Staphylococcus
Family micrococcaeceaeGenus Staphylococcus
3 important species
1. Staphylococcus auerus (Coagulase positive )
2. Staphylococcus epidermidis CoNS
3. Staphylococcus saprophyticus (coagulase negative)
Microscopical appearance
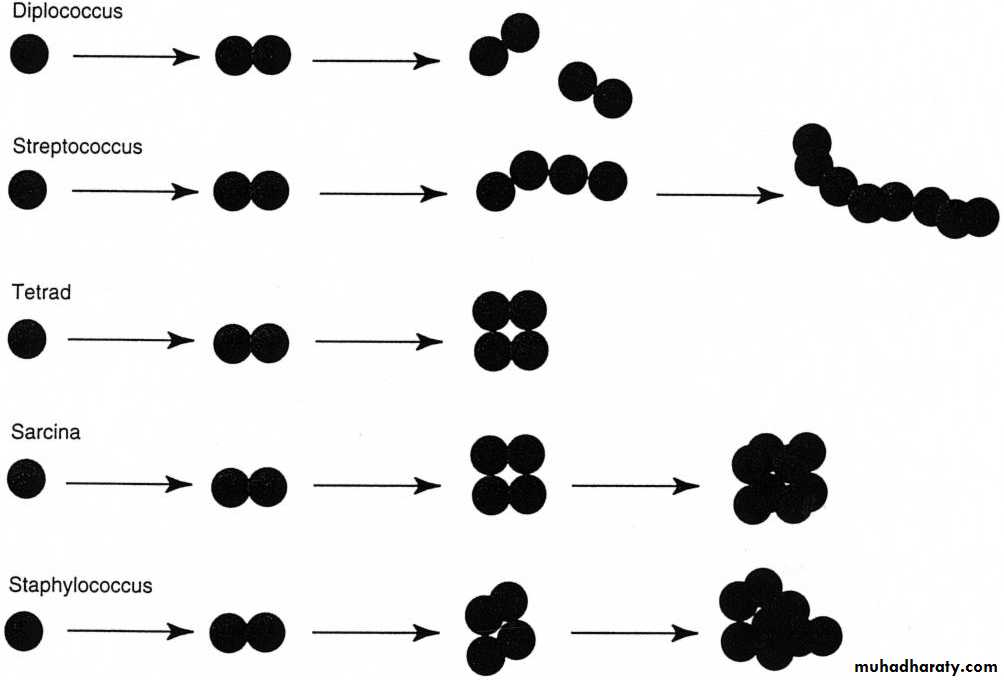
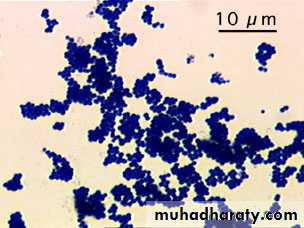
Gram positive cocci , 1 μm in diameter. arranged clusters (grape like), tetrads, pairs, short chains, non motile, non spore forming moo.
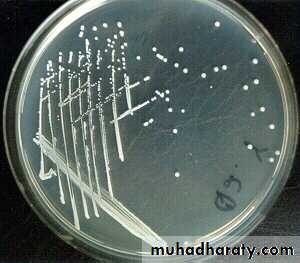
Culture characteristics
Staphylococci grow readily on most bacteriologic media under aerobic or faculatively anaerobic conditions.They grow most rapidly at 37 °C but form pigment best at room temperature (20–25 °C).
