
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
JOINTS DISEASE
Imaging techniques :
1.Plain film examination remains important for imaging joint disease
2.MRI is being used with increasing frequency , MRI is indicated in the following:
.Meniscal & ligamentous tears in the knee .
.Rotator cuff tears of the shoulder
.Avascular necrosis of the hip
.Septic arthritis
3.Artherography :involves injecting contrast medium into the joint space directly& then
performing an MR scan . MRI arthrography has a role in the shoulder and wrist.
Plain film sings of joint disease :
I.Signs indicating the presence of an arthritis .
1.joint space narrowing : it is due to destruction of articular cartilage ,it occur in all forms
of joint disease , except avascular necrosis
2.Soft tissue swelling :swelling of the soft tissue around a joint may be seen in any arthritis
accompanied by a joint effusion , it is a feature of inflammatory ,and particularly
infective , arthritis . discreet soft tissue swelling around the joints can be seen in the
gout due to gouty tophi .
3.Osteoporosis : seen in the bones adjacent to the joints in many painful conditions , the
under use of the bones seems to be an important mechanism , it more severe in
rheumatoid and tuberculous arthritis .occur demenerlization and escaping of Ca++ ions
from the matrix
II.Sings that point to the cause of an arthritis
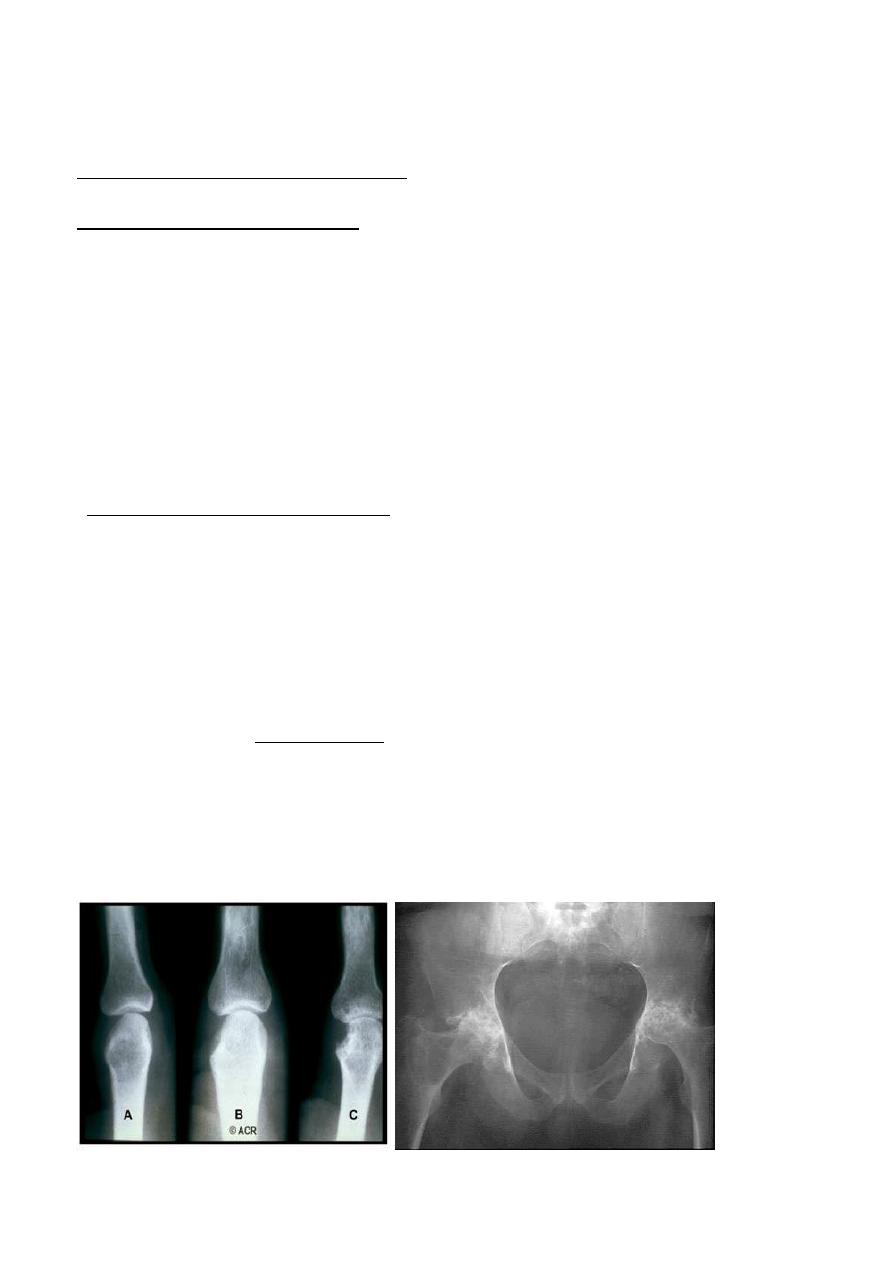
1.Articular erosions : an erosions is an area of destruction of the articular cortex and the adjacent
trabecular bone usually accompanied by destruction of the articular cartilage ,causes of the
erosions :
*Inflammatory overgrowth of the synovium ( pannus ) which occurs in ( DDx)
1.Rheumatoid arthritis ,which is by far the commonest cause of an erosive arthropathy.
2.Juvenile RA ( stills disease ) .
3.Psoriasis.
4.Reiter disease
5.Ankylosing spondylitis.
6.Tuberculosis .
*Response to the deposition of urate crystals in gout . " deposition of urate crystals in synovium and
in articular cartilage cause reactionary inflammation locally to this deposition
*Destruction caused by infection ( pyogenic & tuberculos arthritis ).
*Synovial over growth produced by repeated hemorrhage in hemophilia & relating bleeding
disorders .
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
*Newplastic overgrowth of synovium e.g synovial sarcoma.
2.Osteophytes ,subchondral sclerosis & cyst : are all features of osteoarthritis , a characteristic
increase in the density of subchondral bone is seen in avascular necrosis .
3.Alteration in the shape of the joint : e.g slipped epiphysis , developmental dysplasia of the
hip , osteochondritis dissecans & avascular necrosis in later stage.
Rheumatoid arthritis :
- RA is a polyarthritis caused by inflammatory overgrowth of synovium known as pannus ,
- it is virtually always involves the hands & feet , principally the metacarpo-& metatarso-
phalangeal joints( later on affect the proximal interphalengeal joints ) & the wrist joints and
affect the large joints hip , knee, atlantoaxial joint
- its erosive type of arythropathy
- occur in age 30-35 , more in females
-
The changes seen in plain radiograph :
1. Periarticular soft tissue swelling because the effusion of the inflammatory process into the
synovium and osteoporosis because the synovial hypertrophied
2. Joint space narrowing due to destruction of the articular cartilage by pannus
3. Bony erosions( early sign ) which occur initially at the joint margins which seen first
around the metatarso -or metacarpophalangeal joints ,proximal interphalangeal joints &
on the styloid process of the ulna , later , extensive erosions may disrupt the joint
surface
4. Ulnar deviation is usually present at this stage .with very severe destruction , the condition
is referred to as arthritis mutilans , similar changes are seen in large joints.
5. With severe disease , there may be subluxation at the atlantoaxial joint due to laxity of
the transverse ligaments which holds the odontoid peg against the anterior arch of the
atlas , atlantoaxial instability can be well demonstrated with MRI in lateral view
*** Other erosive arthropathies , such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis & HLA-B27
spondyloarthropathies which include psoriasis and Reiters disease , produce articular erosions.
