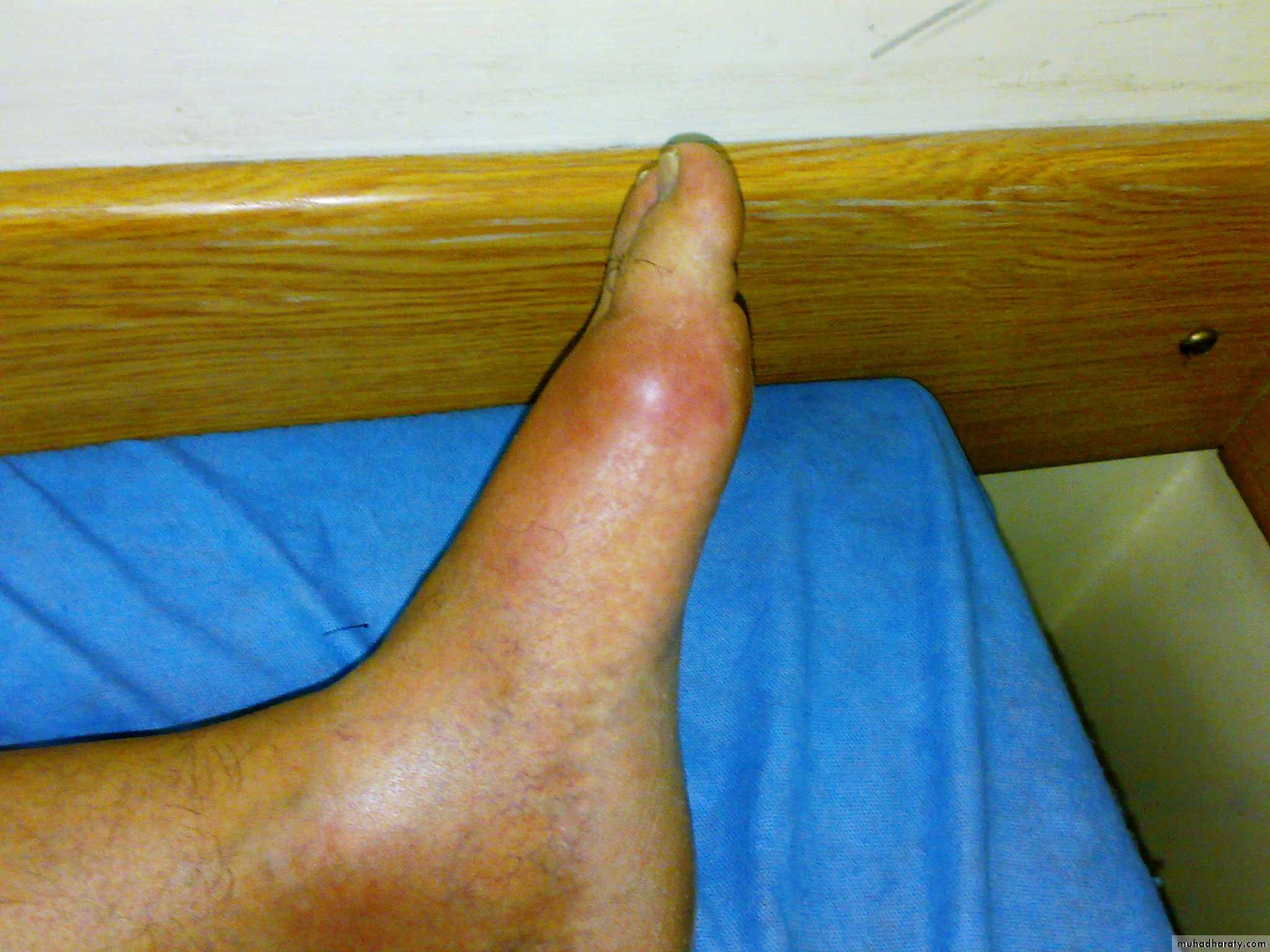
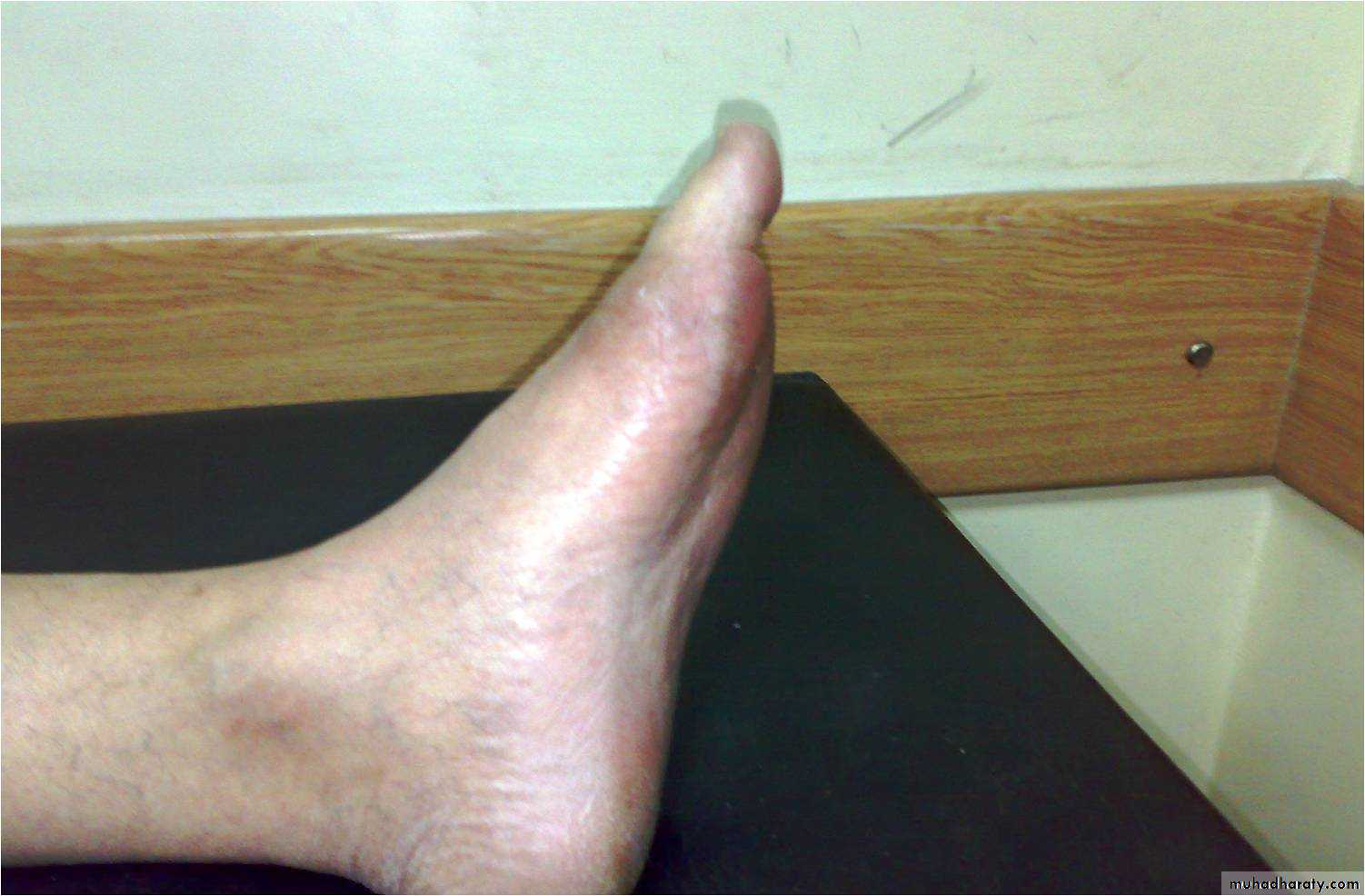
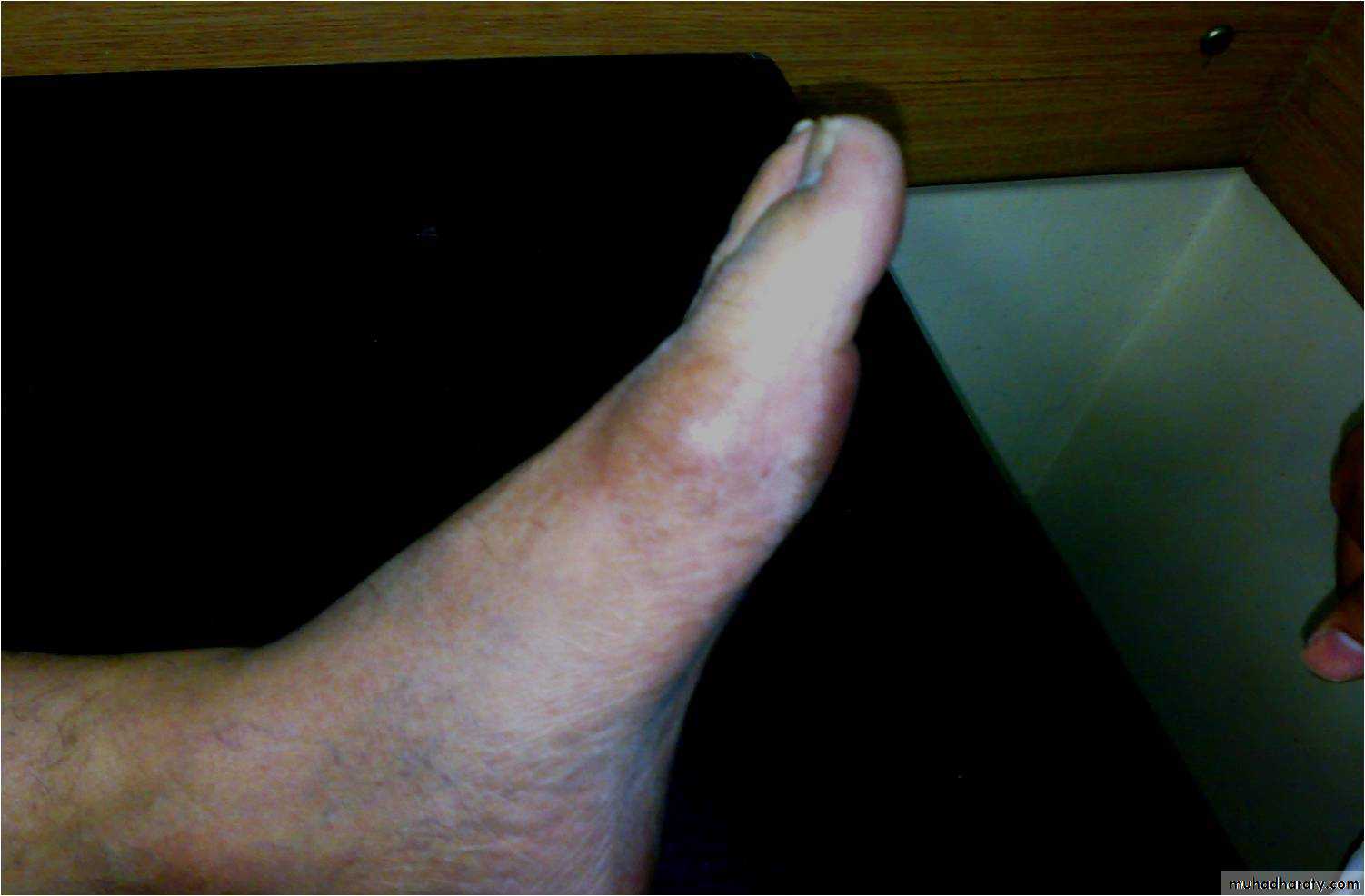
1-acute gouty arthritisA single joint is affected in the first attack and the first MTP is affected in over 50% of cases ( podegra) but ankle , midfoot,knee,wrist and elbow can also be affected.