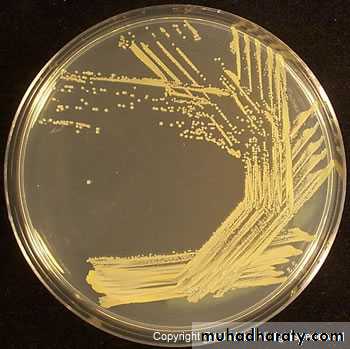
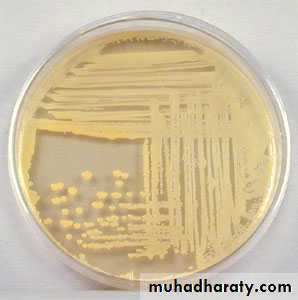
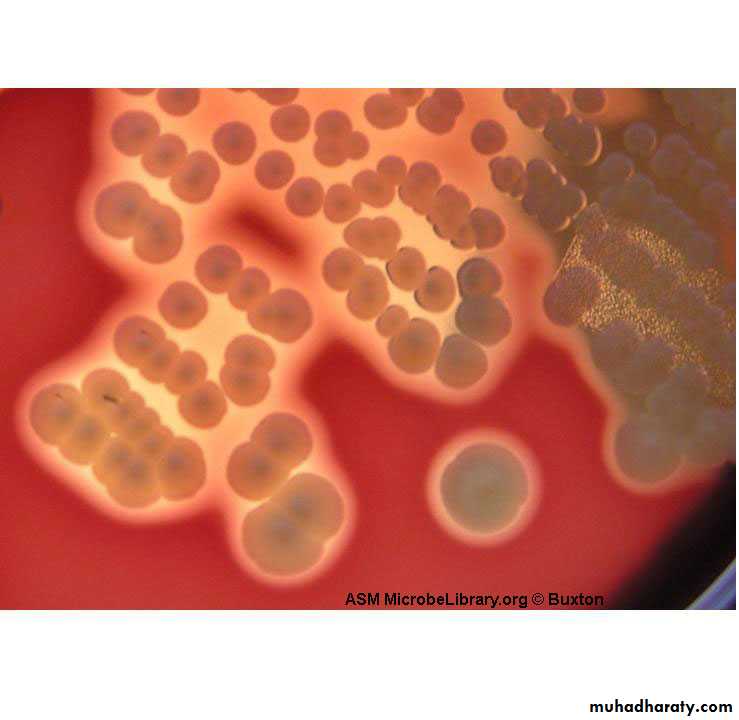
Colonies on solid media are round, smooth, raised, and glistening.
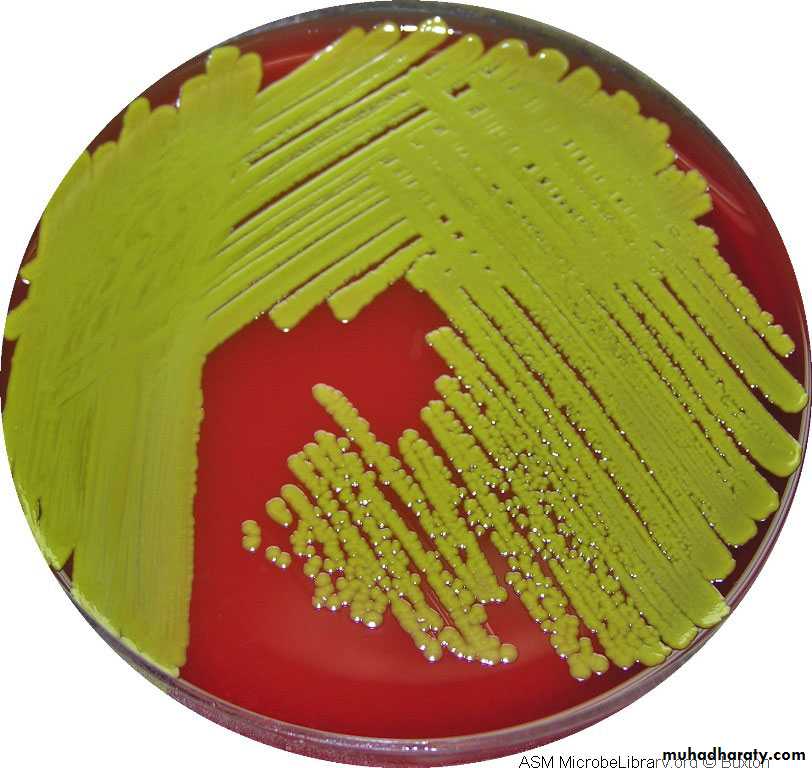
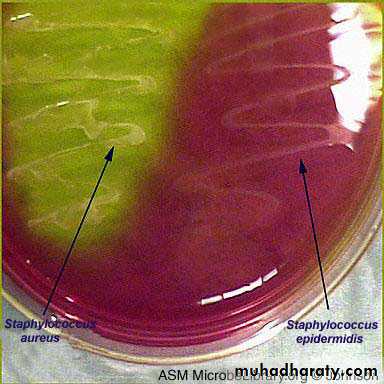
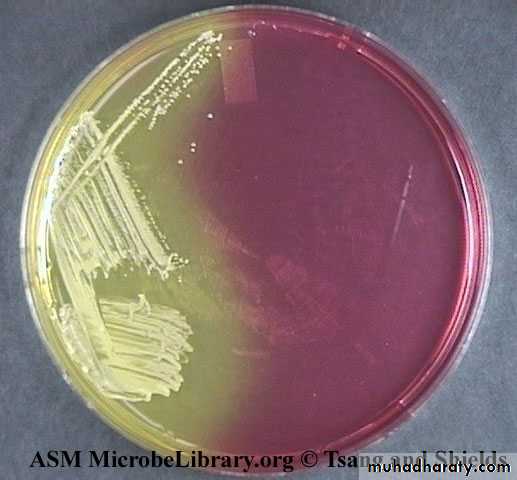
Staph aureus usually forms gray to deep golden yellow colonies.
