Effect of parasympathomimetics on gland secretion
ByPharmacist
Salwan Salem
8-11-2015
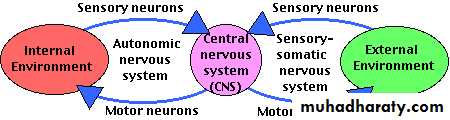
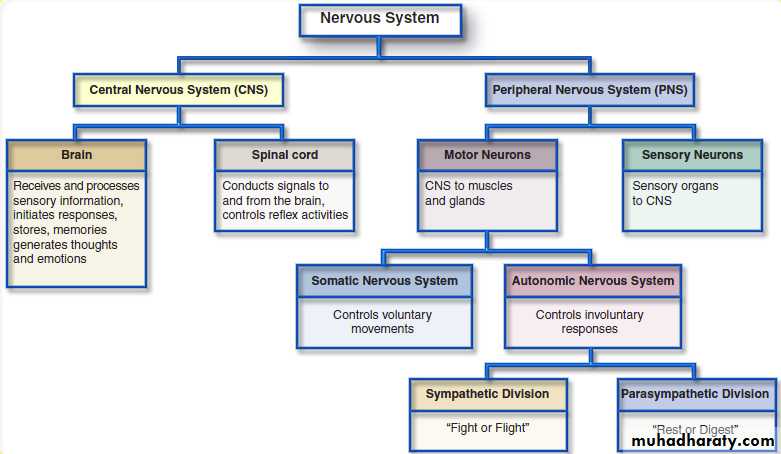
-Central nervous system (CNS)
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS)*CNS: spinal cord and brain
*The PNS consists of:sensory neurons running from stimulus receptors that inform the CNS of the stimuli
motor neurons running from the CNS to the muscles and glands - called effectors - that take action.
Nervous system
* PNS subdivided into :
Autonomic , and somatic
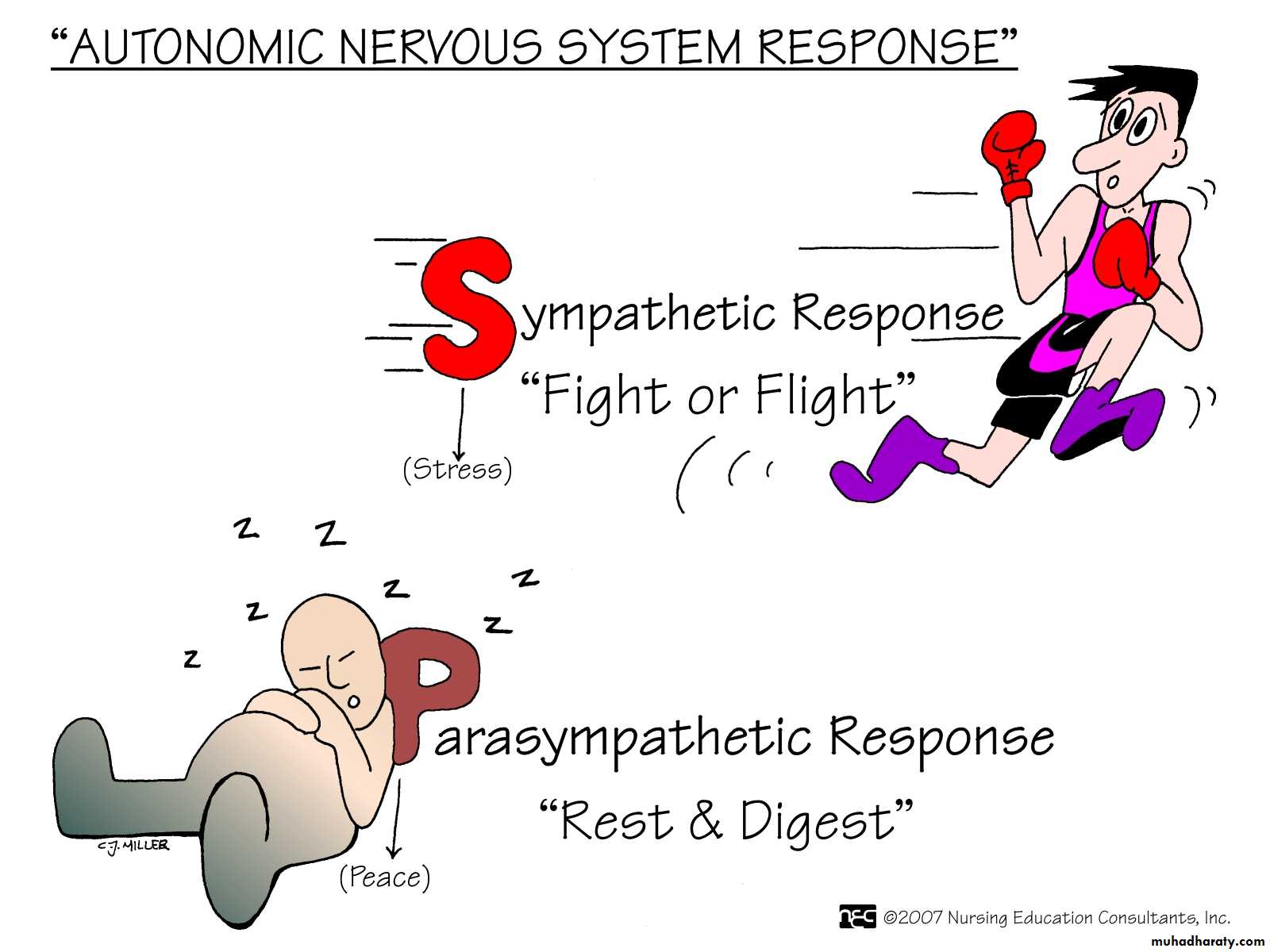
Autonomic NS :
- sympathatic neurons (thorasic and lumbar part of spinal cord)- Parasympathatic neurons (cranial and sacral part of spinal cord)
1.Cardiovascular system :
-ve chronotropic effect-ve inotropic effect
.Decrease SA and AV conductivity
.Increase IC Ca by phosphatidy inositol system
.Production of NO from arginine in endothelial cells
Pharmacological action of Ach
2. GIT:
Increase peristalsis , tone ,circulation , increase secretion , nausea and vomiting3.Urinary tract :
Increase contraction of detrusor muscle of bladder
4. Eye miosis , and decrease IOP
5.Exocrine glands :
Increase secretion of lacrimal , salivary ,and digestive .
6.Respiratory system :
Bronchial constriction , tracheobronchial secretion
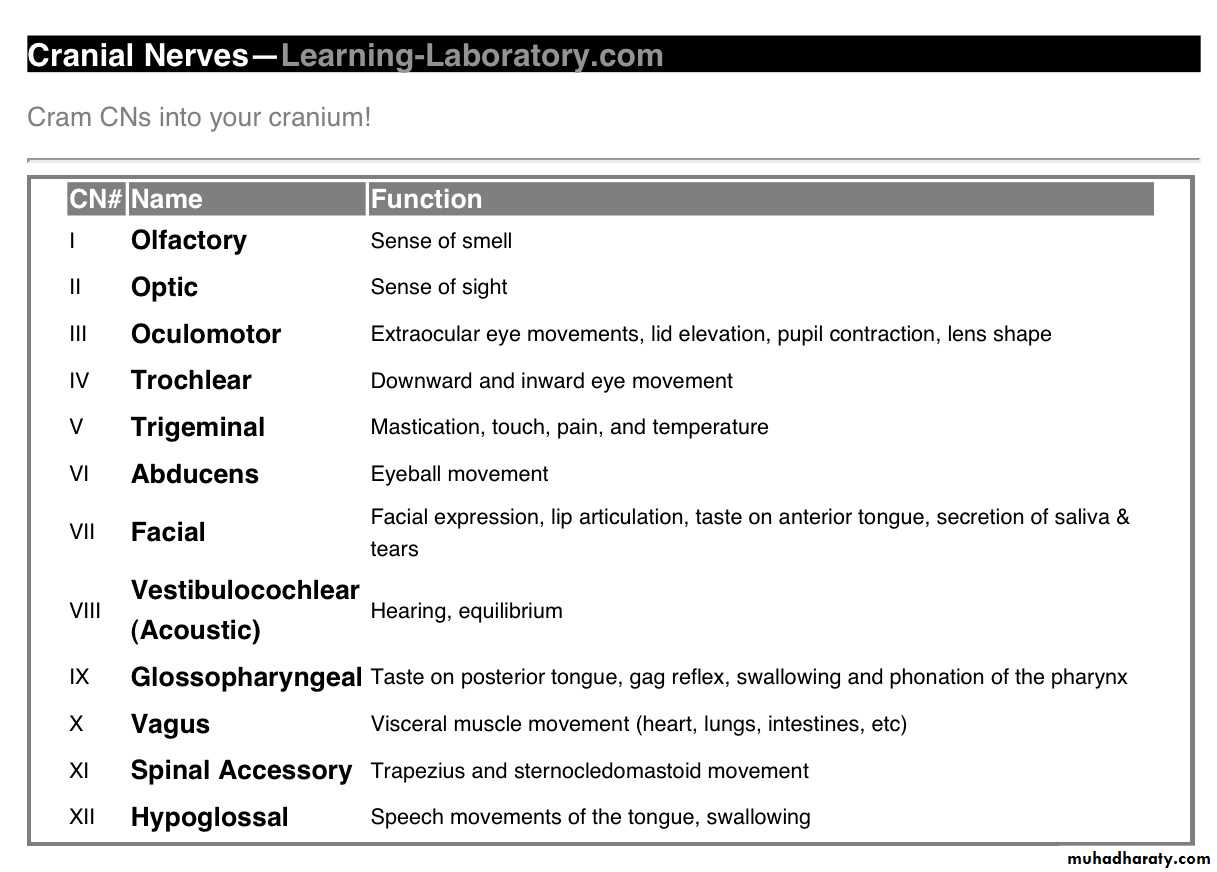
• The Cranial Nerves
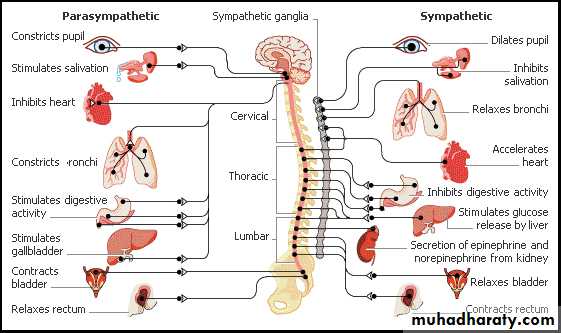
•slowing down of the heartbeat
lowering of blood pressureconstriction of the pupils
increased blood flow to the skin and viscera
peristalsis of the GI tract
Parasympathetic stimulation causes :