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
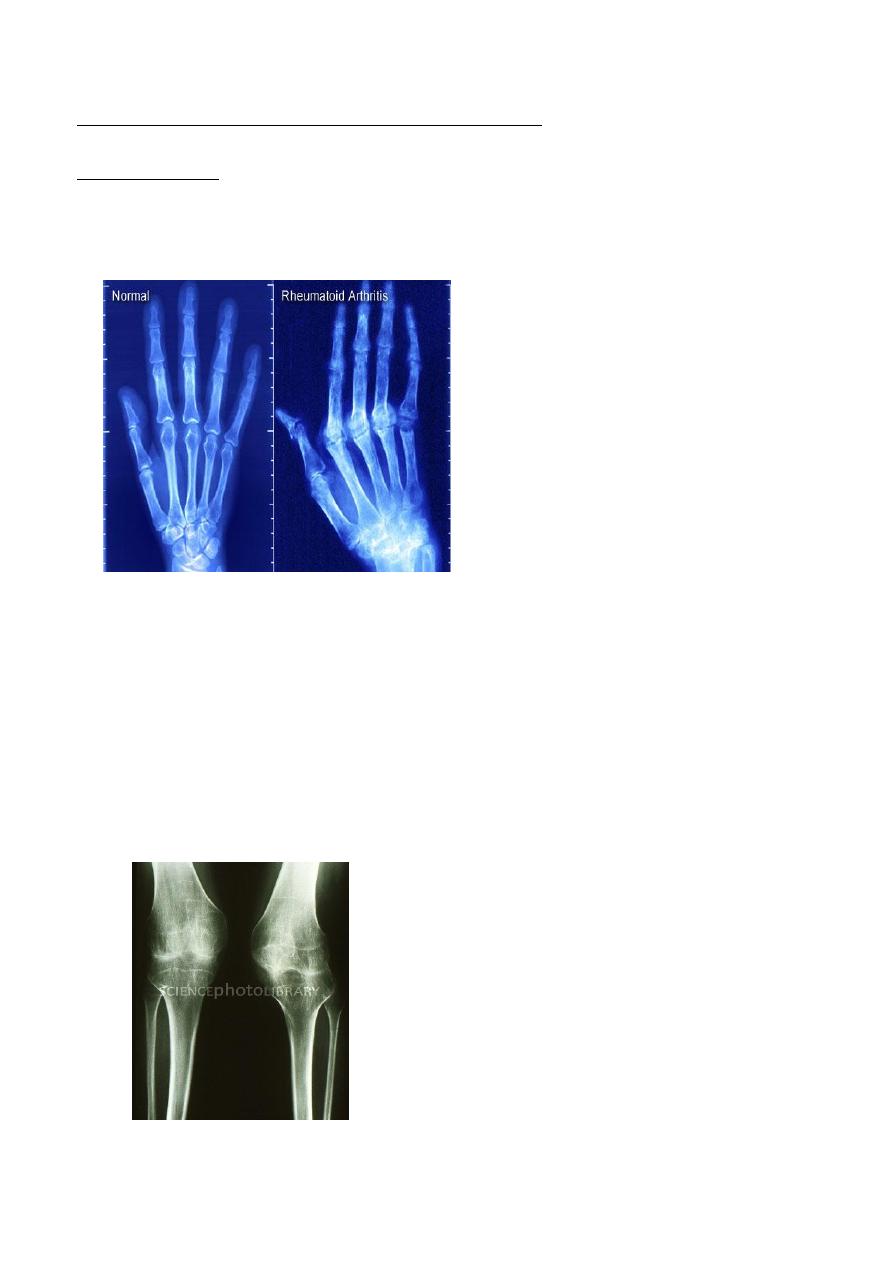
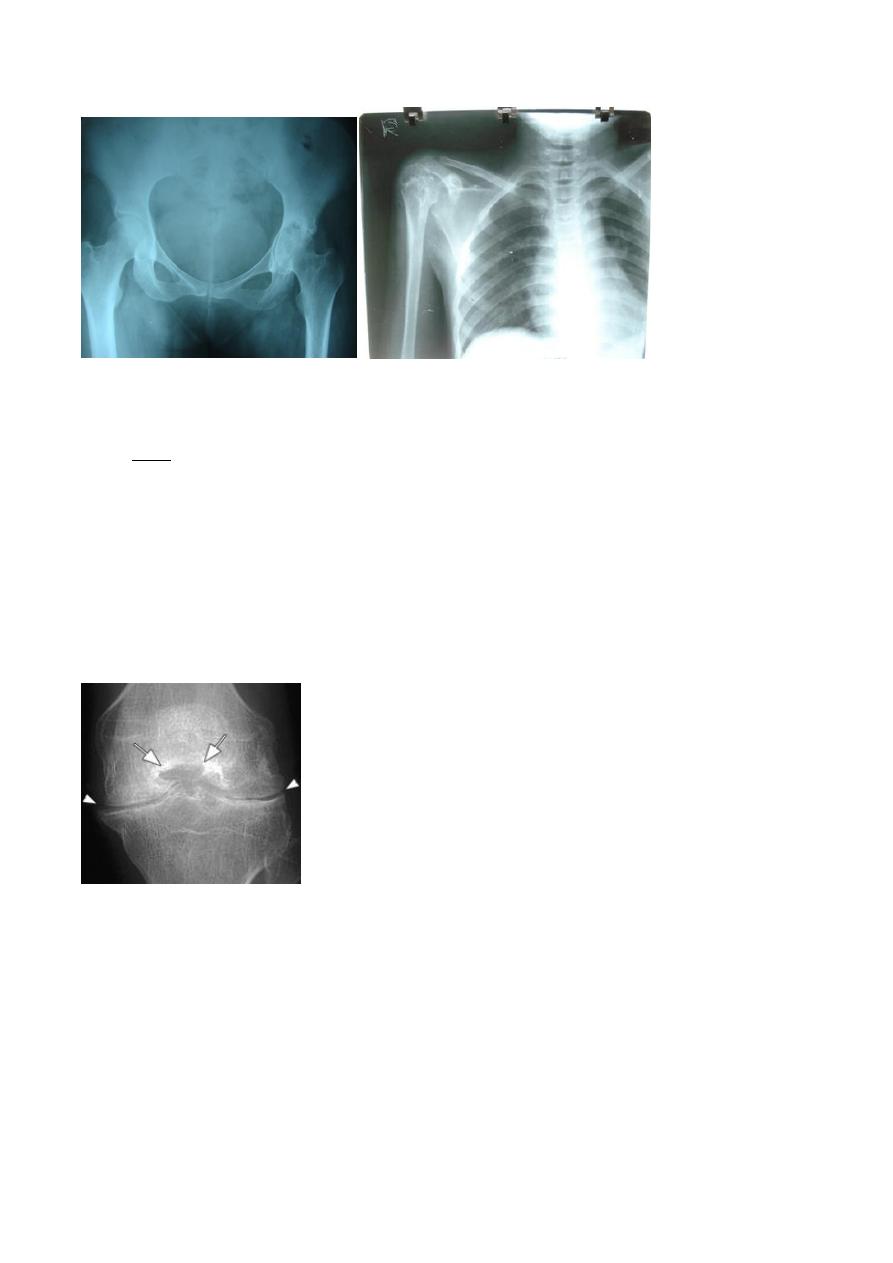
*** the narowing in the joint space afected uniformly and all the joint
The picture of pelvis
(above )
1. Completely oblitrated the joint space and bilateraly
2. Irregular distruction in both articular surfaces
3. Sclerosis
4. Protrudae acetabulae : subluxation an inner displacwement of acetabelum into elvis
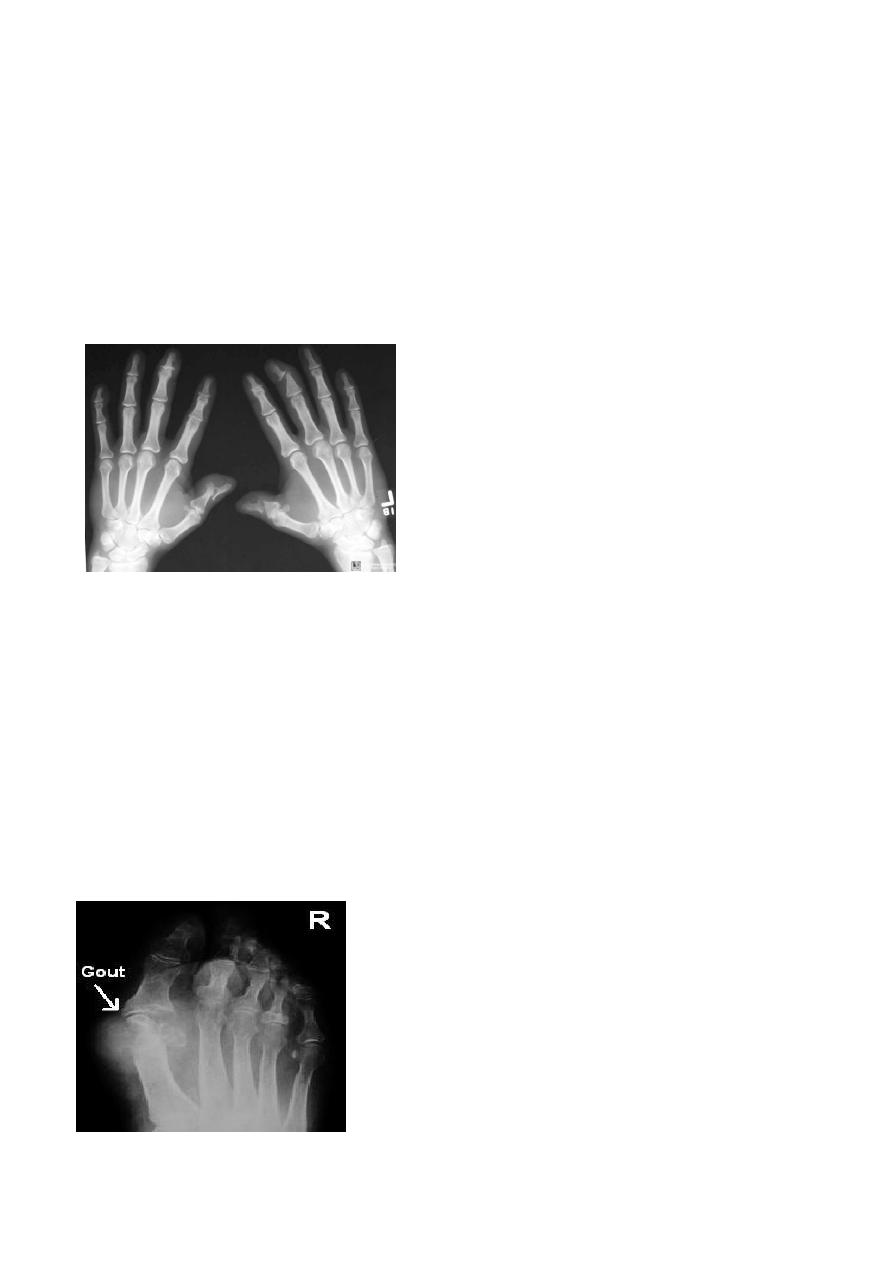
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
(still s disease ; juvenile chronic poly arthritis ):
- Shows many features similar to RA but erosions are less prominent .
- The knee , ankle and wrist are the joints most commonly affected .
- Signs :
- 1. No joint space , uniform
- 2. Localized type of osteoporosis
- 3. Diffuse narrouing in the joint
- 4. Subchondral sclerosis ( distruction in the articular surface )
