THORAX
skinsuperficial fascia
deep fascia and superficial muscles of the thoracic wall
rib and intercostal muscles
endothoracic fascia
parietal pleura
PLEURA & PLEURAL CAVITY
Body Cavities and MembranesVentral Cavity – Two main divisions:
• Thoracic Cavity – It is superior and is
surrounded by the ribs and the muscles of
the chest wall. (Superior to the diaphragm)
• Abdominopelvic Cavity – It is inferior
and is surrounded by the abdominal walls
and the pelvic girdle.
Serous Cavities
Serous cavities include:
• Pleura –
Surrounding the lungs.
• Pericardium –
Surrounding the heart.
• Peritoneum –
Surrounding various organs
of the abdominopelvic cavity.
Serous Cavities
Serous cavities are lined by serousmembranes or serosa. There are 2 parts:
• Parietal Serosa– The outer wall.
• Visceral Serosa – The inner wall that covers the organ.
The two are continuous with each other. Think of the balloon example.
Serous Cavities
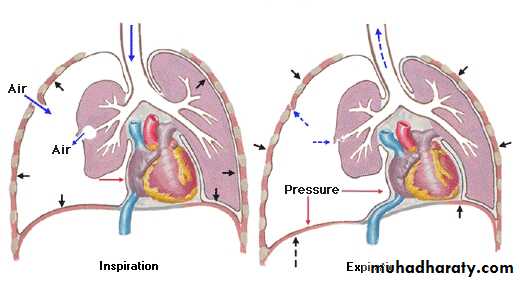
