
Dr. Faiq Isho
Assistant Professor & Consultant
Rheumatologist
Introduction to Rehabilitation Medicine
1

2

Learning objectives
To define: rehabilitation medicine,Physical Therapy,
Occupational therapy, impairment, disability, handicap
To give some practical examples
To describe rehabilitation Team, program
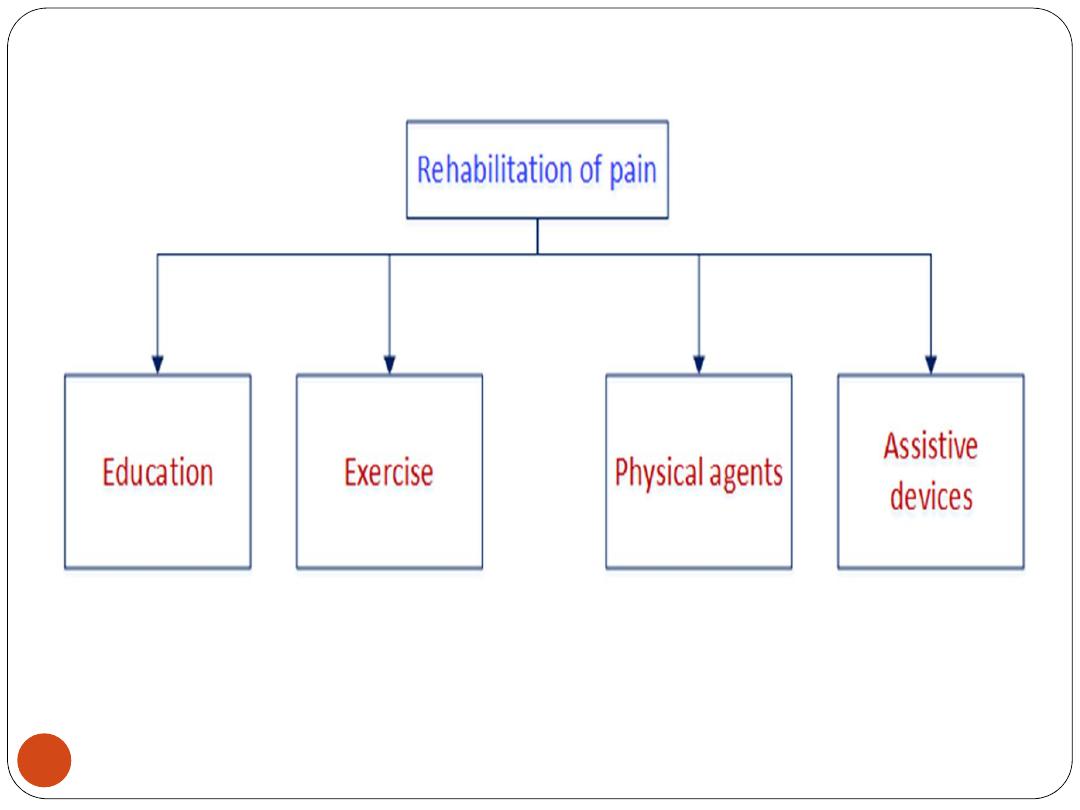
To list and describe methods of rehabilitation of pain
and Inflammation
Summary
Quiz
3

Rehabilitation medicine
a branch of medicine
enhance and restore
functional
ability and
quality
of life
of patients with
physical impairments or
disabilities
4
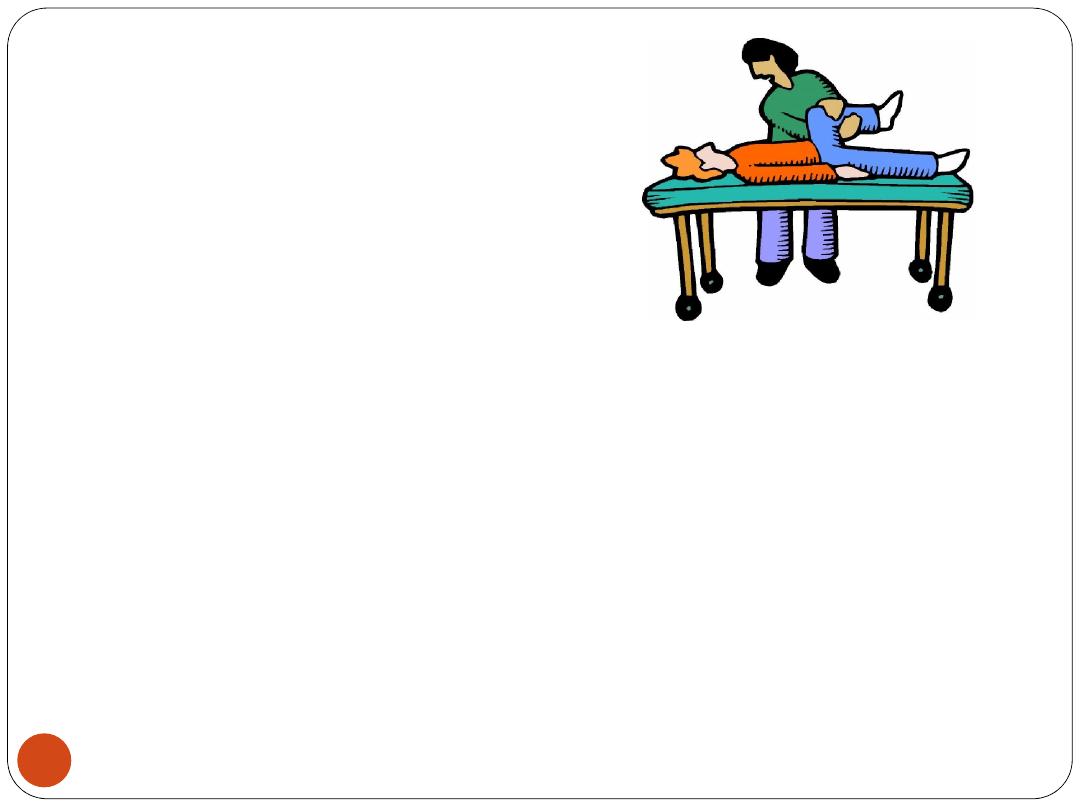

Physical Therapy (PT)
Physical therapy involves
exercising
and
manipulating
the body.
It can
improve joint and muscle function
, helping
people stand, balance, walk, and climb stairs better.
5

Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy is intended to enhance a
person's ability to do
basic self-care activities
, useful
work
, and
leisure activities
.
6

