
Antifungal drugs

Mycoses:
Is an Infection disease caused by
fungi.
Many common mycotic infections are:
Cutaneous mycoses (superficial and only
involve the skin)
Subcutaneous infections (fungi may
penetrate the skin)
Systemic mycoses (most difficult to treat)
Mycoses:
Is an Infection disease caused by
fungi.
Many common mycotic infections are:
Cutaneous mycoses (superficial and only
involve the skin)
Subcutaneous infections (fungi may
penetrate the skin)
Systemic mycoses (most difficult to treat)

Drugs for Subcutaneous and Systemic
Mycotic
Amphotericin B
Naturaly polyene macrolide ,antibiotic
produce by Strptomyces nodosus
Bind to ergosterol in plasma membrane of
sensitive fungal cell they form pores
(channels),disrupt membrane function
allowing electrolyte k to leak from the cell
resulting in cell death
Drugs for Subcutaneous and Systemic
Mycotic
Amphotericin B
Naturaly polyene macrolide ,antibiotic
produce by Strptomyces nodosus
Bind to ergosterol in plasma membrane of
sensitive fungal cell they form pores
(channels),disrupt membrane function
allowing electrolyte k to leak from the cell
resulting in cell death
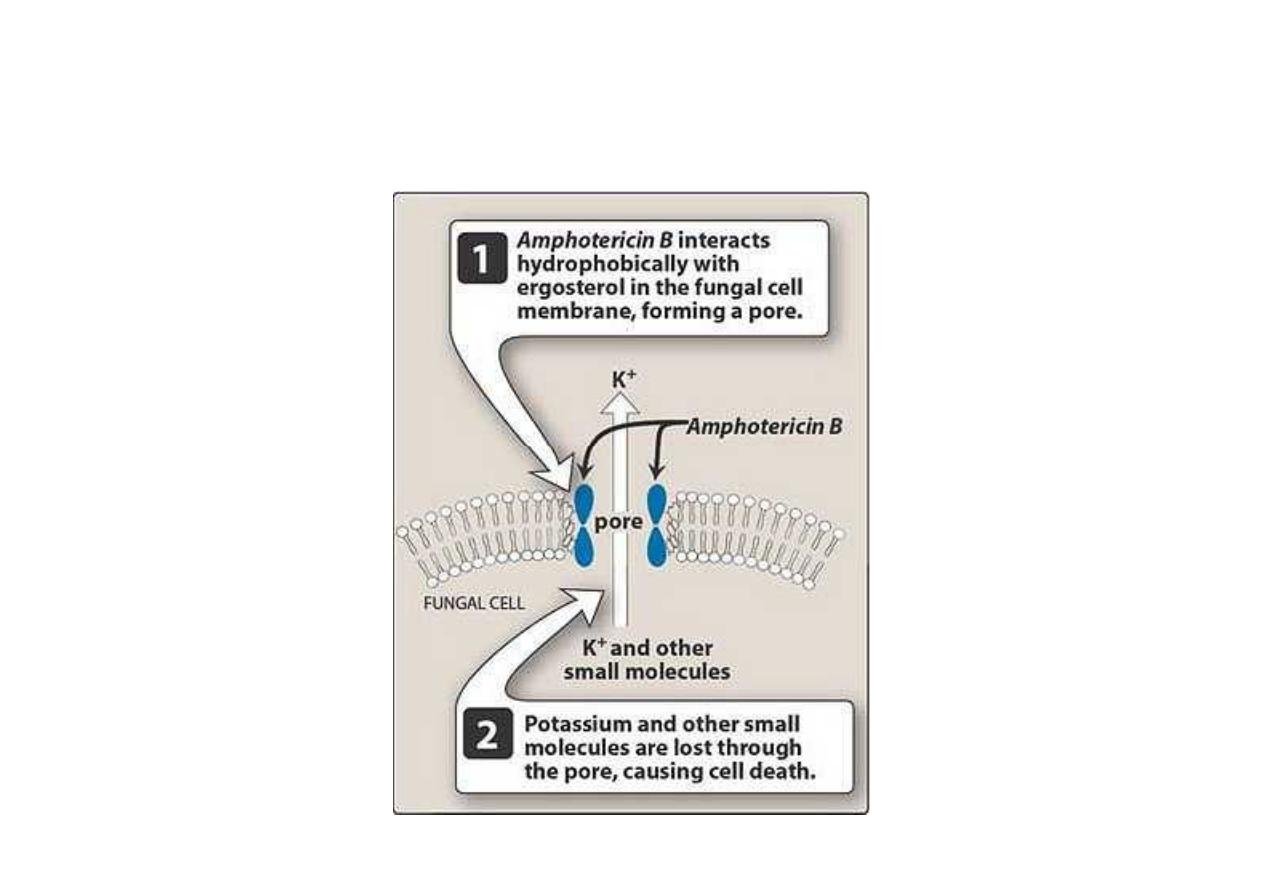
Model of a pore formed by amphotericin B in the lipid
bilayer membrane

Either fungicidal or fungistatic depending on
organism and concentration of drug.
Its acts against Candida albicans and
histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus
neoformans, Blastomyces dermatitidis, and
many strains of aspergillus.
Amphotericin B is also used in the treatment
of the protozoal infection, leishmaniasis.
Either fungicidal or fungistatic depending on
organism and concentration of drug.
Its acts against Candida albicans and
histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus
neoformans, Blastomyces dermatitidis, and
many strains of aspergillus.
Amphotericin B is also used in the treatment
of the protozoal infection, leishmaniasis.