- 5. Pre mature fusion of epiphyseal palate
- 6. hyperemia from joint inflammation from joint inflammation causes epiphyseal
enlargement
-
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
psoriasis erythropathy :
- There is an erosive arthreopathy
- predominant involvement of the terminal interphalangeal joints .
- Signs
- 1.narrowing
- 2. Destruction and erosion
- 3. Destruction and subluxation
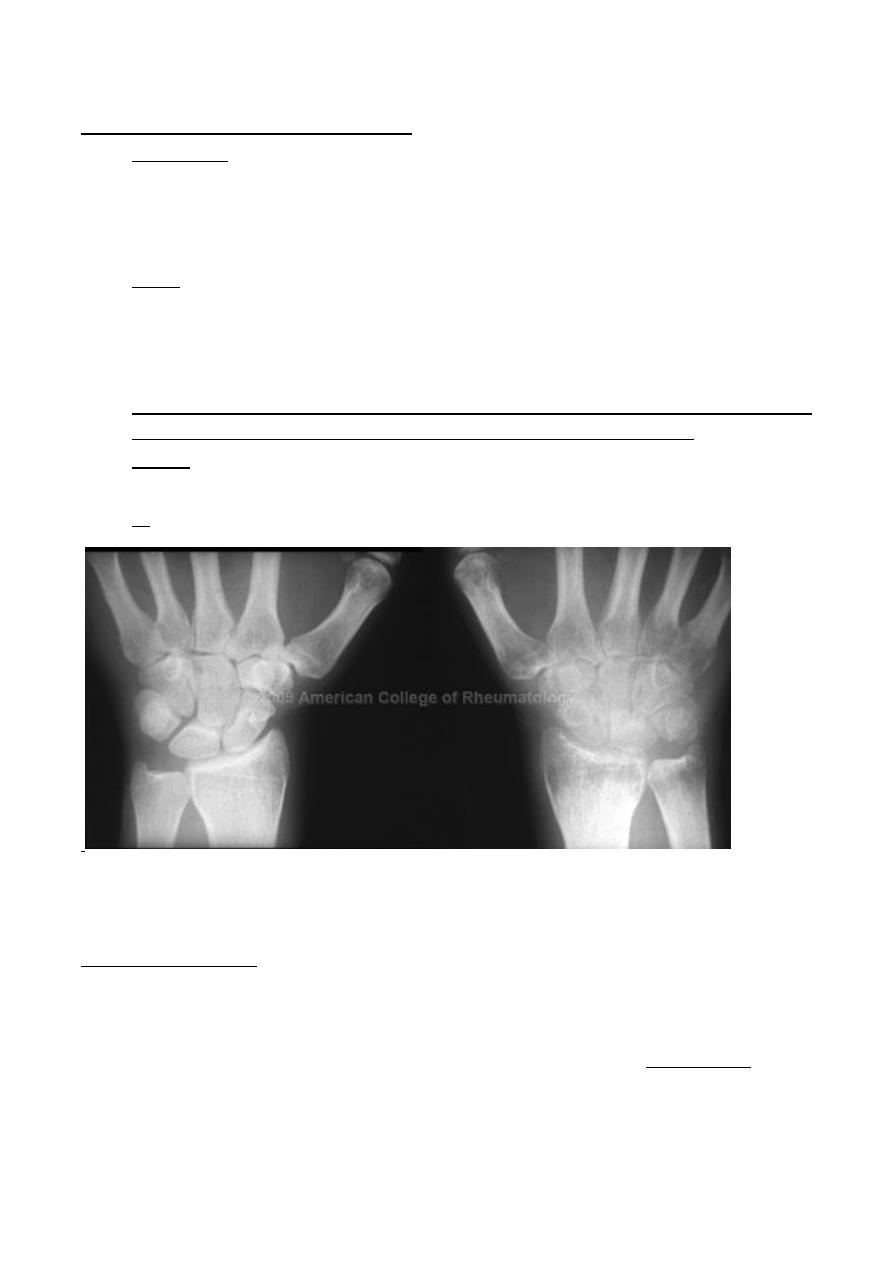
Gout :
- Erosive type
- In gout ,the deposition of the urate crystals in the joint & in the adjacent bone gives arise
to an arthritis which most commonly affects the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big
toe ,
- the radiological changes involving :
1.soft tissue swelling in early stages : swelling uniform
2 . erosions occur later in coarse of disease and may be at distance from the articular cortex
with well defined & often sclerotic edges , produced by deposition of urate crystals .
