Pedodontics
Lec. 1Pediatric dentistry : is an age-defined specialty that provides both primary and comprehensive preventive and therapeutic oral health care for infants and children through adolescence, including those with special health care needs.
Primary Dentition
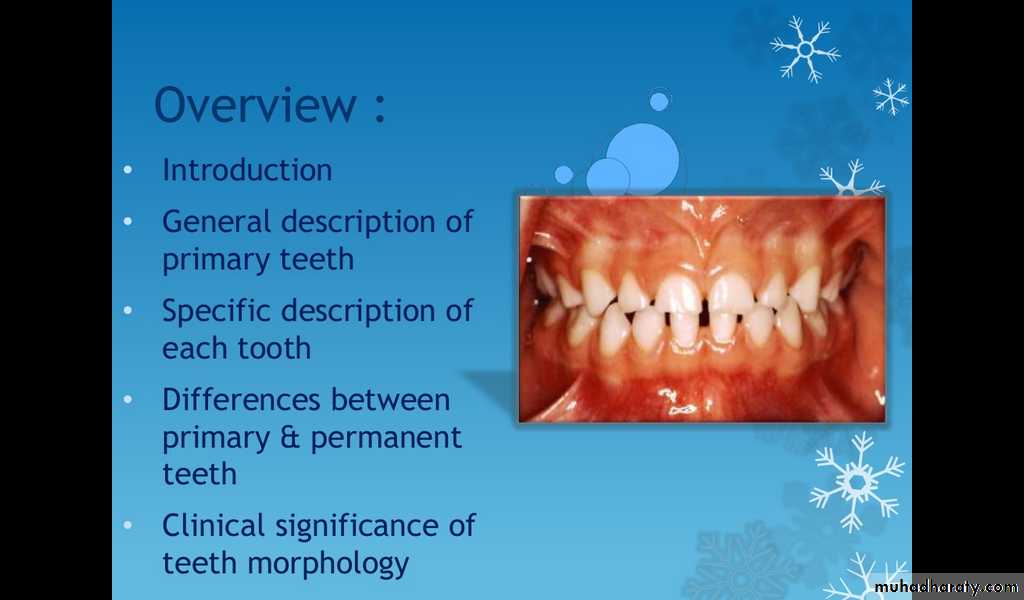
Overview:
Introduction.
General description of primary teeth.
Specific description of each tooth.
Differences between primary and permanent teeth.
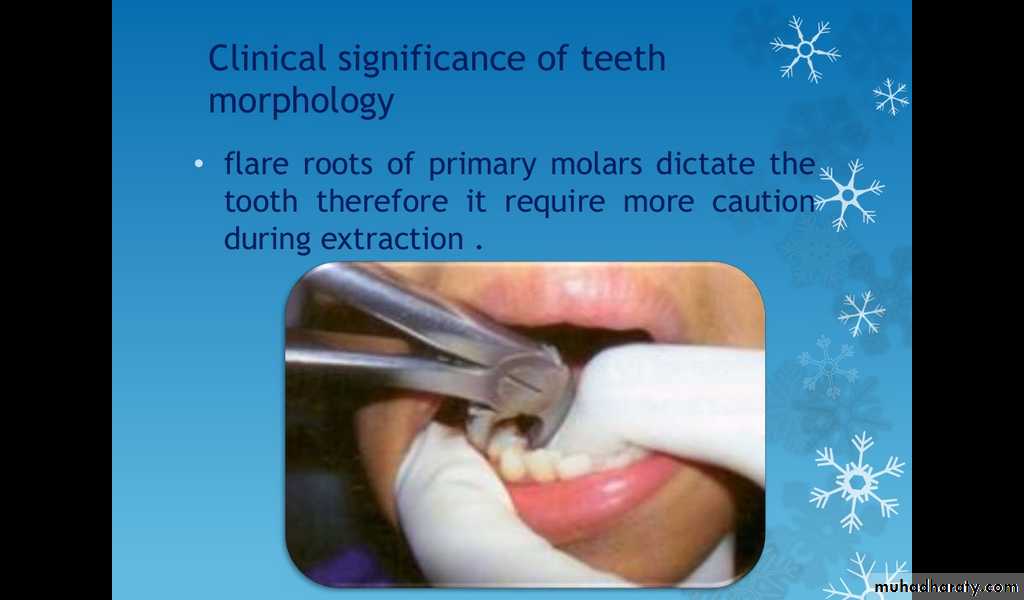
Clinical significance of teeth morphology.
Functions of primary teeth
Developmental anomalies of teeth
Introduction
There are 20 primary teeth as compared to 32 permanent teeth
No premolars in the primary dentition
The primary molars are replaced by the premolars
The permanent molars erupt distal to the primary second molars
General description of primary teeth.
