
Anti Viral Agents
Anti Viral Agents
Antiviral Agents
Antiviral Agents
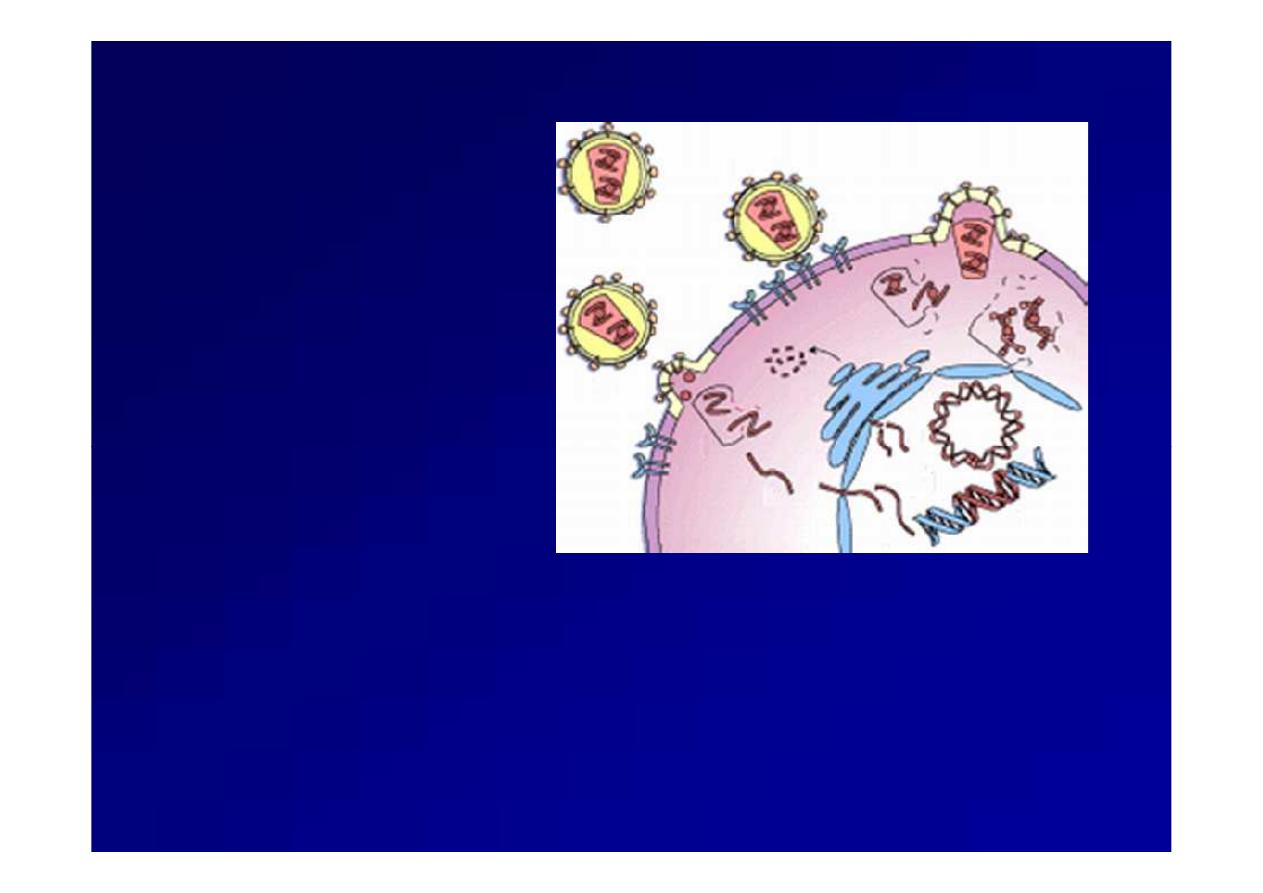
Viral replication
Viral replication
Adsorption
Adsorption
Penetration
Penetration
Uncoating
Uncoating
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Maturation
Maturation
Release
Release
Antiviral Agents
Antiviral Agents
Viral replication
Viral replication
Adsorption
Adsorption
Penetration
Penetration
Uncoating
Uncoating
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Maturation
Maturation
Release
Release

Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral Drugs
Classification of Antiviral Drugs:
Classification of Antiviral Drugs:
Drugs directly impair viral replication
Drugs directly impair viral replication
Drugs modulate the host I
Drugs modulate the host I -- system
system
Agents to treat HSV and VZV infections
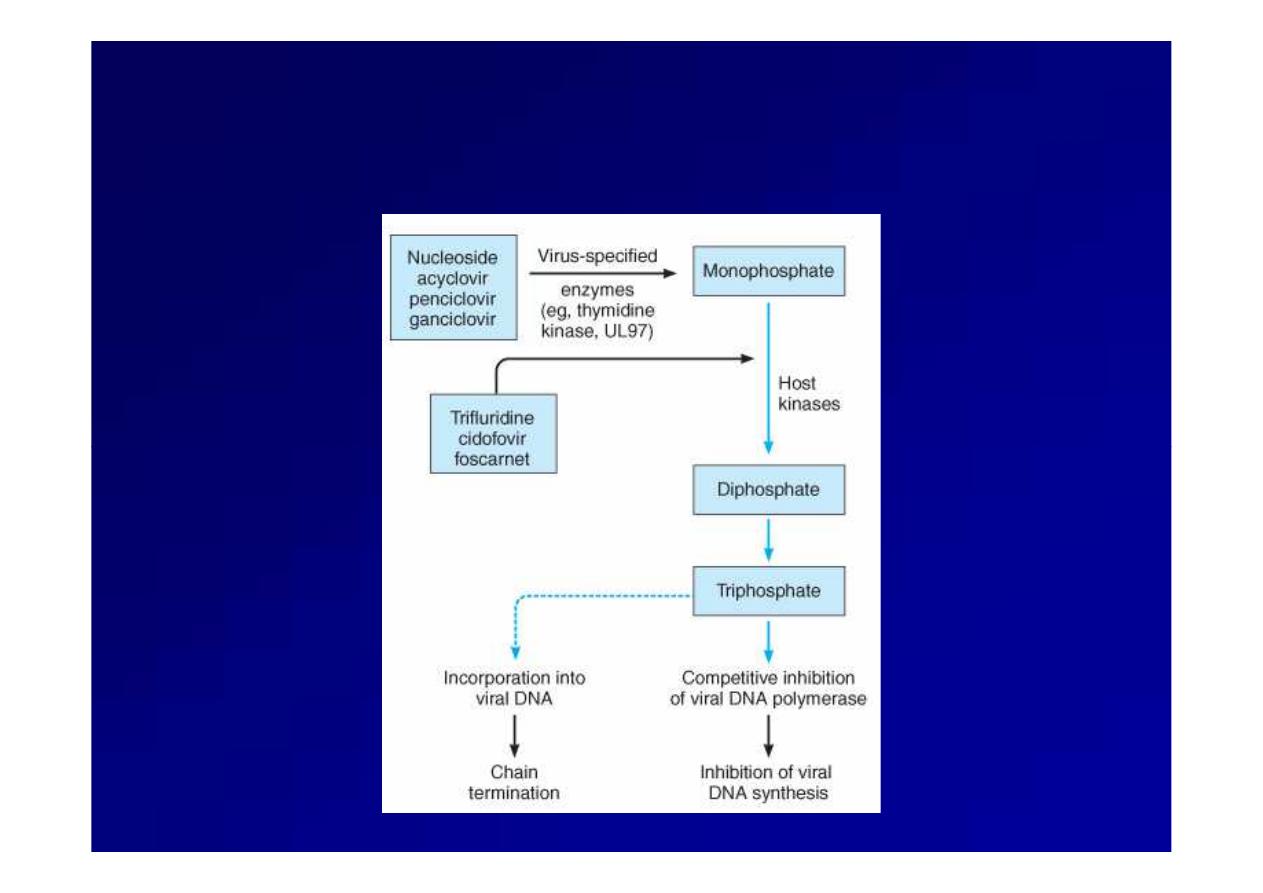
Agents to treat HSV and VZV infections
(Acyclovir,
(Acyclovir, Valacyclovir
Valacyclovir, and
, and Famciclovir
Famciclovir))
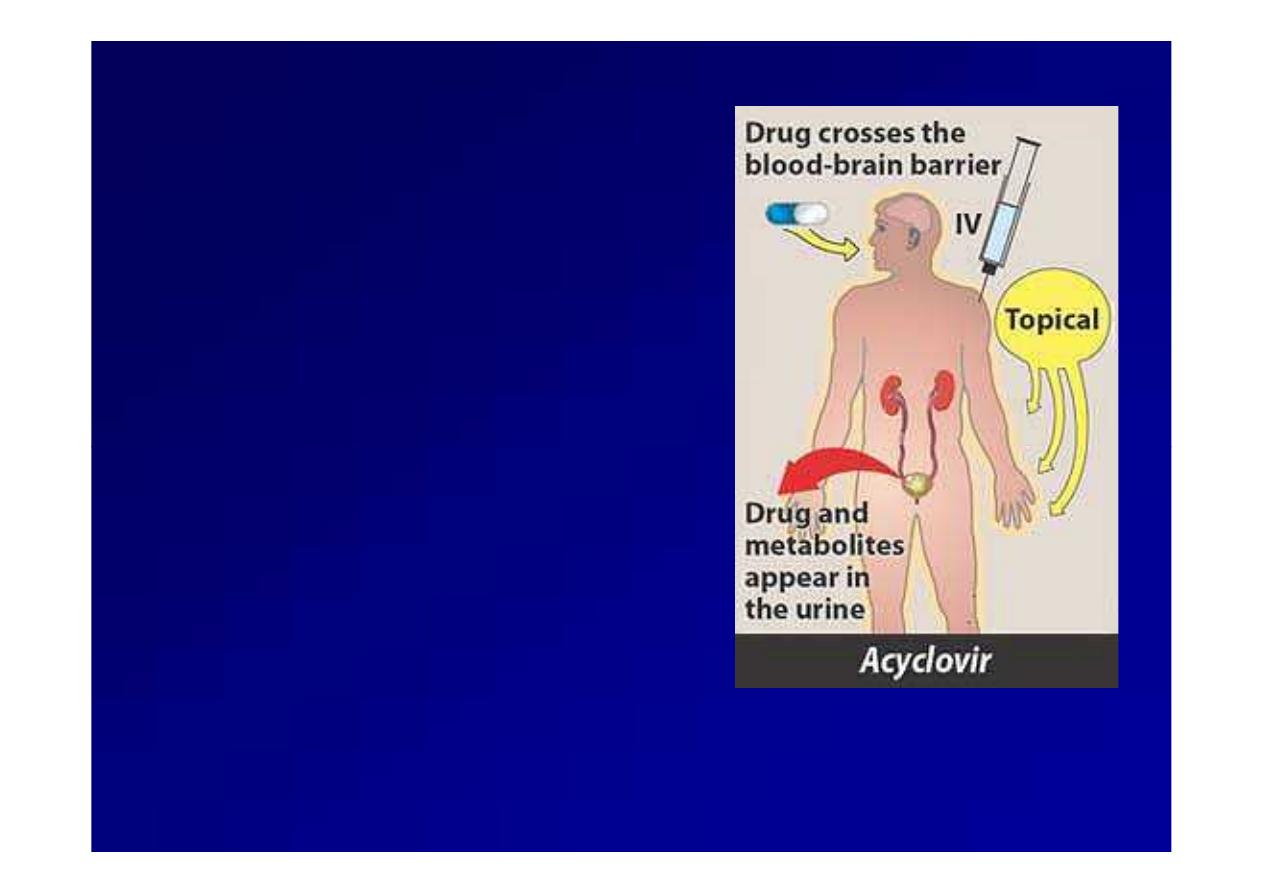
Pharmacokinetic of
Pharmacokinetic of
Acyclovir
Acyclovir
Oral,
Oral, i.v
i.v,, topical.
topical.
Bioavailability is
Bioavailability is 15
15--20
20%.
%.
Cleared primarily by
Cleared primarily by
glomerular filtration and
glomerular filtration and
tubular secretion.
tubular secretion.
TT11\\22==33hr
hr
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
concentrations are
concentrations are 50
50%
% of
of
serum values.
serum values.
Pharmacokinetic of
Pharmacokinetic of
Acyclovir
Acyclovir
Oral,
Oral, i.v
i.v,, topical.
topical.
Bioavailability is
Bioavailability is 15
15--20
20%.
%.
Cleared primarily by
Cleared primarily by
glomerular filtration and
glomerular filtration and
tubular secretion.
tubular secretion.
TT11\\22==33hr
hr
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
concentrations are
concentrations are 50
50%
% of
of
serum values.
serum values.
Administration and
Administration and
metabolism of acyclovir
metabolism of acyclovir