3 . no osteoporosis seen.
4 . localized soft tissue lumps caused by collection of sodium urate , aknown as tophi , which
may be large & sometimes showing calcification .( in late stages )
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
Pyogenic arthritis
: ( septic arthritis )
- Erosive type
- Usually caused by staphylococcus aureus ,
- there is rapid destruction of the articular cartilage followed by destruction of the
subchondral bone and soft tissue swelling seen around joint . Joint effusion is first sing
which can be detected by U/S , MRI is often performed if diagnosis is still in doubt
- Signs :
- 1. Soft tissue swelling
- 2. Localized osteoporosis
- 3. Narrowing in the joint space
- 4. Destruction
- It very progressive arthritis it may come from the adjacent soft tissue or its may be a blood
borne , pt, presented as toxic , very painful arthritis with severe osteoporosis
- Sites: wrist , knee , femur ,hip and can affect the spines and called (
spondyloductitis of the intervertebral disc
-
5. Boney outline erosion is irregular
Tuberculous arthritis:
- affect shoulder , Hip & knee joint are most commonly affected joints
- presentation: less painful late presentation, cant distinguish from other types only by Hx
- Radiological features :
1. Joint space narrowing
2. Erosions which may cause extensive destruction of the articular cortex
3. Severe osteoporosis (striking)
4. In later stages there may be gross disorganization of the joint with calcific debris near the
joint. By this sign can distinguish the tuberculos from pyogenic in addition to the sites
5. very large soft tissue swelling
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
Hemophilia & bleeding disorder :
- Site : knee
- Signs
- Arithroathy and swelling in the joint because of the bleeding
- Premature fusion of epiphyseal palate
- Enlargement of epiphysis
- In more advance disease : accumulation of hemosiderin in fibrocartilgenous structure and
cartilage and cause inflammatory reaction and result in diffuse narrowing in joint space
- Widening of the interchondaylar notch which is indirect sign that called that the epiphyseal is
very large so cause deepening in this notch
- Concave epiphysis and the epiphyseal palate fuse prematurely .
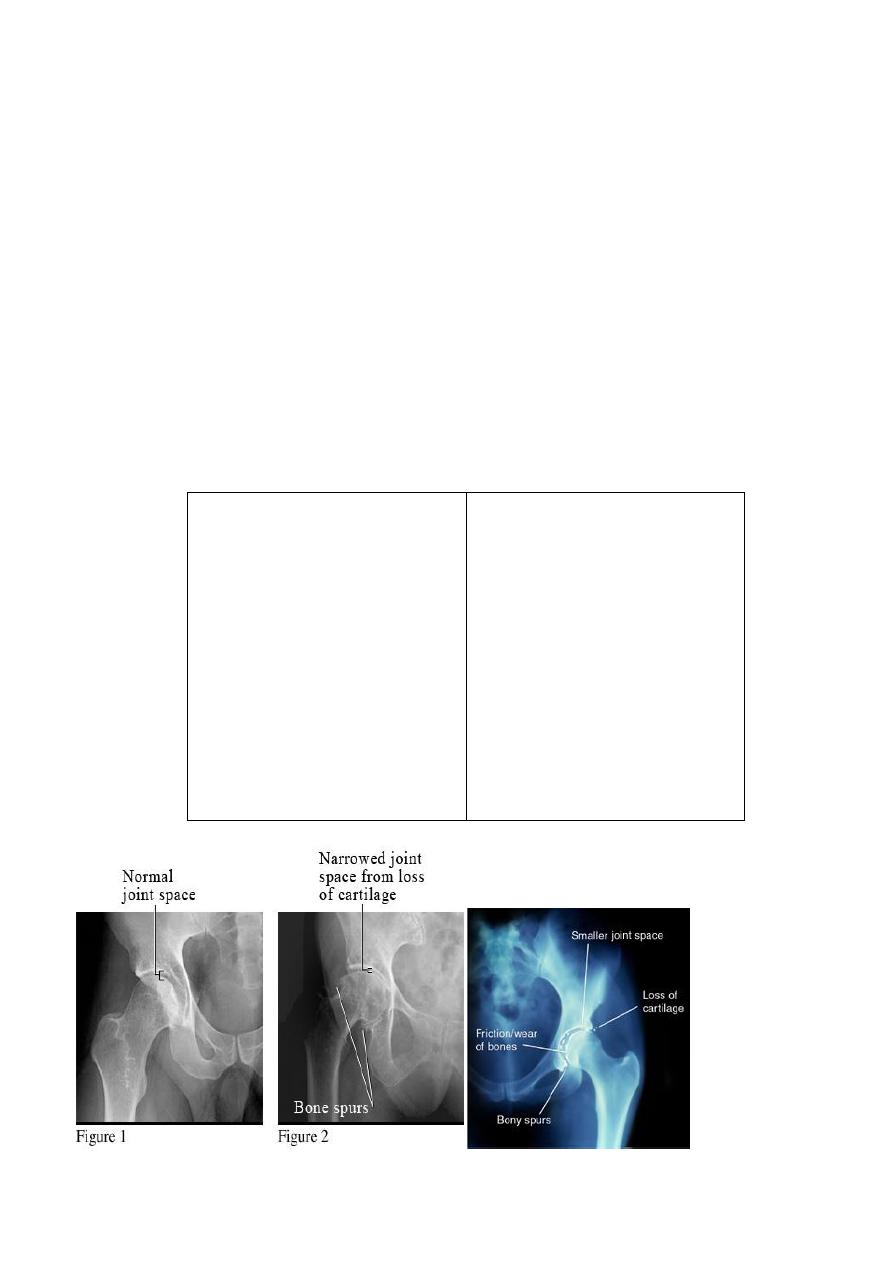
Osteoarthritis :
- OA is the commonest form of arthritis , resulting from wear & teat of the articular
cartilage .
- Occur in older age group
- the hip & knee are frequently involved , the wrist joints of the hand and
metatarsophalngeal joints of the big toe are also frequently involved. the most sites
affected : the joints that applied to high load
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
Features seen in OA :
1. not erosive , in high loaded articular areas so damage to articular cartilage
2. joint space narrowing : with loss of joint space is maximal in the weight bearing portion
of the joint e.g in the hip it is often maximum in the superior part of the joint whereas
in the knee it is the medial compartment that usually narrows
3. Osteophytes are bone bony spurs , often quite large which occur at the articular margin
4. Subchondral sclerosis :increase density of joint below area of narrowing with time it collapse
, usually occur in both side of the joint , occur in most advance areas
5. Subchondral cysts may be seen beneath the articular cortex often in association with
sub chondral sclerosis ,
***RA & OA are the two types of arthritis most commonly encountered , they show many
distinguishable features which listed in the following table :
0A RA
1.joint space narrowing uniform.
2. Erosions a characteristic feature.
3. not a feature but erosion enface
may mimic cysts.
4. sclerosis is not a feature unless
there is secondary OA.
5. osteoporosis often present .
1.joint space narrowing maximal at
weight- bearing site.
2. erosions don’t occur but
crumbling of the joint surface may
mimic erosions.
3.subchondral cyst may be seen.
4.sclerosis is a prominent feature.
5. no osteoporosis.
