Lecture three
Cephalometric assessmentSoft tissues profile analysis
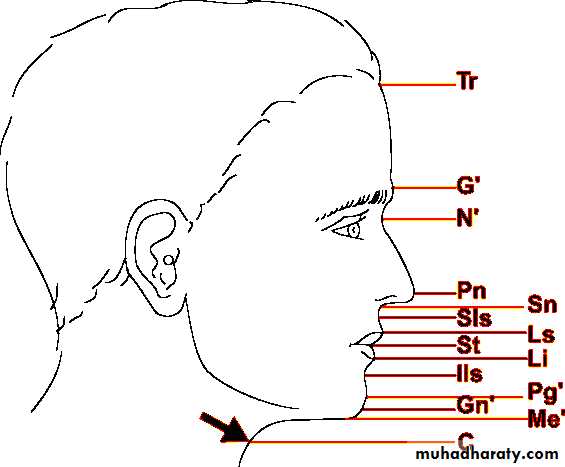
Soft tissue landmarks
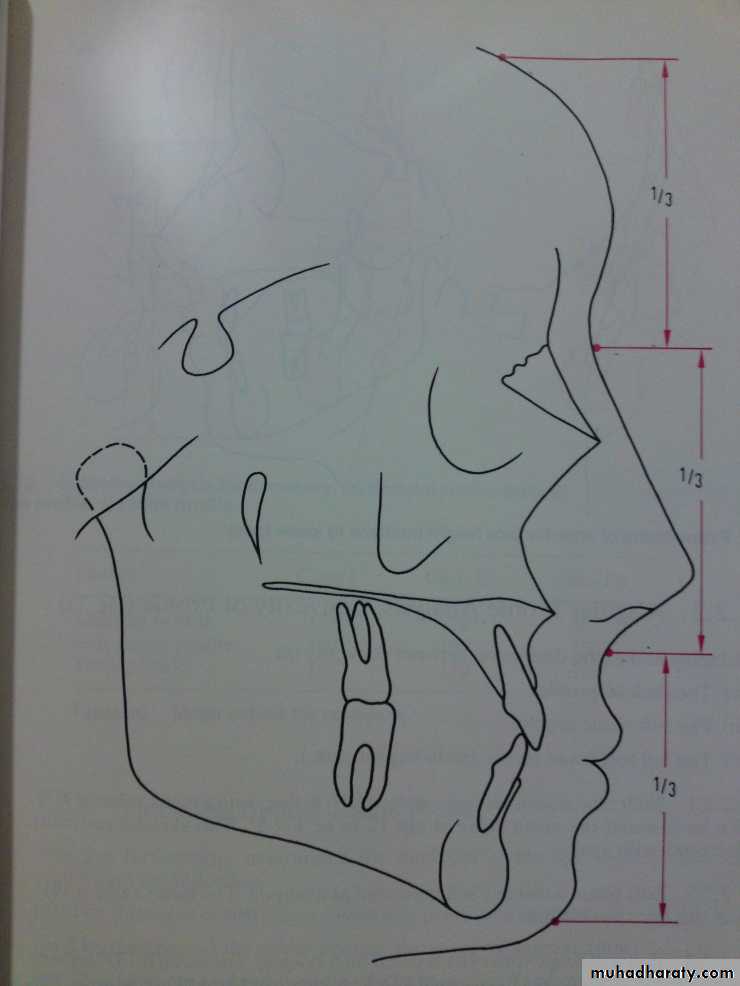
Proportional analysis:Frontal third: tr-n = 1/3