-rapid onset of severe acute pain (2-6 hours)-overlying skin is red ,shiny with marked swelling-self limiting attack over 1-2 weeks with complete return to normality- fever ,malaise ,and even confusion with the attack-pruritis and desequamation of the overlying skin as the attack subsides.- bursitis ,tenosynovitis ,or cellulitis may occur
Acute gouty arthritis
Acute gouty arthritis
ACUTE ATTACK
GOUT
2-intercritical period:
Is asymptomatic period between attacks in most patients , second attack may occur within one year, and later attacks involve several joints3-Chronic tophaceous gout
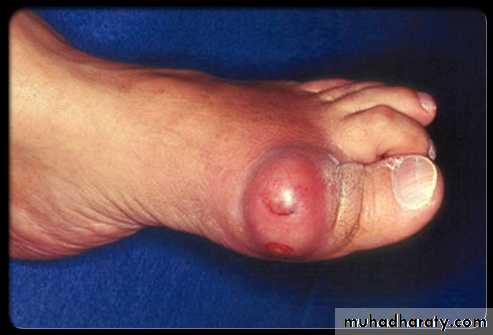
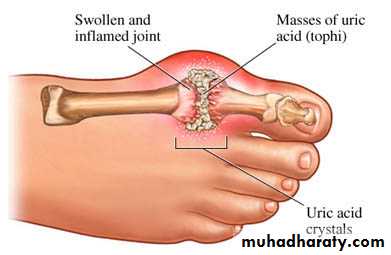
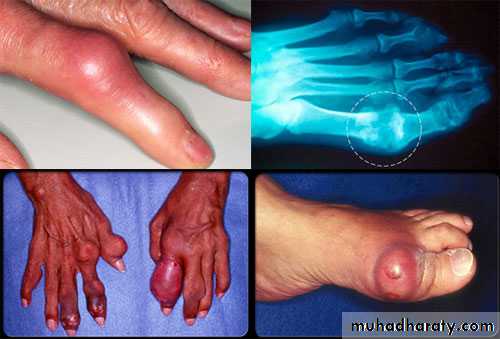
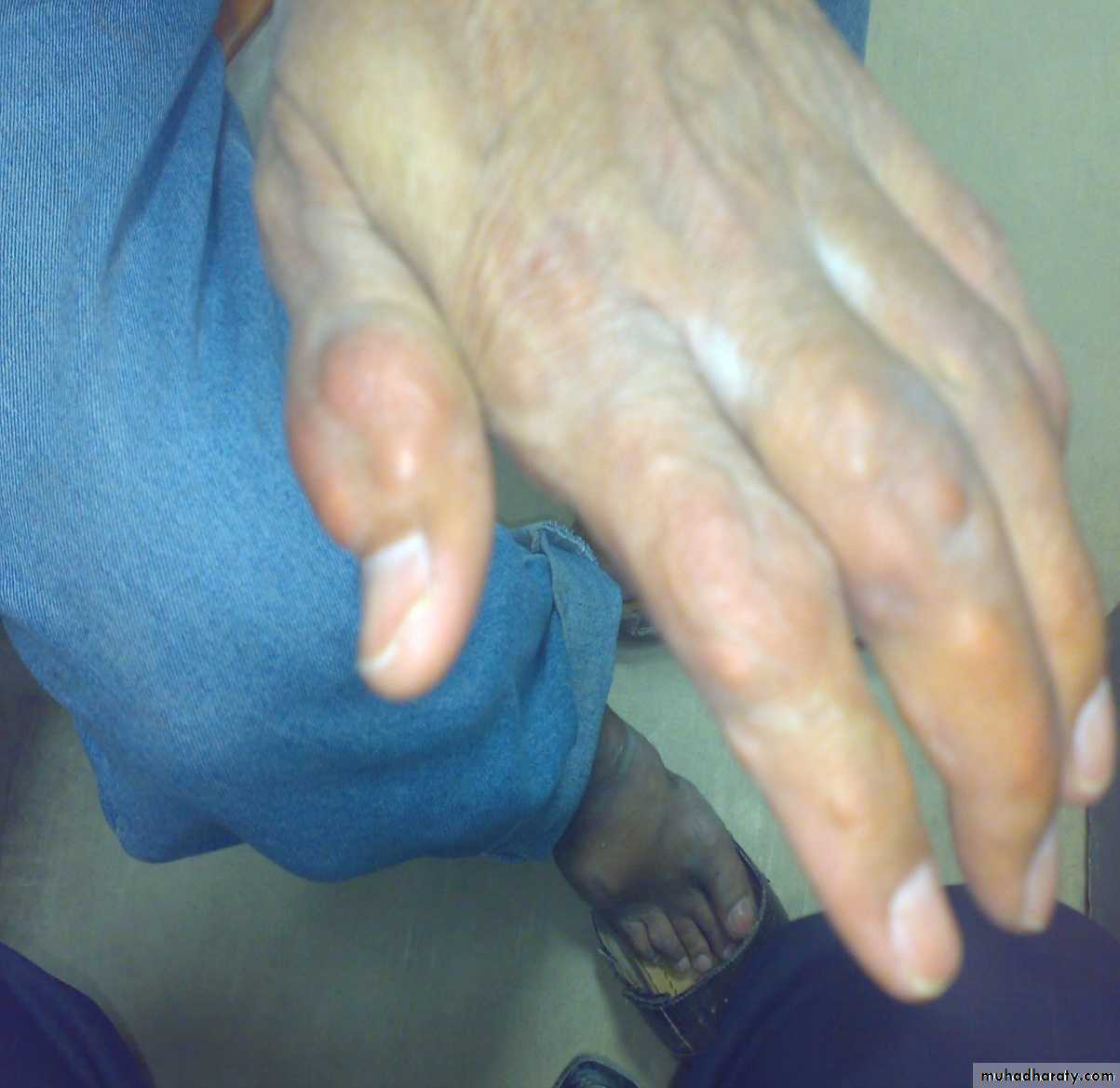
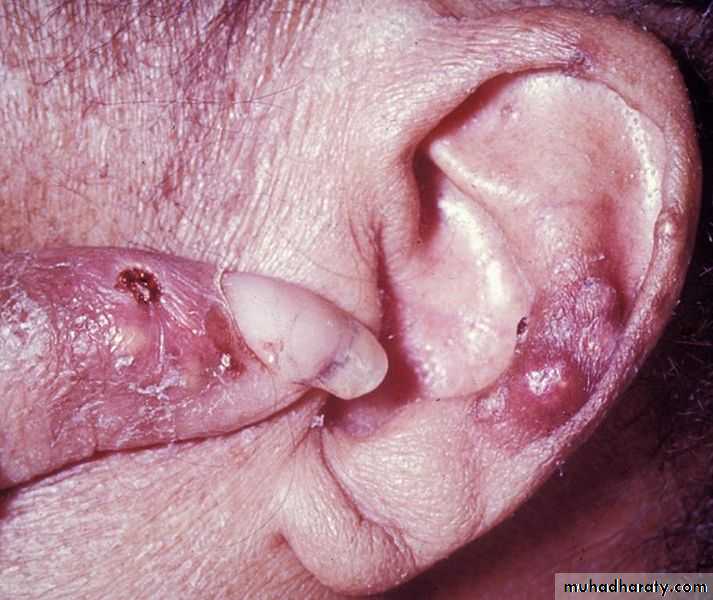
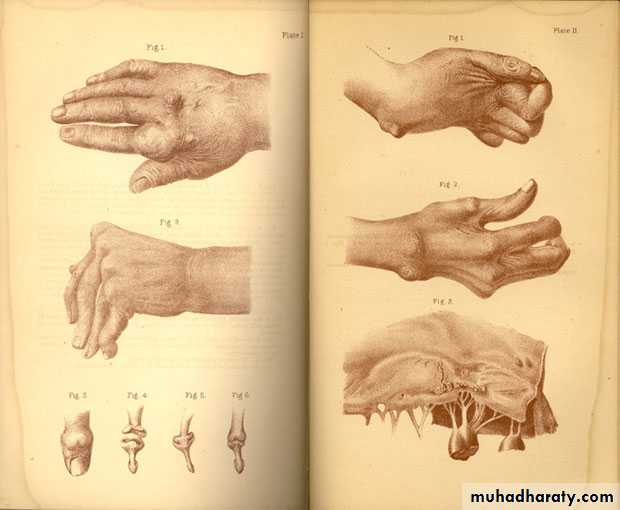
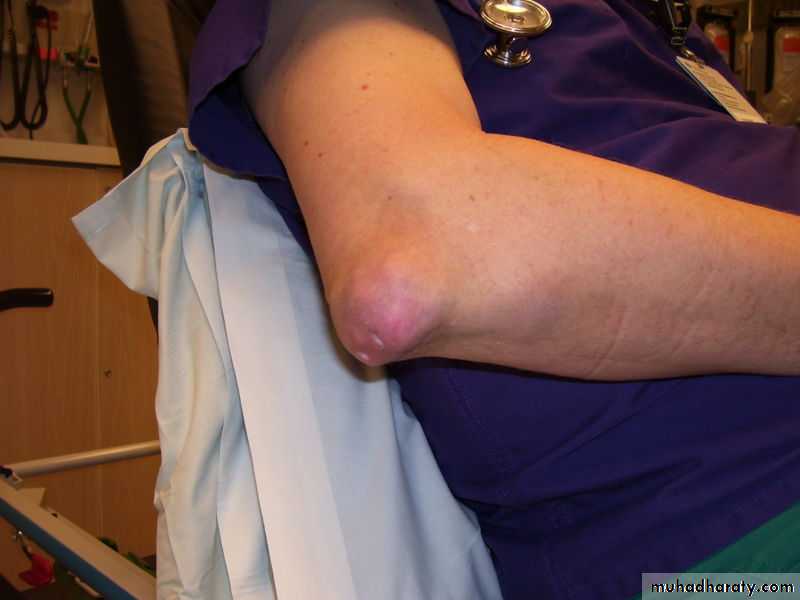
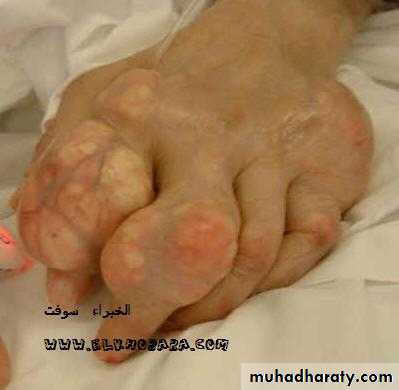
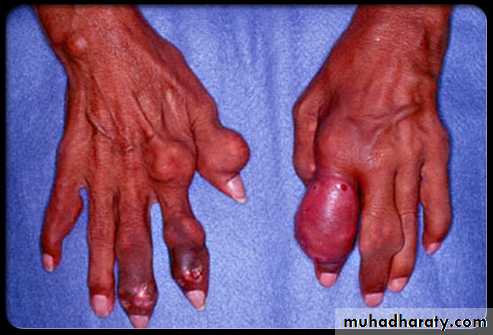