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
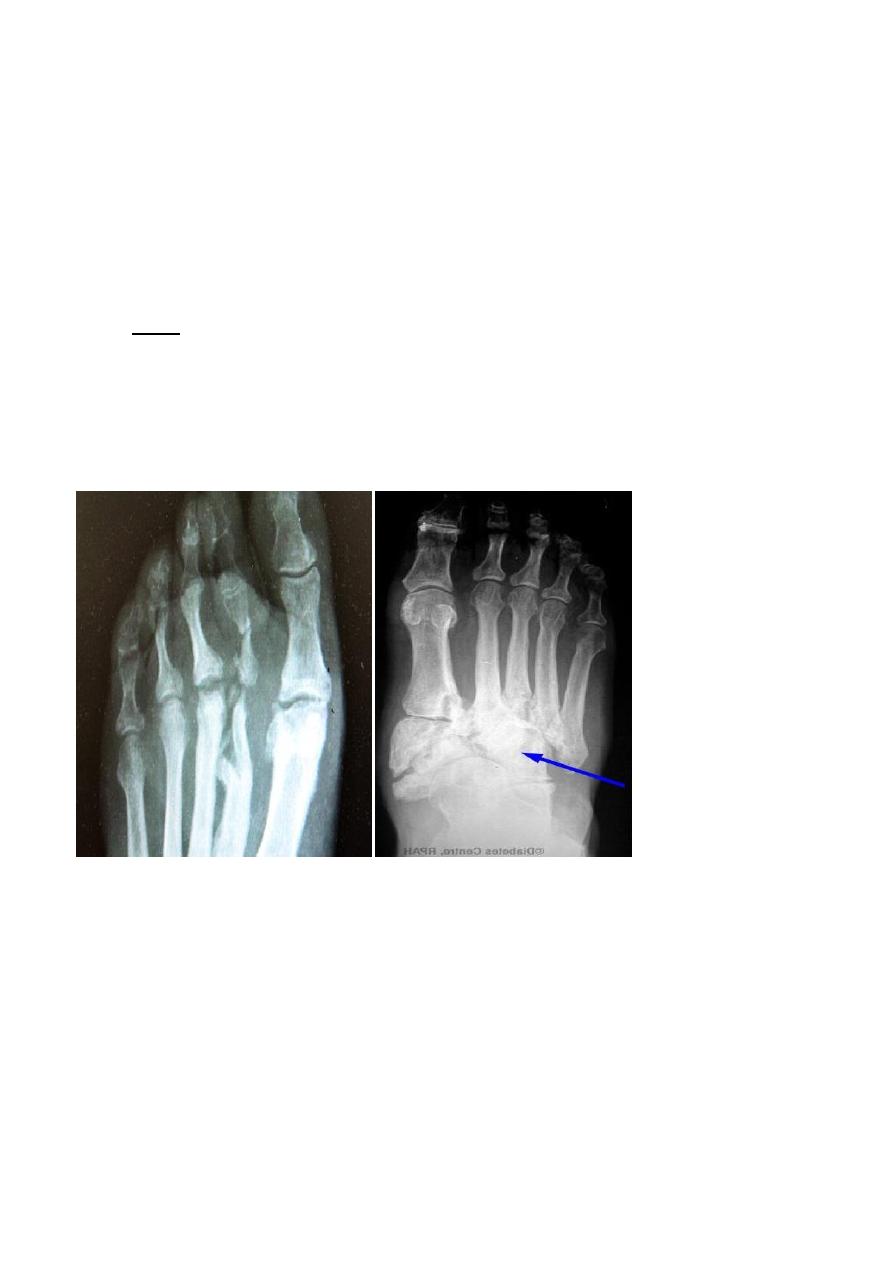
Neuropathic joint :
- Changes are seen in the feet of diabetics with peripheral neuropathy .
- Called neuropathic joint or charcot joint
- The predominant features is resorption of the bones ends and calcification of the arteries
in the feet is often present.
- There may also be bone destruction due to infection .
- Diagnosing osteomylitis in the bones of the feet in diabetic patient can be difficult because
bone destruction can be due to neuropathy ,or to a combination of the two.
- Signs ;
- Resorption and damage of distal bones but irregular . how can differentiate it from OA >? By
history and MRI in sometimes
- Reduction in bone density
- Joint destruction
- Damage in all peripheral terminal bones , irregular eroded
- Metatarsal-phalangeal joint : destructed , sublux , damage
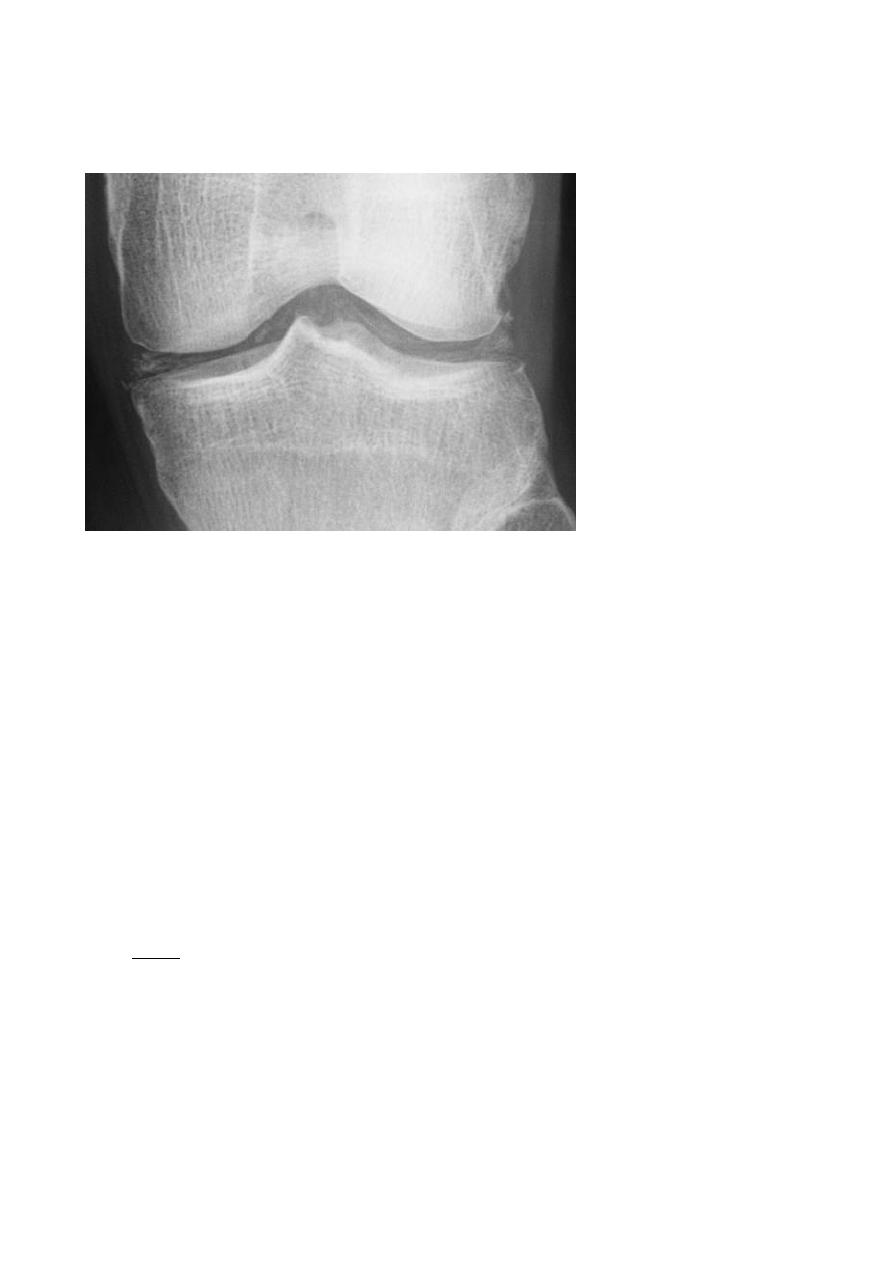
Calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate (CPPD ) crystal deposition disease :
- In this condition there is deposition of CPPD crystals in internal fibro-cartilaginous
structure in all joints
- manifested by chondrocalicinosis , which is a descriptive term for calcification occurring
in articular cartilage , most frequently affected the knee joint ,calcification seen in
fibrocartilage of the mensci as well as articular cartilage ,
- CPPD deposition can give rise to arthritis which clinically simulating gout so the
alternative name is pseudo gout, but chondrocalcinosis is often an incidental
asymptomatic finding .