Crown
Pulp
Root
Crown of Primary Teeth
Shorter
Narrower occlusal table
Constricted in the cervical portion
Thinner enamel dentin layers
Broad and flat contacts
Color is usually lighter
Prominent mesio-buccal cervical bulge seen in primary molars
Incisors have no developmental grooves or mammelons
Enamel rods in the cervical area directed occlusally
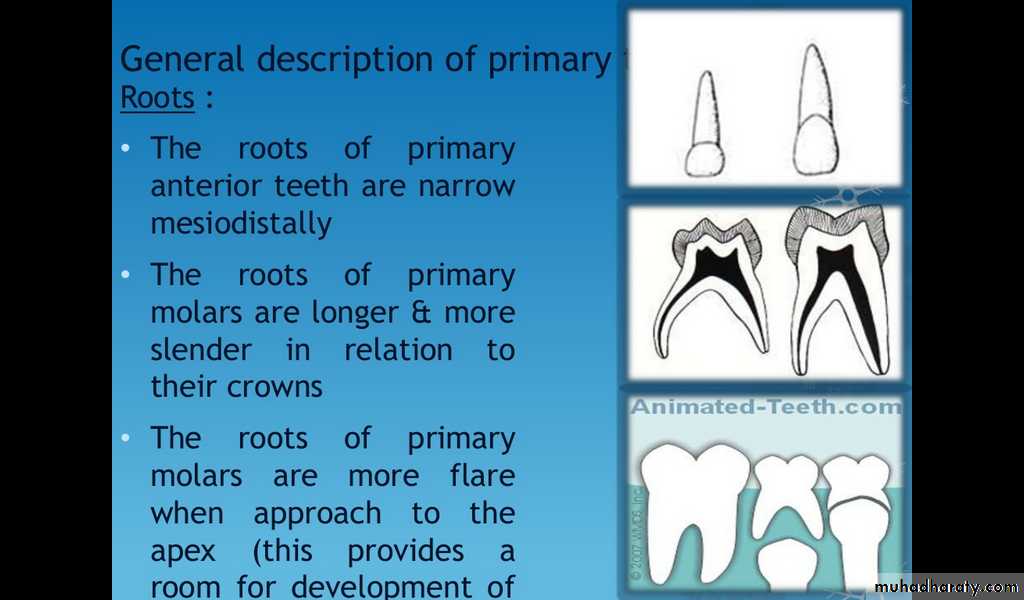
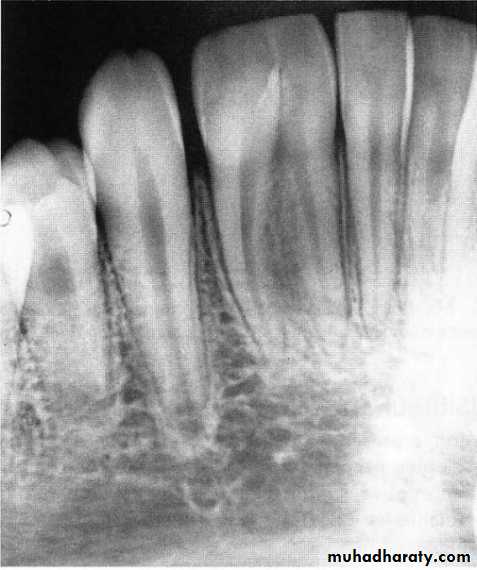
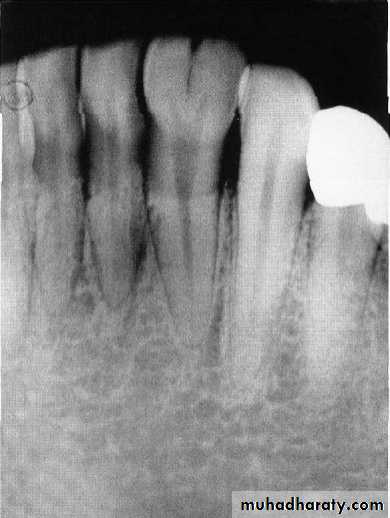
Roots of Primary Teeth
Roots of anterior teeth are narrower mesiodistally
Posterior teeth have longer and more slender roots in relation to crown size
Molar roots flare more as they approach the apex
(this provides a room for development of primary teeth).