Staph epidermidis colonies usually are gray to white
On nutrient agar
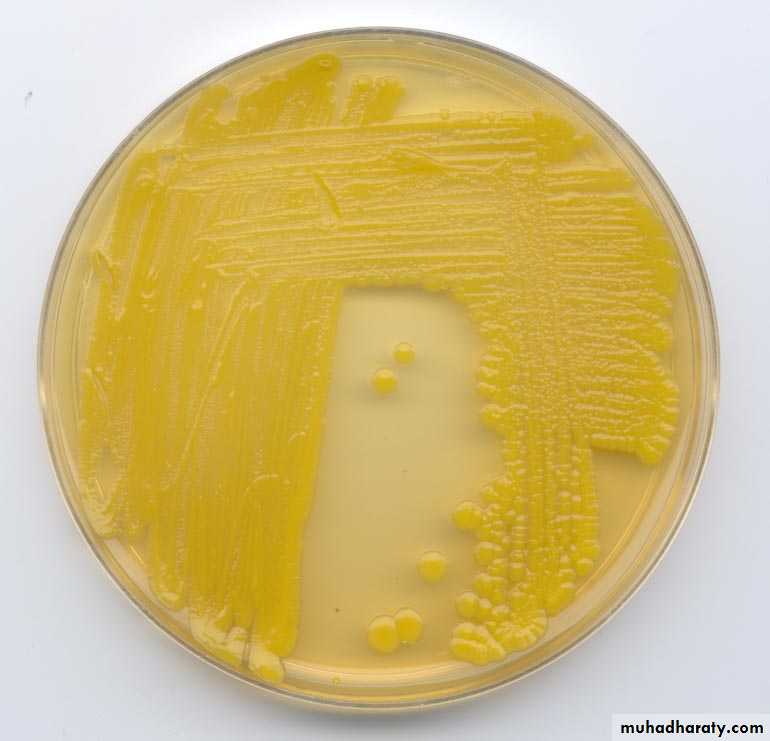
Staph auerus form golden yellow colonies .Staph epidermidis white colonies on nutrient agar
Staph saprophyticus 50 % produce lemon yellow color
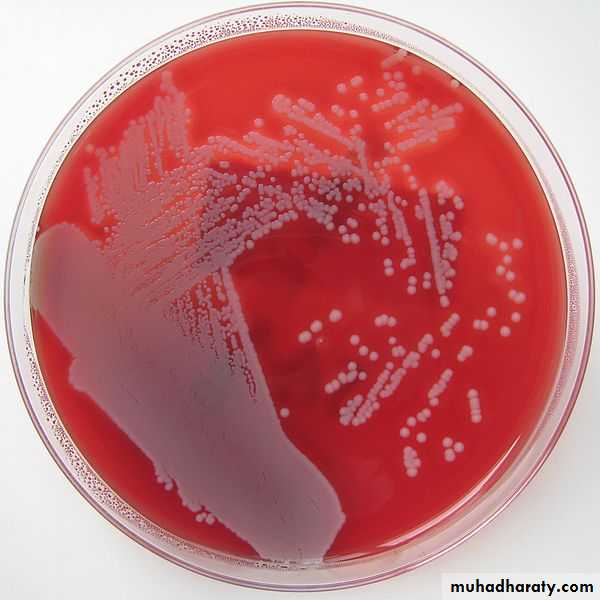
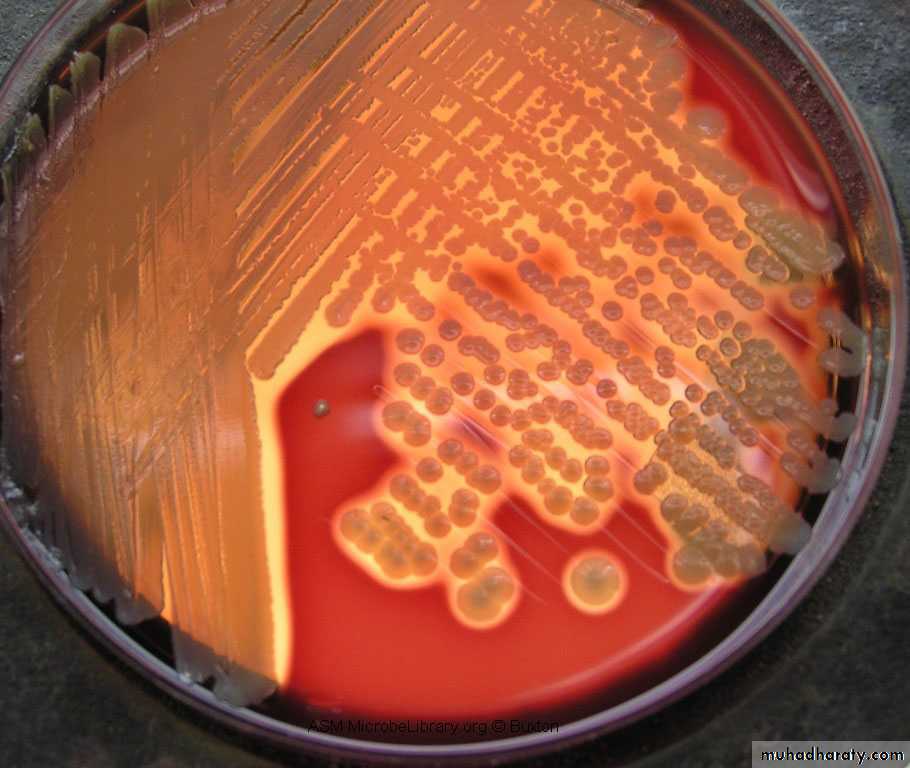
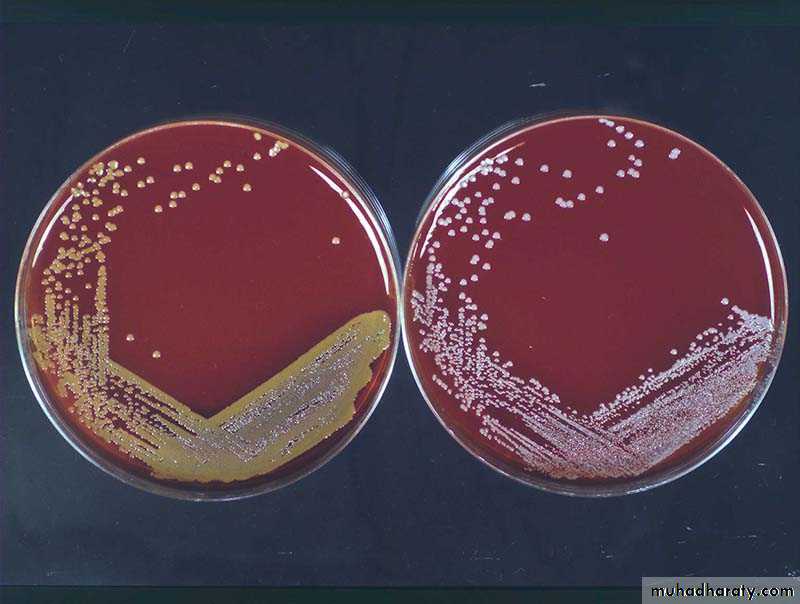
On blood agar
Staph auerus produce complete haemolysis (clear zone around the growth)Staph epidermidis
Staph saprophyticus non-haemolytic
(no change on
blood agar)
Staph aureus on blood agar
Biochemical activities
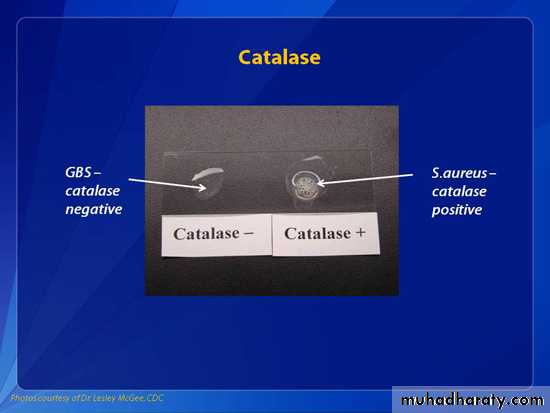
Catalase test : all spp of Staphyloccoci give positive catalase which differentiate it from Streptococci (catalase negative).H2O2 catalase H2O + O2
Catalase POS