Occupational therapists focus on helping people do
specific daily tasks:
7

Terms
Impairment:
loss of structure
or
function
Disability:
activity limitation
Handicap:
disadvantage
resulting
from
an
impairment or disability
that interferes with a
person’s efforts to fulfill a role that is normal for that
person.
8
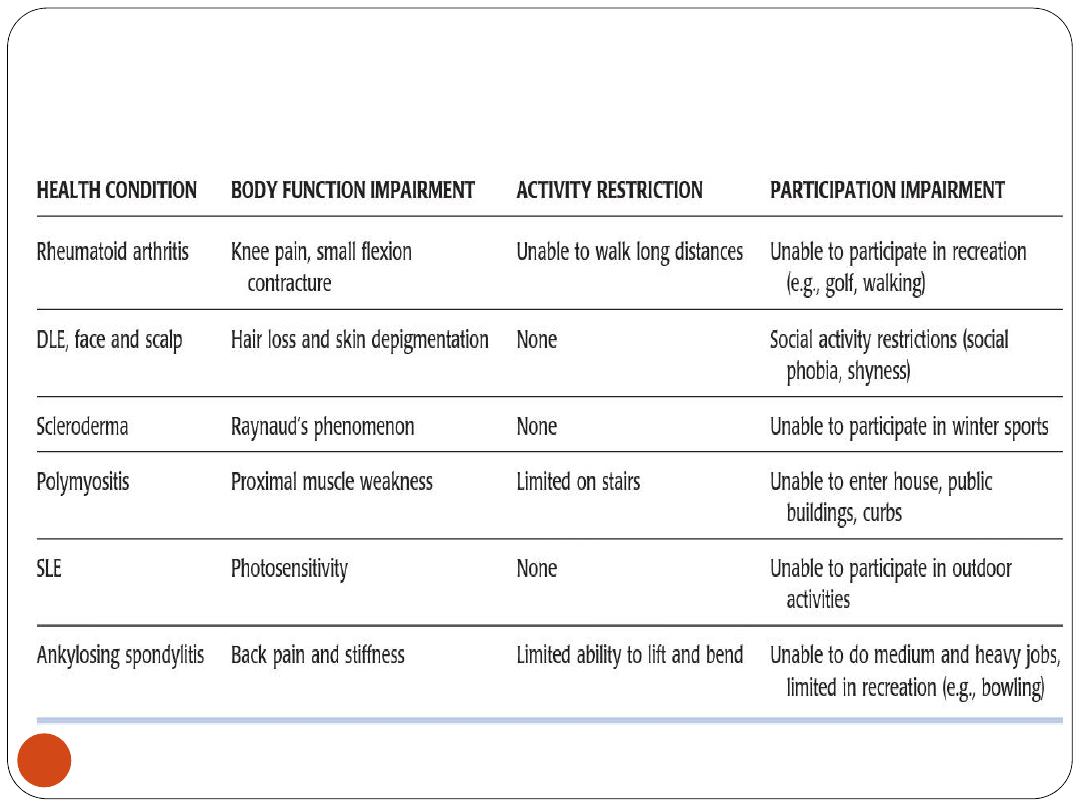
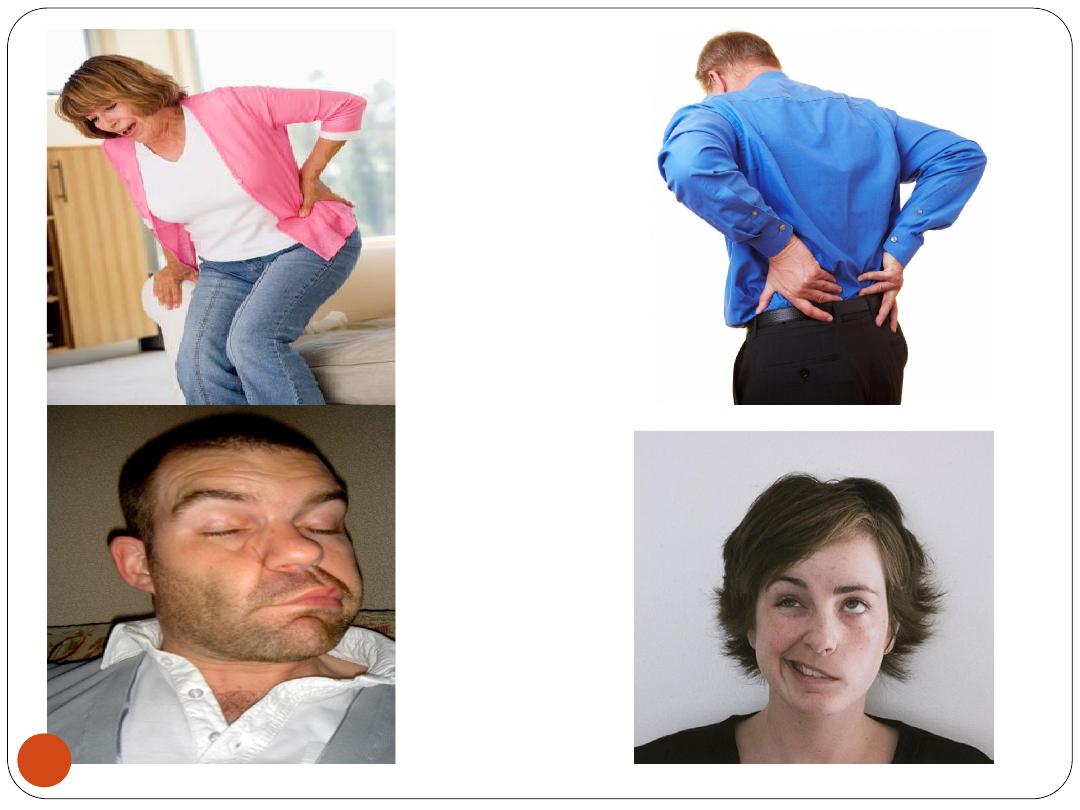
Examples of disability
9

Examples:
-
A pulmonary rehabilitation program is often appropriate
for people who have
COPD.
-
People who become weak after
prolonged bed rest
(for
example, because of a
severe injury or after surgery
) also
need rehabilitation.
10

Rehabilitation team
Treatment involves a team work &
continued
sessions
of training for
many weeks
11
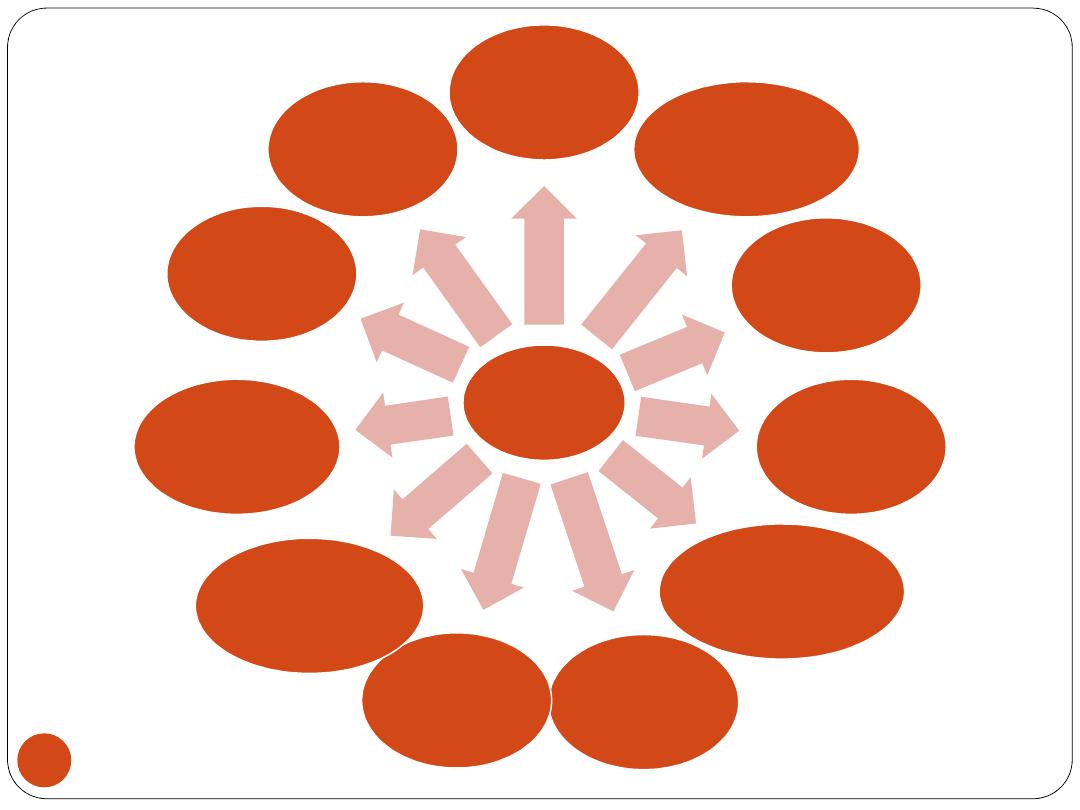
Physician
Physical
therapist
Occupational
therapist
Orthotist
Prosthetist
Psychologists
social
workers
speech
therapists
Audiologists
Recreational
therapist
Dietitian
Other
Systems
12
Rehabilitation program:
To initiate a formal rehabilitation program: A doctor
writes a referral letter to a
rehabilitation center
.
1.
Diagnosis
2.
Goals of therapy
3.
Type of therapy
needed, such as ambulation training
(help with walking) or training in activities of daily
living.
13

Setting
:
Where
rehabilitation
takes
place
depends on the person's needs.
Many people recovering from injuries can be
treated as
outpatients
in a therapist's office.
People with severe disabilities may need care in a
hospital
or
inpatient rehabilitation center
.
14
Goals:
short-term
and
long-term
Goals
Short term: To
provide immediate
achievable target
Long term:
Expected to be
several months
15
16

1) Education
Avoid predisposing factor
Weight reduction
Habits: smoking, drinking
Diet
17
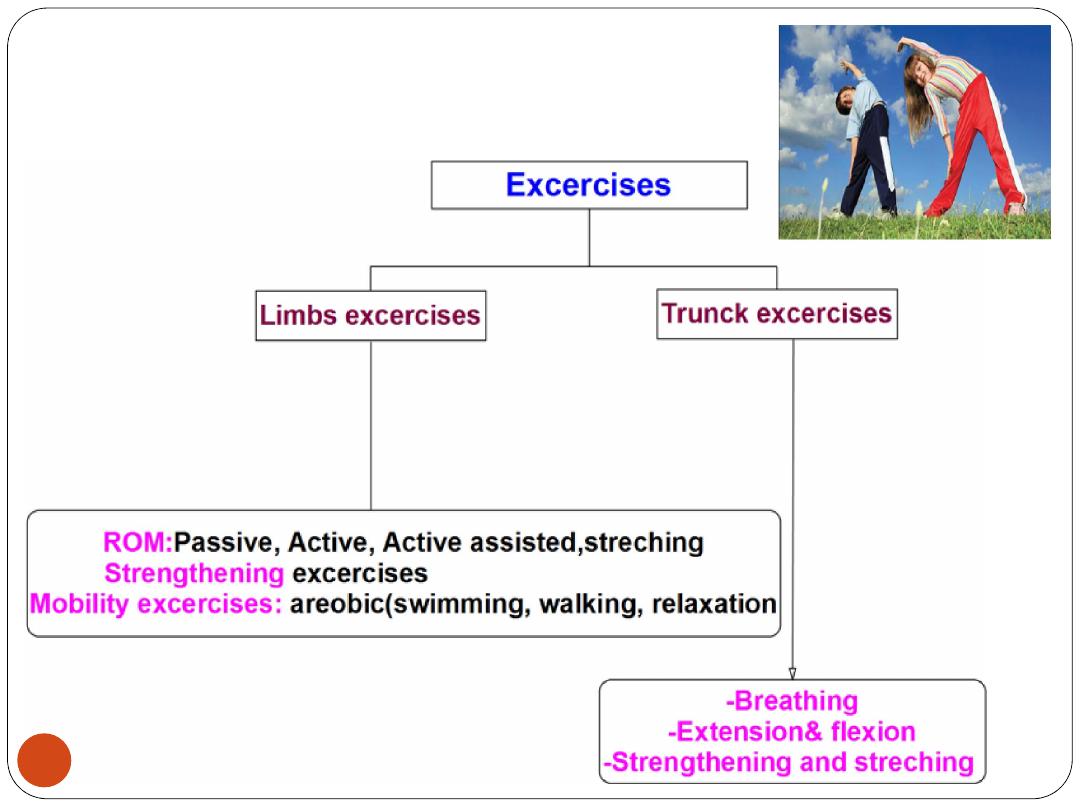
2)Excercises
18

