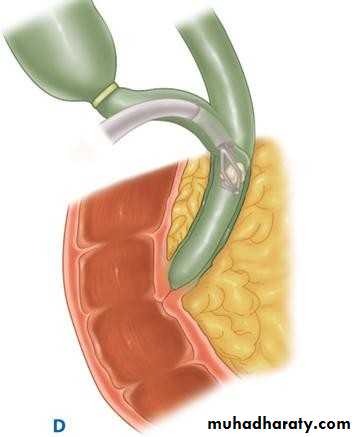
• GALL BLADDER
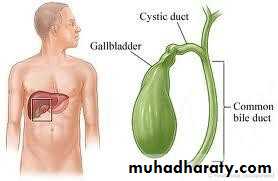
• The gall bladder is:
• Pear shaped, 7.5 – 12 cm• long
• 30 to 50 mL capacity
• Fundus, body, neck, and
• infandibulum
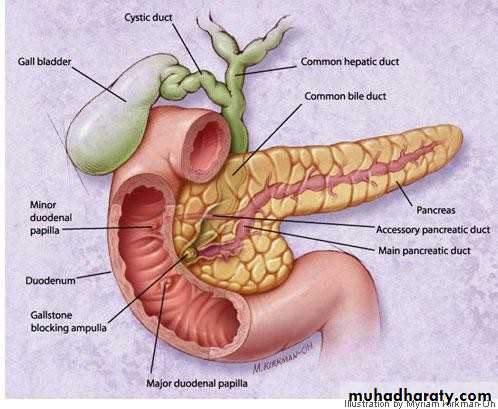
• The cystic duct:
• 3cm in length
• 1-3 mm in diameter
• Valves of Heister
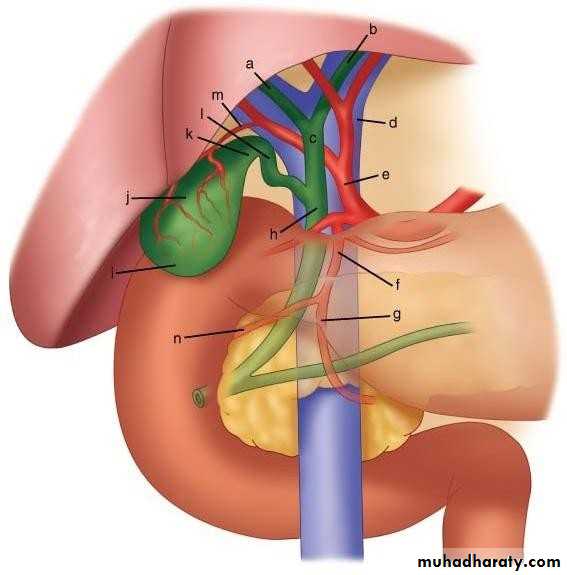
• a RHD b LHD c CHD
• d PV e HAP f GDA h CBDl CD
• k Neck GB
• j Body
• i fundus
• m CA
• The common hepatic duct:
• 2.5 cm in length• Union of R & L hepatic
• ducts
• The common bile duct:
• 7.5cm in length
• Union of cystic and CHD
• 4 parts;
• Blood supply of gall bladder:
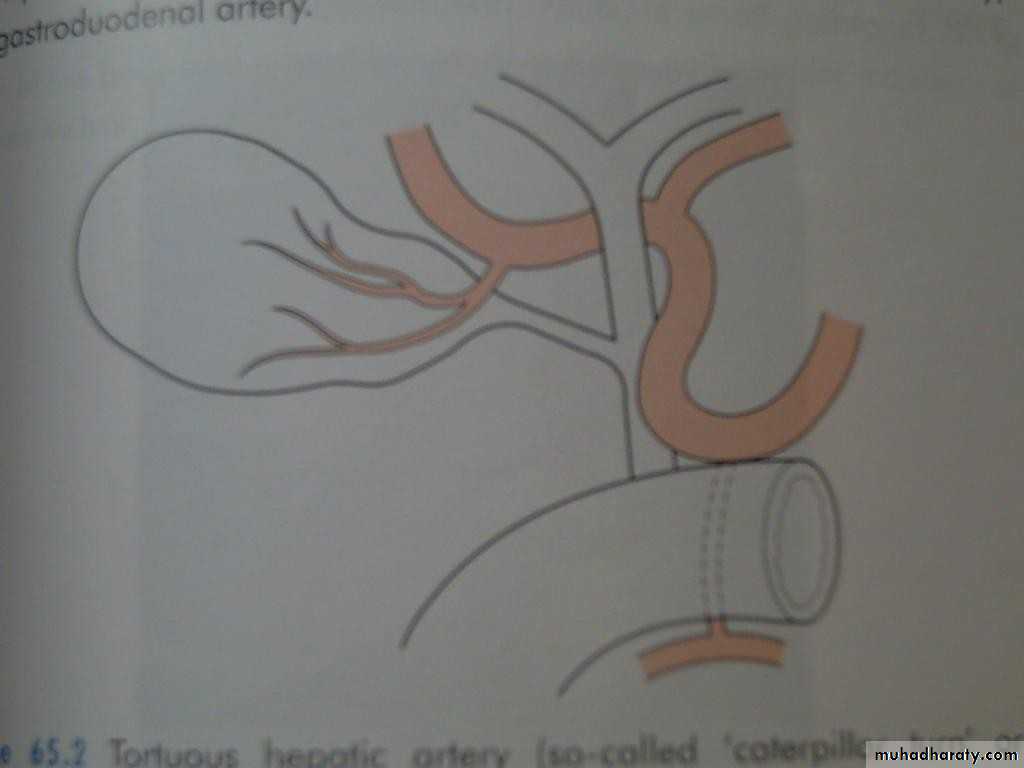
