
1
4th stage
جراحة بولية
Lec-6
.د
نعمان
11/10/2015
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
Urology
Renal surgical infections
Urinary tract infection
(UTI) is an inflammatory response of the urothelium to bacterial
invasion that is usually associated with bacteriuria and pyuria.
Classification:
Non specific
Specific
Acute
Chronic
Non specific acute infection
Bacteriology:
E.coli, Proteous, Staph aurious, Klebsiella
Pathogenesis:
Ascending infection: most common route
Hematogenic
Lymphatic
Direct extension
Susceptibility
Bacterial virulence
Extrinsic factors : male & female
1.
Introitus
2.
Urethra
3.
Prepuce
Intrinsic factors: Ureteral & renal
Bacterial persistence
Urinary calculi
Obstructive uropathy
Renal pathology
Urethral infection
Foreign bodies
Urogenital & intestinal fistulae

2
Kidney Infections
Acute pyelonephritis
Defined as inflammation of the kidney and renal pelvis
It is a clinical syndrome of chills, fever, and flank pain that is accompanied by
bacteriuria and pyuria.
Female > male
Clinical features:
Constitutional symptoms
Flank & hypochondrial pain
Frequency, urgency, & dysuria
Investigations
GUE
Urine culture & sensitivity
U/S
KUB
IVU
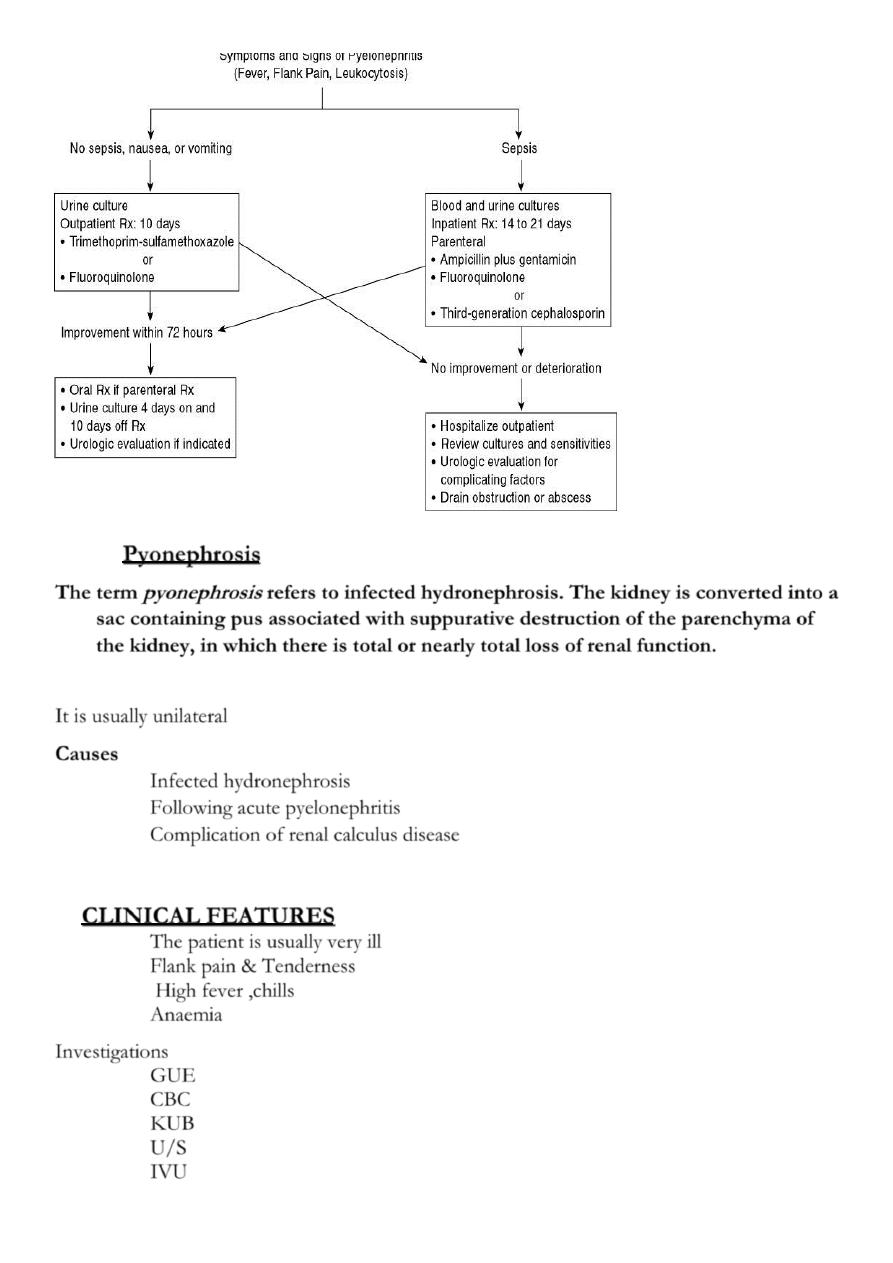
Treatment
Depends on the severity of the infection
Admission to the hospital, Bed rest
Parenteral broad spectrum antibiotics until results of
C&S
Analgesics
Encourage copious drinking of water
otherwise give IVF
N.B. obstructive
Pyelonephritis needs
Drainage
3
Pyonephrosis
The term
pyonephrosis
refers to infected hydronephrosis. The kidney is converted into a
sac containing pus associated with suppurative destruction of the parenchyma of
the kidney, in which there is total or nearly total loss of renal function.
It is usually unilateral
Causes
Infected hydronephrosis
Following acute pyelonephritis
Complication of renal calculus disease
CLINICAL FEATURES
The patient is usually very ill
Flank pain & Tenderness
High fever ,chills
Anaemia
Investigations
GUE
CBC
KUB
U/S
IVU