Treatment of Pain and Inflammation
Techniques include:
1)
Heat therapy
,
2)
Cold therapy
, cryotherapy
3)
Electrical stimulation
,
4)
Traction
5)
Massage
6)
Assistive devices
Cold therapy seems to be more effective for acute
pain.
19

1)Heat Therapy
Heat:
-
Increases
blood flow
-
Makes connective tissue more
flexible
-
Decreases joint stiffness
,
pain
, and
muscle spasms
20

Heat therapy is used to treat:
1.
Inflammation (including various forms of arthritis)
2.
Muscle spasm
3.
Injuries such as sprains and strains.
21

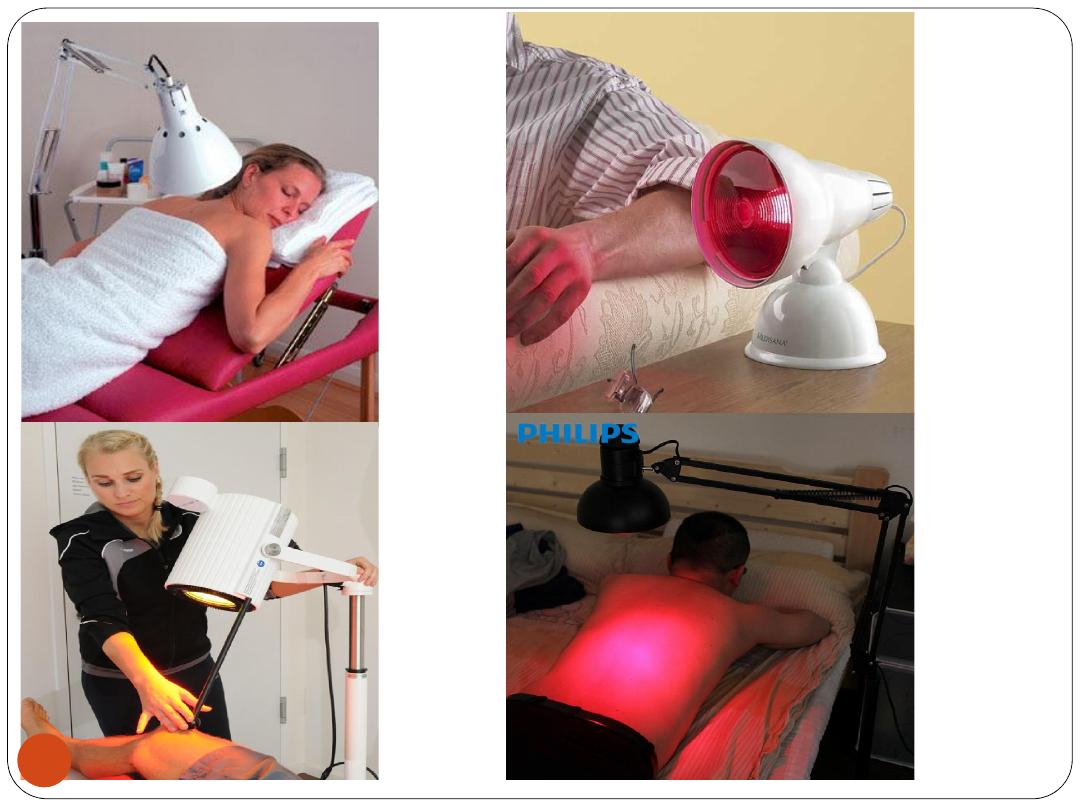
Types of Heat Therapy
A) Heat applied to the body's surface
1. Infrared heat
Heat applied with a
lamp
Care needed to
avoid burns
Indication:
Arthralgia,
Arthritis,
Back
pain,
Fibromyalgia, Muscle spasm, Myositis, Neuralgia,
Sprains, Strains, Tenosynovitis, and Whiplash
injuries
C/I
severe heart, liver, or kidney disorder
,
peripheral vascular disease, or reduced skin
sensation, infection, malignancy
22
23

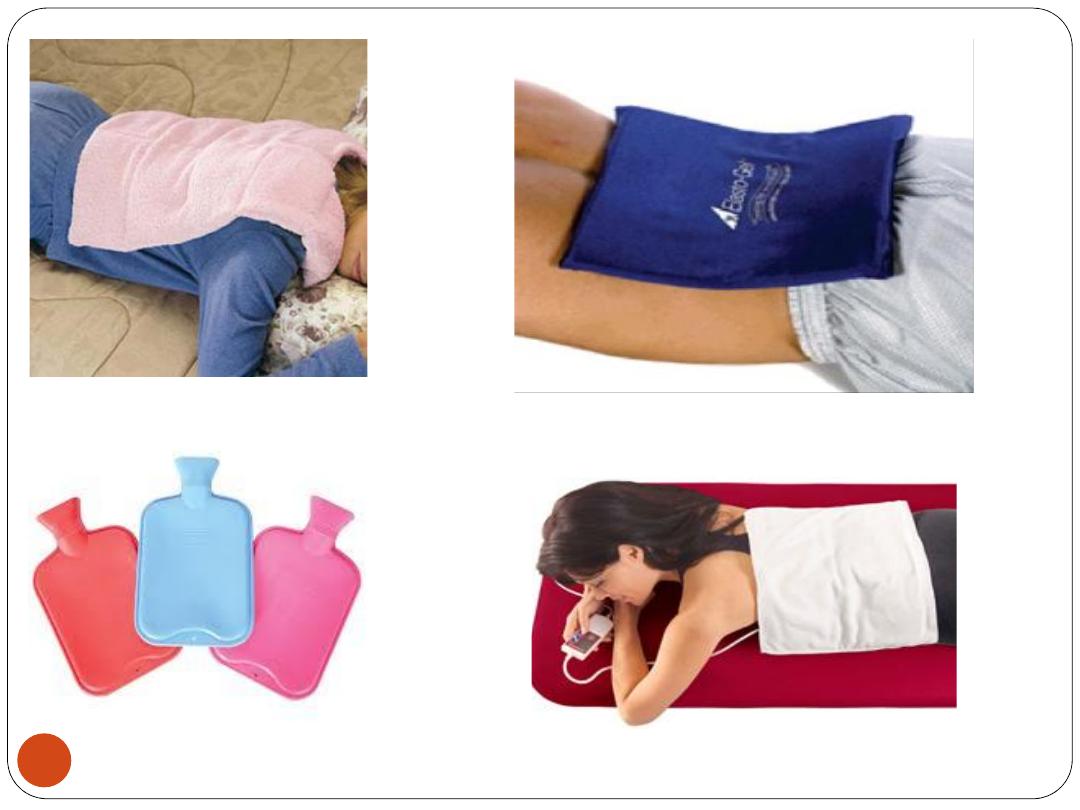
2. Hot packs
Cotton cloth containers filled with silicate gel,
usually warmed in a microwave oven
Uses: Same as for infrared heat
24