Apical foramina may be larger and accessory canals often larger and more numerous.
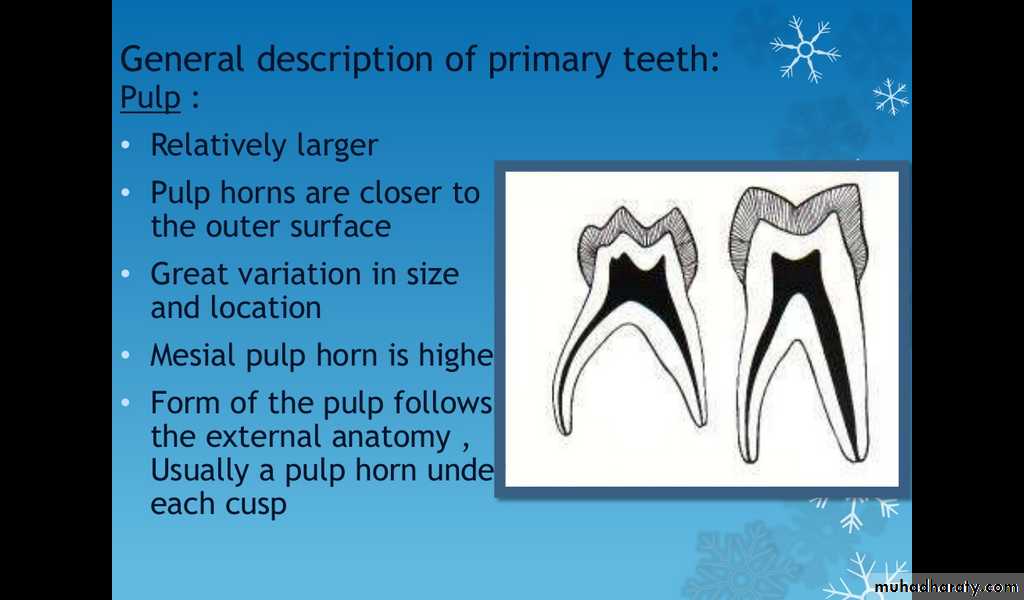
Pulps of Primary Teeth
Relatively larger
Pulp horns are closer to the outer surface
Great variation in size and location
Mesial pulp horn is higher
Pulp chamber shallow
Form of the pulp follows the external anatomy
Usually a pulp horn under each cusp
Specific description of each tooth:
Maxillary central incisor
Only tooth than has a greater mesiodistal width than height
Prominent cingulum
Incisal edge straight
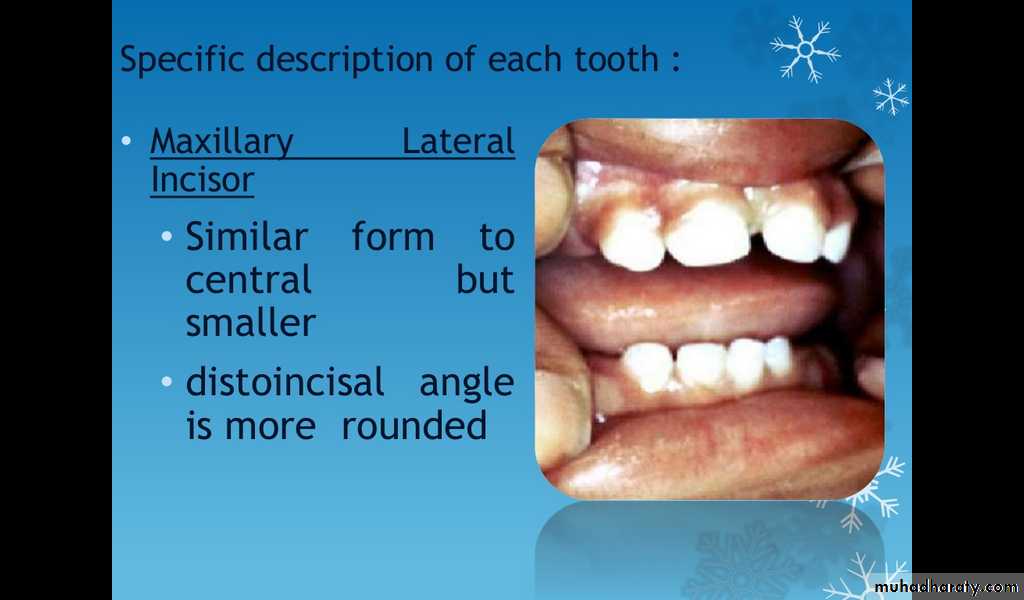
Maxillary lateral incisor
Similar form to central but smallerDisto incisal angle is more rounded
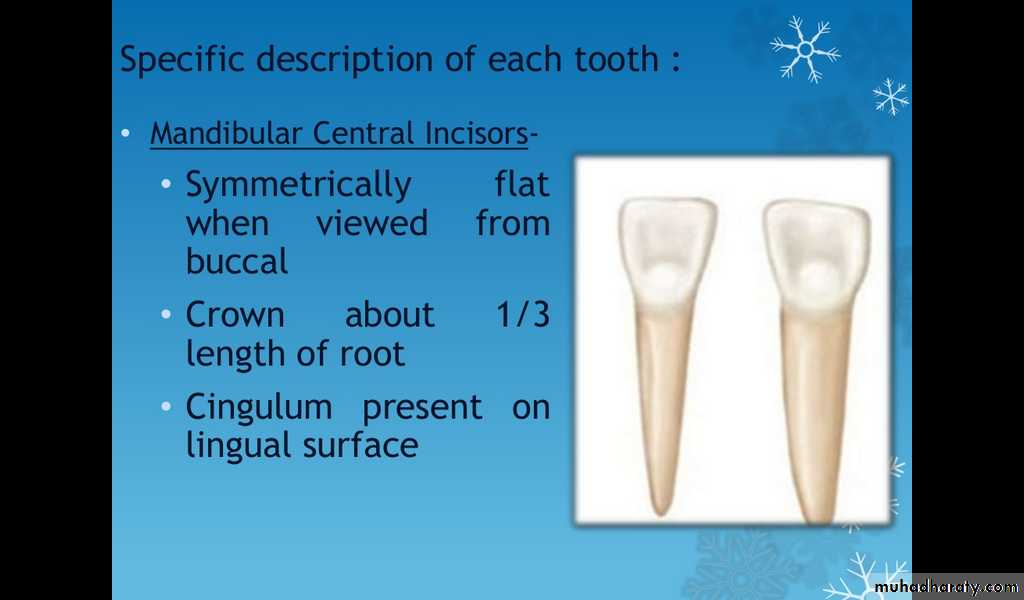
Mandibular central incisor
Symmetrically flat when viewed from buccal