are neuron receptor that signal for muscular contractions . They are cholinergic receptors .-NR found in :
1-NMJ
2-Autonomic ganglia
3-Adrenal medulla
4-ligand gated ion receptor
Nicotinic receptor agonist is nicotine .
NR Blocked by tubocurarine and doxacurium .
Cholinergic receptors :Nictonic receptors (nAch R)
Types of MR:
M1 : in CNS , Gastric parietal cellsM2: heart
M3: exocrine gland , smooth muscle, bronchia ,bladder , sweat and salivary glands.
M4 and M5 : in CNS , but function not fully understood .
Muscarinic receptors (mAch R)
1.Cardiovascular system :
-ve chronotropic effect
-ve inotropic effect
.Decrease SA and AV conductivity
.Low dose … V.D and tachycardia
.Increase IC Ca by phosphatidy inositol system
Production of NO from arginine in endothelial cells
Pharmacological action of Ach
2. GIT:
Increase perstalsis , tone ,circulation , increase secretion , nausea and vomiting3.Urinary tract :
Increase contraction of detrusor muscle of bladder
4. Eye miosis , and decrease IOP
5.Exocrine glands :Increase secretion of lacrimal , salivary ,and digestive .
6.Respiratory system :
Bronchial constriction , tracheobronchial secretion
. Direct acting
. Indirect actingA -Direct acting :
Cholinesters (esters of Ach ) carbacol , bethanicol .
Alkaloids
Cholinomimitics drugsCholinergic agonists
-rarely used
- S/E : produce miosis and decrease IOP- Has profound effect on CVS and GIT due to ganglionic stimulating activity .
- Activate N receptors in adrenal medulla .
carbacol
not Hydrolysed by AchE , while hydrolyzed by other esterases .Used for treatment of bladder and GIT atony .