25
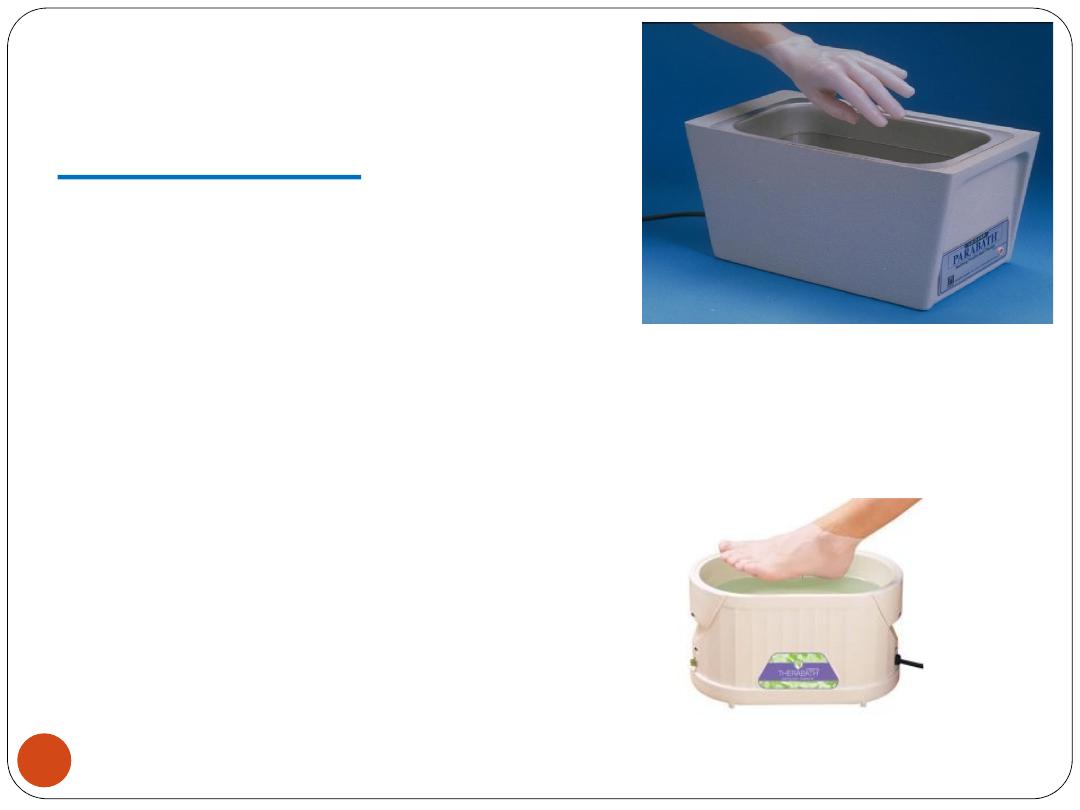

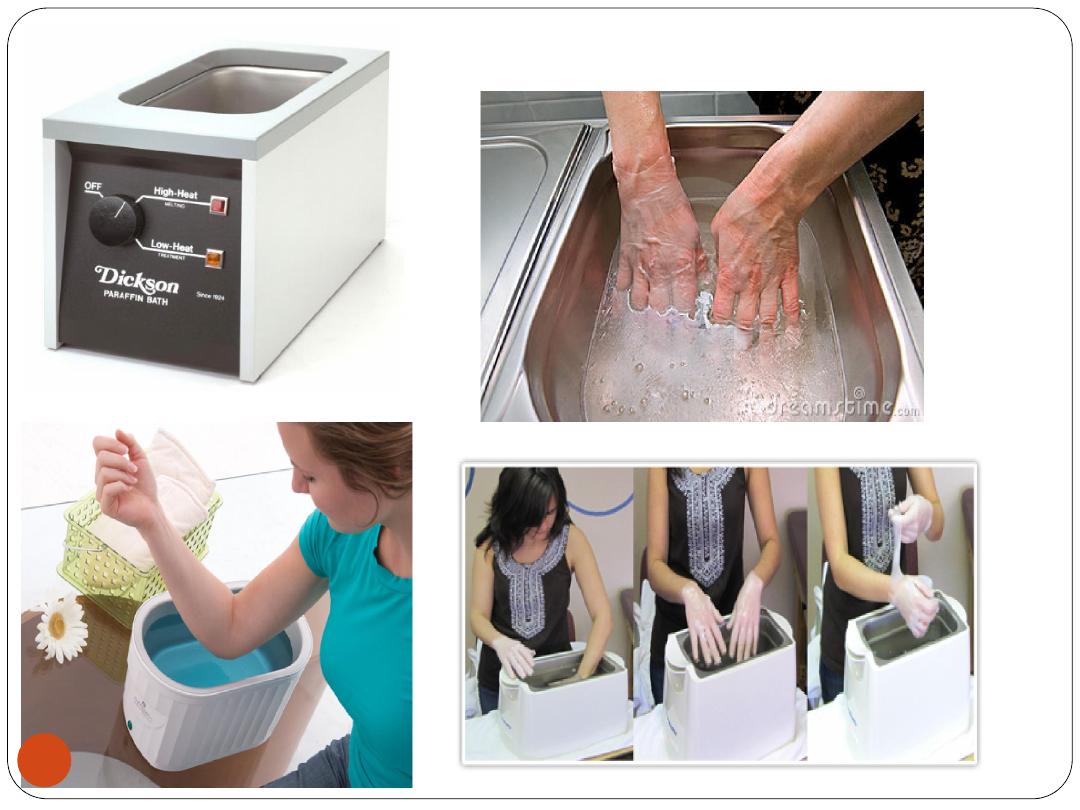
3. Paraffin bath
Dipping in, or painting with wax
Usually applied to small joints, such as those of
the hand, knee, or elbow
Not used for open wounds
26

27

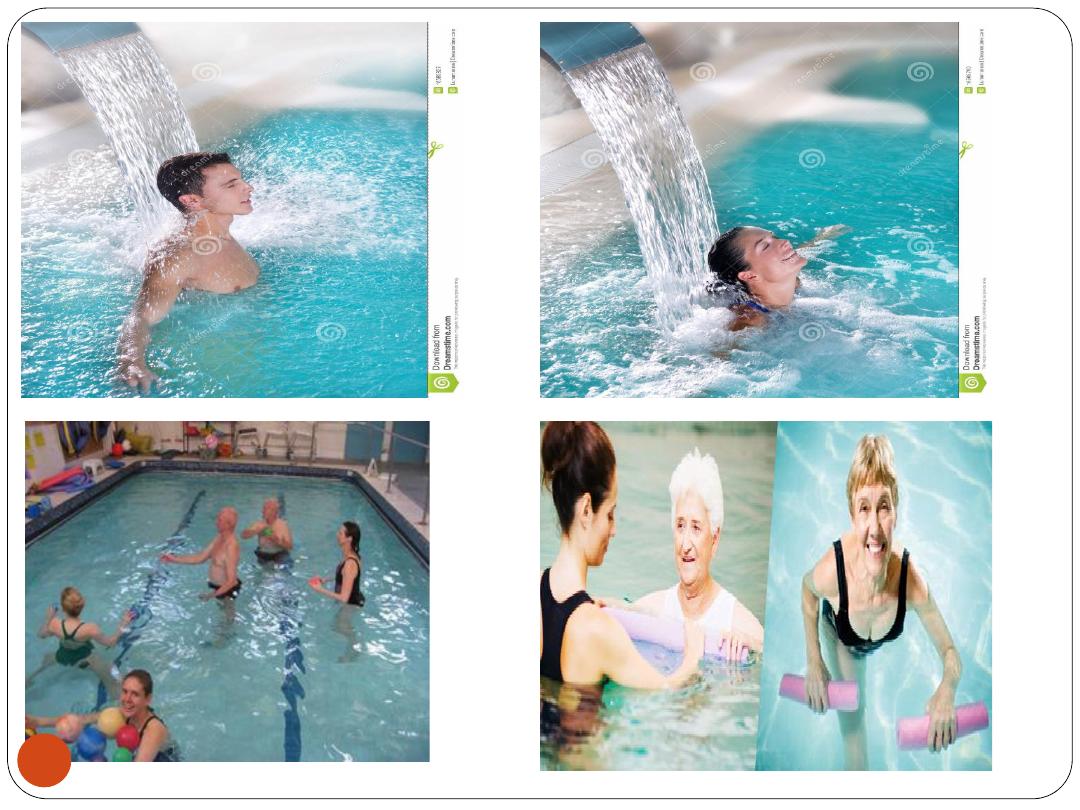
4. Hydrotherapy
Immersion in agitated warm water
In a large industrial whirlpool
Enhances wound healing by
stimulating blood
flow
and helping
clean out burns and wounds
Relaxes muscles
and
relieves pain
Helps with
range-of-motion exercises
28

29

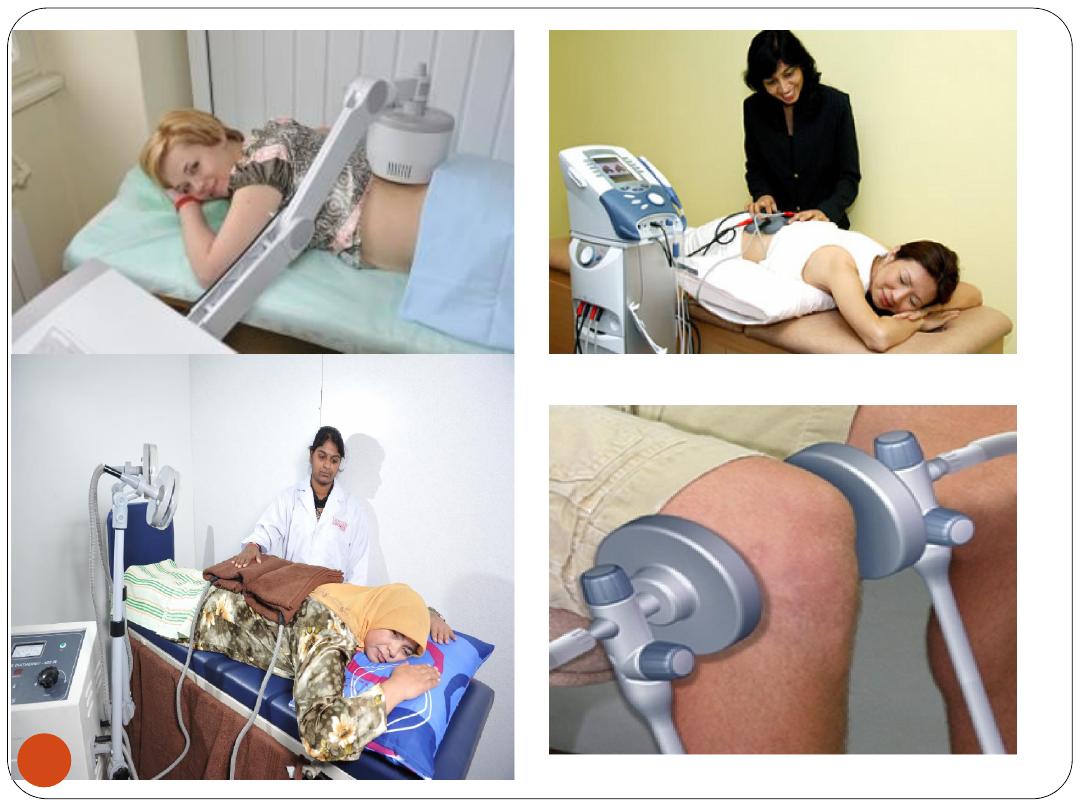
B) Heat applied to deep tissues
1. Shortwave Diathermy
Heat produced by an oscillating, high-frequency
electromagnetic field
Simple to apply
Warms deep tissues (such as muscles) without
heating of the skin
Uses:
Mechanical pains, Pain due to kidney
stones, pelvic infections, or sinusitis (short-term
or chronic.
30
31