Pharmacokinetic of Amphotericin B
Intravenous infusion (slow)
The intrathecal for the treatment of
meningitis caused by fungi that are
sensitive to the drug (more dangerous).
Bound to plasma protein .
Excreated by urine and bile.
Pharmacokinetic of Amphotericin B
Intravenous infusion (slow)
The intrathecal for the treatment of
meningitis caused by fungi that are
sensitive to the drug (more dangerous).
Bound to plasma protein .
Excreated by urine and bile.
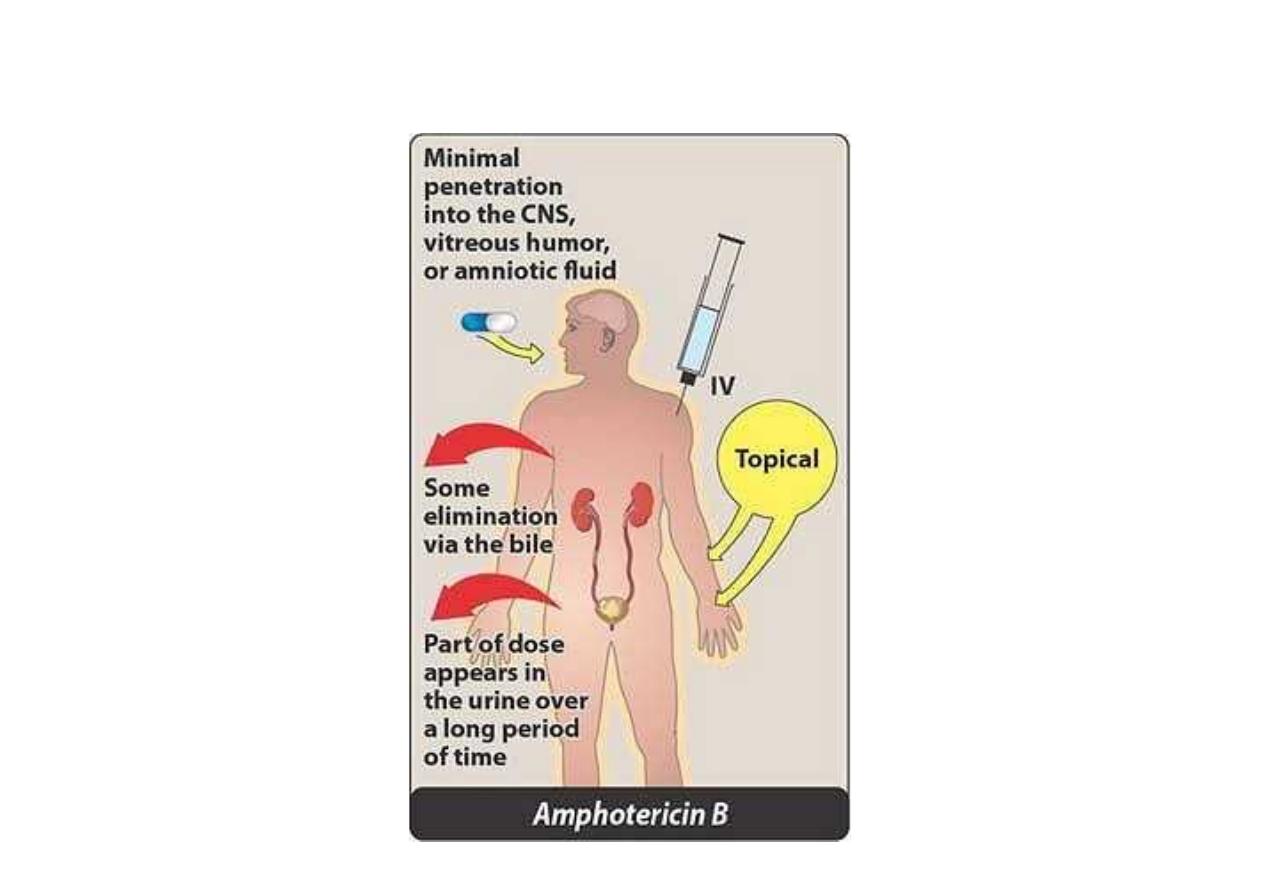
Administration and fate of amphotericin B
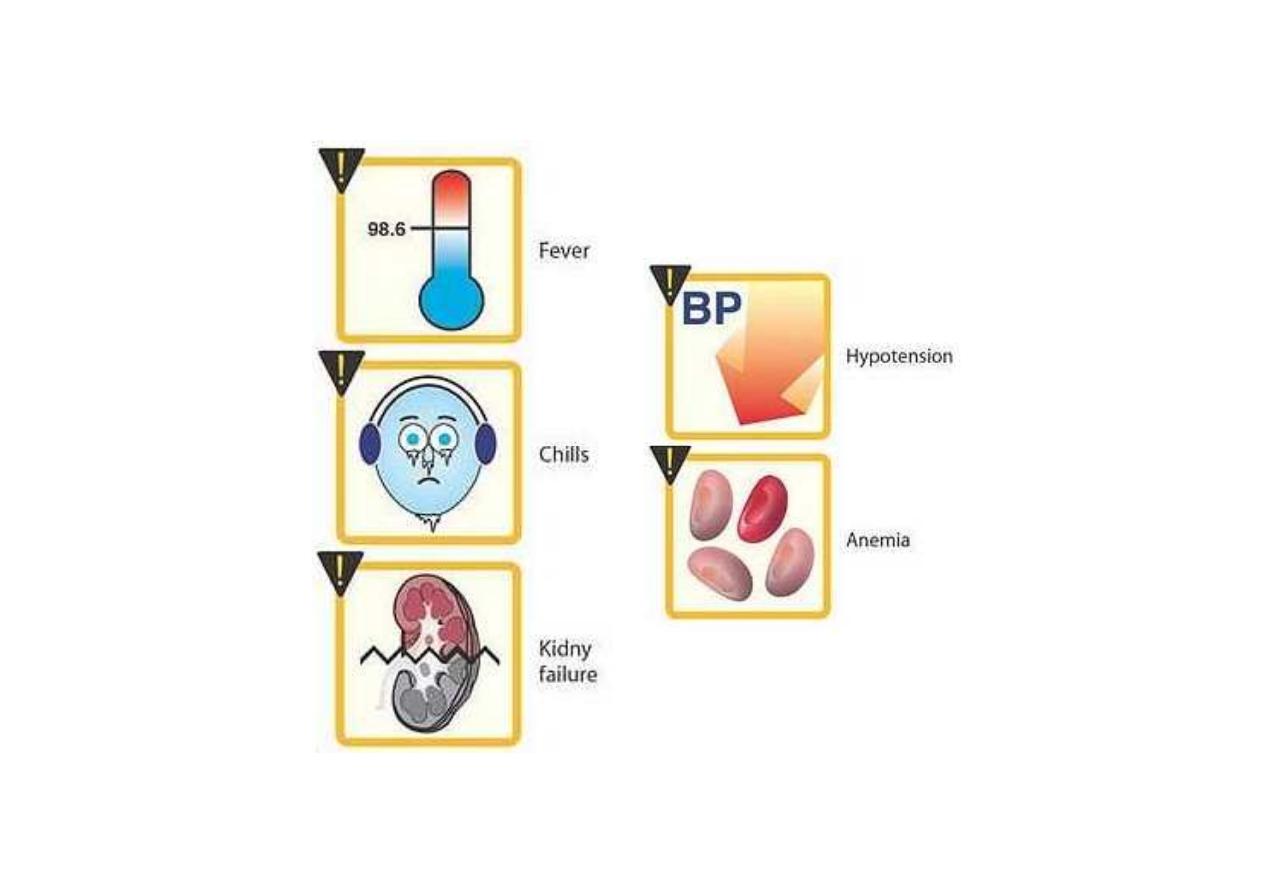
Adverse effects of amphotericin B