• The cystic artery a branch of• R hepatic artery
• Accessory CA from GD art.
• In 15% RHA anterior to CHD
• Toutuous RHA and short CA, Caterpillar turn or Moynihan’s hump.
• Lymphatics:• Subserosal and submucus lymphatics to the cystic LN of
• Lund hilum of liver coeliac LN
• Subserosal lymphatics to subcapsular lymphatics of liver
• SURGICAL PHYSIOLOGY
• Bile:• 40ml hour
• 97% water
• Bile salts 1-2%, bile pigments 1%, cholestrol, and fatty
• acids
• Functions of gall bladder:
• Reservoir
• Concentration of bile, 5 - 10 times
• Secretion of mucus– 20ml/day
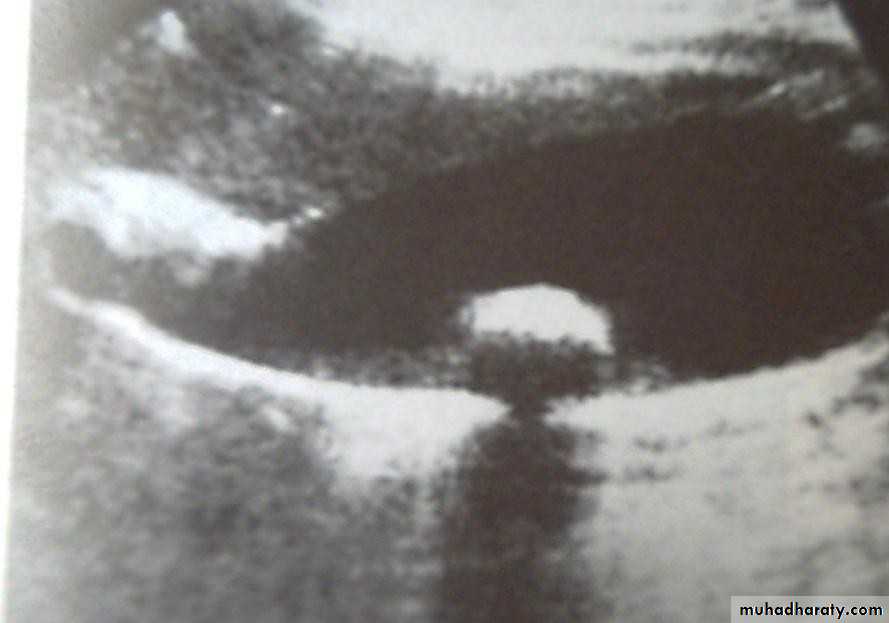
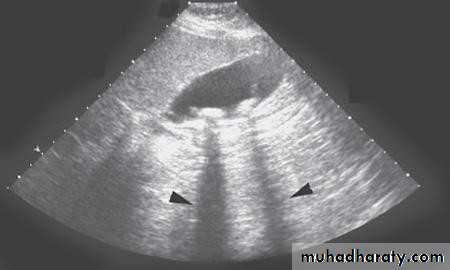
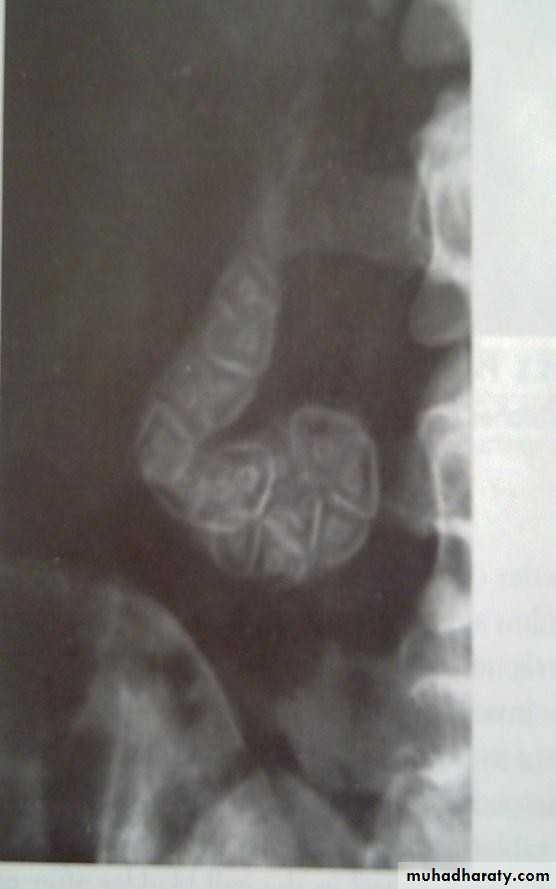
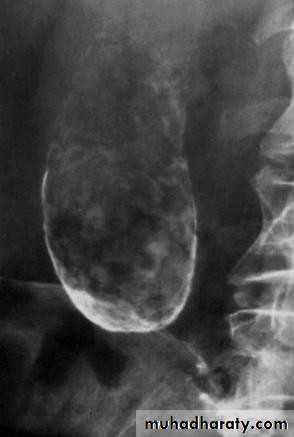