2. Microwave diathermy
Heat produced by microwaves
Simpler
to apply and
more comfortable
than
shortwave diathermy
Evenly warms deep tissues (such as muscles)
without heating of the skin
32
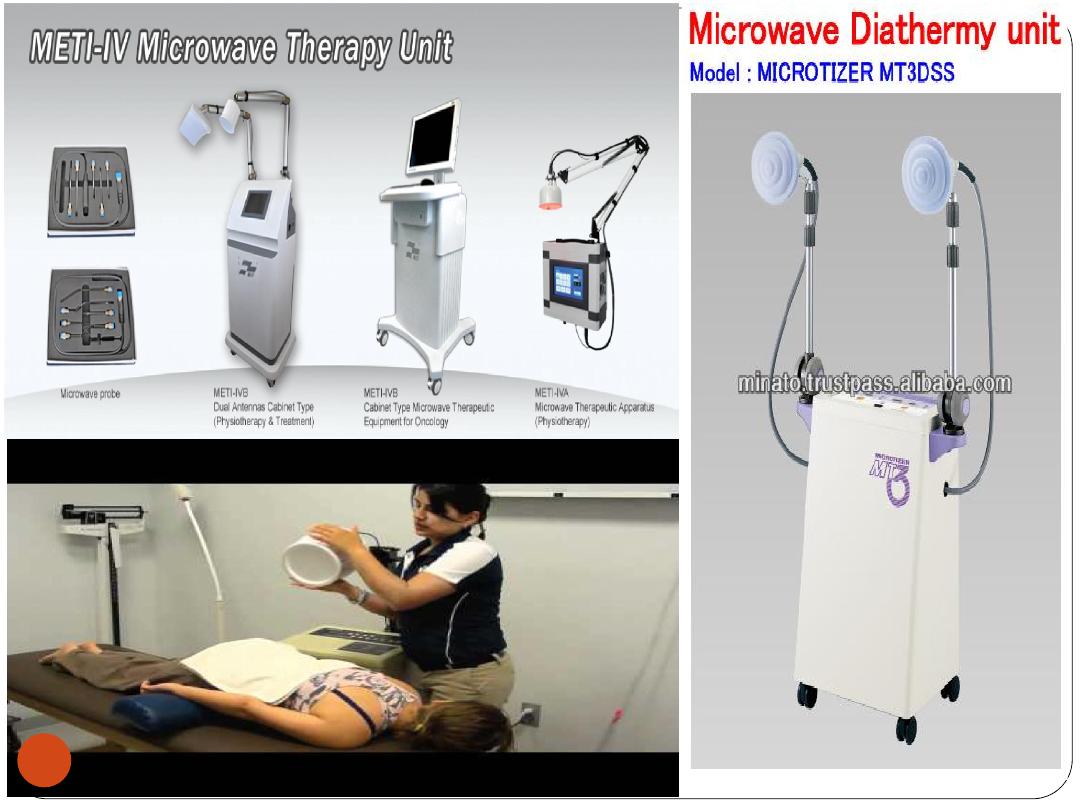
33
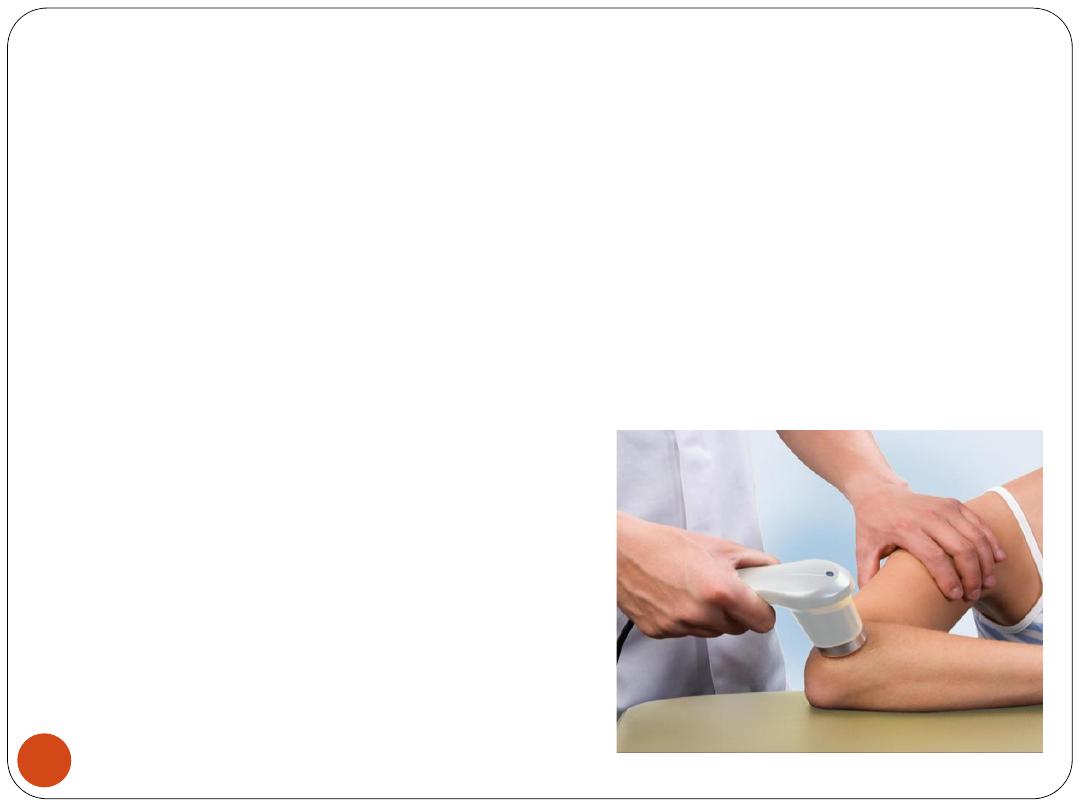
3. Ultrasound
High-frequency sound waves
to penetrate deep into
tissues
C/I
in :
ischemia
,
infected areas
,
bones that are
healing
, or
eyes, brain, spinal cord, ears, heart, or
reproductive organs), tendency to bleed or cancer
Uses:
Bone injuries, Bursitis
, Complex regional pain syndrome
, Contractures, Osteoarthritis
, Tendinitis
34
35
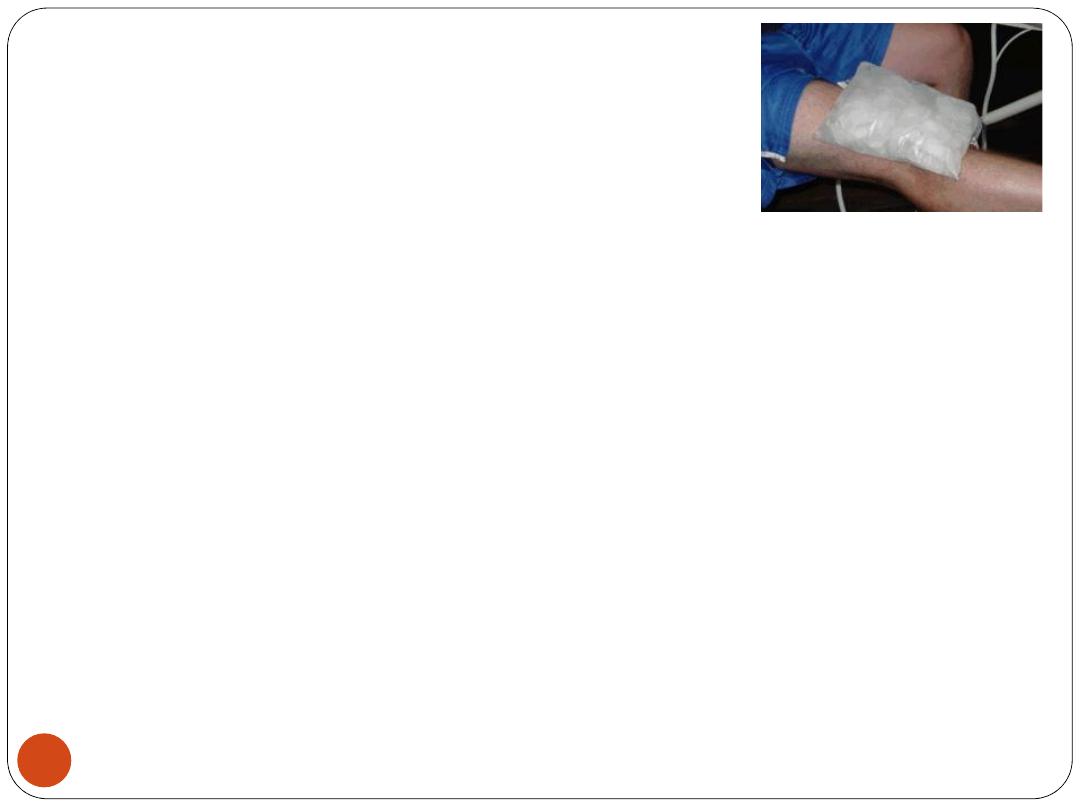

