Viral infections
Objectives:1- Describe the clinical features and treatment of herpes simplex, chicken pox and viral warts
2- differentiate genital herpes from other causes of genital ulcers.
3- describe the clinical features and lines of treatment of pox virus infections.
4- describe the clinical features of measles and rubella
Herpes simplex
Cause: herpes virus hominis, DNA virus.HSV I: mostly oral, transmitted by saliva
HSV II: mostly genital transmitted by sex
Virus entry primary infection latent infection recurrent attacks
Clinical features
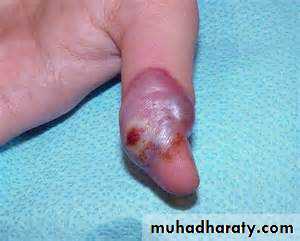
*Primary type I: usually asymptomatic, children.Symptomatic gingivostomatitis-vesicles
and erosions- 2 weeks
keratitis
whitlow
*Primary type II: genital vesicles and painful erosions
Recurrent attacks (type I):
Herpes labilais or cold sore: Recurrent vesicles
pustules erosions in the lips and near skin
Ppt. factors: sunlight, menstruation, viral and bacterial infections.
recurrent attack usually last 1 week.
Recurrent type II:
*Recurrent genital ulcers affecting the penis, vulva, vagina, anus.*type II recur more frequent than type I
* It is a common STD
*represent a bad stigma with guilt feeling because of its persistence for many years.
complications
MeningitisEncephalitis
Disseminated inf.
Secondary impetigo
Corneal ulceration
Treatment
Primary:
Mild cases: rest, symptomatic, acyclovir 200mg 5 times daily for 10 days.
Disseminated inf. In immunocompromised : intravenous acyclovir 5-10mg/ kg 8 hourly
recurrent attacks: suppressive therapy
Acyclovir 400mg twice dailyAcyclovir not eradicate the HSV from the ganglia, but decrease the recurrence
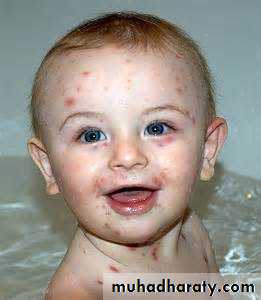
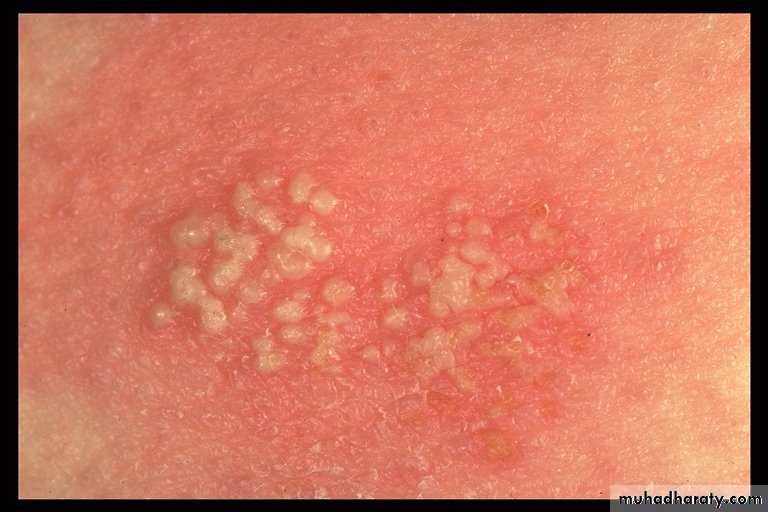
Varicella
V-Z virus.Transmission: direct contact and respiratory
Prodromal symptoms: flu like
Pink papules vesicles pustules crusted erosions
Centripetal distribution
Treatment: symptomatic, acyclovir for adults, severe cases and immunocompromised
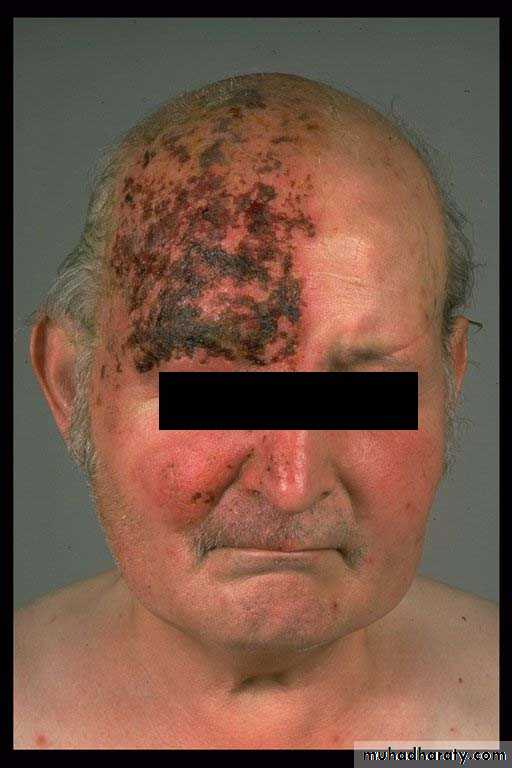
Herpes zoster
Caused by reactivation of V-Z virus acquired from previous chicken pox inf.
