Antipsychotic Agents (Neuroleptic Drugs)
Dr. Shamil H. ALNoaimySchizophrenia is a chronic psychotic illness characterized by disordered thinking and a reduced ability to comprehend reality.
Symptoms of Scizophrenia
Positive symptoms: hallucinations, delusions, disordered thinking, combativeness, agitation and paranoia.Negative symptoms: social withdrawal, emotional withdrawal, lack of motivation, poverty of speech, poor insight, poor judgment and poor self-care.
Schizophrenia:
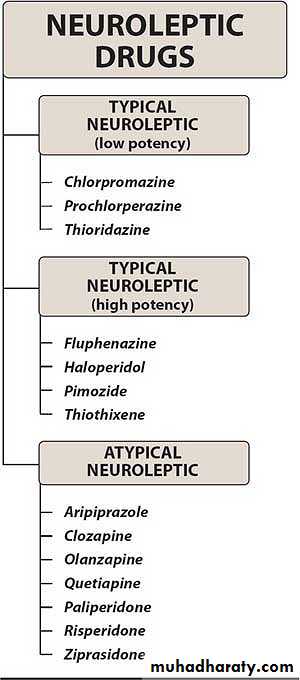
Conventional antipsychoticsAtypical antipsychotics
ClassificationConventional agents block receptors for dopamine &result in extrapyramidal symptoms.
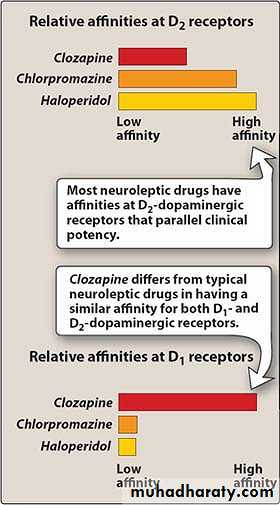
The atypical agents have stronger blockade of receptors for serotonin, the risk of extrapyramidal reactions is low.
Conventional antipsychotic agents relieve positive symptoms more effectively than negative symptoms.
In contrast, atypical antipsychotic agents relieve both types of symptoms.
Classification by potency:
Low potency: Chlorpromazine, thioridazine.Medium potency: Loxapine, molindone, perphenazine.
High potency: Trifluoperazine, , fluphenazine, haloperidoleConventional Antipsychotic Agents
Chemical Classification:1.Phenothiazine group: chlorpromazine, trifluperazine.
2. Thioxanthene: thiothixene.
3. Butyrophenone: haloperidole.
4. Dihydroindolone: molindone
5. Dibenzoxazepine: loxapine
6. Diphenylbutylpiperadine: pimozide.
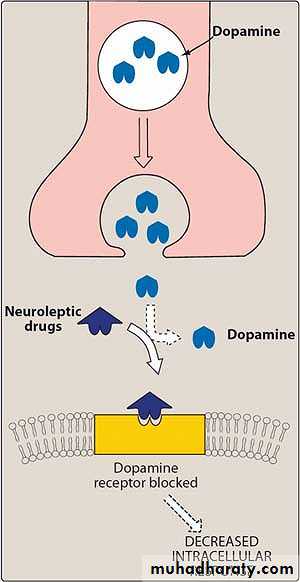
Conventional antipsychotic drugs suppress symptoms of psychosis by blocking dopamine (D2) receptors in the mesolimbic and mesocortical areas of the brain regions.
Mechanism of action:
After oral administration: absorption is unaffected by food
These agents readily pass into the brain, bind well to plasma proteins, are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system in the liver
Fluphenazine decanoate, haloperidol decanoate, and risperidone are slow-release (up to 2 to 4 weeks) injectable formulations administered via deep gluteal IM injection.
The neuroleptic drugs produce some tolerance but little physical dependence.
Absorption and metabolismSchizophrenia
Bipolar disorder (manic-depressive illness)Tourette's syndrome
Prevention of emesisOther applications
Therapeutic uses:
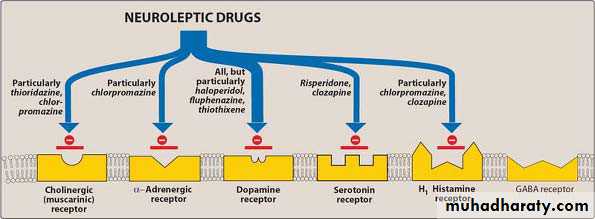
Extrapyramidal symptoms (ES):
Acute dystonia: spasm of muscles of tongue, face, neck and back.Parkinsonism: bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity.
Akathisia: compulsive, restless movement, symptoms of anxiety and agitation.
Tardive dyskinesia: Choreoathetoid movements of lips, tongue, face, jaws, and limbs and sometimes trunk.Adverse effects
Neuroleptic Malignant syndromeAnticholinergic effects
Orthostatic hypotensionSedation
Endocrine effectsSeizures
Sexual dysfunctionDermatologic effects
Agranulocytosis
Clozapine
RisperidoneOlanzapine
Atypical Antipsychotic AgentsAtypical agents cause few or no extrapyramidal symptoms.
Atypical agents can relieve positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.