Side effects of Amphotericin B
Fever and chills
Renal impairment
Hypotension ,hypokalemia
Anemia
Neurologic effects (by Intrathecal
administration)
Thrombophlebitis
Side effects of Amphotericin B
Fever and chills
Renal impairment
Hypotension ,hypokalemia
Anemia
Neurologic effects (by Intrathecal
administration)
Thrombophlebitis
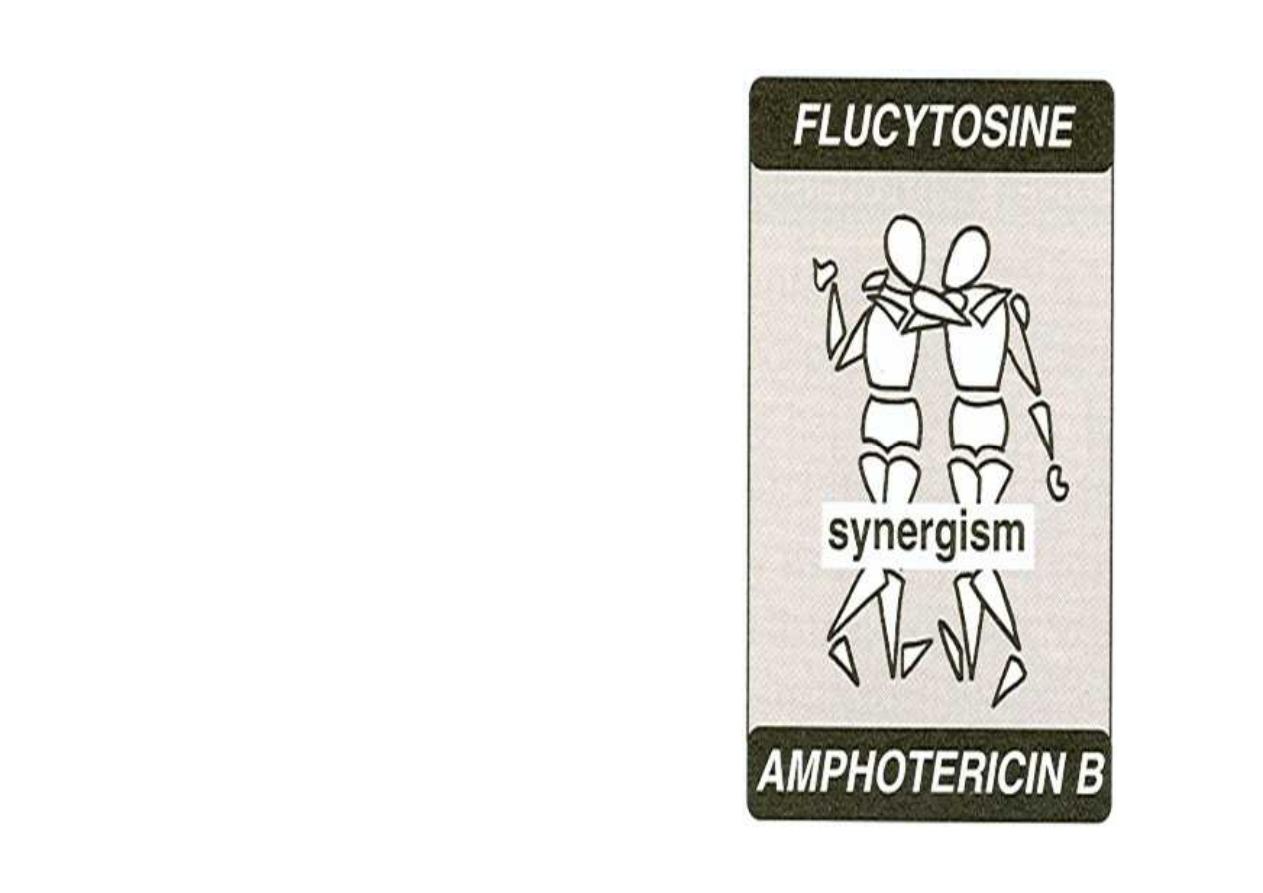
Flucytosine
•
Used in combination with
amphotericin B (for the
treatment of systemic
mycoses and for meningitis
caused by Cryptococcus
neoformans and Candida
albicans)
Flucytosine
•
Used in combination with
amphotericin B (for the
treatment of systemic
mycoses and for meningitis
caused by Cryptococcus
neoformans and Candida
albicans)