2) Cold Therapy (Cryotherapy):
Applying cold may help
numb tissues
and relieve
muscle spasms
,
acute low back pain
, and
acute
inflammation
.
C/I in :
tissues with a reduced blood supply
(
peripheral arterial disease
).
Cold may be applied using an
ice bag
, a
cold
pack
, or
fluids
(such as ethyl chloride) that cool by
evaporation.
36
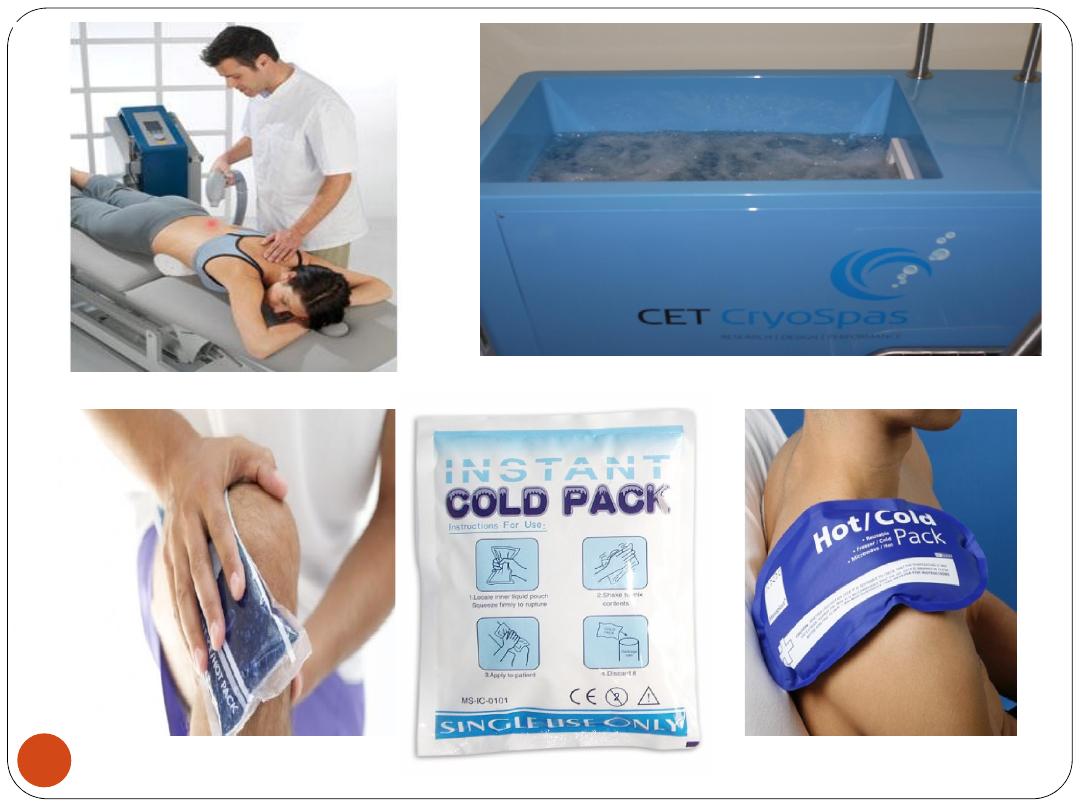
37

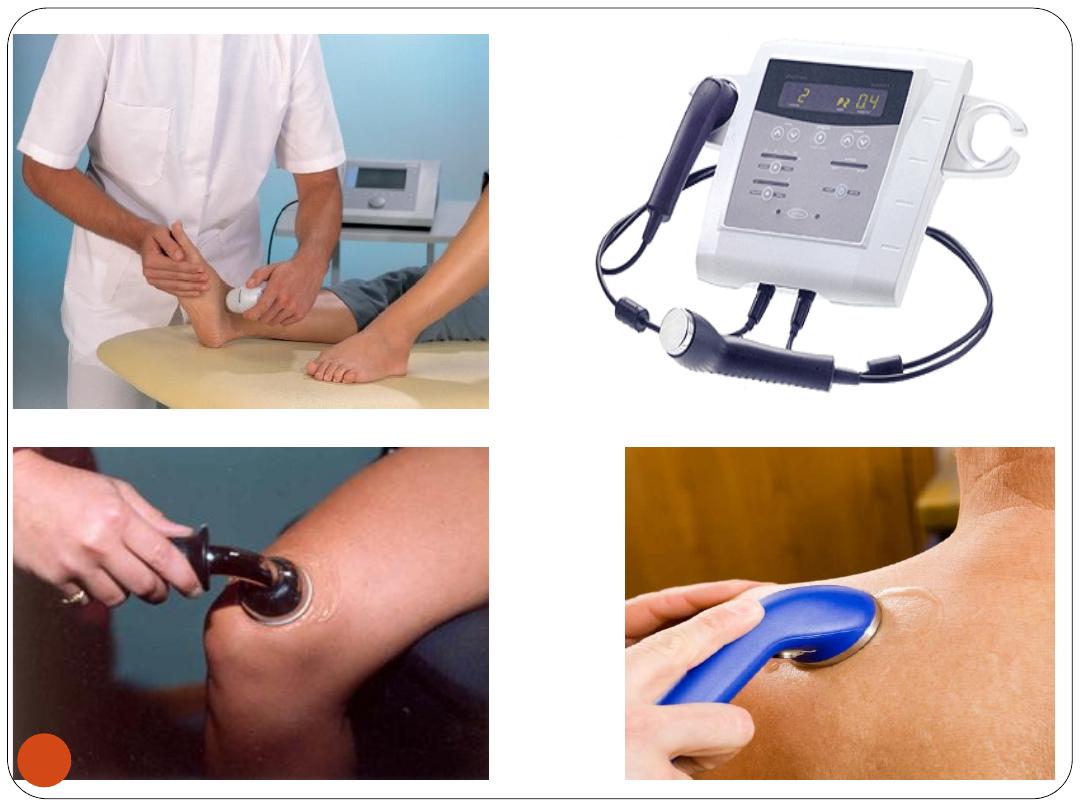
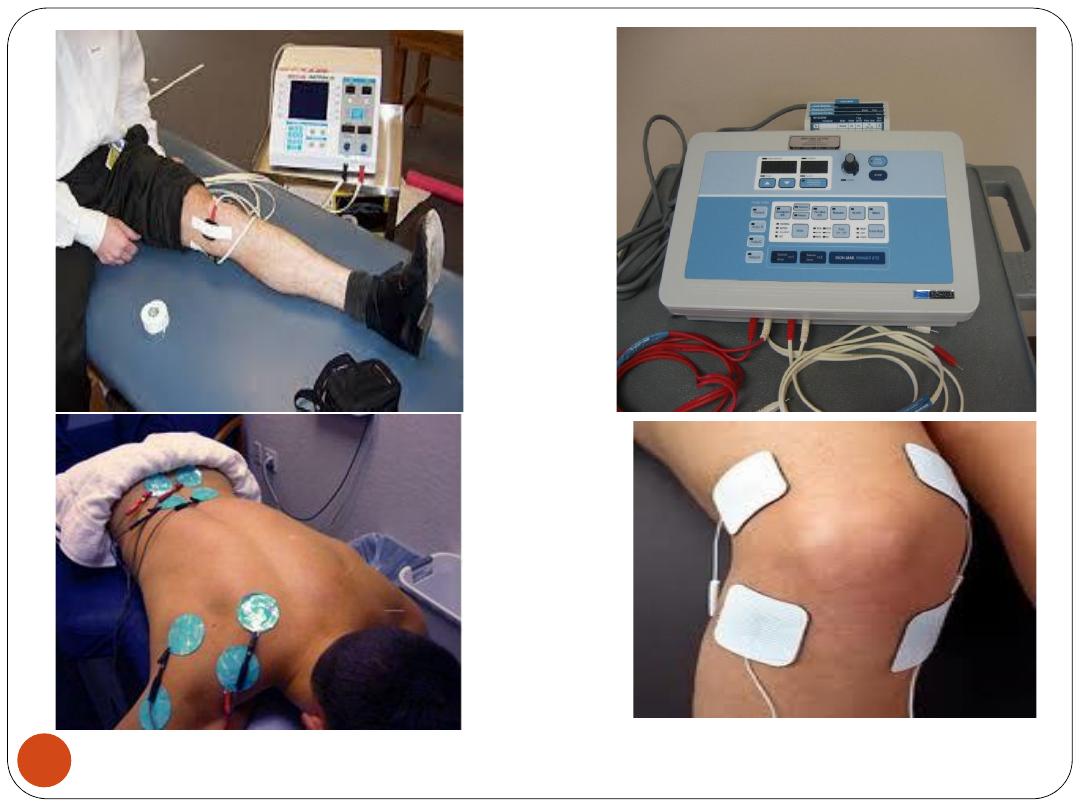
3) Electrical Stimulation:
Indications
:
peripheral nerve injury, spinal cord
disorder, or stroke
muscles
atrophy, chronic
back pain
,
RA
, a
sprained ankle
,
shingles
, or a
localized area of pain
.
C/I
a severe
heart disorder
or a
pacemaker
(
arrhythmias
) or
near the eyes
.
38
39
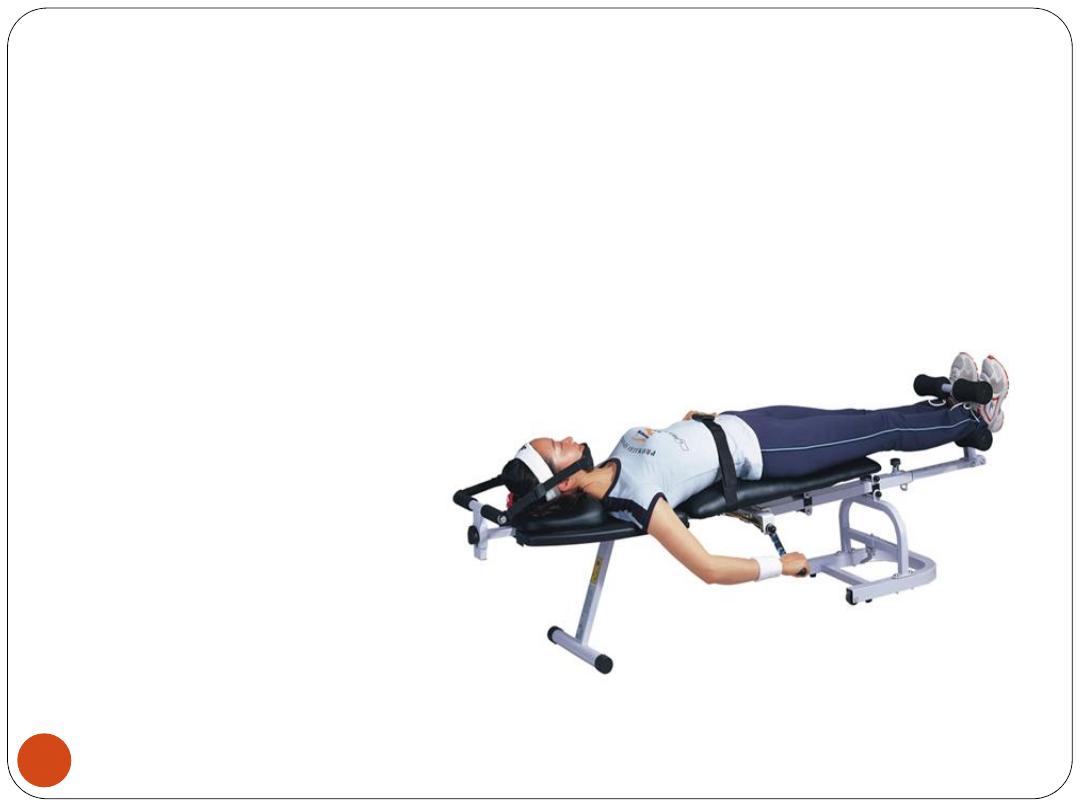