Crown about 1/3 length of root
Cingulum present on ligual surface
Mandibular latral incisor
Similar form to centralUsually longer
Incisal edge slopes toward distal and distoincisal angle more rounded
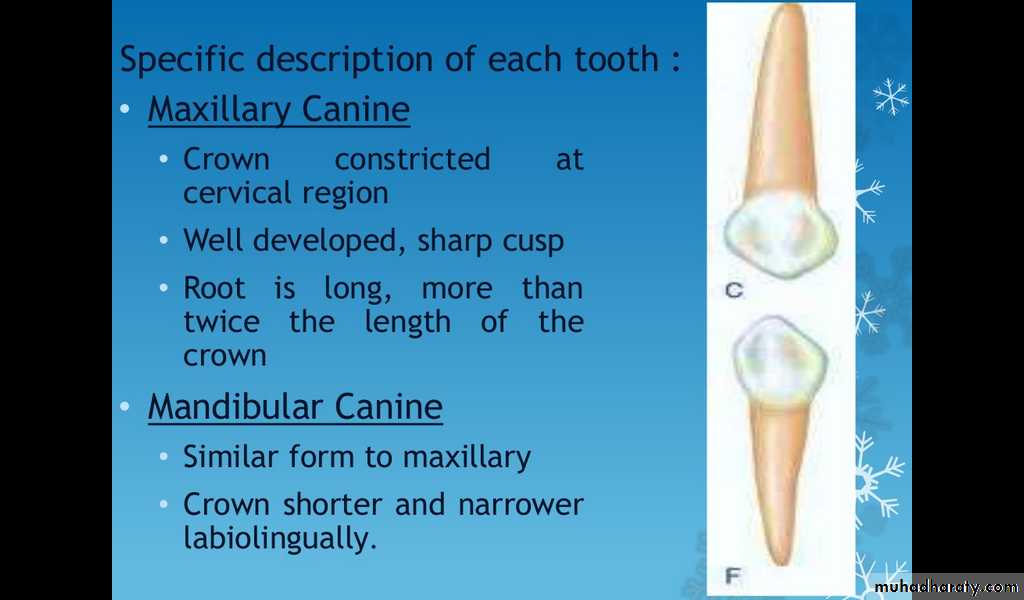
Maxillary canine
Crown constricted at cervical region
Well developed sharp cusp
Root is long more than twice the length of the crown
Mandibuular canine
Similar form to maxilliaryCrown shorter and narrower labiolingually
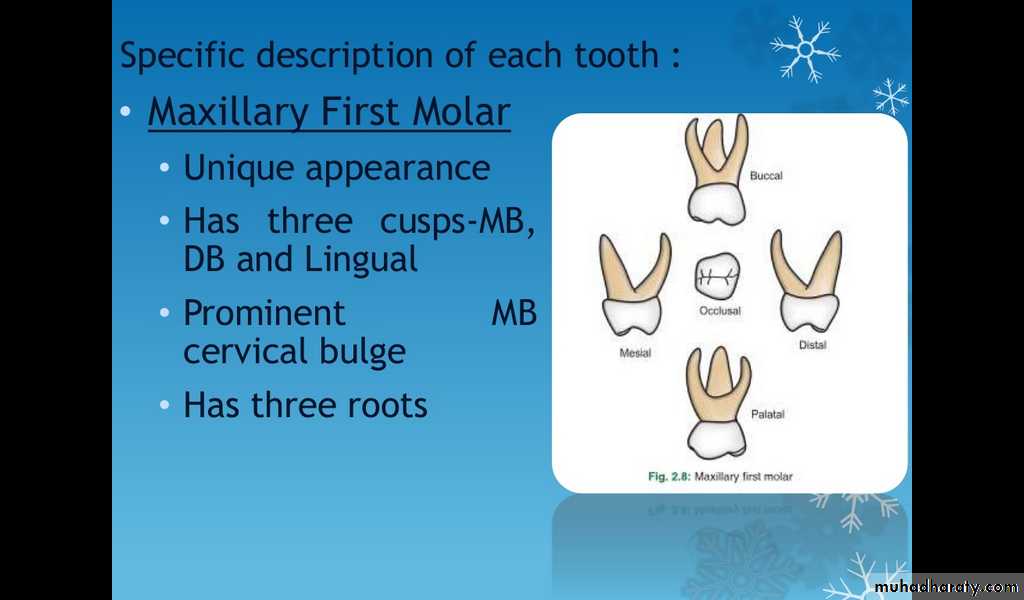
Maxillary first molar
Unique appearanceHas three cusps-MB, DB and Lingual
Prominent MB cervical bulge
Has three roots
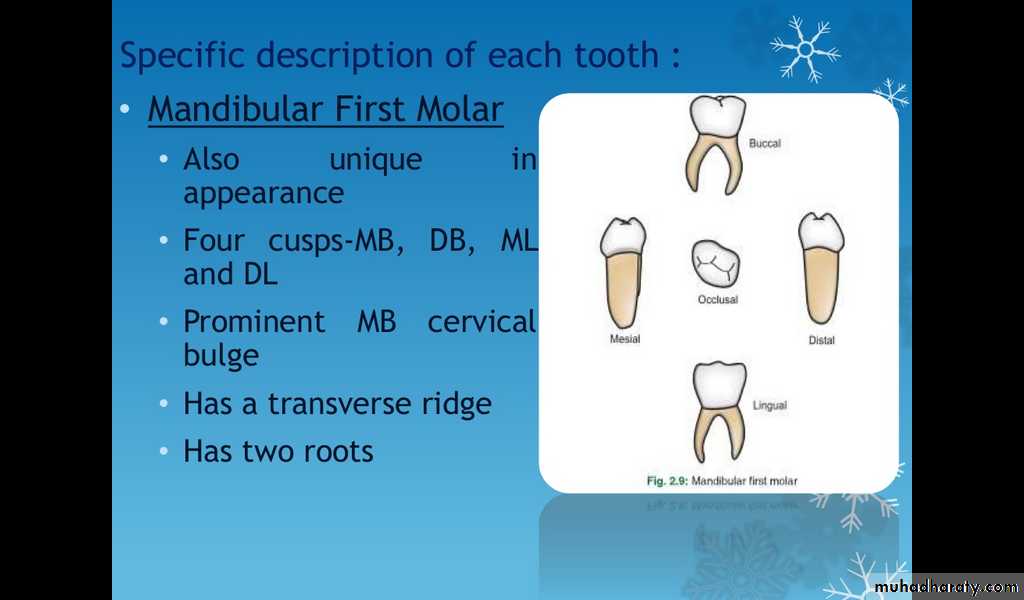
Mandibullar first molar
Also unique in appearanceFour cusps-MB, DB, ML and DL.