Nasal third: n-sn = 1/3
Gnathic third: sn-gn = 1/3
n-sn = 45%
sn-gn = 55%
Lip analysis
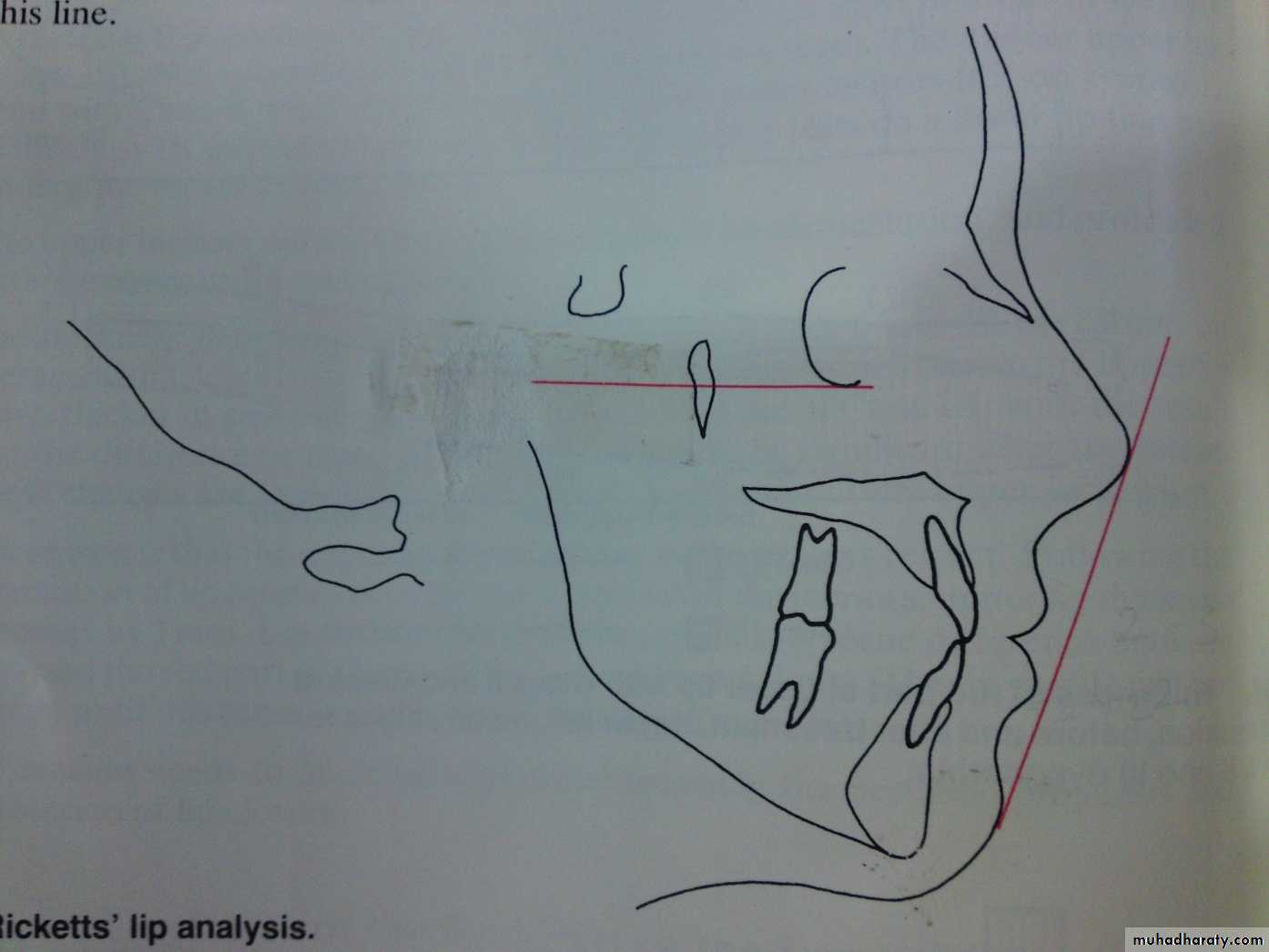
1- Ricketts lip analysisThe reference line used by Ricketts(esthetic line) tip of nose to skin pogonion