- Increase the density in the internal structure which are normally translucent
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
- Cause little pain
- Predisposing to early OA changes( 45 Yrs )
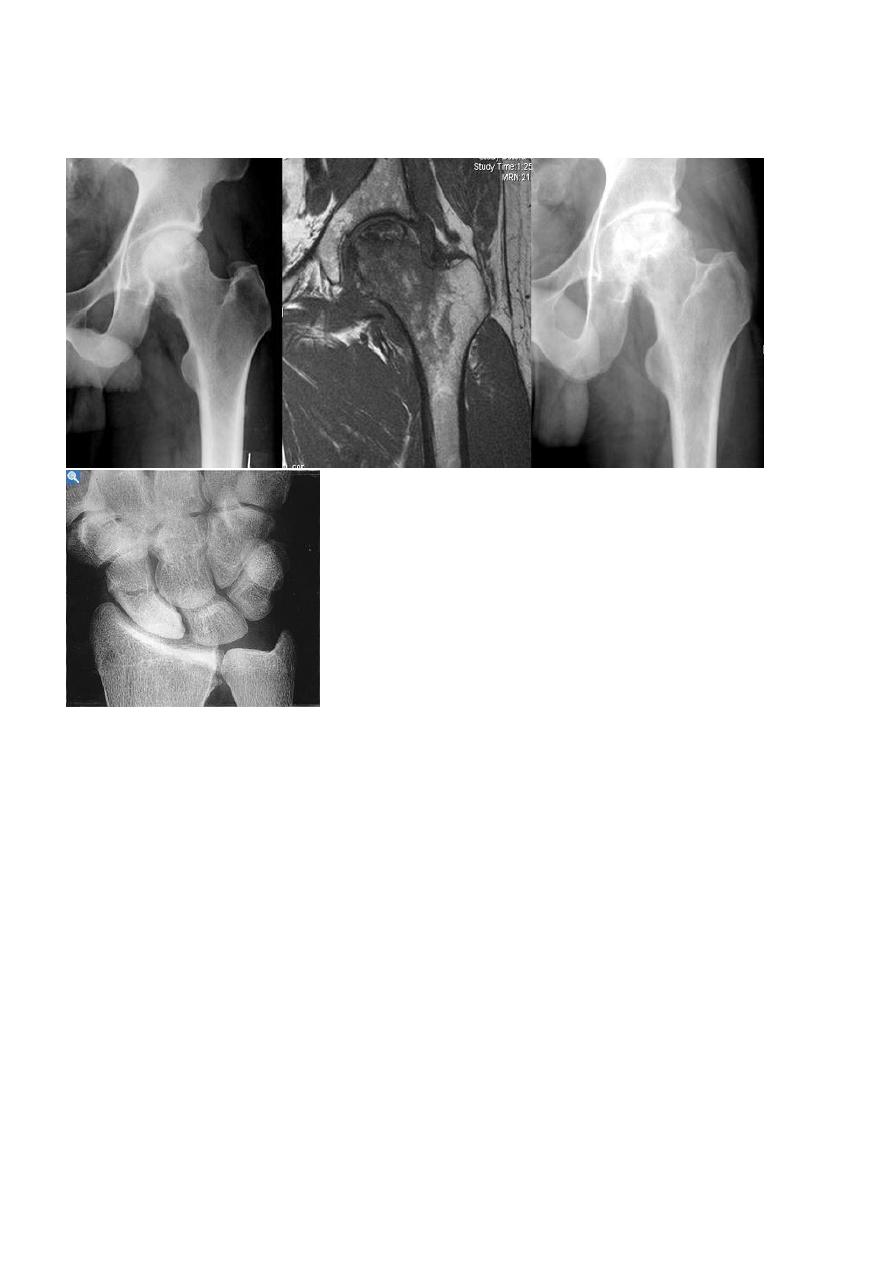
A vascular ( a septic ) necrosis :
- Avascular necrosis , also known as osteonecrosis , is where there Necrosis occur in bone
ends in intraarticular secondary to due to interruption of the blood supply . It occur most
commonly in the intra articular portions of the bones , is associated with following
conditions :
Steroid therapy .
Collagen vascular disease.
Radiotherapy .
Sickle cell disease .
Exposure to high pressure environment e.g tunnel workers & deep-sea divers ( caisson
disease ) .
Fracture.
- Sites : hip and scaphoid bone ( in waist )
- Signs :
- Increase density of the subchondral bone with irregularity of the articular contour or
even fragmentation of the bone with epiphyseal collapse .
- Characteristic crescentic lucent line may be seen just beneath the articular cortex.
- Articular cartilage space is preserved until degenerative changes super even.
- in sub capital fracture of the femoral neck & fracture through the waist of the scaphoid
bone , the femoral head & proximal pole of the scaphoid become fragmented & dense
due to the ischemia .
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
MRI is imaging modality of choice for demonstrating a vascular necrosis and may show changes
at time so early when radiograph may be normal .
Osteochondritis
A group of conditions , in which no associated cause for a vascular necrosis can be found . but
the osteochondritis are now regarded as being due to impaired blood supply associated with
repeated trauma .
Perth's disease :
A vascular necrosis of the femoral head in children , is the most important example of the
osteochondritis .
the plain radiograph changes :
1.The earliest change is increase in density and flattening of the femoral epiphyses which later
on progress to collapse & fragmentation .
2. metaphysis widened & consequently the femoral neck enlarge and may contain small cyst .
3.Joint space is widened but the accetabulum not affected .
4.With healing, the femoral head reforms but remain permanently flattened & therefore responsible
for OA in later life .
Freibergs disease :
A vascular necrosis of the metatarsal heads.
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
Kohlers disease :
A vascular necrosis affecting the navicular bone of the foot.
Osgood- schlatters disease :
Avascular necrosis of the tibial tuberosity .
Kienbock disease :
Affecting the lunate bone in the wrist .