StaphylococcusCatalase NEG
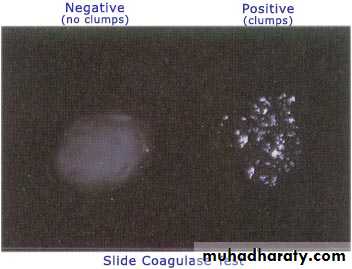
Coagulase test
The coagulase test has traditionally been used to differentiate Staphylococcu auerus from coagulase-negative staphylococci . S.aureus produces two forms of coagulase (i.e., bound coagulase and free coagulase). Bound coagulase, otherwise known as "clumping factor", can be detected by carrying out a slide coagulase test, and free coagulase can be detected using a tube coagulase test.Slide coagulase (Bound) causes bacterial cells to agglutinate in the plasma
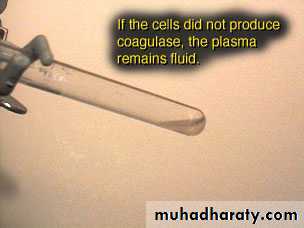
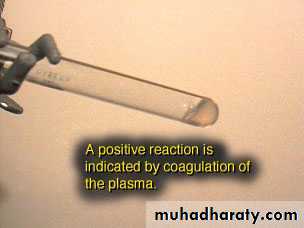
Free coagulase (tube) active enzyme produced by S aureusFibrinogen Fibrin
S. aureus
Coagulase NEG
Coagulase POS
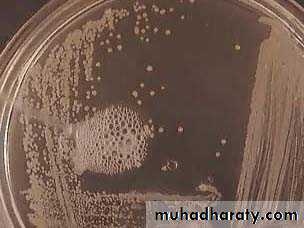
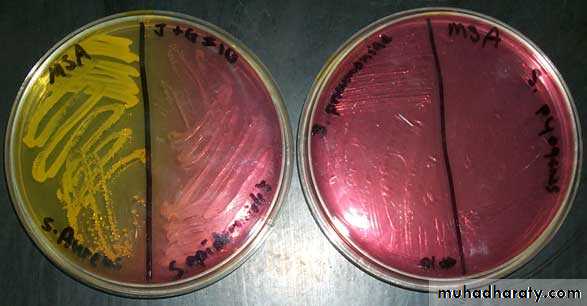
Staphylococcus aureusGrowth on mannitol salt agar and mannitol fermentation
MSA is a selective and differential medium in microbiology It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. It contains a high concentration (7.5%-10%) of salt (NaCl), making it selective for gram positive bacterium Staphylococci since this level of NaCl is inhibitory to most other bacteria.It is also a differential medium for mannitol-fermenting staphylococci, containing carbohydrate mannitol and the indicator phenol red a pH indicator for detecting acid produced by mannitol-fermenting Staphylococci. Staphylococcus aureus produce yellow colonies with yellow zones, whereas other Staphylococci produce small pink or red colonies with no colour change to the medium.