Upper lip 2-3 mm behind this line
lower lip 1-2 mm behind this line
Esthetic line
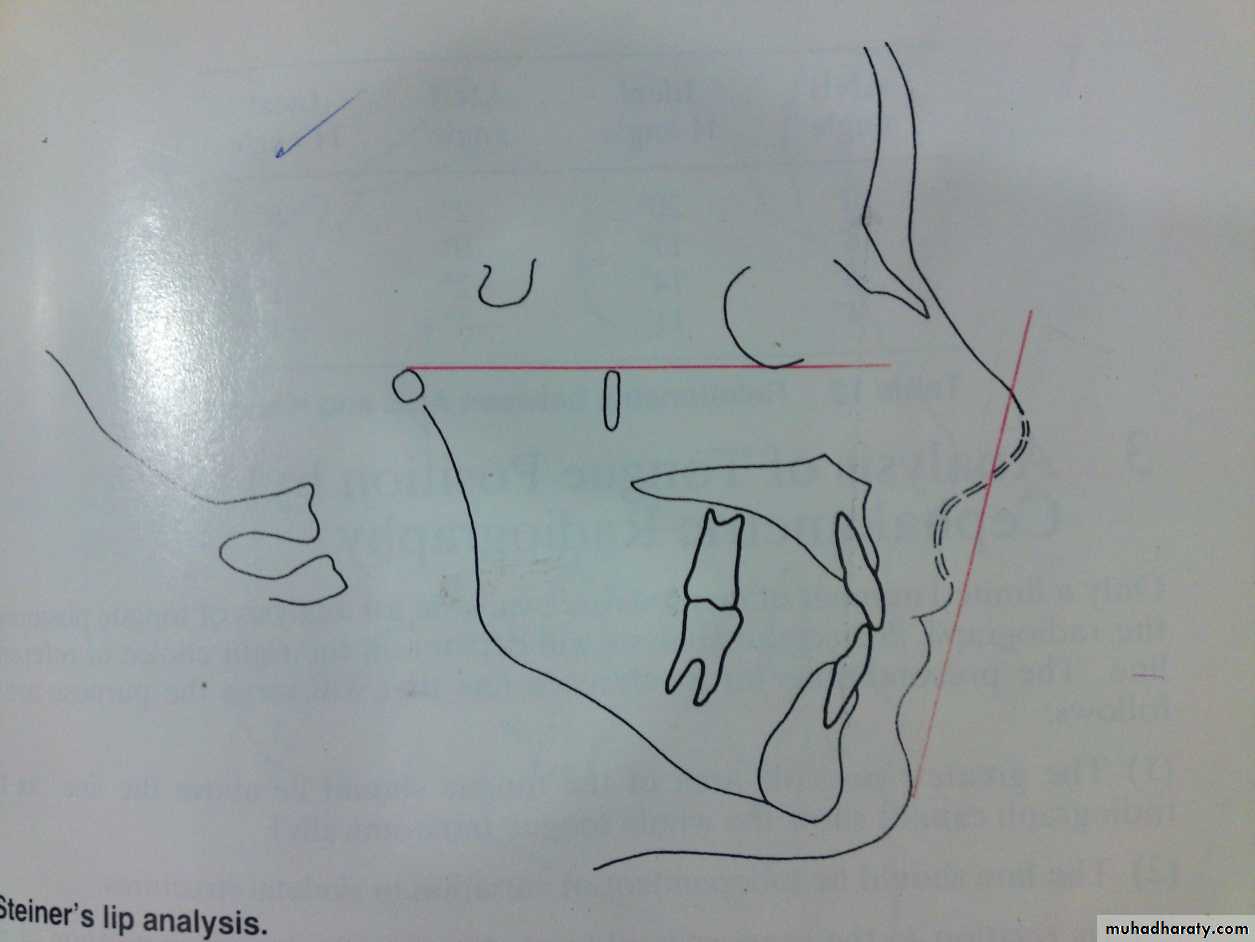
2- Steiners lip analysis:Reference line is center of (S) shape between tip of nose and upper lip and soft tissue pog.