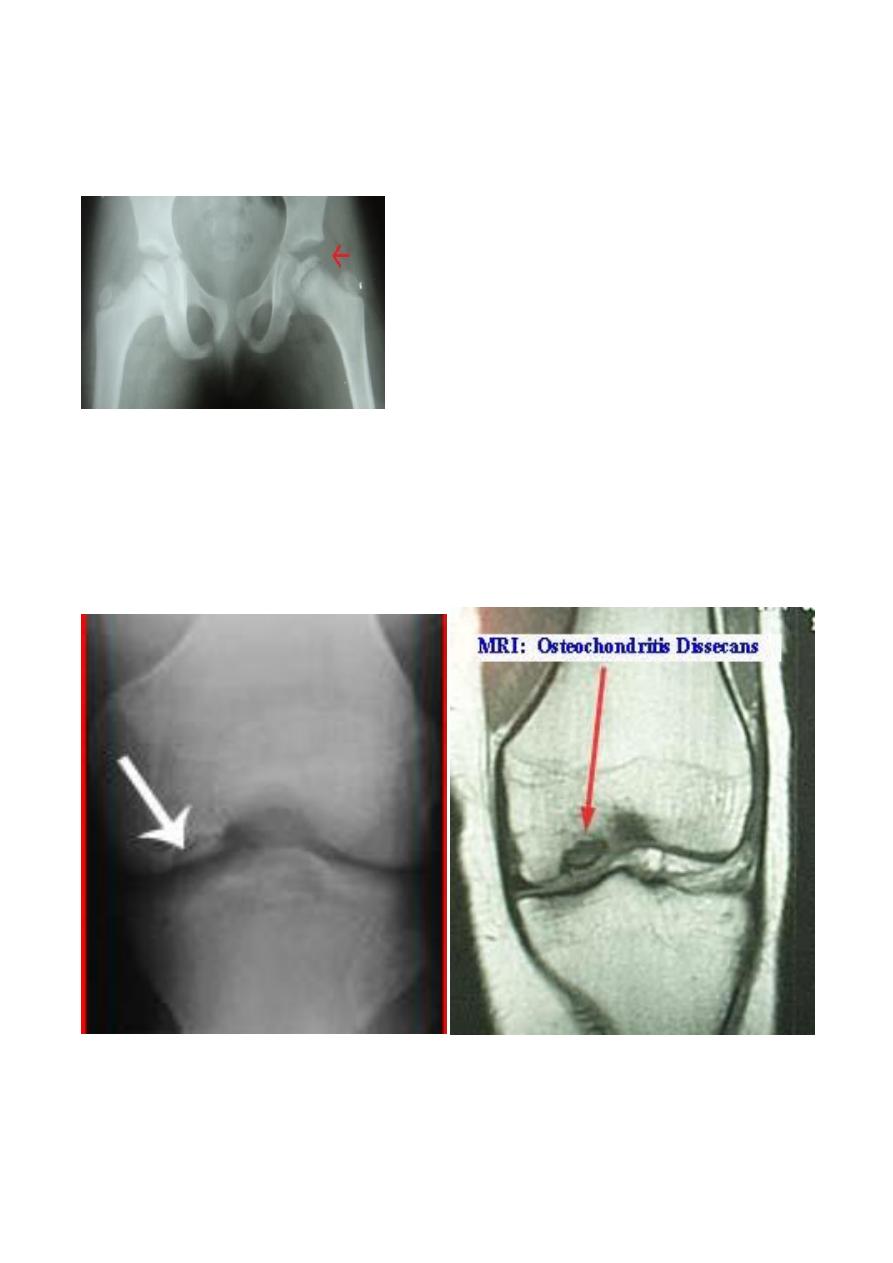
Osteochondritis dissecans :
- It is localized form of the a vascular necrosis ,
- small fragment of bone becomes separated from the articular surface of a joint leaving a
defect , and the bony fragment can often be detected lying free within the joint ,
- this condition occur most frequently in the knee & ankle joints , DX can be established by
plain film , but MRI & CT are excellent imaging methods.
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
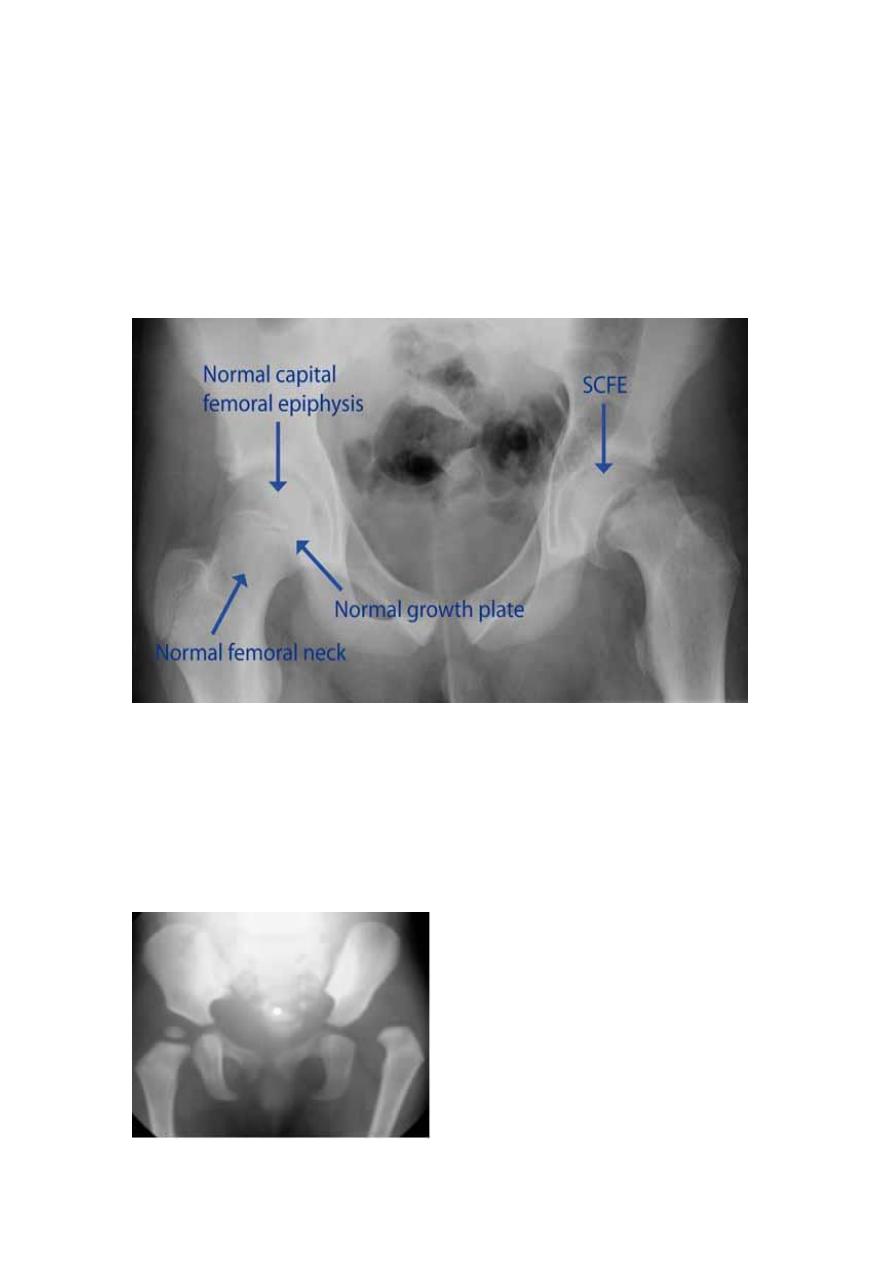
Slipped femoral epiphysis :
- Occurs between the age of 9 and 17 years ,
- and may present with pain in the hip or pain referred to the knee .
- the epiphysis slips posteriorly from normal position it is best appreciated on a lateral film of
the hip ,
- with a greater degree of slip , the condition can be recognized on the frontal view as down ward
displacement of the epiphysis .
-
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH ) :
- Referring to the dislocation or subluxation of the hip in infant .
- Best imaging modality is U/S as the head still cartilaginous
- in this age group not seen in plain film , but later in life condition is easier to DX by plain
film
- the features are lateral and upper displacement of the head of the femur, increased slope to
the acetabular roof is sometimes seen .
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
Scleroderma :
May cause calcification and atrophy of soft tissues of the hands with loss of the tips of the terminal
phalanges .