4
Treatment
It is Surgical Emergency
Parenteral antibiotics
Drainage of the kidney
..nephrostomy: --percutaneous
-- open
.. JJ stint
Then the stone is removed
Or nephrectomy
Renal Abscess or Renal Carbuncle
Renal abscess or carbuncle is a collection of purulent material confined to the renal
parenchyma.
The renal parenchyma contains an encapsulated necrotic mass
Insidious onset (may run > 2 weeks)
Fever
Local pain
Symptoms of the primary cause
Tender renal angle
Tender mass : differentiate from malignant lesion
Bacteriology
Hematogenic infection
Commonly coliforms & staph aureous, proteous, klebsiella.
Predisposing factors
Diabetic patients
I.V drug therapy
Hemodialysis
Immunocompromized
Skin infection
Rarely ascending infection
5
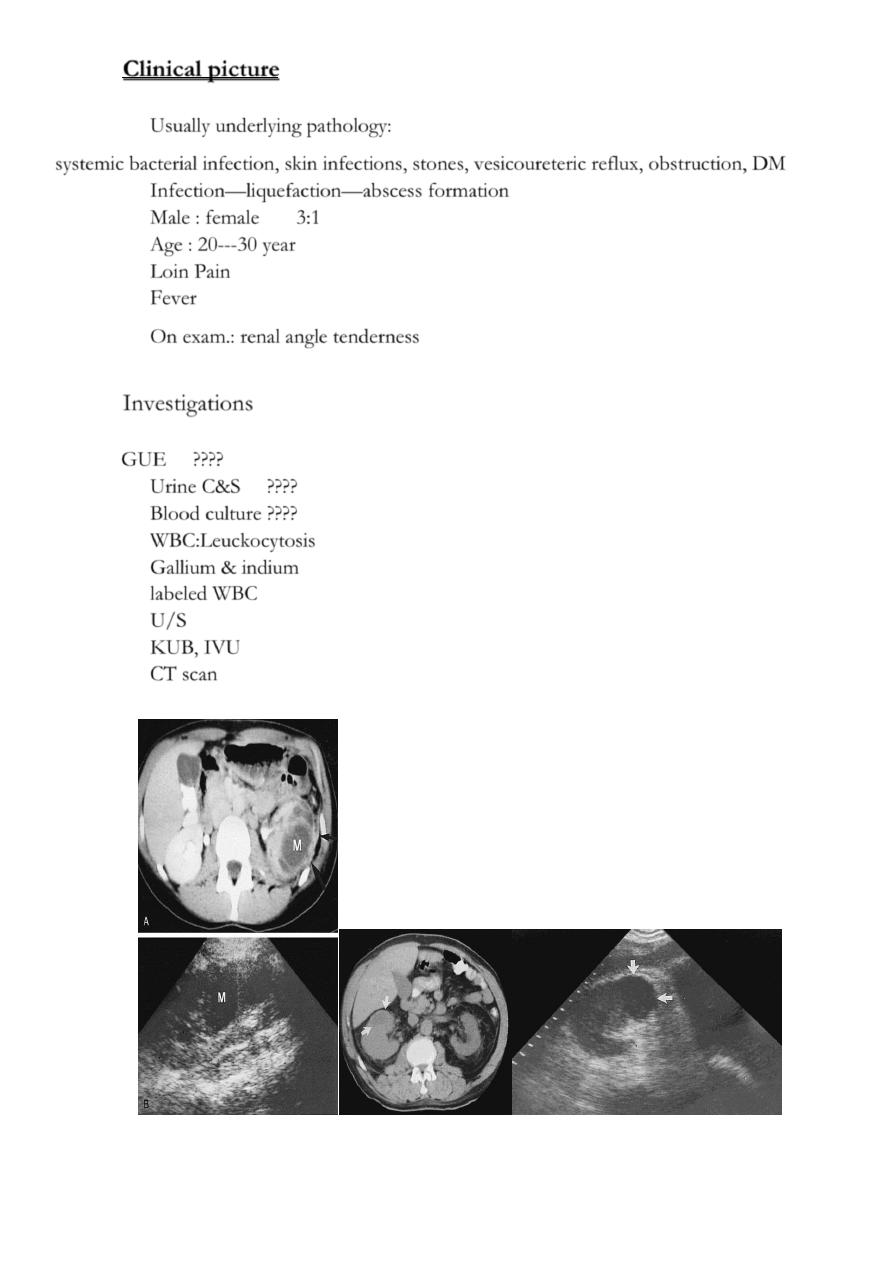
Clinical picture
Usually underlying pathology:
systemic bacterial infection, skin infections, stones, vesicoureteric reflux, obstruction, DM
Infection—liquefaction—abscess formation
Male : female 3:1
Age : 20---30 year
Loin Pain
Fever
On exam.: renal angle tenderness
Investigations
GUE ????
Urine C&S ????
Blood culture ????
WBC:Leuckocytosis
Gallium & indium
labeled WBC
U/S
KUB, IVU
CT scan