V-Z virus latent in the cranial or dorsal root ganglia, its reactivation herpes zoster at the dermatome of corresponding nerve
Usually its risk increase with age and low immunity
Clinical features
Unilateral dermatomal pain for 3-5 daysvesicles ulcerations.
Last 2-6 weeks according to the age
Sites of involvement: thoracic, cervical, trigeminal, lumbosacral
Complications
Secondary bact. Inf.Corneal ulceration in ophthalmic zoster
Motor nerve involvement
Post herpetic neuralgia
Treatment
Mild cases: rest, symptomaticSevere cases, ophthalmic zoster, low immunity
acyclovir within 2-3 days
analgesics, antidepressants
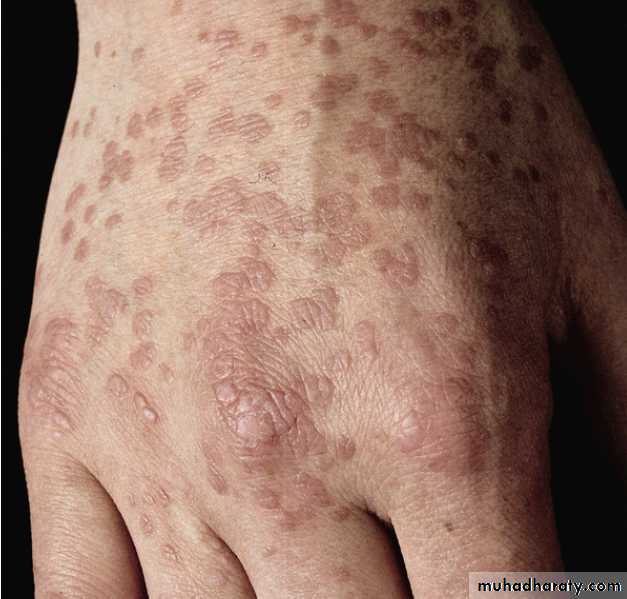
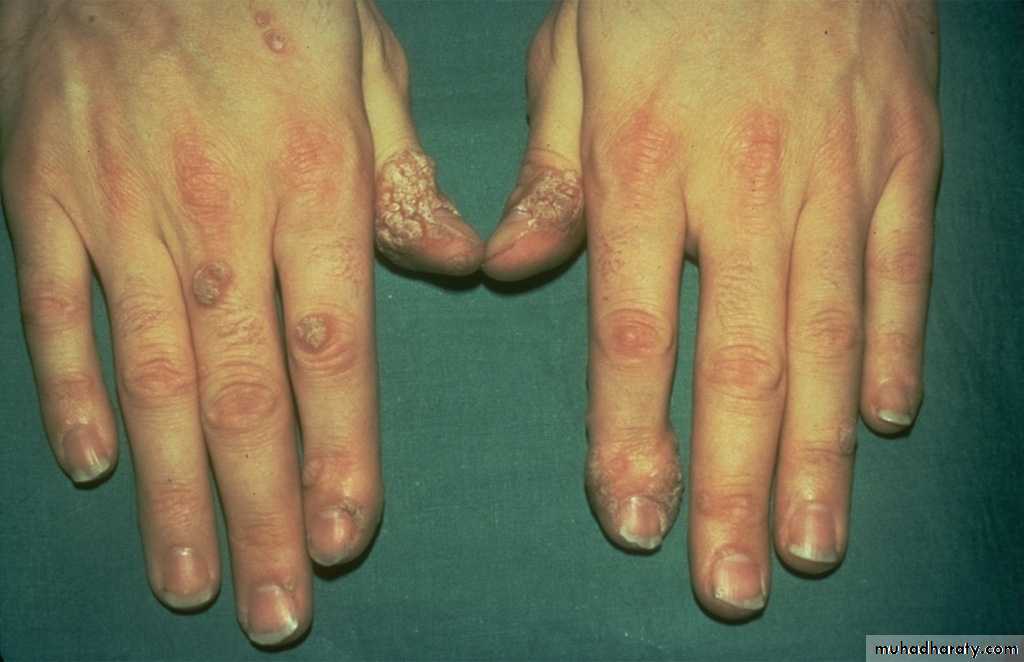
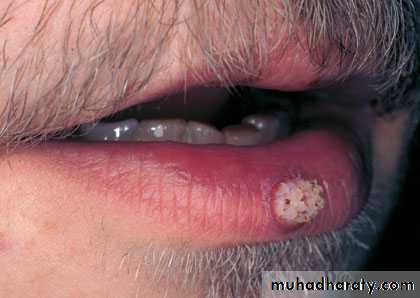
Viral warts
Cause: HPV, more than 60 subtypes
Transmission: direct contact and sex.
Usually affects young people
Immune deficiency extensive warts
Type 16 and 18 cause cervical ca.
Clinical features
Common warts ( verruca vulgaris): single or multiple papules with rough surface.Usually affect the hands, but can appear anywhere.