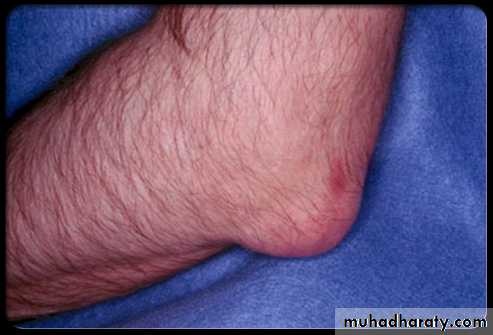
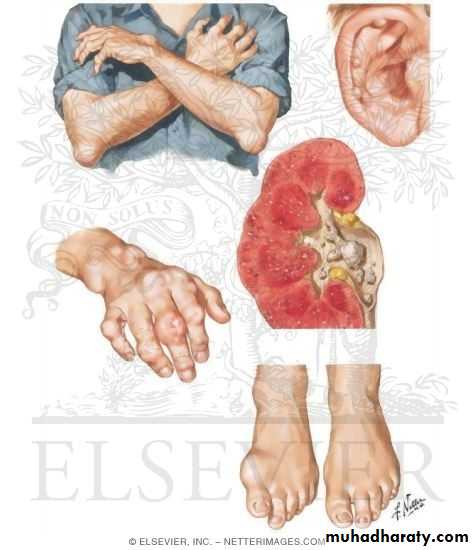
Large MSU crystal deposit produce firm nodules (tophi) and the usual sites for nodules are around the extensor surfaces of the fingers,hand, forearm,elbow,helix of the ear and Achilis tendon.Nodules may ulcerate.
-joints commonly affected are :1st MTP,midfoot and wrist with severe deformity
Chronic gout
Chronic tophaceous gout
Chronic tophaceous gout
Chronic tophaceous gout
Chronic tophaceous gout
4-Urolithiasis
• Uric acid stones cause renal colic in 10% of gouty patients, the incidence is higher in hot climate and is favoured by:
• 1- purine overproduction
• 2-uricosuric drugs
• 3-dehydration and lowering in urine PH as in chronic diarrhea
• 4-chronic urate nephropathy
Complication of gout
Untreated severe tophaceous gout causes tissue damage with MSU crystal deposit in the renal interstitium and secondery pyelonephritis will develop.