Indications for Acyclovir
Indications for Acyclovir
1.
1. Herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus
2.
2. Varicella
Varicella -- zoster virus:
zoster virus:
Chickenpox
Chickenpox
Shingles
Shingles

Adverse reactions
Adverse reactions
Stinging sensation and a diffuse
Stinging sensation and a diffuse
superficial punctate
superficial punctate keratopathy
keratopathy..
Gastrointestinal symptoms,
Gastrointestinal symptoms, headache
headache
and neuropsychiatric reactions,
and neuropsychiatric reactions,
severe local inflammation with
severe local inflammation with i.v.
i.v.
Agents to treat
Agents to treat
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
(CMV)
Infections
Infections Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir,,
Valganciclovir
Valganciclovir,, Cidofovir
Cidofovir
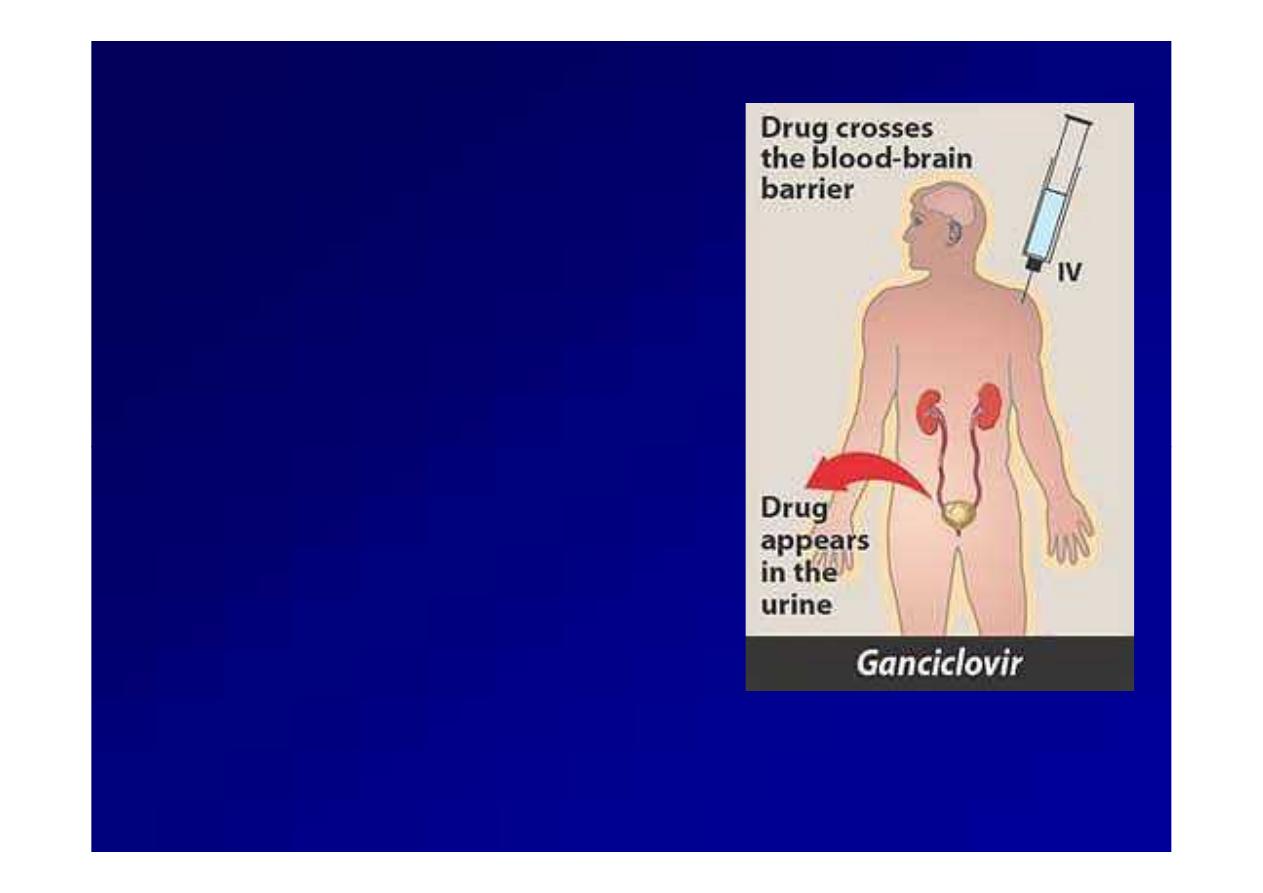
Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir
Orall
Orall or
or i.v
i.v,,
Poor bioavailability.
Poor bioavailability.
Eliminated in the urine,
Eliminated in the urine,
mainly unchanged (
mainly unchanged (tltl//2 4
2 4h).
h).
Agents to treat
Agents to treat
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
(CMV)
Infections
Infections Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir,,
Valganciclovir
Valganciclovir,, Cidofovir
Cidofovir
Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir
Orall
Orall or
or i.v
i.v,,
Poor bioavailability.
Poor bioavailability.
Eliminated in the urine,
Eliminated in the urine,
mainly unchanged (
mainly unchanged (tltl//2 4
2 4h).
h).
Administration and
Administration and
metabolism of
metabolism of ganciclovir
ganciclovir

Indications for
Indications for Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir Include
Include
Life
Life -- threatening (CMV) infection
threatening (CMV) infection
For maintenance suppressive treatment
For maintenance suppressive treatment
of retinitis in patients with AIDS
of retinitis in patients with AIDS
Prevention (CMV)
Prevention (CMV) following organ
following organ
transplantation
transplantation

Adverse Reactions of
Adverse Reactions of Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir
Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
fever, rash, gastrointestinal symptoms,
fever, rash, gastrointestinal symptoms,
confusion and seizure
confusion and seizure
Concomitant use of potential marrow
Concomitant use of potential marrow --
depressant drugs, e.g.
depressant drugs, e.g. cotrimoxazole
cotrimoxazole,,
zidovudine
zidovudine,, should be avoided.
should be avoided.
Adverse Reactions of
Adverse Reactions of Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir
Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
fever, rash, gastrointestinal symptoms,
fever, rash, gastrointestinal symptoms,
confusion and seizure
confusion and seizure
Concomitant use of potential marrow
Concomitant use of potential marrow --
depressant drugs, e.g.
depressant drugs, e.g. cotrimoxazole
cotrimoxazole,,
zidovudine
zidovudine,, should be avoided.
should be avoided.

Antiretroviral Agents
Antiretroviral Agents
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase
inhibitors (NRTIs).
inhibitors (NRTIs).
Non nucleoside reverse transcriptase
Non nucleoside reverse transcriptase
inhibitors (NNRTIs).
inhibitors (NNRTIs).
Protease inhibitors (PIs).
Protease inhibitors (PIs).