Flucytocin is taken by fungal cell and
its converted intracellurally to 5
FluorouraciL
(
5-FU)which is inhibit DNA and RNA
synthesis.
Note:
Amphotericin B increases cell
permeability, allowing more
(Flucytocin )5-FC to penetrate the cell.
Flucytocin is taken by fungal cell and
its converted intracellurally to 5
FluorouraciL
(
5-FU)which is inhibit DNA and RNA
synthesis.
Note:
Amphotericin B increases cell
permeability, allowing more
(Flucytocin )5-FC to penetrate the cell.
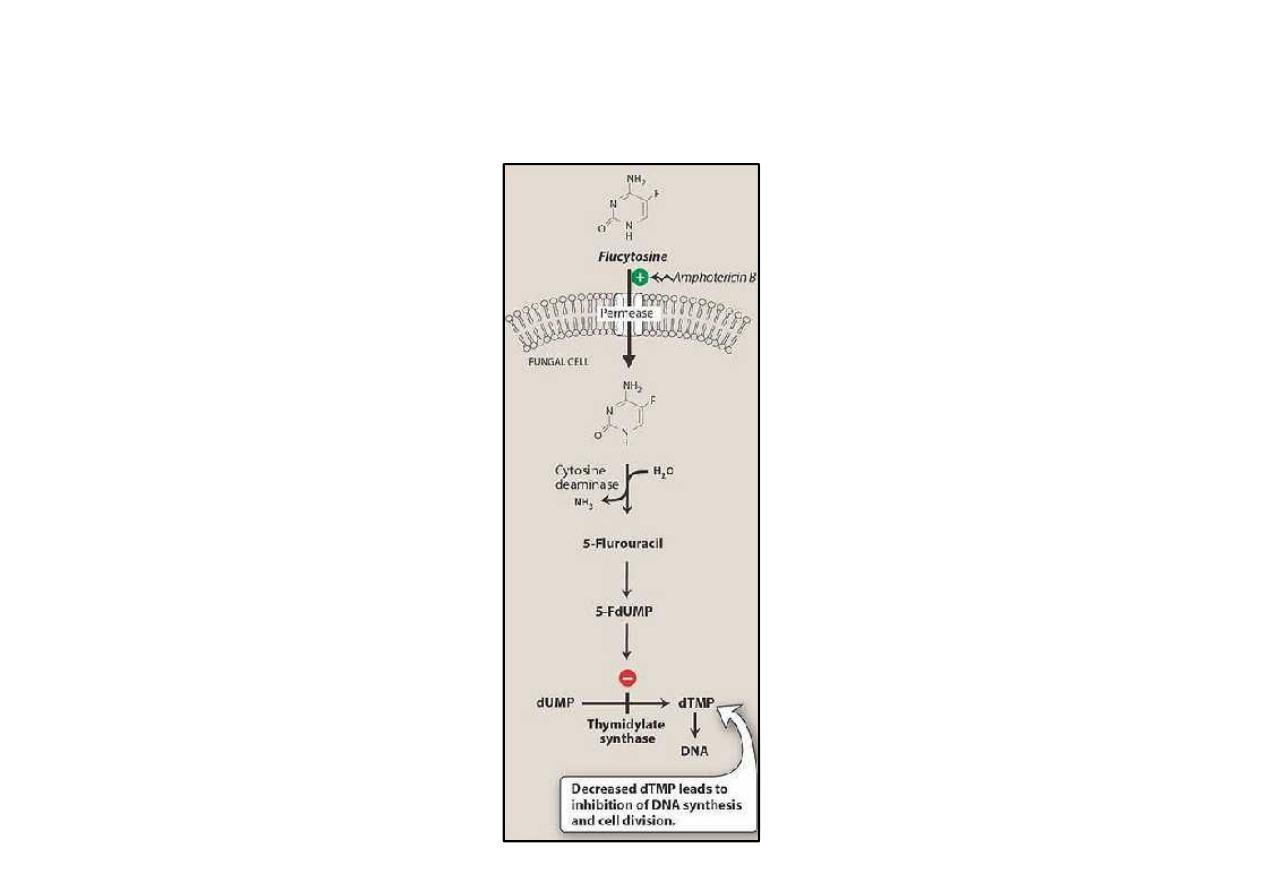
Mode of action of flucytosine. 5-FdUMP = 5-fluorodeoxyuridine
5'-monophosphate; dTMP = deoxythymidine 5'-monophosphate