Foods helps to protect or reduce the risk of gout 1-lamon2-grapes juice3-apple juice 5-annanas6-green tea7-pineapple
Foods to be avoided1-meat and chicken skin2-liver,kidney and brain of animals3-fat rich fishes like salmon and sardine4-aubergine , cauliflower , spinach 5-spices & nuts
INVESTIGATIONS
- DEFINITE DIAGNOSIS IS BY DETECTING MSU CRYSTALS IN THE ASPIRATE FROM A JOINT , BURSA OR TOPHUS.-serum uric acid is high (but normal level does not exclude gout)
-24 hour urine uric acid measurement to detect overproducers
- blood urea and serum creatinine
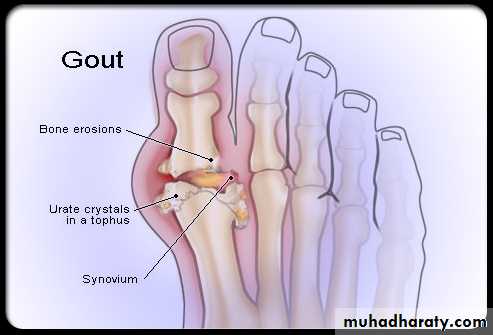
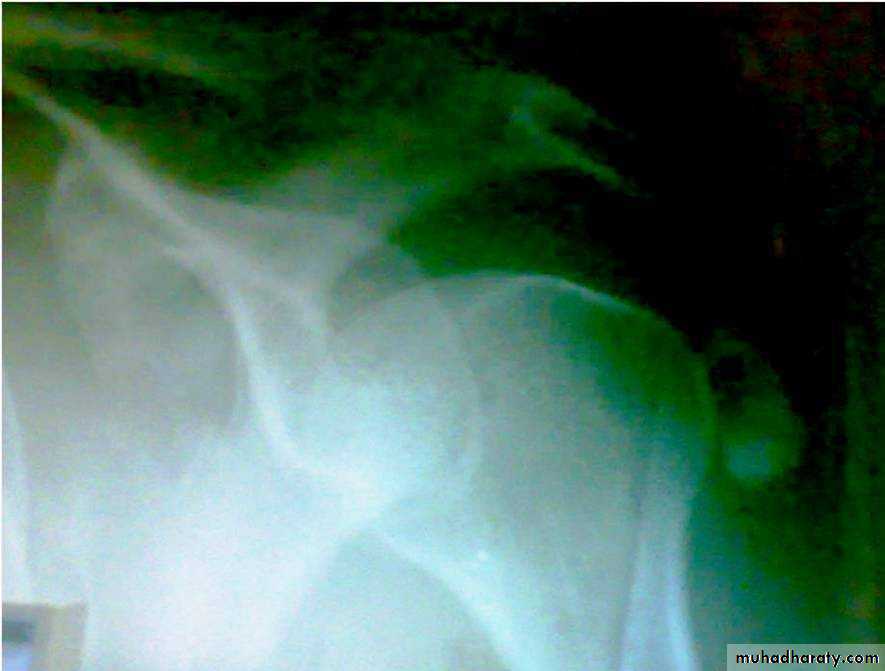
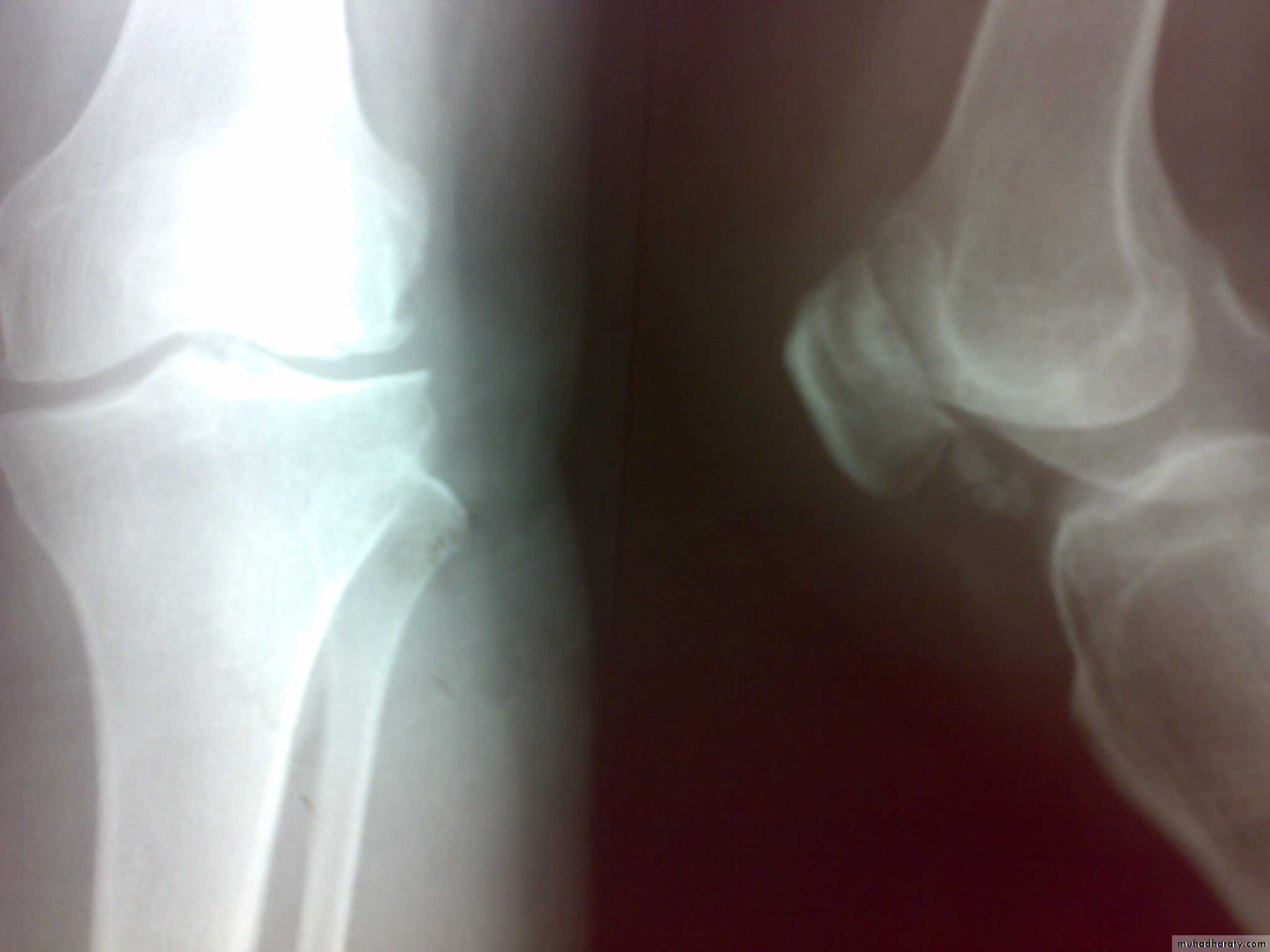
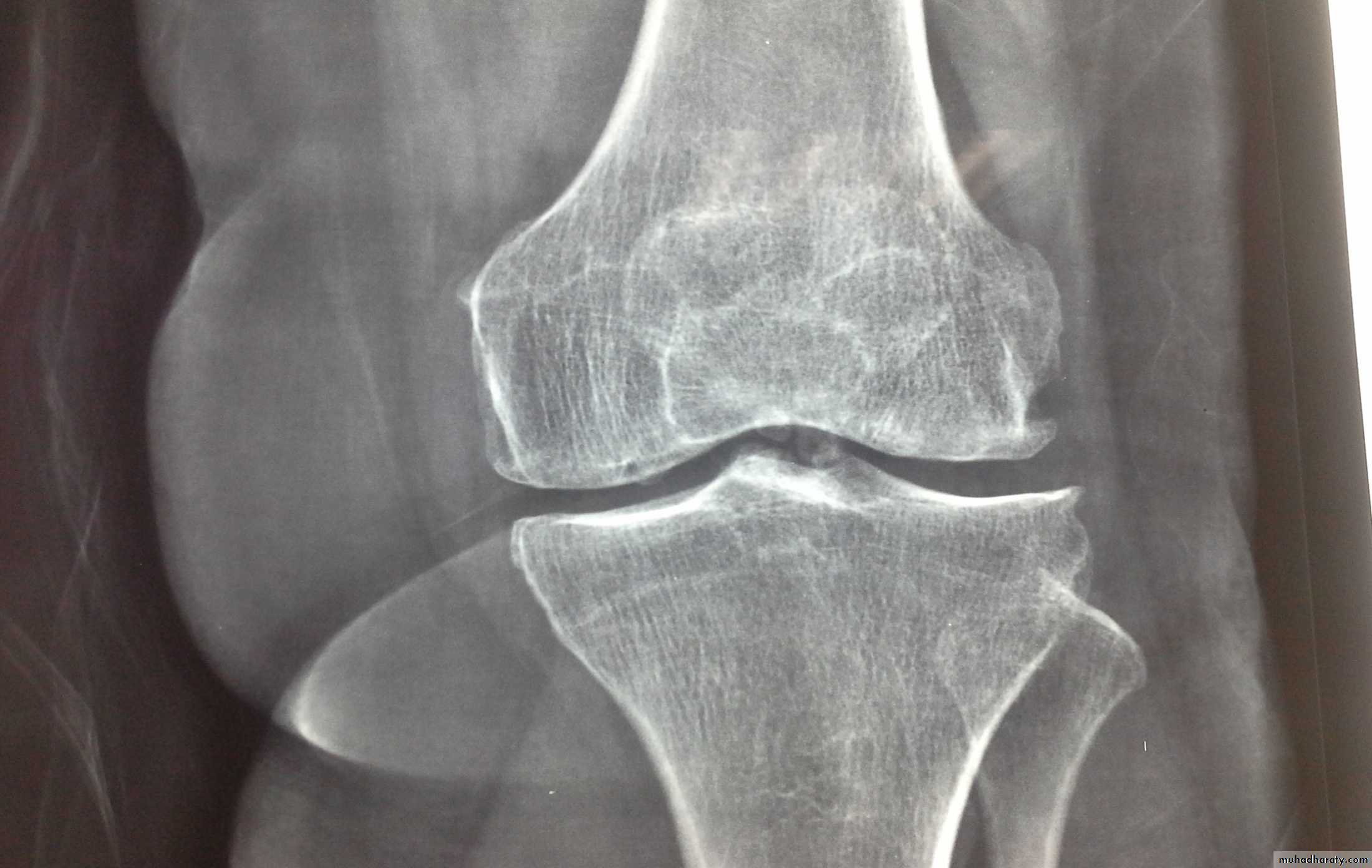
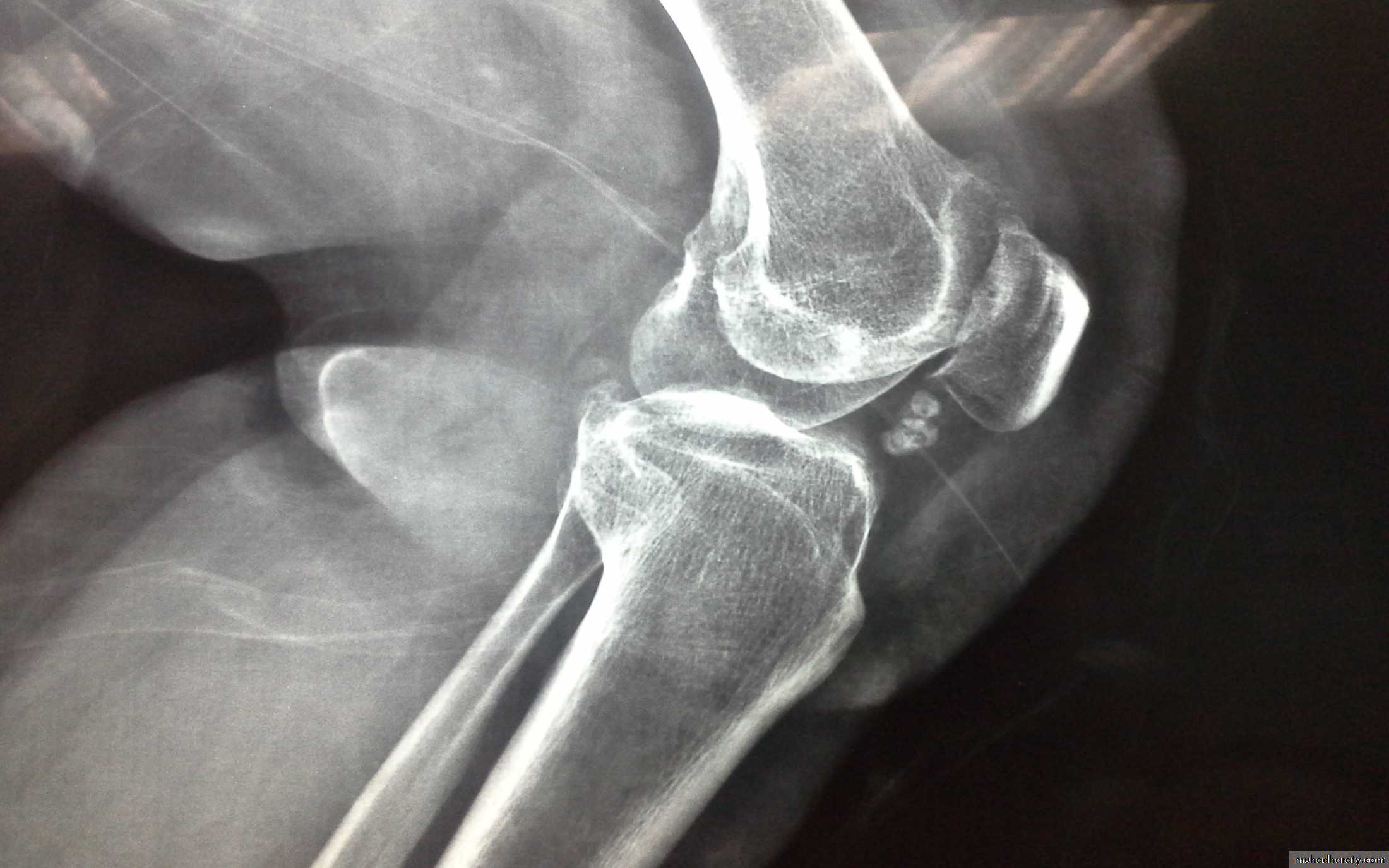
Dx of gout is established by Monosodium urate crystals viewed under the polarizing microscope. X-ray demonstrating typical gouty erosions at the first MTP joint, with well-demarcated erosions, away from the joint line, some with overhanging edges, and adjacent hazy tophaceous material.
The use of ultrasonography to diagnose acute and chronic gout is increasing . The characteristic findings are a superficial, hyperechoic, irregular band on the surface of articular cartilage, the so-called 'double contour sign' or 'urate icing', and nonhomogeneous tophaceous material surrounded by an anechoic rim. MRI and CT are even more sensitive than ultrasound at detecting gout [Thiele and Schlesinger, 2007; Wright et al. 2007; Dalbeth and McQueen, 2009].
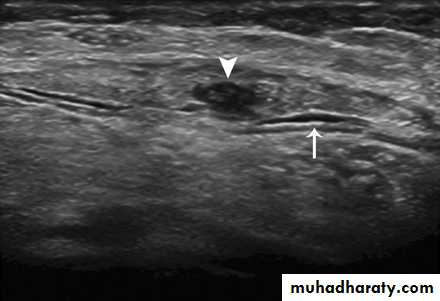