Zidovudine
Zidovudine (NRTIs)
(NRTIs)
Well absorbed
Well absorbed
Distributed to most body tissues and
Distributed to most body tissues and
fluids.
fluids.
Eliminated primarily by renal excretion
Eliminated primarily by renal excretion
following
following glucuronidation
glucuronidation in the liver.
in the liver.

Indications for
Indications for Zidovudine
Zidovudine
HIV infection in patients with acquired
HIV infection in patients with acquired
immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or
immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or
AIDS related complex.
AIDS related complex.

Drug Interaction of
Drug Interaction of Zidovudine
Zidovudine
Myelosuppressive
Myelosuppressive drugs such as
drugs such as
ganciclovir
ganciclovir,, ribavirin,
ribavirin, and cytotoxic
and cytotoxic
agents
agents
toxicity.
toxicity.
Probenecid
Probenecid,,
Serum levels of
Serum levels of
zidovudine
zidovudine acid through decreased
acid through decreased
its clearance.
its clearance.
Drug Interaction of
Drug Interaction of Zidovudine
Zidovudine
Myelosuppressive
Myelosuppressive drugs such as
drugs such as
ganciclovir
ganciclovir,, ribavirin,
ribavirin, and cytotoxic
and cytotoxic
agents
agents
toxicity.
toxicity.
Probenecid
Probenecid,,
Serum levels of
Serum levels of
zidovudine
zidovudine acid through decreased
acid through decreased
its clearance.
its clearance.
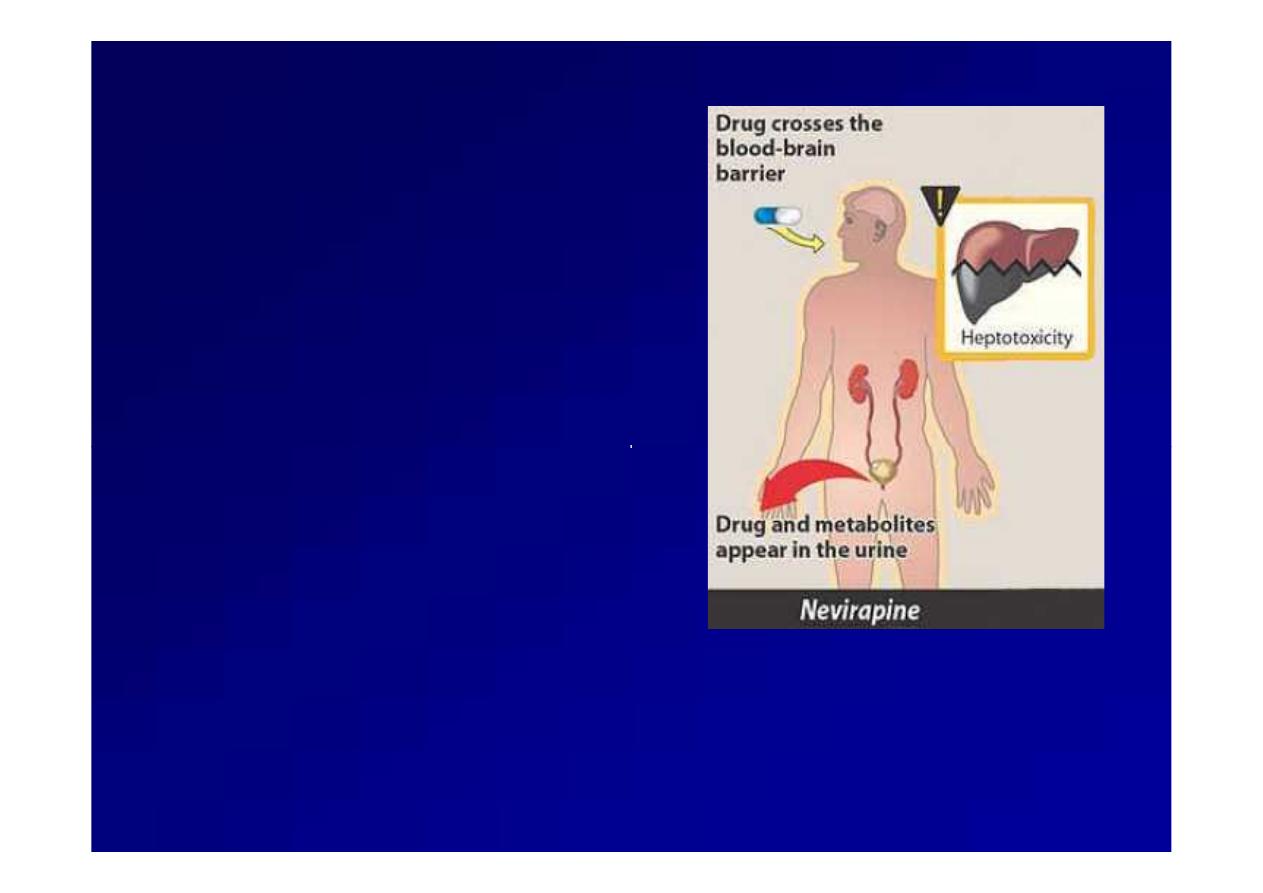
(NNRTIs)
(NNRTIs) Nevirapine
Nevirapine
It used in combination
It used in combination
with at least two other
with at least two other
antiretroviral
antiretroviral
It penetrates the CSF
It penetrates the CSF
HHepatic metabolism.
epatic metabolism.
Rash and hepatitis are
Rash and hepatitis are
the commonest side
the commonest side
effects.
effects.
(NNRTIs)
(NNRTIs) Nevirapine
Nevirapine
It used in combination
It used in combination
with at least two other
with at least two other
antiretroviral
antiretroviral
It penetrates the CSF
It penetrates the CSF
HHepatic metabolism.
epatic metabolism.
Rash and hepatitis are
Rash and hepatitis are
the commonest side
the commonest side
effects.
effects.
Administration, metabolism,
Administration, metabolism,
and toxicity
and toxicity of nevirapine