Plantar warts: rough slightly raised papules.
Plane warts: slightly raised skin colored- grey- pink smooth papules. Face and hands
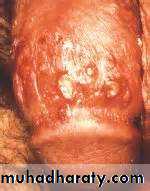
Anogenital warts (condylomata acuminata)
Affects skin and m.m. of the genital area.Papillomatous or cauliflower lesions
D.Dx:
Condylomata lata: flat papules, other features of secondary syphilis.
Treatment
Local therapy:*Keratolytics: 12-20% salicylic acid
* caustic agents: TCA for genital warts
* cytotoxics: 5-FU for plane warts.
podophylline for genital warts
* Surgical: curretage, electrocautery, cryotherapy
* immunomodulators: imiquimod for plane and genital
warts
* Retinoic acid: for plane warts
Systemic therapy
For extensive warts
Zinc sulfate, BCG vaccine, retinoids
Pox virus infections
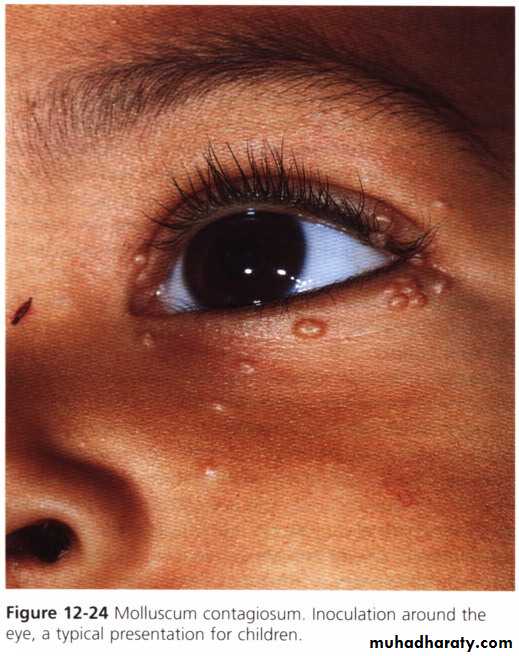
Molluscum contagiosum* Pox virus, transmitted by direct contact and sex
* Clinical features: I.P. 2-6 weeks
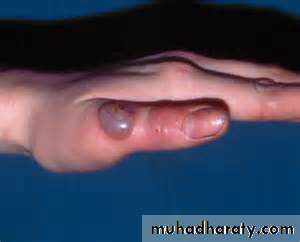
Shiny white or pink papule with central punctum in some cases.
* usually disease of children, especially affects the face.
* In adults involvement of the genital area indicates STD.
treatment
Squeezing, curretage, cryotherapy, cautery, phenol puncture, retinoic acidOrf
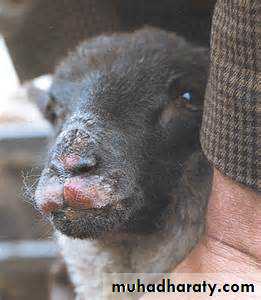
orf
Caused by parapox v.
Transmitted from sheep.
I.P. 1 week
Firm papule pustular nodule
Clear in about 6 weeks spontaneously.
No treatment required.
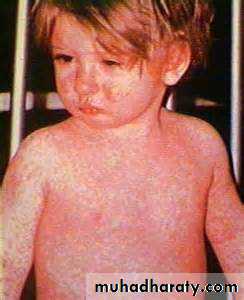
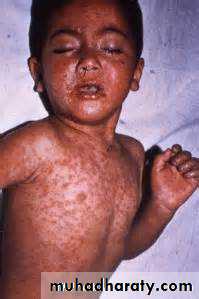
Measles
Paramyxovirus, droplet transmission.I.P. 10 days
Catarrhal stage:2 days of fever, running nose, red eyes, then photophobia and koplik’s spots
Days 3-4 maculopapular rash covering the body in 3 days
Days 6-7 days fever and rash subside fever and rash.
complications
Pneumonia, keratitis, otitis media, encephalitis, weight lossTreatment
Symptomatic, antibiotics for secondary bact. Inf.Rubella (German measles)
Caused by toga virus, droplet inf.
I.P. 18 days.
Less severe than measles, trivial in children, more severe in adults.
Prodromal symptoms with suboccipital LAP
Fine maculopapular rash covering the body in one day and disappear in the 3rd day.
AIDS
Caused by HIV, which target the CD4 T cellsSkin manifestations of AIDS
*Tumors: kaposi sarcoma, extensive with systemic involvement
* dermatitis: seborrheic derm.
* infections: opportunistic inf. ex candidiasis, severe HSV and HZV.
27
28
30
31
32
33
Summary
Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis…. ChildrenRecurrent orolabial herpes… children and adults.
Recurrent genital herpes ….guilt feeling.
Varicella: polymorphic rash, centripetal
H. zoster: severity is age dependent.
viral warts: verrucous surface, usu. Self limited
Measles: toxic, maculopapular rash and fever
Rubella: milder than measlesMolluscum contagiosum: Easily treated.
Orf: sheep. باجة