6
Treatment
Medical: Rest
Analgesia
Antibiotics
Follow up
Surgical: Abscess drainage
Nephrectomy
Perinephric Abscess
Route of infection:
Rupture of renal abscess
Infected perinephric hematoma
Extension from nearby organs: Appendix, Gall Bladder, Pelvic organs.
Hematogenic: Tonsillitis, boils, etc.
Bacteriology
Ecoli
Staph aureous
Proteous
Klebseilla
Pathology
Cortical abscess coallese, enlarge, rupture to the perinephric space, form a
perinephric abscess
Fluid filled inflammatory mass
Thick wall, adhesions.
Clinical picture
Fever , rigor
Dysurea, frequency
Renal tenderness
Visible loin mass, tender, +ve fluctuation

7
Investigations
Leucocytosis, Anemia
Pyurea, +ve bacterial culture
Chest x ray : ? Reactionary pleural effusion
KUB : soft tissue mass, stones.
IVU , Tomography : functional &anatomical study
U/S
CT scan
Treatment
Bed rest
Antibiotics & analgesics
Always combined with drainage:
Under U/S or ct scan guidance
Open drainage
Chronic non specific infection
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis
Rare, severe, chronic renal infection typically resulting in diffuse renal destruction.
Commonly affect middle age
Mixed bacteria: E coli, Proteous mirabilis
Predisposing factors:
Diabetic
Renal stone disease
Neurogenic uropathy
Obstructive uropathy

8
Clinical picture
Chronic
Loin pain
Low grade fever & malaise
Weight loss
Renal mass
Multiple fistulae
Macroscopic appearance: Excessive fatty infiltration, Xanthene deposit
Investigations
GUE
KFT
U/S
KUB
IVU
CT scan
Treatment
Always surgery… Nephrectomy
Under antibiotic cover
Prostatitis
Acute prostatitis
bacteria: E. coli, staph aureus, S. faecalis N. gonorrhoea
Route of infection: -hematogenous
-2ry to UTI

9
Clinical features
Fever, shivers , rigor
Backache, perineal pain
Irritative voiding symptoms: dysuria, frequency
Obstructive urinary symptoms
Pain on defecation
O/E: DRE : enlarged, extremely tender, hot prostate
Treatment
Admission ?
Bed rest
Analgesics
Antipyretics
Parenteral antibiotics
If abscess: drainage
If retention: suprapubic catheterization.
Renal Tuberculosis
Bacteria: Mycobacterium TB
Pathogenesis: Hematogenic
Start unilateral , late bilateral affection.
The 1
st
lesion starts usually in the pyramids
Chronic: Asymptomatic until late stage
TB granuloma, caseation, open to the calyces.
Renal destruction, calcification.
The ureteric upper & lower 1/3
rd
is affected
Ureteral & bladder involvement is commonly secondary
Clinical picture
Always suspect if:
Endemic area
Age : 20----30 year
Male : female 2:1
Chronic symptoms
Non responsive UTI to adequate therapy.
Unexplained hematuria.
loin pain
Night sweating, Wt loss

11
Fever when secondary bacterial infection
Chronic renal sinuses.
TB is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients
Investigations
GUE : RBC , Sterile acid pyurea.
-ve urine C&S
Three successive morning urine samples for AFB.
24 hours urine collection for AFB.
TB culture & sensitivity.
ESR
WBC total & differential.
KUB: Renal calcification
IVU
CXR
Cystoscopy and bladder biopsy: for lower tract involvement.
Treatment
Medical:
Surgical:
If complicated
No clinical control
Correct obstruction
Nephrectomy
.
Complications
Perinephric abscess
Pyonephrosis
Renal stones
Ureteral strictures
Renal cutaneous sinuses
Chronic renal failure.
Autonephrectomy in ureteral obstruction
Bladder contracture( thimble bladder)