Protease Inhibitors
Protease Inhibitors
((Ritronavir
Ritronavir,, Indinavir
Indinavir,, Saquinavir
Saquinavir))
HIV produces protein and also a protease
HIV produces protein and also a protease
which cleaves the protein into component
which cleaves the protein into component
parts that are subsequently reassembled
parts that are subsequently reassembled
into virus particles; protease inhibitors
into virus particles; protease inhibitors
disrupt this essential process.
disrupt this essential process.
Protease Inhibitors
Protease Inhibitors
((Ritronavir
Ritronavir,, Indinavir
Indinavir,, Saquinavir
Saquinavir))
HIV produces protein and also a protease
HIV produces protein and also a protease
which cleaves the protein into component
which cleaves the protein into component
parts that are subsequently reassembled
parts that are subsequently reassembled
into virus particles; protease inhibitors
into virus particles; protease inhibitors
disrupt this essential process.
disrupt this essential process.
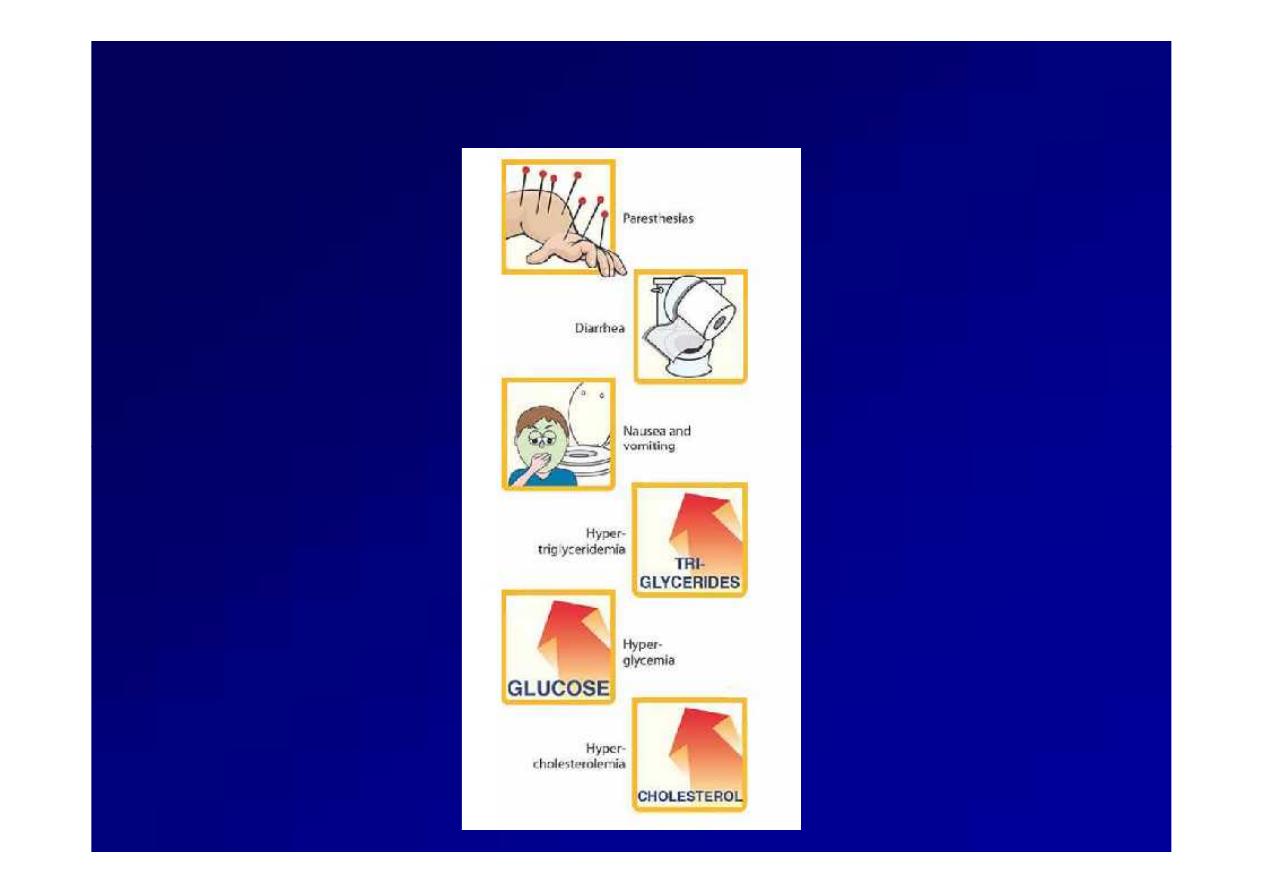
Some
Some Adverse effect of HIV protease inhibitors
Adverse effect of HIV protease inhibitors

