Assistant Professor
Dr.Khudair Al-bedriConsultant Rheumatology & Internal Medicine .
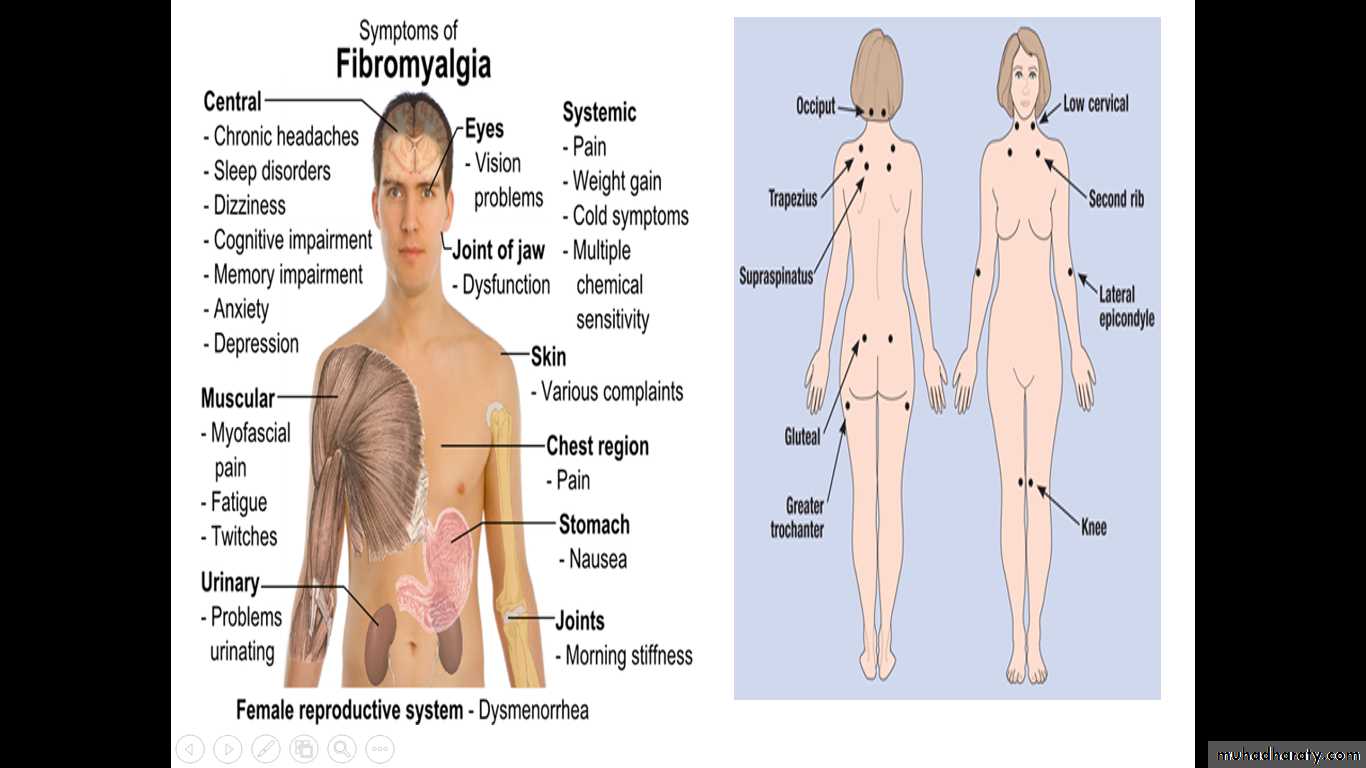
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a syndrome of chronic pain and the presence of hyperalgesic points at specific anatomical sites ,as well as a range of other physical and psychological symptoms with no identifiable organic cause .FAST FACTS
. Fibromyalgia affects two to four percent of people , mostly women ..Doctors diagnose fibromyagia based on all the patients relevants symptoms (what you feel ), no longer just on the number of tender points .