Prominent MB cervical bulge
Has a transverse ridge
Has two roots
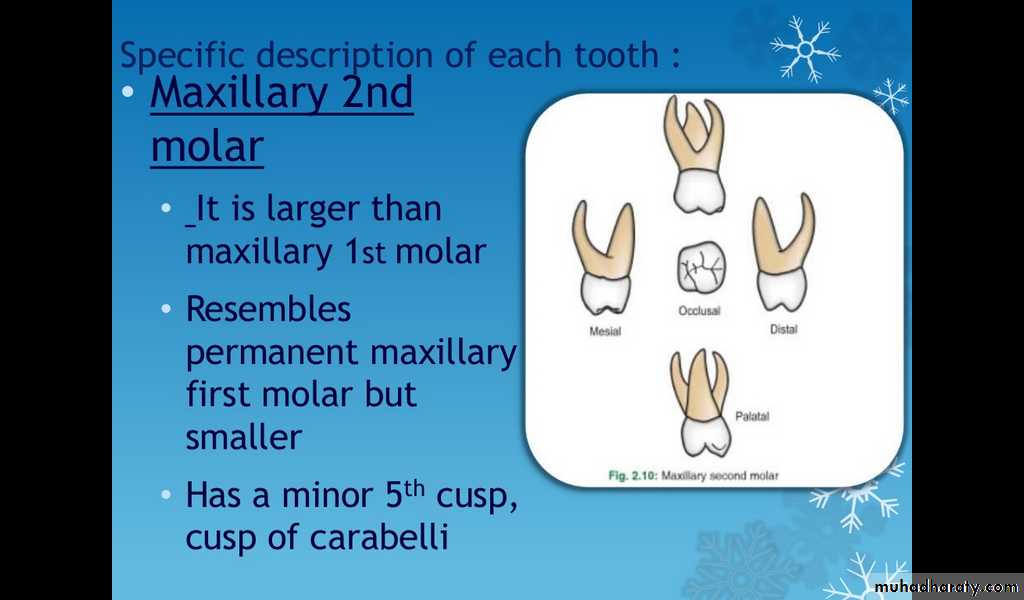
Maxillary 2nd molar
It is larger than maxillary 1st molarResembles permanent maxilliary 1st molar but smaller
Has a minor 5th cusp, cusp of carabelli.
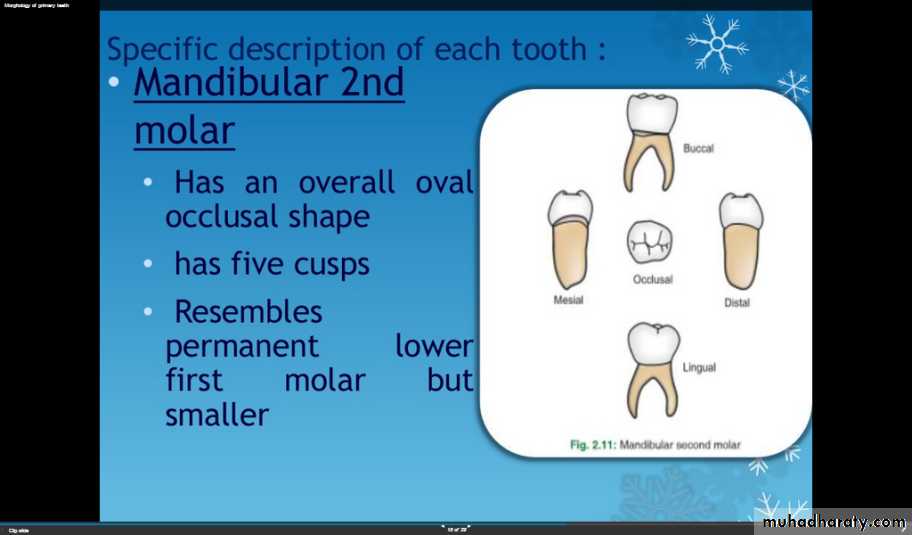
Mandibular 2nd molar
Has an overall oval occlusal shapeFive cusps
Resembles permanent lower first molar but smaller
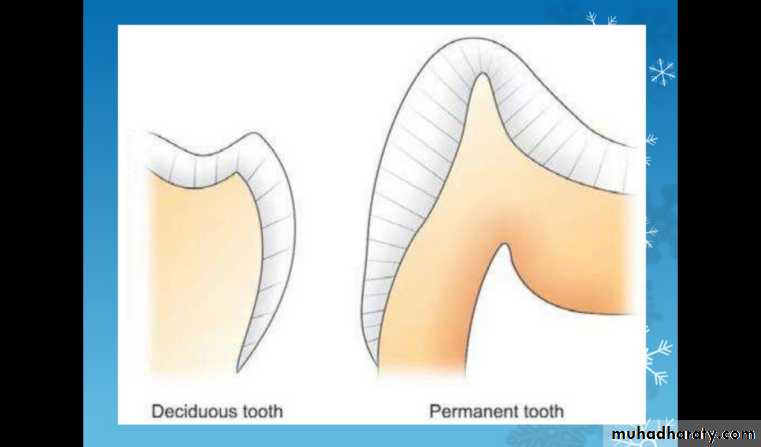
Differences between primary and permanent teeth
The primary teeth show marked constriction at the cervix (cervical region of the crown) and a pronounced cervical bulge particularly the buccal surfaces of he primary molars (especially the mesiobuccal cervical bulge).The enamel and dentin layers of the primary teeth are approximately equal in thickness and are generally thinner than permanent teeth.