54-year-old woman with gout, palpable mass, and painful dorsiflexion of foot. Sagittal ultrasound shows partial rupture of Achilles tendon (arrowhead), thickening, and surrounding fluid (arrow).
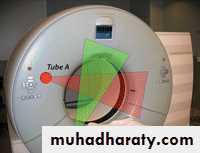
dual-energy CT scanner. Two detector tubes are mounted on one gantry at 90° to one another. Each tube can obtain 64 slices. Tube A, which is similar to standard single-source detector, has 50-cm field of view. Tube B also
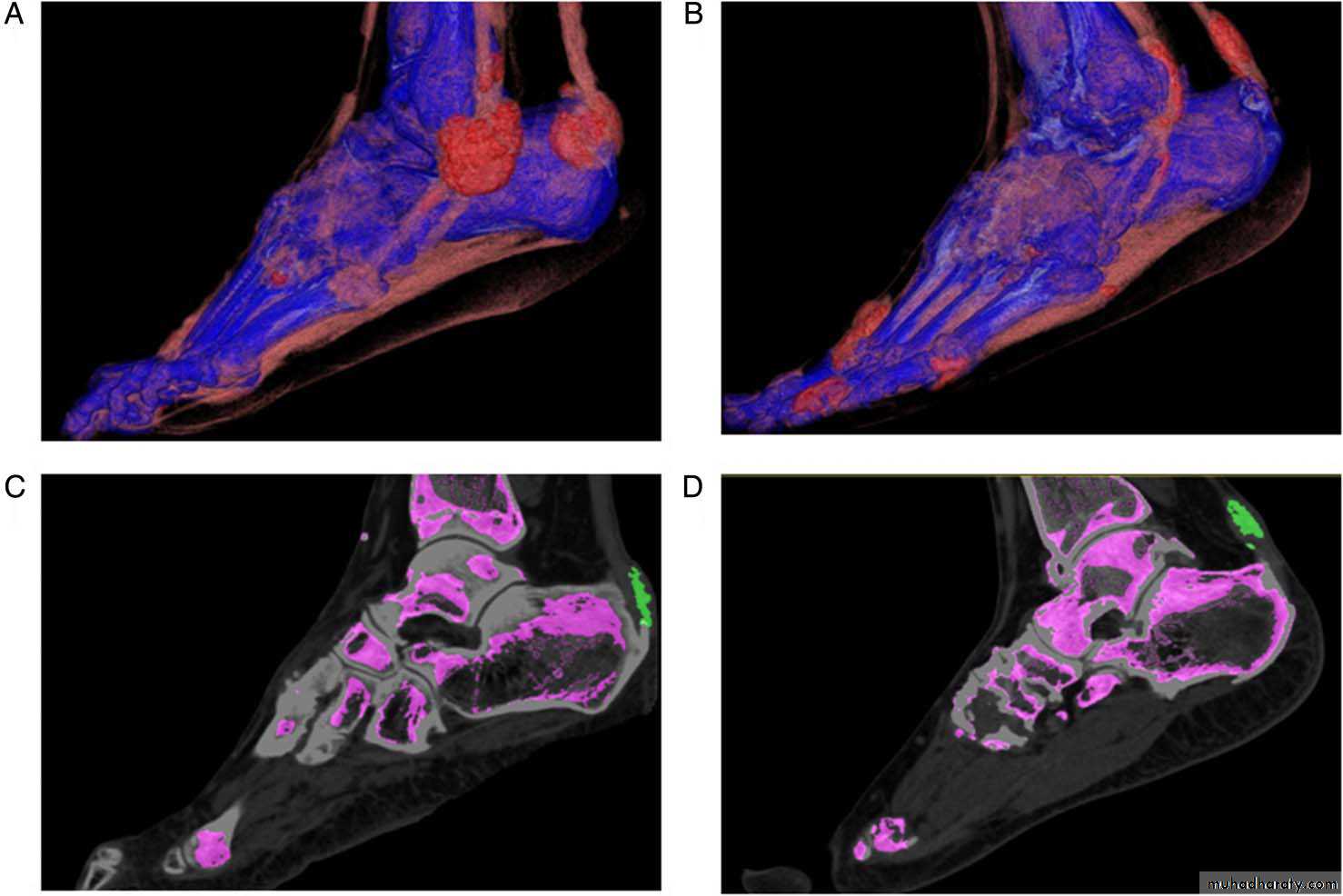
dual-energyCT images showing involvement oftendons in two patients withtophaceous gout. (A) and (B) showthree-dimensional volume-renderedimages demonstrating monosodiumurate (MSU) crystal deposition in theAchilles and peroneal tendons in bothpatients. (C) and (D) Two-dimensionalsagittal images confirming MSU crystaldeposition (green) at (C) the Achillesenthesis and (D) within the body ofthe Achilles tendon.
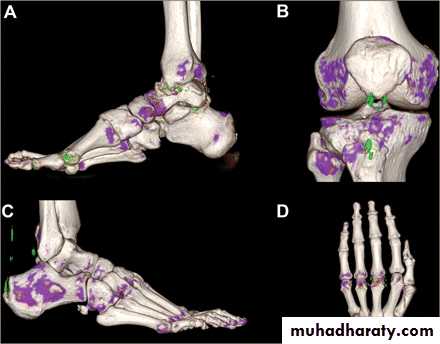
Dual energy CT images of urate deposits in patients with acute gout symptoms.
Dual energy CT images of urate deposits in patients with acute gout symptoms.
-Fasting lipid profile
-full blood count and ESR-CRP
-Radiograghs which is :
a-Normal in early stage
b-Later :joint space narrowing ,sclerosis,cyst, osteophyte and gouty erosions( para articular punched out defects)
-
HOW TO Mx GOUT.
MANAGEMENT
THE ACUTE ATTACKa- NSAID
b- Colchicine orally( S/E vomiting and diarrhea)c-aspiration and local steroid injection
2- long term management
a-patient education about the nature of the disease and therapy