. There is no test to detect this disease , but you may need lab tests or X-ray to rule out other health problems.
.Though there is no cure ,medications can relieve symptoms.
.Patients also may feel better with proper self-care ,such as exercise and getting enough sleep.
Aetiology
Two abnormalities have consistently been reported:1-Sleep abnormality: Delta waves are distruption ( characteristic of the deep stage (4) of non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep, which usually occurs in the first few hours and is thought to have primarily a restorative function..
People with fibromyalgia have reduced delta sleep.
Aetiology
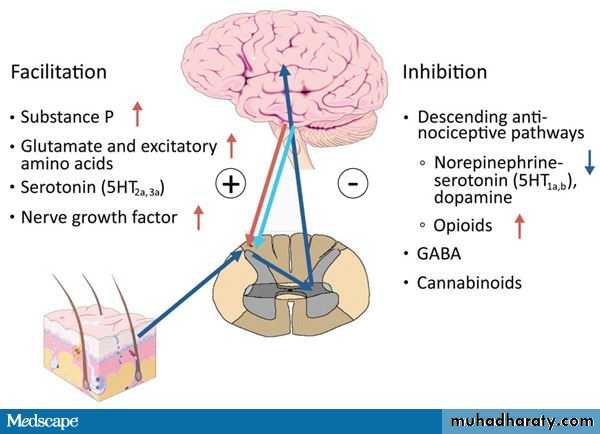
• 2-Abnormal pain processingA reduced threshold to pain perception and tolerance at characteristic sites throughout the body is a central feature of fibromyalgia
Aetiology
Affected people also have:-
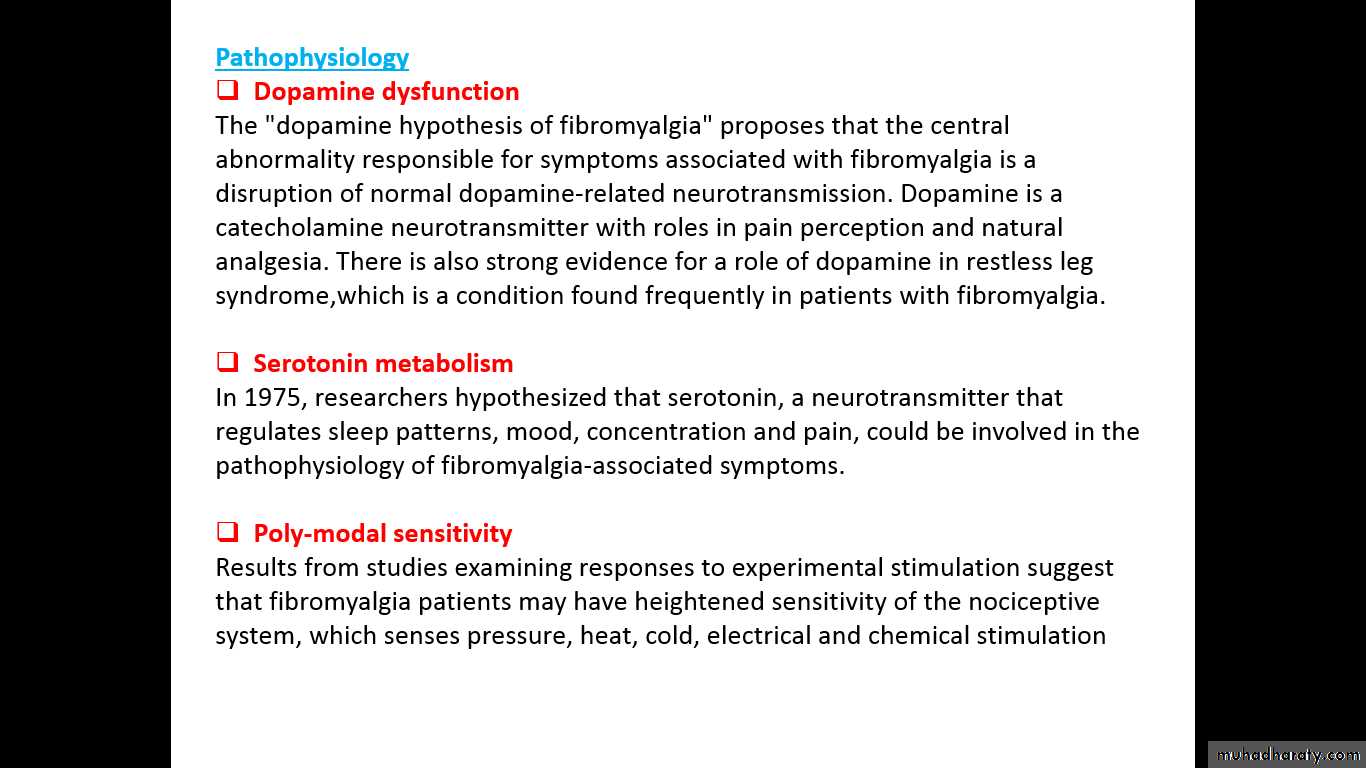
1-Abnormal levels of neurotransmitters :-
A- Substance P is increase .
B- Nerve growth factor is increase .
C- Serotonin is low .
All above in neurotransmitters changes reducing pain threshold.
Aetiology
2- fibromyalgia have reducing hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (HPA) response to stressThe main HPA abnormalities in FMS are:-
-Low free cortisol levels in 24 h urine samples.
-Loss of the normal circadian rhythm with elevated evening cortisol level.
-Insulin-induced hypoglycaemia associated with an overproduction of pituitary ACTH.
-Low levels of growth hormone .
-Reduce adrenal release of glucocorticoids in response to ACTH stimulation.
Pathophysiology
The cause of fibromyalgia is poorly understood but abnormal central and peripheral pain processing is thought to be responsible for reduced pain threshold , hyperalgesia (amplification of pain ) and allodynia (pain produced by a non-noxious stimulus).Epidemiology and risk factors
The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the general population is approximately 2-4%,but it is a condition that is underdiagnosed.
The incidence of fibromyalgia in primary care in the UK is approximately 14 700 new cases per year .
There are recognized risk factors for fibromyalgia but they only contribute approximately 5-10% to disease development (Table 1).
Risk factors for fibromyalgia
Table 110 x more common in women than men .
GenderMore common in individuals aged 20-50 .
Age
For example whiplash type injuries to the neck and trunk.
Physical trauma
Stress , anxiety and depression .
Psychological trauma
May occur as a post-viral syndrome.
Viral infections
Diagnosis
A full social ,personal ,family and psychological history should be taken to reveal any past physical disturbance .FMS PAIN IS NOT ARTICULAR.
The most widely accepted set of classification criteria for Dx of FMS, the ACR 1990, define fibromyalgia according to the presence of the following criteria:
A history of widespread pain lasting more than three months.