Pharmacokinetic of Flucytocin
Well absorbed by the oral route.
penetrates well into the CSF
Excretion of both the parent drug and its
metabolites is by urine
Adverse effects of Flucytocin
1. Neutropenia, thrombo-cytopenia, bone
marrow depression
2. Reversible hepatic dysfunction
3. Gastrointestinal disturbances and severe
enterocolitis
Pharmacokinetic of Flucytocin
Well absorbed by the oral route.
penetrates well into the CSF
Excretion of both the parent drug and its
metabolites is by urine
Adverse effects of Flucytocin
1. Neutropenia, thrombo-cytopenia, bone
marrow depression
2. Reversible hepatic dysfunction
3. Gastrointestinal disturbances and severe
enterocolitis

AZOLE
Ketoconazole
Itraconazole
Fluconazole
Voriconazole

Ketoconazole
Was the first orally active azole for the
treatment of systemic mycoses.
Block the demethylation of lanosterol to
ergosterol which the principle sterol of fungal
membrane (inhibit fungal cell growth).
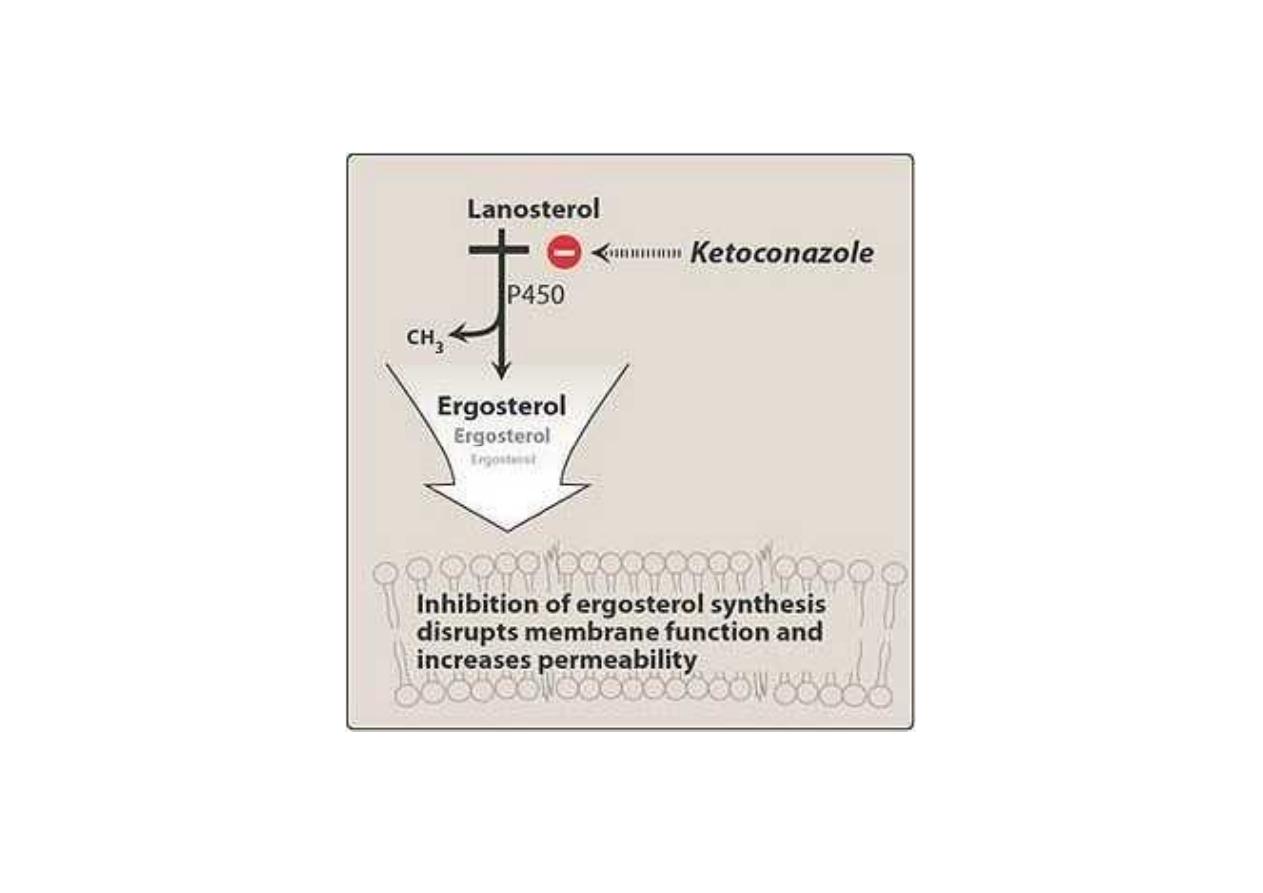
Mode of action of ketoconazole