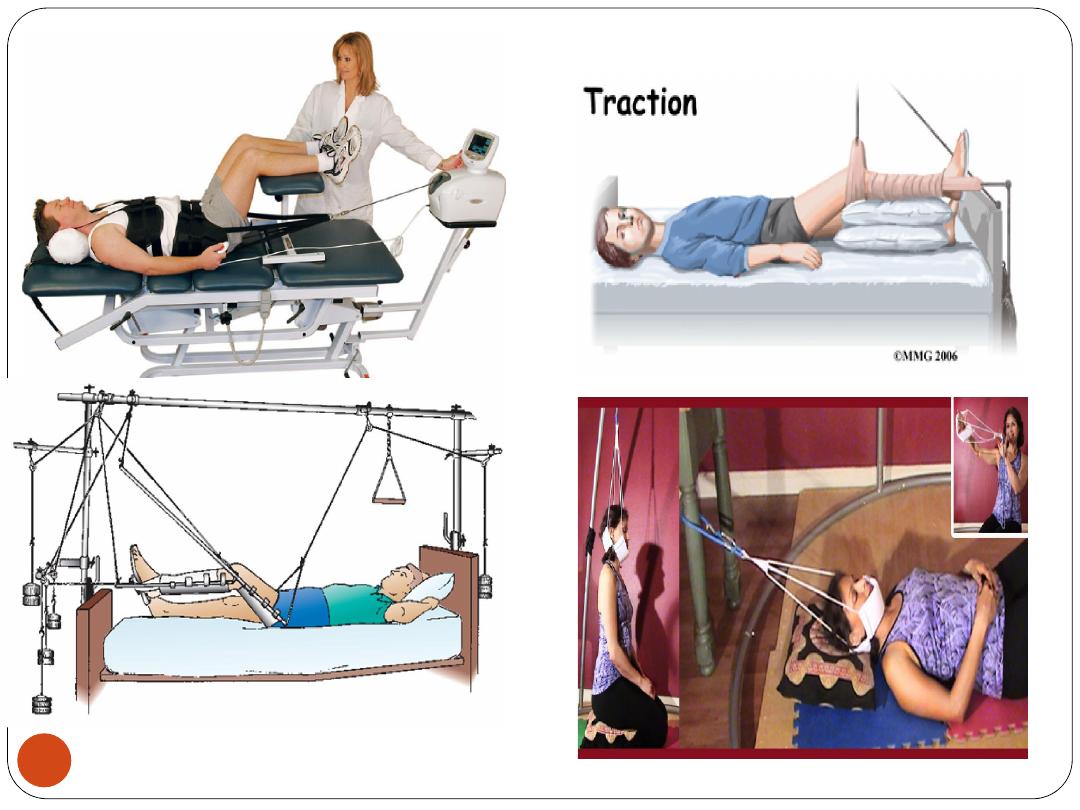
4) Traction:
Neck (cervical) traction may be used to treat
chronic neck pain
due to:
•
Cervical spondylosis
•
Disc prolapse
•
Whiplash injuries
•
Torticollis.
40
41