Bethanicol
AlkaloidsIs Muscarinic agonist
Mainly used in opthalmology , caused miosis
S/E : sweating and salivation because enter CNS
Pilocarpine
Reversible AchE inhibitors and irreversible AchE inhibitors .
Reversible :1- Physostigmine :
-Act on MR , N gang , and N NMJ
-uses : GIT , bladder atonty , and glucoma .
- S/E : bradycardia , convulsions .
B-Indirect acting cholinergic drugs
2-Neostigmine
-Polar , so doesn’t pass BBB-effect on skeletal muscle is greater than that of pysostigmine .
- used for Mysthemia Gravis , and antidote for tubocurarine .
3- Pyridostigmine :
-for long term management of M.G because of longer duration of action .4- Edrophomium :
Used for diagnosis of M.G
-Has duration 10-12 min
- organophosphorous cpds / insectsides
- Isoflurophate-Echothiophate
- clinically used for glucoma
Irreversible AchE inhibitors
Atropine
-causes : eye medryasis , and cycloplagia
-in low dose block M1R , cause bradycardia
-in high dose (>1 mg ) block M2R , cause tachycardia.
- dilate cutaneous vasculature
Antimuscarinic drugs
-No effect on arterial blood pressure .-GIT: decrease motility and secretion
-urinary tract : reduce hyper motility of bladder
-secretions: decrease salivation , sweating , and lacrimal secretion .
Cont. Atropine
-antispasmodic , antidote for anticholinergic , reduce secretion prior to surgery , and cause medriasis in ophthalmology.
-other anti Muscarinic :
Scopolamine : motion sickness
Pirenzepine : gastric ulcer reduce HCL
Ipratropium : bronchodilator used for asthma .
Uses of atropine
Thank you for paying attention