11
Bilharziasis
Trematode: schistosoma haematobium
Male: female 3:1
Endemic in Nile valley, Iraq, & middle east in general.
Marshes & slow running fresh water is the habitat of the fresh water snail ( bulinus truncatus )
which is the intermediate host.
Mode of infestation
The bifid tailed embryos (cercariae) penetrate the skin, enter the blood vessels, flourish in the
liver, develop into male & female worms, they pass to the vesical venous plexus
The female pass to the submucous venule to lay its eggs with its terminal spine which penetrate
the vessel wall & pass with urine & if reach fresh water it penetrates the intermediate host.
Clinical features
Urticaria ( swimming itch )
Fever , sweating
Hematuria: intermittent, terminal
Lymphadenopathy & splenomegaly
Investigations
GUE : early morning samples for several consecutive days – ovae with terminal
spines
Leukocytosis – eosinophilia
Cystoscopy
Bilharzial pseudotubercles , nodules, sandy patches, ulceration, fibrosis,
granulomas, papillomas, carcinoma (SCC).
12
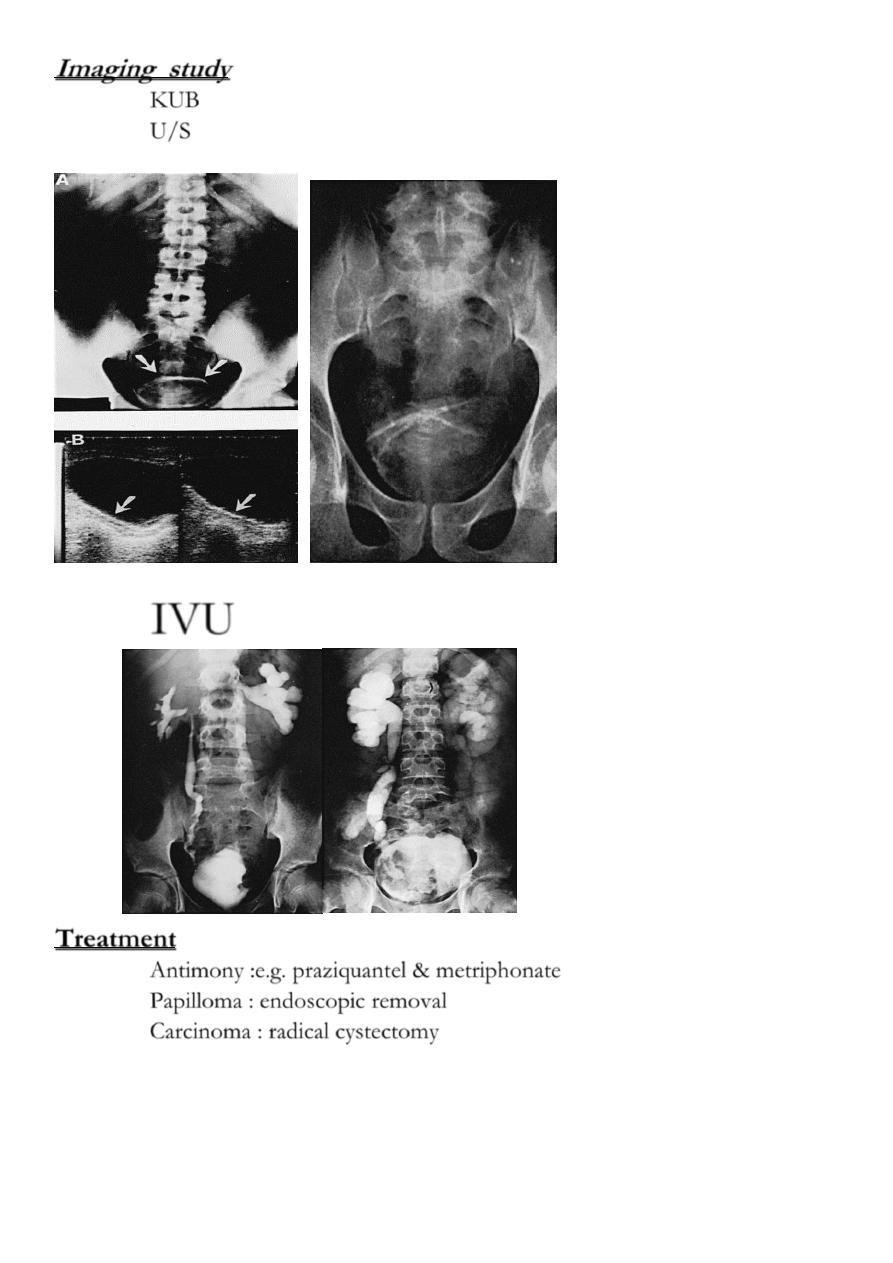
Imaging study
KUB
U/S
IVU
Treatment
Antimony :e.g. praziquantel & metriphonate
Papilloma : endoscopic removal
Carcinoma : radical cystectomy

13
Complications
2ry bacterial infection
Vesical & ureteric calculus formation
Terminal ureteric stricture : needs dilatation or ureteric reimplantation
Prostatoseminal vesiculitis
Fibrosis of the bladder & bladder neck
Urethral stricture & fistula formation