If lips behind this line too flat.
If lips anterior to it too prominent.
Harmony line (Holdaway line): Vermelian border of upper lip to a tangent of the soft tissue pog
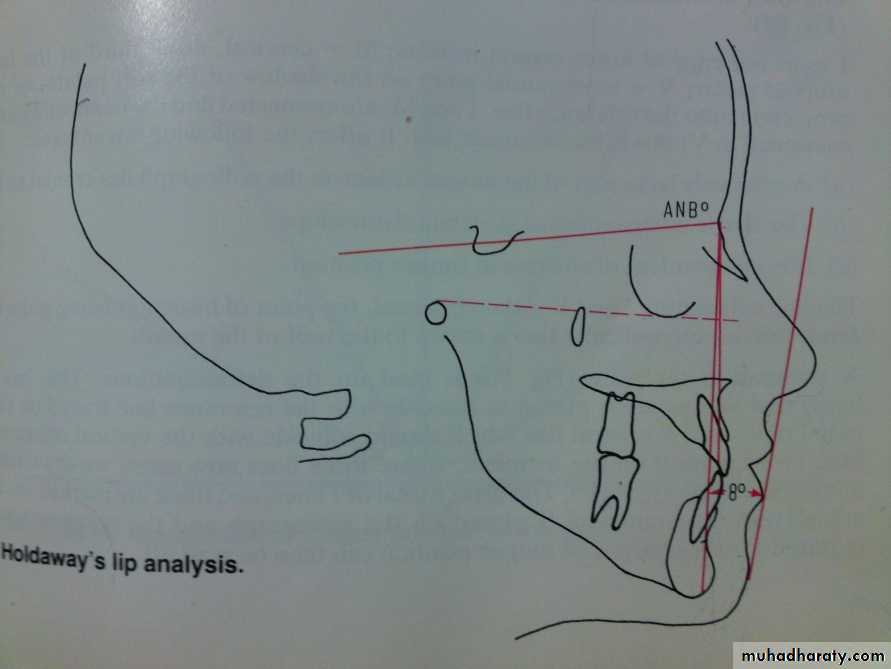
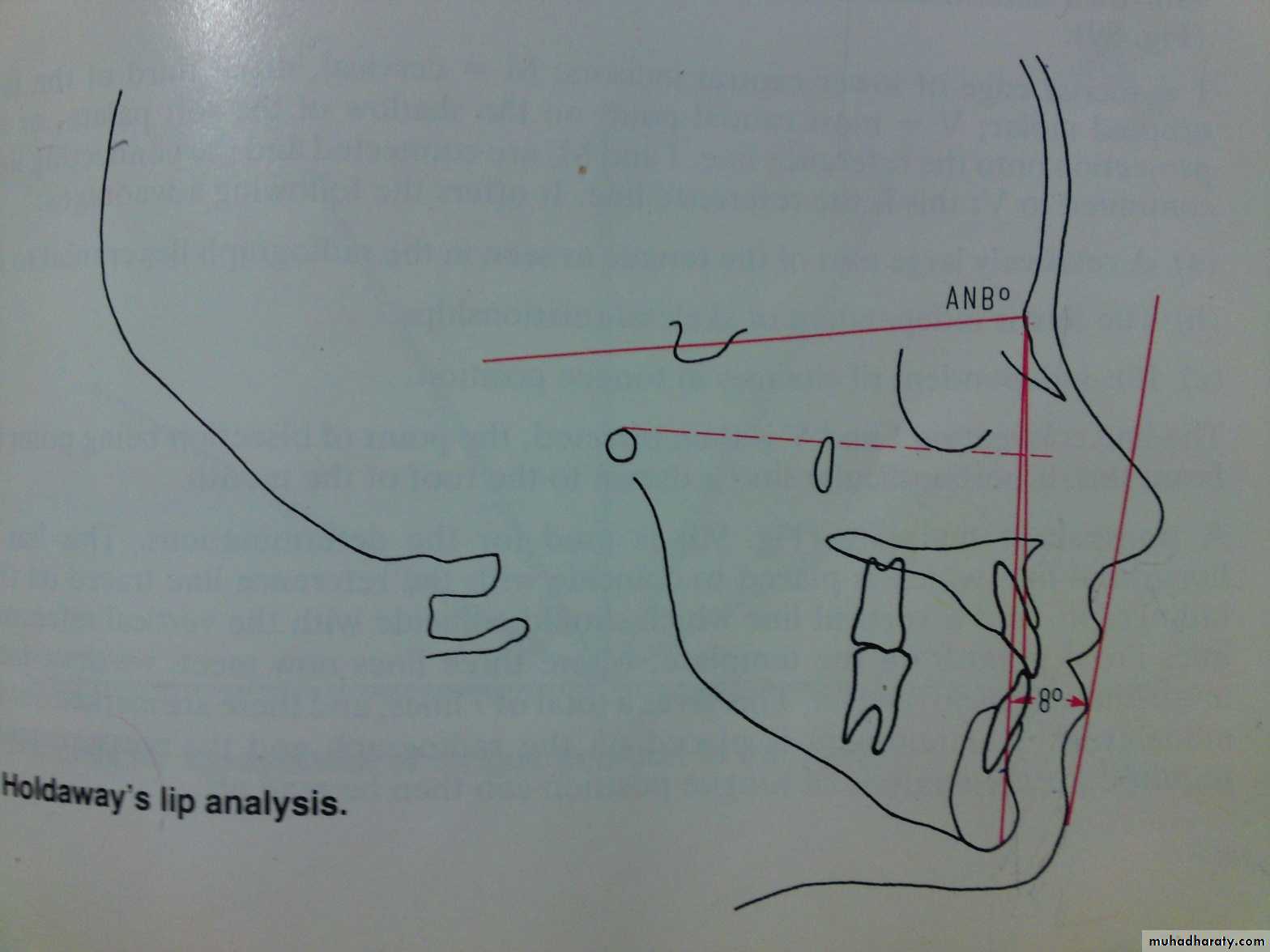
3- Holdaway analysis
Holdaways lip analysis:Angle between a tangent to the upper lip and the NB line (H angle)
ANB angle of 1-3⁰ H angle should be 7-8⁰.
Holdaway define the perfect profile as:
a. ANB angle 2 H angle 7-8
b. Lower lip touching soft tissue line
c. The relative proportion of nose and upper lip are balanced (soft tissue line bisects the S curve)
d. Tip of nose is 9 mm anterior to soft tissue line.
e. There is no lip tension.
Growth evaluation
Growth EvaluationSuperimposition on cranial base structures:
To examine overall changes in the facial pattern including changes in maxilla and mandible in relation to the cranial base
It is made on:
1- De Coster line2- SN line
Growth Evaluation
Superimposition on maxillaTo record changes in:
1- Maxilla2- Maxillary teeth in the maxilla
It is made on :
1- Anterior surface of zygomatic process
2- Maxillary plane ??!
Growth Evaluation
Superimposition on mandible:To record changes in:
1- Mandibular teeth in the mandible2- Remodeling in the mandible
It is made on :
1- Contour of the mandibular canal2- Inner contour of the cortex of the mandibular symphysis
3- Tooth bud of the 3rd molar
Other diagnostic records:
These diagnostic aids may be required only in certain cases and may require specialized equipments, which might not be available in every dental clinic. These includes:
1- Specialized radiographs: like
a. Occlusal view of maxilla and/or mandible.
b. Selected lateral jaw views.
2- Electromyographic examination of muscle activity.
3- Hand-wrist radiographs.
4- Computed axial tomography (CT scan).
5- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
6- Endocrine tests and/or other blood tests.
7- Estimation of basal metabolic rate.
8- Sensitivity (vitality) tests.
9- Biopsy.