Serous cavities are filled with a thinlayer of serous fluid (watery).
• Serous fluid is secreted by both serous membranes.
• Allows visceral organs to move with little friction across the cavity walls.
Outer balloon wall
(comparable to parietal serosa)
Air
(comparable to serous cavity)
Inner balloon wall
(comparable to visceral serosa)
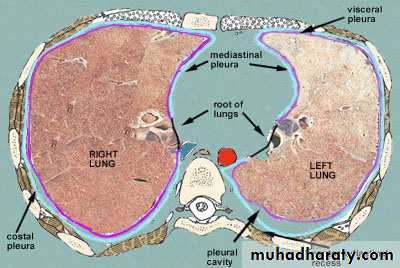
Pleura
Pleural CavityPleural Recesses
Blood Vessels
• Pleura
• Parietal pleura• Visceral pleura
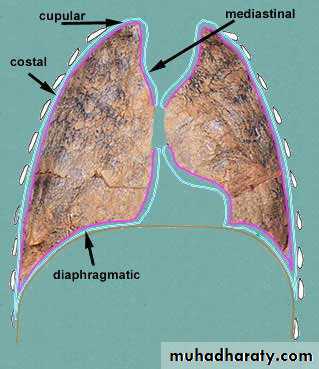
• costal
• diaphragmatic• cupular
• mediastinal
Pleura
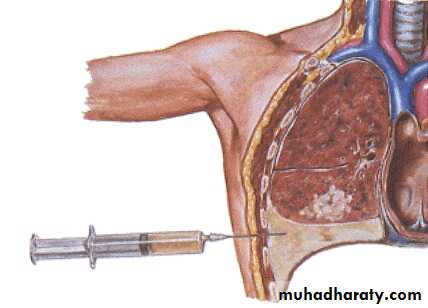
• Tension Pneumothorax
• Hemothorax
• Chylothorax
Pleural Recess
Costodiaphragmatic recessCostomediastinal recess
• Costomediastinal recess
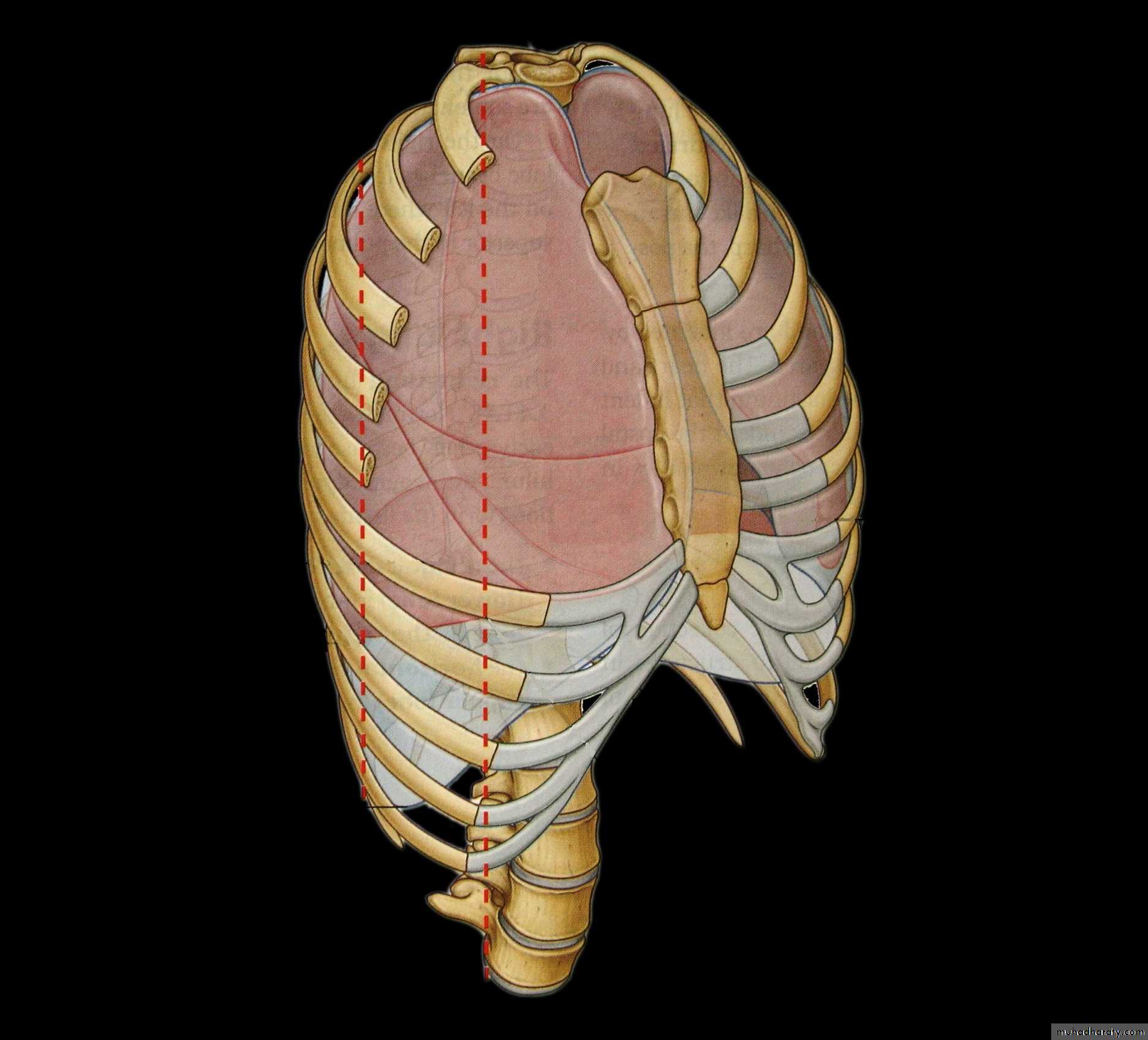
• Costodiaphragmatic recess• Midclavicular line
• Midaxillary line• Scapular line
• Paravertebral line
• Inferior border of the lung
• Rib 6
• Rib 8
• Rib 10
• T10
• Inferior border of the pleura
• Rib 8
• Rib 10
• Rib 11
• T12