Pharmacokinetics of Ketoconazole
Orally administion
It requires gastric acid for dissolution and is
absorbed through the gastric mucosa.
Bound to plasma proteins.
Although penetration into tissues is limited, it
is effective in the treatment of histoplasmosis
in lung, bone, skin, and soft tissues.
Metabolism occurs in the liver, excretion
through the bile.
Levels of parent drug in the urine are too low
to be effective against mycotic infections of the
urinary tract
Pharmacokinetics of Ketoconazole
Orally administion
It requires gastric acid for dissolution and is
absorbed through the gastric mucosa.
Bound to plasma proteins.
Although penetration into tissues is limited, it
is effective in the treatment of histoplasmosis
in lung, bone, skin, and soft tissues.
Metabolism occurs in the liver, excretion
through the bile.
Levels of parent drug in the urine are too low
to be effective against mycotic infections of the
urinary tract

Adverse effects of Ketoconazole
1. Allergic reaction
2. GIT disturbance
3. Hepatic dysfunction
4. Endocrine effect (blocking androgen and
adrenal steroid synthesis) so may cause
gynaecomastia,impotence in men and
menstrual irregularities in women
Adverse effects of Ketoconazole
1. Allergic reaction
2. GIT disturbance
3. Hepatic dysfunction
4. Endocrine effect (blocking androgen and
adrenal steroid synthesis) so may cause
gynaecomastia,impotence in men and
menstrual irregularities in women