Drug Interactions with protease
Drug Interactions with protease
inhibitors
inhibitors
1.
1. Enzyme inducer P
Enzyme inducer P450
450 (( e.g
e.g))
rifampicin.
rifampicin.
2.
2. Enzyme inhibitors (
Enzyme inhibitors (e.g
e.g))
ketoconazole, cimetidine.
ketoconazole, cimetidine.
Drug Interactions with protease
Drug Interactions with protease
inhibitors
inhibitors
1.
1. Enzyme inducer P
Enzyme inducer P450
450 (( e.g
e.g))
rifampicin.
rifampicin.
2.
2. Enzyme inhibitors (
Enzyme inhibitors (e.g
e.g))
ketoconazole, cimetidine.
ketoconazole, cimetidine.

Anti
Anti--influenza Agents
influenza Agents
Amantadine
Amantadine
Active against influenza A virus
Active against influenza A virus
Mechanism of action: interfering with
Mechanism of action: interfering with
the
the uncoating
uncoating and release of viral
and release of viral
genome into the host cell.
genome into the host cell.
PK:
PK:
Well absorbed from the GIT.
Well absorbed from the GIT.
It Is eliminated in the urine.
It Is eliminated in the urine.
Anti
Anti--influenza Agents
influenza Agents
Amantadine
Amantadine
Active against influenza A virus
Active against influenza A virus
Mechanism of action: interfering with
Mechanism of action: interfering with
the
the uncoating
uncoating and release of viral
and release of viral
genome into the host cell.
genome into the host cell.
PK:
PK:
Well absorbed from the GIT.
Well absorbed from the GIT.
It Is eliminated in the urine.
It Is eliminated in the urine.