b- correction of any predisposing factors
Like weight reduction,stop alcohol and diuretics
Hyperuricemic drug therapy is indicated for
1- recurrent acute gouty attacks2- tophi
3- evidence of joint or bone damage
4- renal disease
5-gout with greatly high serum uric acid
Allopurinol
Is the drug of choice, it inhibits xanthine oxidase, but it can trigger acute attack of gout which can be reduced by using lower staring doses or by adding oral colchicine for the first few weeks . it must not be started in patients with acute gouty attack (till acute attack subsides)New drugsFebuxostat ;it is xanthine oxidase inhibitor through a differentmechanism than Allopurinol.Recombinant unmodified Aspergillus flavus uricase(Rasburicase) ;oxidize uric acid to allantoinىز....Rىrrnew
New drugs Febuxostat (Uloric©) is a potent xanthine oxidase inhibitor that was approved for the treatment of gout on the basis of extensive clinical trials, It is of a different chemical class than allopurinol and a more selective inhibitor of enzyme activity. [Becker et al. 2005, 2009, 2010; Schumacher et al. 2008, 2009]. Rىrrnew
Recombinant unmodified Aspergillus flavus uricase(Rasburicase) ;oxidize uric acid to allantoin. Pegloticase (KRYSTEXXA) is a pegylated mammalian (porcine-like) recombinant uricase [Richette et al. 2007]
Recently several IL-1 inhibitors, are approved both for treatment and prophylaxis of gout flares. These agents include Anakinra, an IL-1R antagonist,Rilonacept, an IL-1 decoy receptor, or Trap, andCanakinumab, an anti-IL-1b monoclonal antibody