The mesiobuccal cusp tends to be very high with a corresponding high pulpal horn beneath it.
The ratio of pulpal tissue to coronal hard tissue is much greater in the primary teeth than in the permanent. The pulp champers in primary teeth follows the outline of the occlusal crown surface, thus a pulp horn is present under each cusp(mesial pulp horns are closer to the outer surface than distal pulp horns). Mandibular molars usually have larger pulp champers than maxillary molars.
Primary teeth have more tortuous and irregular pulp canals.
Roots of the primary molars being more delicate and divergent(flare) as they approach the apex , this to accommodate the succedaneous bicuspid , this point is very important when you extract the primary molars with unresorbed roots(care should be taken to the permanent successor).
The interproximal contact area of the primary teeth are flat and broad compared to those of the permanent teeth which are pointed and narrow.
Resorption of the primary teeth is physiologic whereas of the permanent teeth tend to be pathologic.
The color of the primary teeth being bluish white as compared to the yellows and greys color of the permanent teeth(this is because of the greater water content of the primary dentition than permanent).
Enamel rods in the gingival one third extending in a slightly occlusal direction from the dentino-enamel junction, while in the permanent teeth these rods extends slightly apically.
Pulp pathosis of the primary molars in the form of lamina dura breakdown occurs in the furcation areas while in the permanent teeth occurs at the apical area(apex).
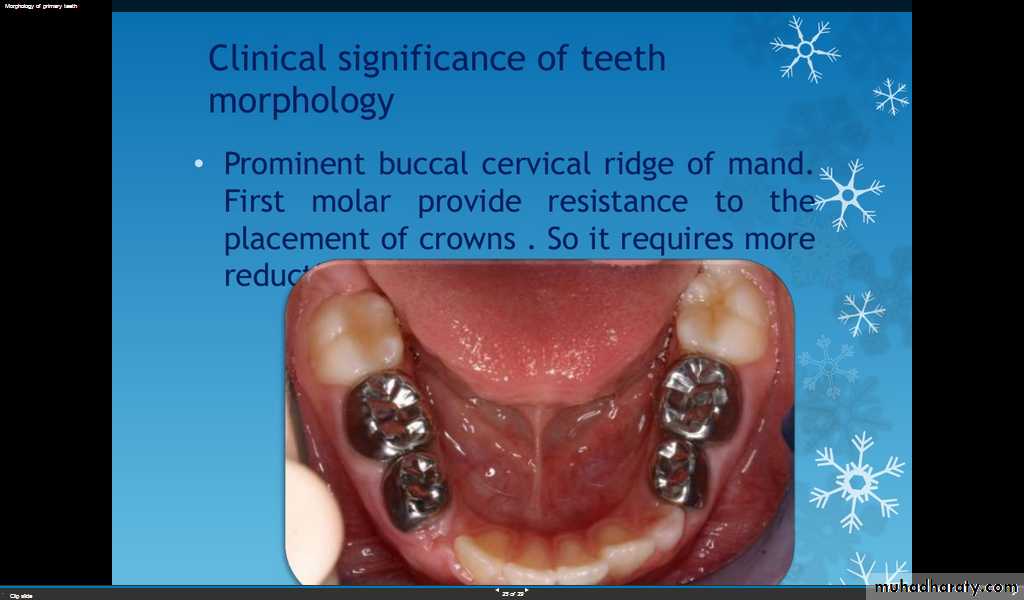
Clinical significance of primary tooth morphology
The progress of caries is much faster in the primary dentition, so incipient lesions should be restored sooner than later!
Thinner enamel and dentin
Mesial pulp horn higher
Procedures in Primary Teeth
Restorative Dentistry
Enamel is thinner, therefore modifications are necessary in the cavity preparation
Broad contacts need to be restored
Beware of the mesio-buccal pulp horn
May need to do stainless steel crown if both proximal surfaces involved
Preserve the buccal cervical ridge to obtain mechanical retention for SSC
Surgical Procedures
Conical anterior roots facilitate easy removal
Flared roots of the molars- use caution as premolar buds are located betweenthe roots
Functions of primary teeth
Chewing foodTeeth are a part of the digestive system. They are used for chewing food.Pronunciation and articulation Pronunciation is basically controlled by vocal cord, but it needs to work with the teeth to pronounce accurately.
Keep pleasant appearanceTeeth can keep our facial profile. Without teeth, our face will look collapsed. If teeth are kept healthy, our appearance will even be better.
Reserve space for permanent teeth to eruptNormally, underneath each deciduous tooth, there is a developing permanent tooth. Deciduous teeth reserve space for permanent teeth to erupt. When permanent teeth erupt, deciduous teeth will naturally fall off and be replaced by permanent teeth.If deciduous teeth are lost prematurely, the adjacent teeth will then move toward the empty space, leaving insufficient room for the permanent teeth to erupt. The permanent teeth may have poor alignment. Premature loss of deciduous teeth leading to poor alignment of teeth due to space loss
Developmental anomalies of teeth
The primary and permanent dentition are subject to considerable variation in the number, size, form of teeth and the structure of the dental tissue.Anomalies in the number of teeth
Anodontia: a complete absence of one or both dentition.