Drug Interaction of Ketoconazole
Inhibit P450 Cytochrome can potentiate the
toxicity of cyclosporin, phenytoin, warfarin.
Rifampin, H2 Inhibitors decrease the action
of ketaconazole
H
2
-receptor blockers, antacids, proton-
pump inhibitors, and sucralfate, can
decrease absorption of ketoconazole
Drug Interaction of Ketoconazole
Inhibit P450 Cytochrome can potentiate the
toxicity of cyclosporin, phenytoin, warfarin.
Rifampin, H2 Inhibitors decrease the action
of ketaconazole
H
2
-receptor blockers, antacids, proton-
pump inhibitors, and sucralfate, can
decrease absorption of ketoconazole
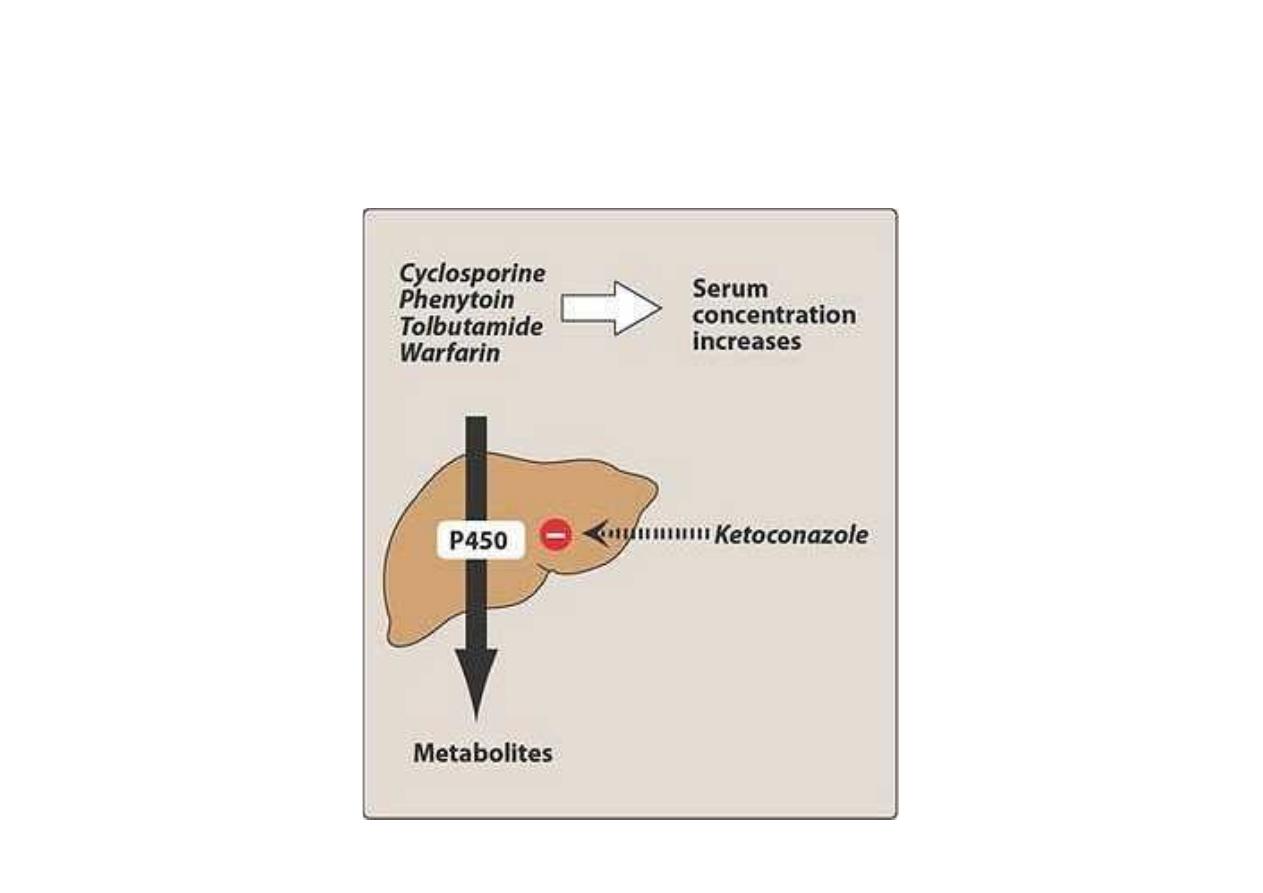
By inhibiting cytochrome P450, ketoconazole can
potentiate the toxicities of other drugs

Fluconazole
Its same as ketoconazole.
Its effective against all form of candidiasis
Given orally or I.V.
Indicated for treatment of meningitis
(Penetrate CSF)
Excreted via kidney.
Lack of endocrine effect of ketoconazole
Have GIT disturbance.
Teratogenic effect
Fluconazole
Its same as ketoconazole.
Its effective against all form of candidiasis
Given orally or I.V.
Indicated for treatment of meningitis
(Penetrate CSF)
Excreted via kidney.
Lack of endocrine effect of ketoconazole
Have GIT disturbance.
Teratogenic effect

Itraconazol
For treatment of blastomycosis,
histoplasmosis, AIDS.
Given orally require acid for dissolution.
Metabolize by liver.
Side effects of Itraconazol
Nausea ,vomiting, Rash, Hypertension
hypokalemia, edema, and headache.
Itraconazol
For treatment of blastomycosis,
histoplasmosis, AIDS.
Given orally require acid for dissolution.
Metabolize by liver.
Side effects of Itraconazol
Nausea ,vomiting, Rash, Hypertension
hypokalemia, edema, and headache.

Echinocandins (Caspofungin,
micafungin, and Anidulafungin)
Caspofungin
Echinocandins interfere with the synthesis of
the fungal cell wall leading to lyses and cell
death
Echinocandins (Caspofungin,
micafungin, and Anidulafungin)
Caspofungin
Echinocandins interfere with the synthesis of
the fungal cell wall leading to lyses and cell
death

Caspofungin
It is a second-line antifungal for those who
have failed or cannot tolerate amphotericin B
or an azole.
Not active by the oral route.
Bound to serum proteins
It is slowly metabolized by hydrolysis and N-
acetylation.
Urinary and fecal elimination.
Adverse effects of Caspofungin
Fever, rash, nausea, phlebitis and flushing
Caspofungin
It is a second-line antifungal for those who
have failed or cannot tolerate amphotericin B
or an azole.
Not active by the oral route.
Bound to serum proteins
It is slowly metabolized by hydrolysis and N-
acetylation.
Urinary and fecal elimination.
Adverse effects of Caspofungin
Fever, rash, nausea, phlebitis and flushing

Drugs for Cutaneous Mycotic Infections
Fungi that cause superficial skin infections are called
dermatophytes
Terbinafine
Fungicidal
The drug of choice for treating dermatophytoses and,
especially, onychomycoses (fungal infections of nails).
More effective than either itraconazole or griseofulvin.
Inhibits fungal squalene epoxidase, thereby decreasing
the synthesis of ergosterol , accumulation of toxic
amounts of squalene result in the death of the fungal
cell.
Note
: Significantly higher concentrations of terbinafine
are needed to inhibit human squalene epoxidase, an
enzyme required for the cholesterol synthetic pathway.
Drugs for Cutaneous Mycotic Infections
Fungi that cause superficial skin infections are called
dermatophytes
Terbinafine
Fungicidal
The drug of choice for treating dermatophytoses and,
especially, onychomycoses (fungal infections of nails).
More effective than either itraconazole or griseofulvin.
Inhibits fungal squalene epoxidase, thereby decreasing
the synthesis of ergosterol , accumulation of toxic
amounts of squalene result in the death of the fungal
cell.
Note
: Significantly higher concentrations of terbinafine
are needed to inhibit human squalene epoxidase, an
enzyme required for the cholesterol synthetic pathway.