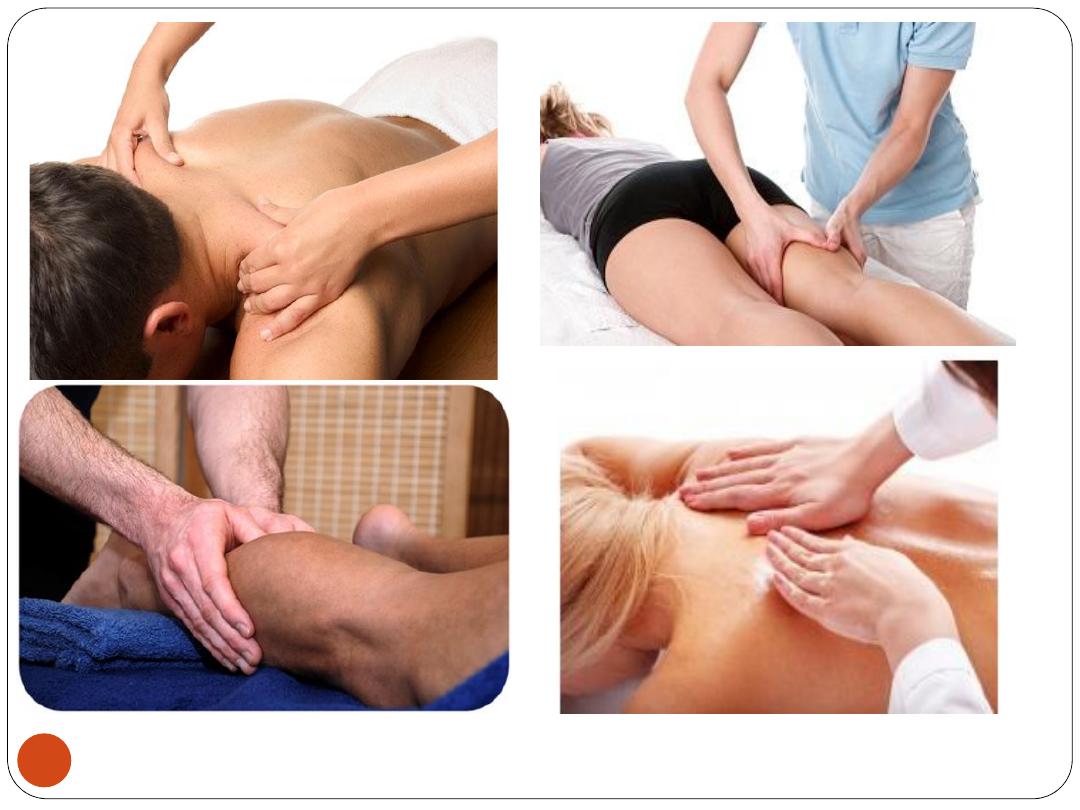
5)Massage:
Massage may
relieve pain
,
reduce swelling
, and help
loosen contracted tissue
.
Some
Uses
for Massage
Arthritis, bursitis, periarthritis, Fibromyalgia
Sprains(lig.inj), Strains ( m. or tendon inj), contracted
tissues, Fractures, Joint injuries
Hemiplegia, Paraplegia, Quadriplegia
Low back pain
Neuritis, Peripheral nerve injuries
42
43
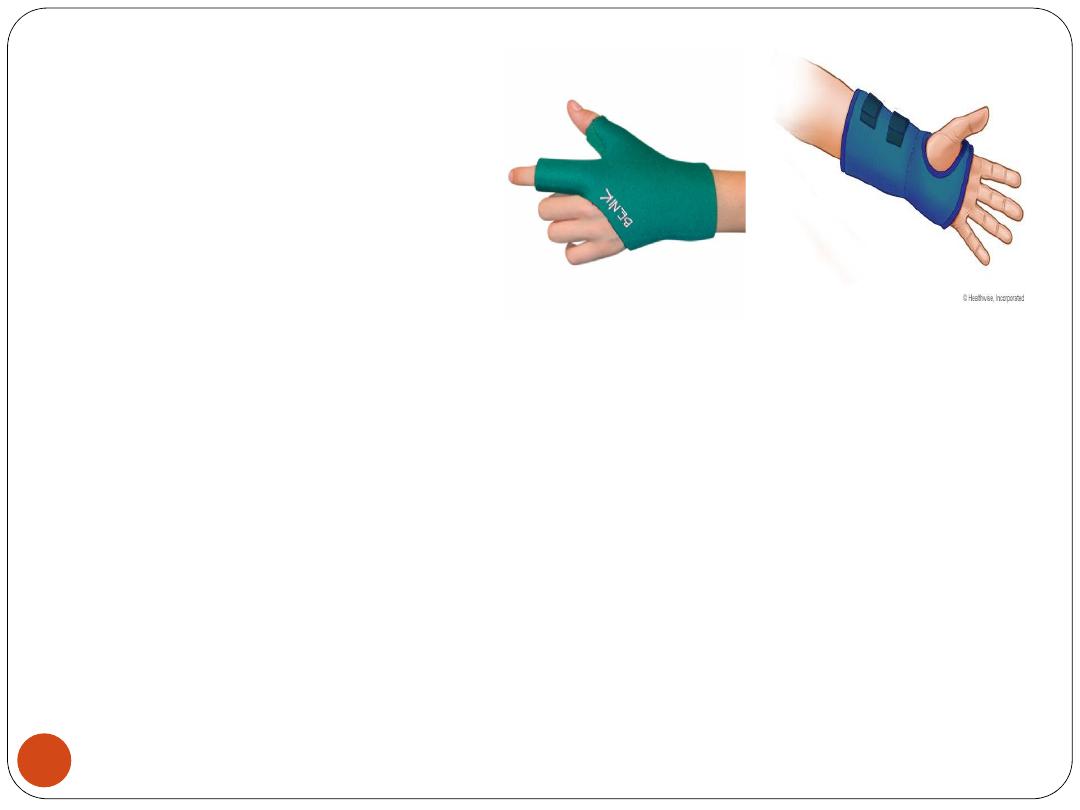
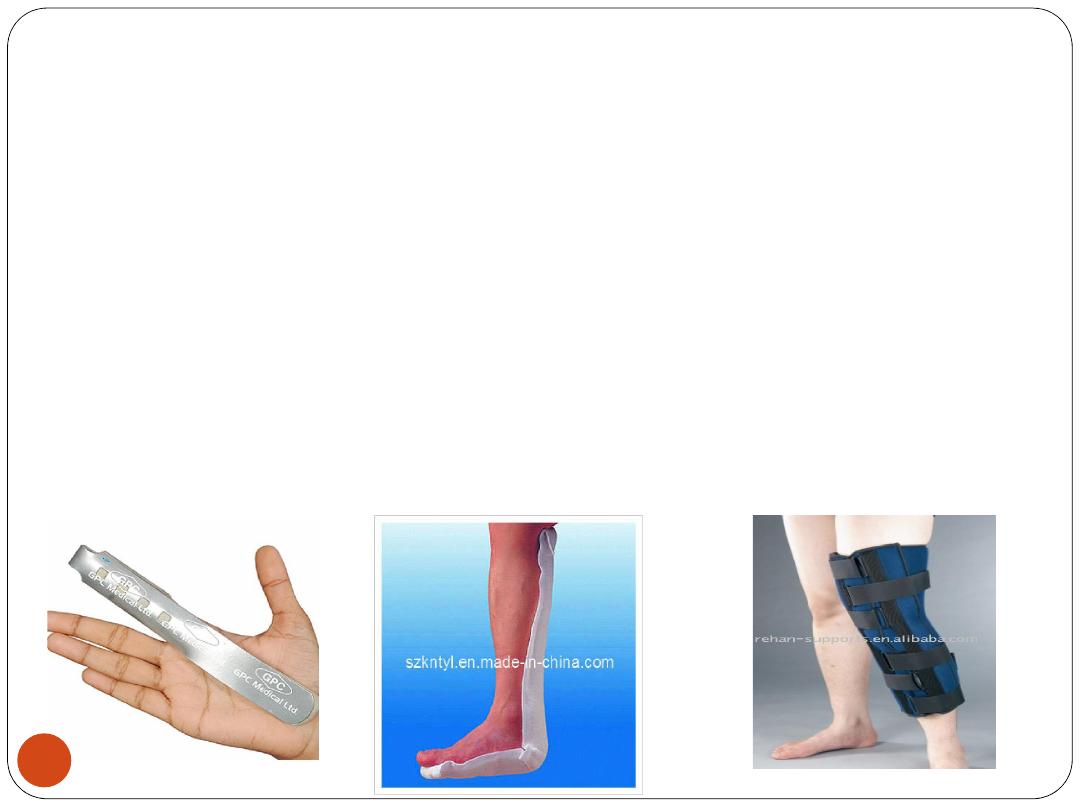
6) Assistive Devices:
Occupational therapists recommend devices to
help people
function more independently
.
For example, a person with
arthritis
can be fitted
with a
splint
to prevent joints from freezing in an
abnormal position (deformity) or
to support damaged joints, ligaments, tendons,
muscles, and bones (
orthoses
).
44
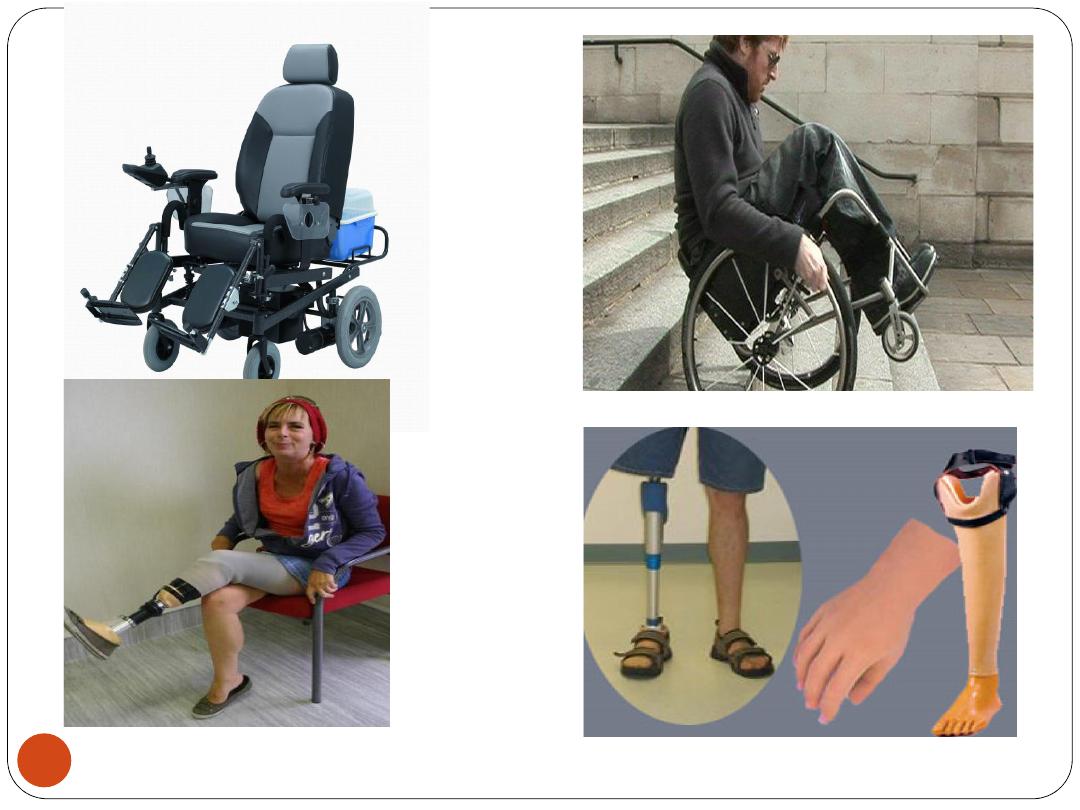
For a person who has had an
arm amputated
,
therapists
may
recommend
an
artificial
arm
(
prosthesis
).
Most
occupational
therapists
can
recommend
appropriate
wheelchairs
and train people who have
had an arm amputated to use their artificial limb or
other devices to help them with daily tasks.
45
46

Summary
Rehabilitation
is important to restore normal function
& quality of life of patients
Physical therapy
: skills for LL( excercises)
Occupational therapy
: skills UL (ADL)
Rehabilitation:
team, program
Physical agents
: Heat Tx( superficial: IR, Hot pack,
paraffin, hydroTx; deep: diathermy SWD, MWD, US),
Cold ( Cryo Tx), ElectroTx, Traction, Massage,
Assistive devices
47