2. Hypodontia (partial anodontia): a deficiency in tooth number.
Hyperdontia (Supernumerary Teeth): an excess in tooth number.
Anomalies of tooth size
Macrodontia: teeth which exceeds the normal range of variations
Microdontia: teeth smaller than normal may be either of the usual form or conical/peg shape.
Anomalies of Shape
Fusion of the teeth
Fusion represents the union of two independently developing primary or permanent teeth. The condition is almost always limited to the anterior teeth.
Cause
The phenomena of tooth fusion arises through union of two normally separated teeth, and depending upon the stage of development of the teeth at the time of union, it may be either complete or incomplete fusion.
The radiograph may show that the fusion is limited to the crowns and roots. Fused teeth will have separate pulp chambers and separate pulp canals
Fusion of a permanent central and lateral incisor
Treatment
There is a groove that runs down the back of the tooth that is prone to decay and may necessitate a filling.
Gemination
Germination is a dental phenomenon where a developing tooth splits in to two separate teeth, it is seen in both primary and permanent teeth, though it probably appears more frequently in primary teeth.
Cause
The phenomenon of germination arises when two teeth develop from one tooth germ and, as a result the patient has a larger tooth but a normal number of teeth overall, in contrast to fusion, where the patient would appear to be missing one tooth.
Treatment
There is a groove that runs down the back of the tooth that is prone to decay and may necessitate a filling. It can represent a problem if they do not fall out in the right time and interfere with the eruption of permanent tooth..
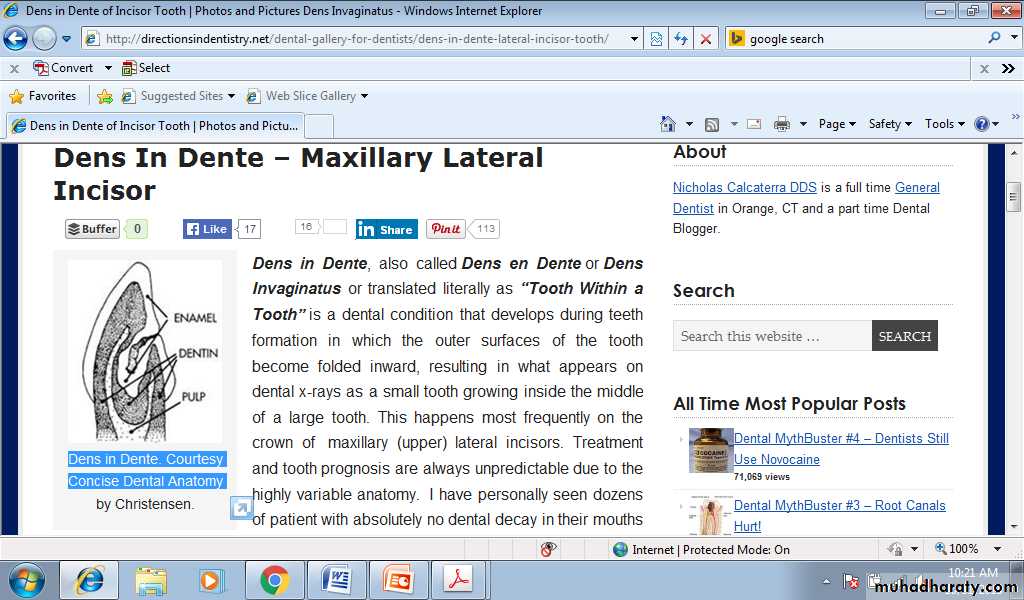
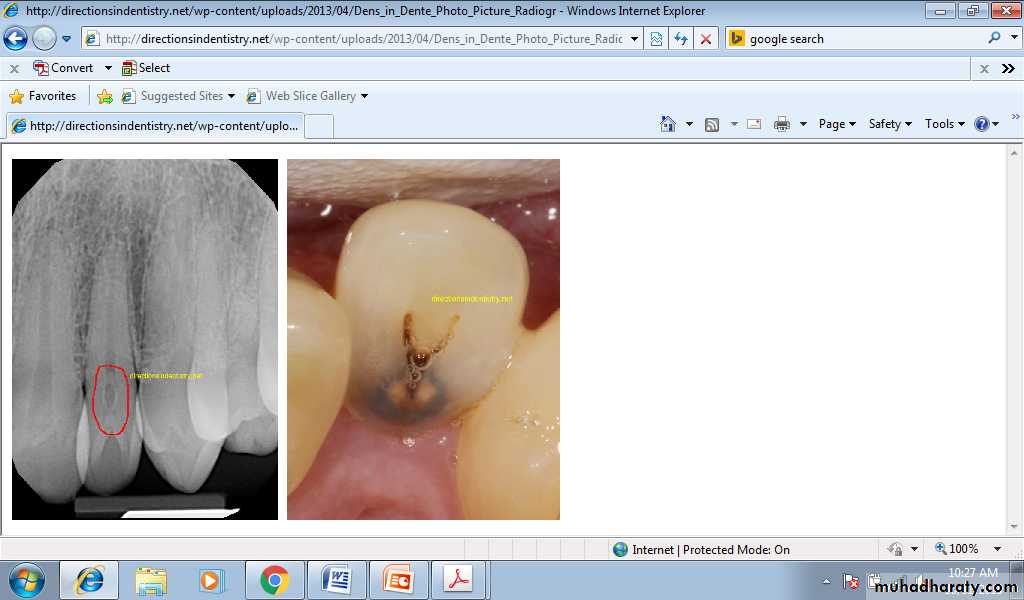
Dense in dente (Dens invaginatus)
Dense invaginatus or dens in dent means tooth with in a tooth. This condition can occur in primary and permanent teeth. Dens in dente is most often seen in the permanent maxillary lateral incisors. The condition should be suspected whenever deep lingual pits are observed in maxillary permanent lateral incisors.Cause
A developmental disturbance in tooth formation resulting from invagination of the epithelium associated with coronal development in to the area that was to be pulp space.