Pharmacokinetics of Terbinafine
Orally active
Bioavailability is only 40 percent due to first-
pass metabolism.
Terbinafine is greater than 99 percent bound
to plasma proteins.
It is deposited in the skin, nails, and fat.
A prolonged terminal half-life of 200 to 400
hours may reflect the slow release from
these tissues.
Patients with either moderate renal
impairment or hepatic cirrhosis have
reduced clearance
Pharmacokinetics of Terbinafine
Orally active
Bioavailability is only 40 percent due to first-
pass metabolism.
Terbinafine is greater than 99 percent bound
to plasma proteins.
It is deposited in the skin, nails, and fat.
A prolonged terminal half-life of 200 to 400
hours may reflect the slow release from
these tissues.
Patients with either moderate renal
impairment or hepatic cirrhosis have
reduced clearance

Adverse effects of Terbinafine
1. Gastrointestinal disturbances
2. Headache and rash
3. Taste and visual disturbances
4. Transient elevations in serum liver enzyme
5. Hepatotoxicity and neutropenia (rarely)
Adverse effects of Terbinafine
1. Gastrointestinal disturbances
2. Headache and rash
3. Taste and visual disturbances
4. Transient elevations in serum liver enzyme
5. Hepatotoxicity and neutropenia (rarely)

Griseofulvin
largely replaced by terbinafine for the treatment of
dermatophytic infections of the nails.
Griseofulvin requires treatment of 6 to 12 months in
duration.
It is only fungistatic,
Griseofulvin accumulates in newly synthesized, keratin-
containing tissue, where it causes disruption of the
mitotic spindle and inhibition of fungal mitosis
Duration of therapy is dependent on the rate of
replacement of healthy skin or nails.
The gastrointestinal tract absorption is enhanced by
high-fat meals.
Enzyme inducer, increases metabolism anticoagulants.
Griseofulvin potentiates the intoxic effects of alcohol.
Griseofulvin
largely replaced by terbinafine for the treatment of
dermatophytic infections of the nails.
Griseofulvin requires treatment of 6 to 12 months in
duration.
It is only fungistatic,
Griseofulvin accumulates in newly synthesized, keratin-
containing tissue, where it causes disruption of the
mitotic spindle and inhibition of fungal mitosis
Duration of therapy is dependent on the rate of
replacement of healthy skin or nails.
The gastrointestinal tract absorption is enhanced by
high-fat meals.
Enzyme inducer, increases metabolism anticoagulants.
Griseofulvin potentiates the intoxic effects of alcohol.

Nystatin
Is a polyene antibiotic
Resemble of amphotericin B in (its structure,
chemistry, mechanism of action)
Have systemic toxicity (Its use is restricted
to topical treatment of Candida infections)
The drug is negligibly absorbed from the
gastrointestinal tract, and it is never used
parenterally.
It is administered as an oral agent for the
treatment of oral candidiasis.
Excretion in the feces
Nystatin
Is a polyene antibiotic
Resemble of amphotericin B in (its structure,
chemistry, mechanism of action)
Have systemic toxicity (Its use is restricted
to topical treatment of Candida infections)
The drug is negligibly absorbed from the
gastrointestinal tract, and it is never used
parenterally.
It is administered as an oral agent for the
treatment of oral candidiasis.
Excretion in the feces

Topical agents
Miconazole, clotrimazole, butoconazole and
terconazole
Their mechanism of action and antifungal spectrum are
the same as those of ketoconazole.
Topically active drugs that are only rarely administered
parenterally because of their severe toxicity
Topical use is associated with contact dermatitis, vulvar
irritation, and edema.
Miconazole is a potent inhibitor of warfarin metabolism
and has produced bleeding in warfarin-treated patients
even when miconazole is applied topically.
No significant difference in clinical outcomes is
associated with any azole or nystatin in the treatment of
vulvar candidiasis
Topical agents
Miconazole, clotrimazole, butoconazole and
terconazole
Their mechanism of action and antifungal spectrum are
the same as those of ketoconazole.
Topically active drugs that are only rarely administered
parenterally because of their severe toxicity
Topical use is associated with contact dermatitis, vulvar
irritation, and edema.
Miconazole is a potent inhibitor of warfarin metabolism
and has produced bleeding in warfarin-treated patients
even when miconazole is applied topically.
No significant difference in clinical outcomes is
associated with any azole or nystatin in the treatment of
vulvar candidiasis