Amantadine Adverse Reactions
Amantadine Adverse Reactions
Dizziness, insomnia, headedness and
Dizziness, insomnia, headedness and
nervousness, Drowsiness, hallucinations,
nervousness, Drowsiness, hallucinations,
delirium, coma may occur in patients with
delirium, coma may occur in patients with
impaired renal function. Convulsions may
impaired renal function. Convulsions may
be induced, and amantadine should be
be induced, and amantadine should be
avoided in epileptic patients.
avoided in epileptic patients.
Amantadine Adverse Reactions
Amantadine Adverse Reactions
Dizziness, insomnia, headedness and
Dizziness, insomnia, headedness and
nervousness, Drowsiness, hallucinations,
nervousness, Drowsiness, hallucinations,
delirium, coma may occur in patients with
delirium, coma may occur in patients with
impaired renal function. Convulsions may
impaired renal function. Convulsions may
be induced, and amantadine should be
be induced, and amantadine should be
avoided in epileptic patients.
avoided in epileptic patients.
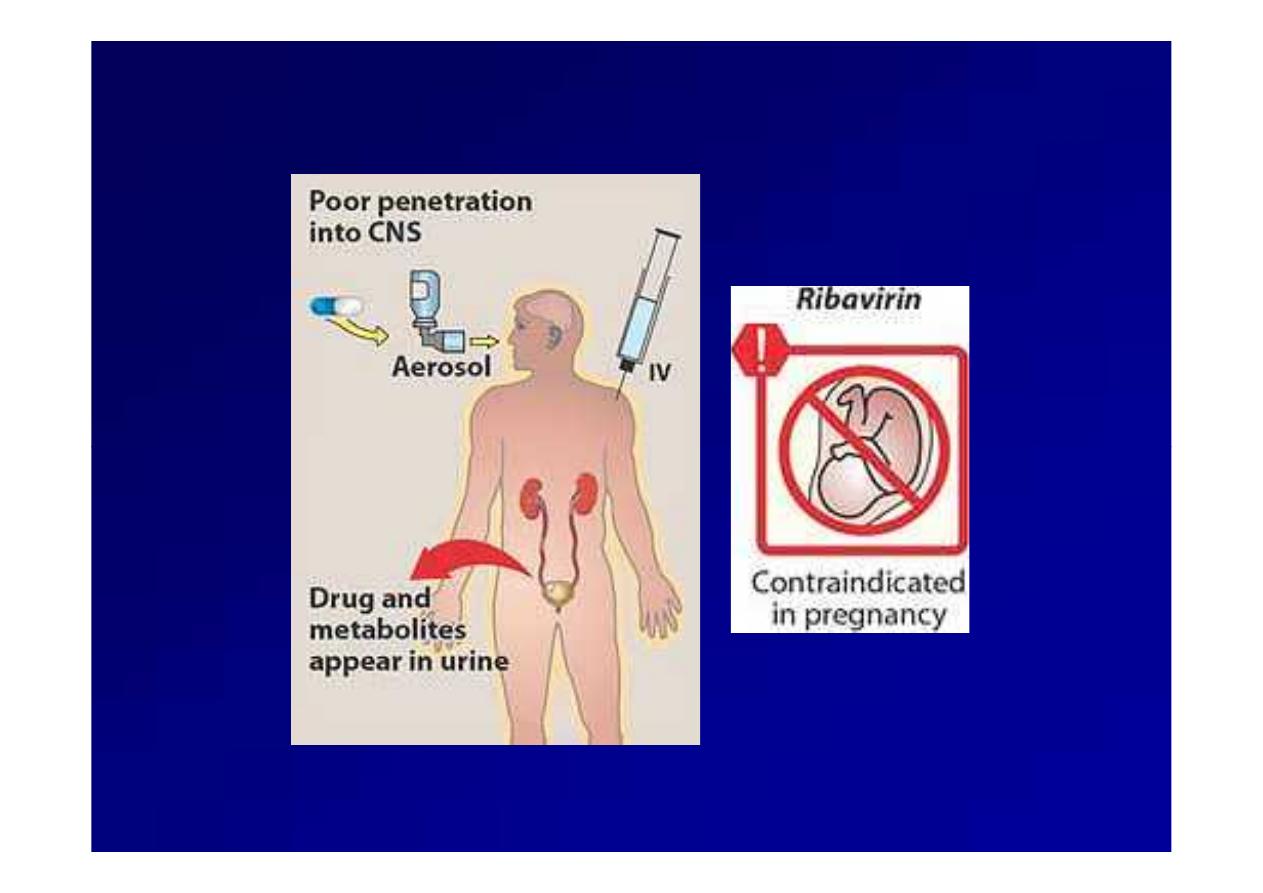
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RIBAVIRIN)
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RIBAVIRIN)

Interferons
Interferons (Hepatic Viral Infection)
(Hepatic Viral Infection)
1.
1. Directly on uninfected cells to induce
Directly on uninfected cells to induce
enzymes that degrade viral RNA.
enzymes that degrade viral RNA.
2.
2. Indirectly by stimulating the immune
Indirectly by stimulating the immune
system.
system.

Uses of
Uses of Interferon
Interferon
AAlfa Interferon used for hairy cell
lfa Interferon used for hairy cell
leukaemia
leukaemia, recurrent or metastatic renal
, recurrent or metastatic renal
cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS
cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS
patients
patients
Alfa
Alfa--22αα and
and --22b improve the
b improve the
manifestations of viral hepatitis, B and C.
manifestations of viral hepatitis, B and C.
hepatitis C may need prolonged therapy.
hepatitis C may need prolonged therapy.
Uses of
Uses of Interferon
Interferon
AAlfa Interferon used for hairy cell
lfa Interferon used for hairy cell
leukaemia
leukaemia, recurrent or metastatic renal
, recurrent or metastatic renal
cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS
cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS
patients
patients
Alfa
Alfa--22αα and
and --22b improve the
b improve the
manifestations of viral hepatitis, B and C.
manifestations of viral hepatitis, B and C.
hepatitis C may need prolonged therapy.
hepatitis C may need prolonged therapy.

Adverse reactions of
Adverse reactions of interferon
interferon
An influenza
An influenza--like syndrome
like syndrome
Fatigue &
Fatigue &anoroxia
anoroxia
Convulsions, depression
Convulsions, depression
Hypotension, hypertension, cardiac
Hypotension, hypertension, cardiac
arrhythmias
arrhythmias
Bone marrow depression.
Bone marrow depression.
It inhibit the metabolism of theophylline
It inhibit the metabolism of theophylline
Adverse reactions of
Adverse reactions of interferon
interferon
An influenza
An influenza--like syndrome
like syndrome
Fatigue &
Fatigue &anoroxia
anoroxia
Convulsions, depression
Convulsions, depression
Hypotension, hypertension, cardiac
Hypotension, hypertension, cardiac
arrhythmias
arrhythmias
Bone marrow depression.
Bone marrow depression.
It inhibit the metabolism of theophylline
It inhibit the metabolism of theophylline

Inosine
Inosine Pranobex
Pranobex
Mucocutaneous
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex
herpes simplex
and genital warts.
and genital warts.
It is administered by mouth and
It is administered by mouth and
metabolised
metabolised to uric acid.
to uric acid.