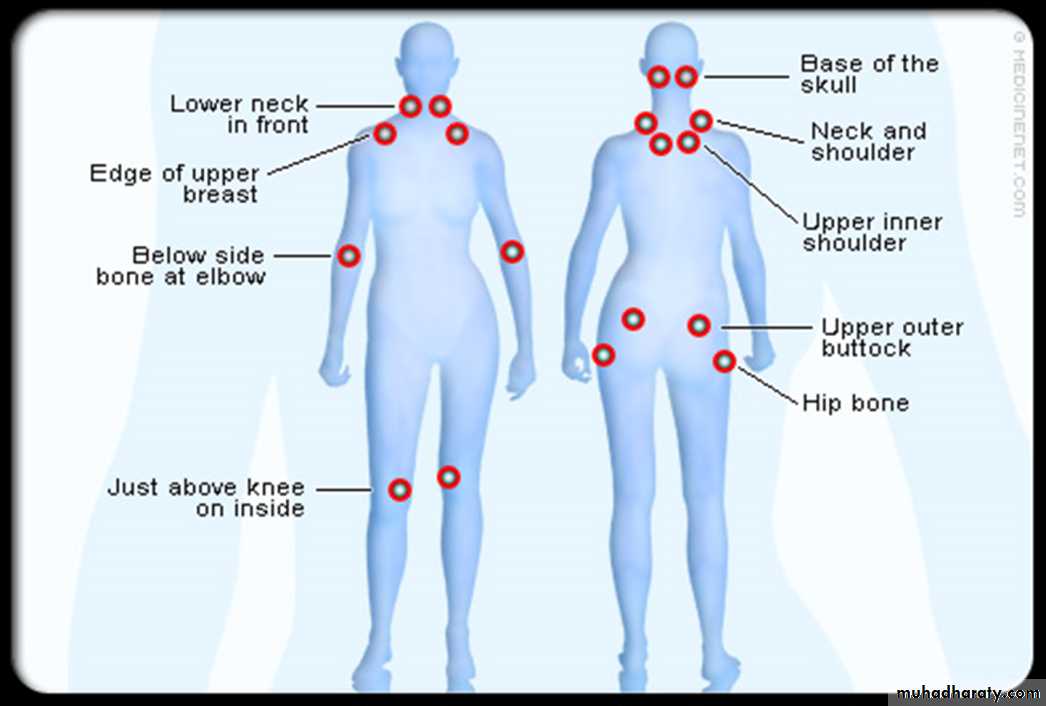
Tender points—there are 18 designated possible tender points
Diagnosis
Tender points .
Examination disclosed
Widespread pain ,above and below the waist as well as the axial skeletal system ,for at least 3 months.The presence of 11/18 tender points .
Digital palpation using the thumb to assess tender points. The pressure applied should be just enough to blanch the examiner’s thumb nail . In the absence of fibromyalgia , the palpation would not be enough to cause pain .
Diagnosis of FMS
ACR 2010 replace the tender point count Widespread Pain Index(WPI) and Symptom Severity Scale(SSS).In the WPI patients asked to indicate the regions (maximum 19 regions ) of the body has been experience during the past week,and each positive regions given a Score of 1(WPI rangs from 0-19).
SSS is the sum of the severity of the three symptoms (fatigue ,waking unrefreshed ,cognitive symptoms) plus the extent (severity) of somatic symptoms in general, SSS Score 0-3(0 =no problem ,1= mild, 2=moderate ,3= severe problem ) .
A patient satisfies the criteria for FMS if the following conditions are met. WPI>7 and SSS>5 , or WPI 3-6 and SSS >9.
Investigation revealed
Blood test normalHaematology .
Biochemistry.
Immunology.
Imaging normal
Differenational diagnosis
Hypothyroidism.
Polymyalgia rheumatic.
Polymyositis.
RA .
SLE.
Osteomalacia.
Management
General points :Pain and function should be assessed in a psychosocial context.
Access to a multidisciplinary team with treatments taking into account the patient’s needs including pain intensity , function ,depression , fatigue and sleep disturbance.Non-pharmacological treatment
Can improve pain and function with or without exercise.Heated pool treatment
Individually tailored exercise programmes which include aerobic training and muscle strengthening.
Exercise programmes
A form of psychotherapy that is based on scientific principles that help people change the way they think , feel and behave.
Cognitive behavioural
Therapy (CBT)
Relaxation , rehabilitation , physiotherapy and psychological support.
Others
Pharmacological treatment
A moderate opioid which is recommended for pain management.
Tramadol
Paracetamol and weak opioids such as codeine can also be considered .
Mild pain reliefReduce pain and improve function e.g. fluoxetine , amitriptyline and duloxetine.
AntidepressantsDuloxetine and Minaciprans .
Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitorsRelatively new treatment which reduce pain.
α2 agonists eg ,gabapentinPregabalin