Treatment
This condition may result in early pulp necrosis so need root canal treatment but it is difficult due to the complex anatomy of tooth.Anomalies of tooth structure
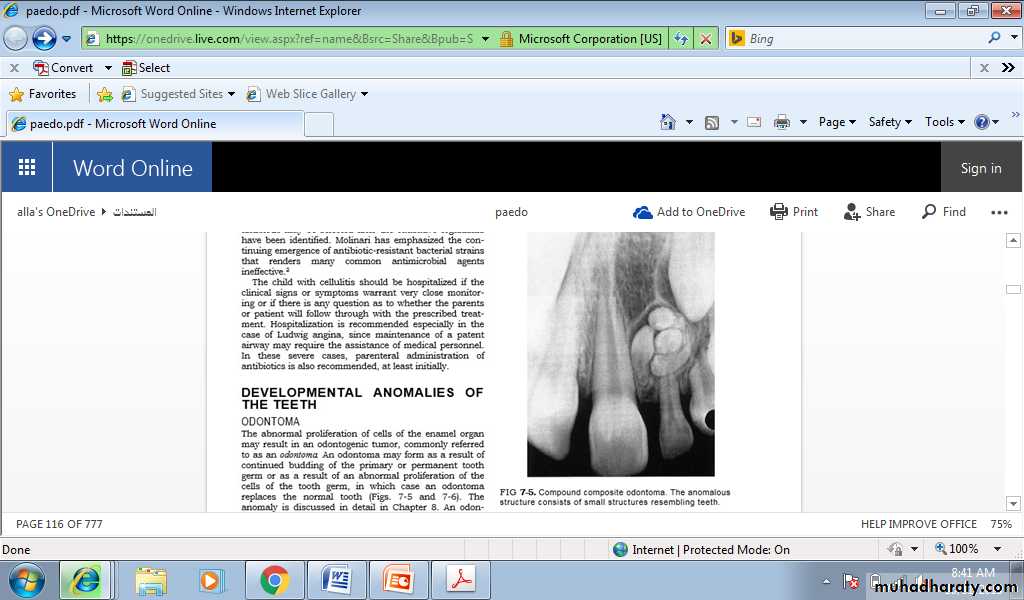
OdontomaThe abnormal proliferation of cells of the enamel organ may result in an odontogenic tumor, commonly referred to as an odontoma.
Cause
An odontoma may form as a result of continued budding of the primary or permanent tooth germ or as a result of an abnormal proliferation of the cells of the tooth germ, in which case an odontoma replaces the normal tooth.
Treatment
An odontoma should be surgically removed before it can interfere with eruption of teeth in the area.
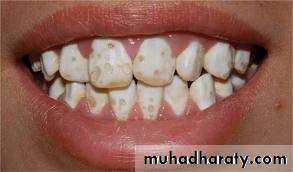
Amelogenesis imperfecta
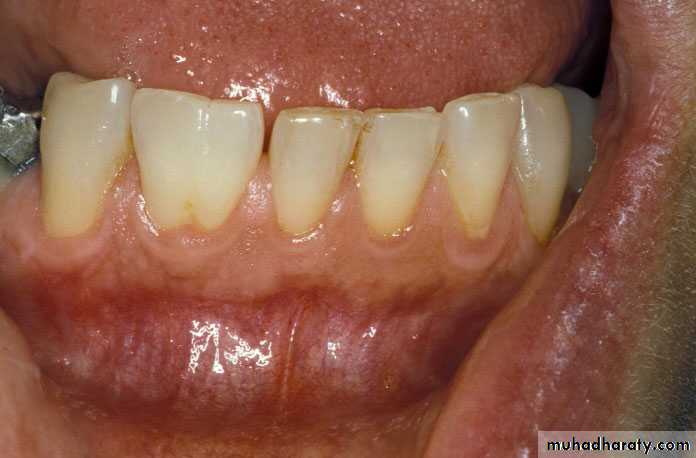
It is an abnormal formation of the enamel or external layer of teeth. People affected with amelogenesis imperfect have teeth with abnormal color, yellow, brown or grey. The teeth have a higher risk for dental caries and are sensitive to temperature changes. This disorder can affect any number of teethCause
Group of conditions caused by defects in the genes encoding enamel matrix proteins.Treatment
No treatment except for improvement of appearance.
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
It’s a genetic disorder of tooth development, this condition causes teeth to be discolored (most often a blue-grey or yellow-brown color) and translucent. Teeth are also weaker than normal, making them prone to rapid wear, breakage and loss. These problems can affect both primary and permanent teeth.Cause
Inherited defect in collagen formationTreatment
Treatment involves placement of stainless steal crowns on the teeth at least on the posterior region and composite resin on anterior teeth.