The aim of treatment
The aim of treatment To bring serum uric acid level into the lower half of the normal rangeAllopurinol will need to be used indefinitely
Uricosuric drugs
Need to maintain high urine flow1-Probenecid
2-Sulfinpyrazone
3- Benzbromarone
They are contraindicated in
a-overproducers
b-patients with renal involvement
c-patients with renal stones
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Is treated if
1- strong family history of gout or renal stones
2-persistant very high level(>0.6mmol/L)
3- urolithiasisCALCIUM HYDROXYAPATITE DEPOSITION DISEASE
HA is the primary mineral of bone and teeth.Abnormal accumulation can occur in areas of tissue damage (dystrophic calcification), in hypercalcemic or hyperparathyroid states (metastatic calcification), and in certain conditions of unknown cause .
CALCIUM HYDROXYAPATITE DEPOSITION DISEASE
HA may be released from exposed bone and cause the acute synovitisoccasionally seen in chronic stable osteoarthritis (e.g., “hot”Heberden’s nodes). ).HA deposition is also an important factor in an extremely destructive chronic arthropathy of the elderly that occurs most often in knees and shoulders (Milwaukee shoulder).
Conditions Associated with Hydroxyapatite Deposition Disease
AgingOsteoarthritis
Hemorrhagic shoulder effusions in the elderly (Milwaukee shoulder)
Destructive arthropathy
Tendinitis, bursitis
Disease-associated
Hyperparathyroidism
Renal failure/long-term dialysis
Connective tissue diseases (e.g., progressive systemic sclerosis,