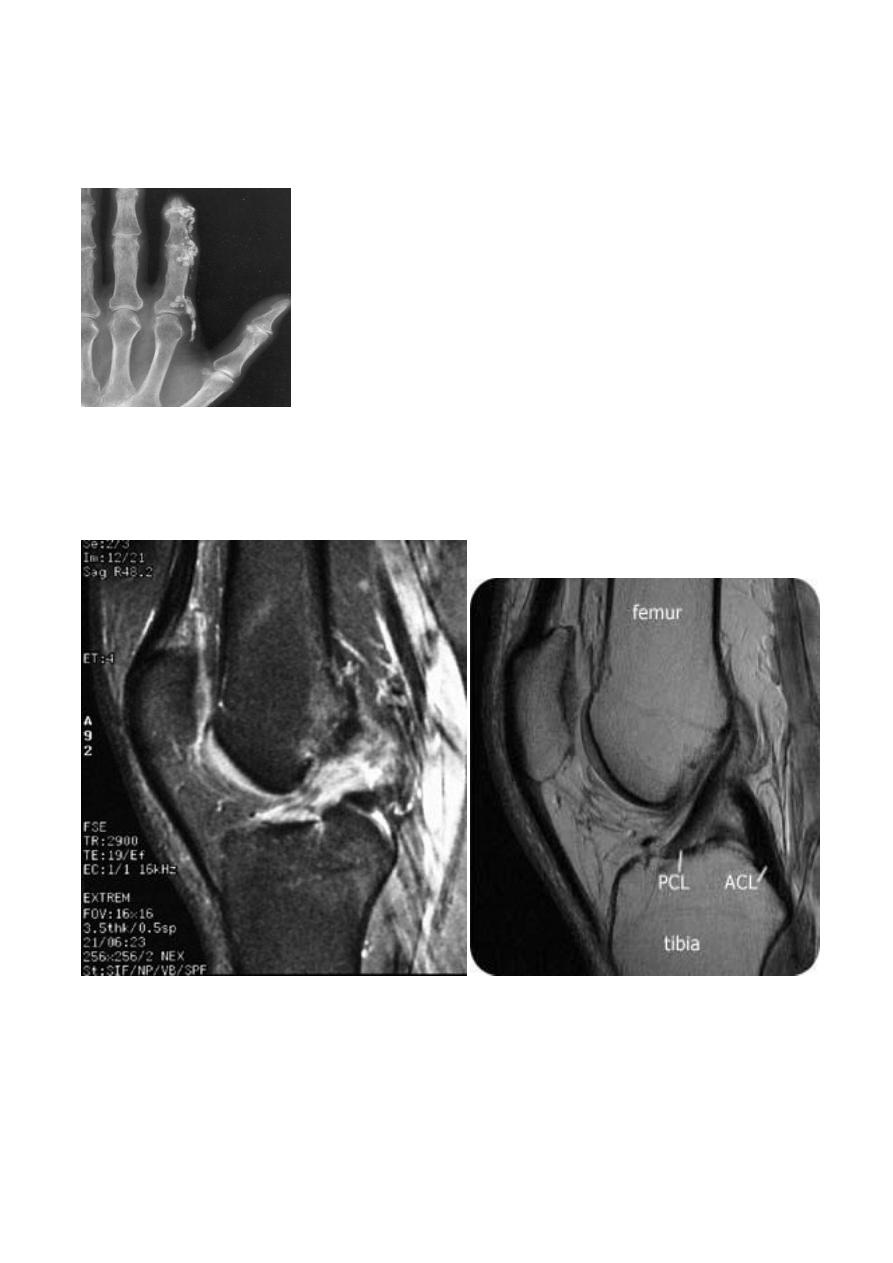
Internal derangements of the knee joint:
Most knee injuries produce soft tissue damage , notably meniscal or ligamentous tears ,either
alone or in conjunction with bony fracture . Plain film examination can only demonstrate the state of
bones and show an effusion , MRI is the best imaging modality for detecting internal derangement ,
and assessed menisci , cruciate ligaments , collateral ligaments .
Radiology L:3 د.نجالء
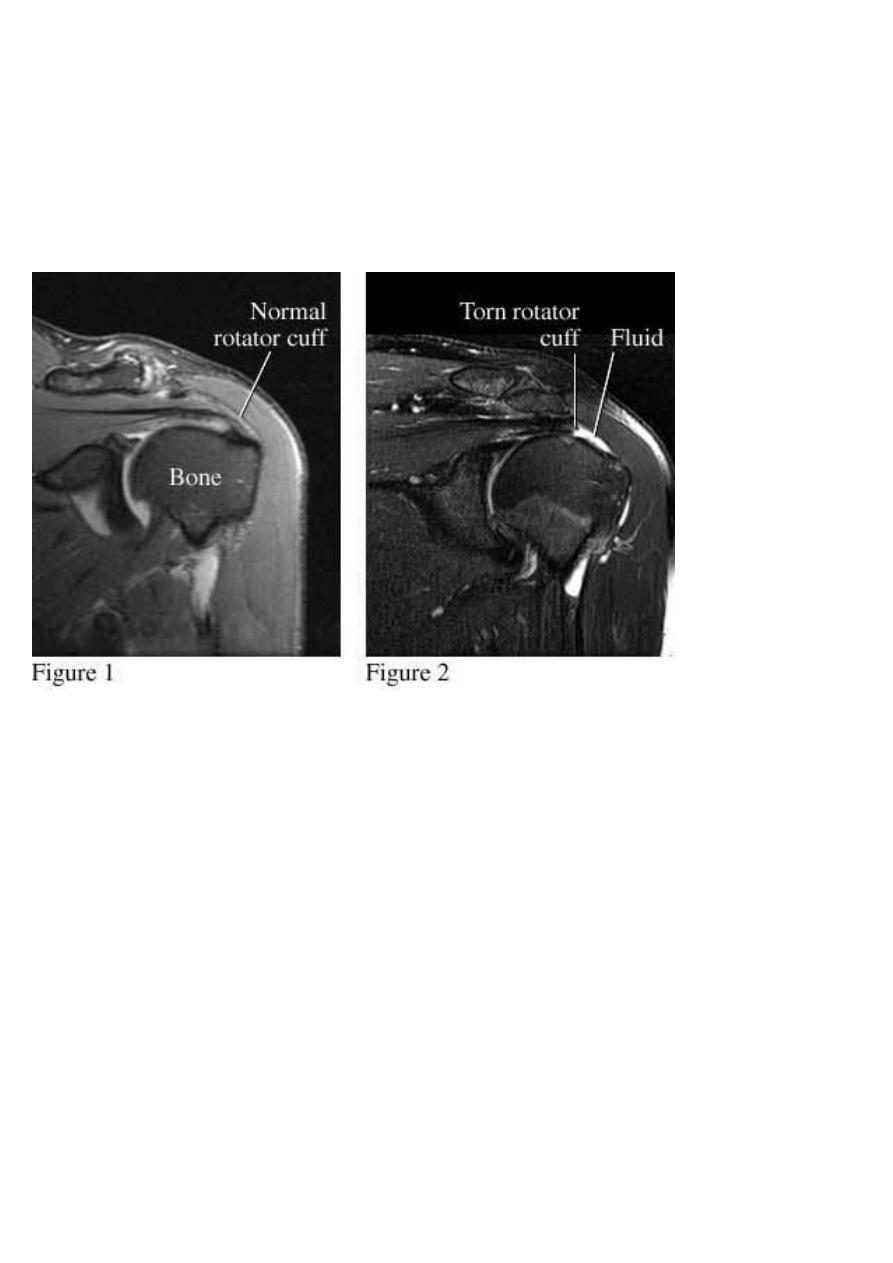
Shoulder rotator cuff degeneration /tear:
Is best evaluated by MRI , showing supraspinatus tear with high sensitivity , the low signal of
the supraspinatus tendon is interrupted by the higher signal of fluid , and in complete tears it may
be possible to see the retracted ends of the torn tendon-muscle junction .
Noor Rahman