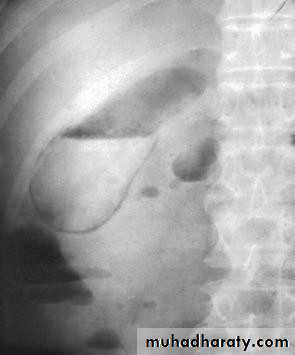
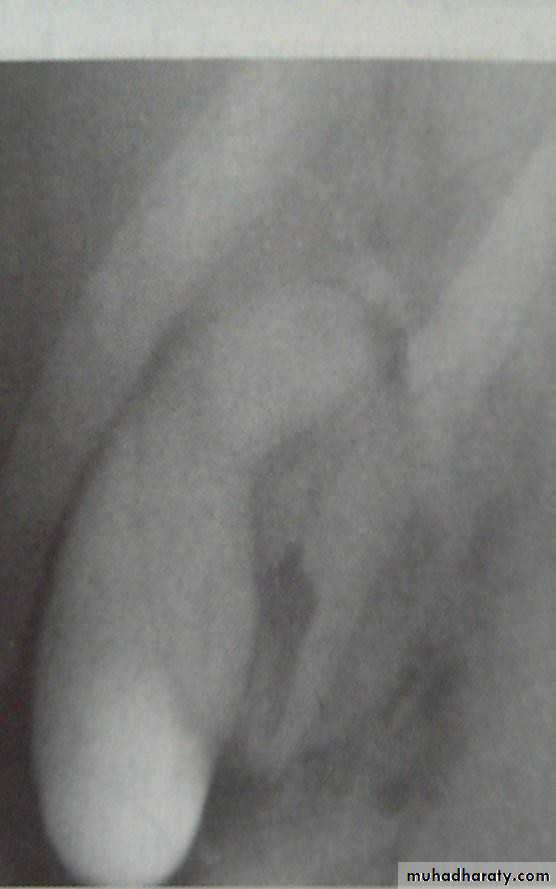
• Ultrasound; stones and size
• Plain radiograph; calcification• MRCP; anatomy and stones
• CT scan; cancer and anatomy
• HIDA scan; function
• ERCP; stones, and strictures
• Ultrasonography:
• Non-invasive• Standard initial imaging for patient suspected to
• have a gall stone and in jaundiced patients.
• Ultrasonography:can demonstrate
• Gall stones• GB size, thickness of its wall, presence of inflammation around it, pericystic edema.
• Size of CBD, occasionally stones in it.
• Tumour of pancreas.
• Endoscopic ultrasound;
• Stone and obstruction
• of lower CBD
• Plain radiogaph:
• Radiopaque gall stones in 10%• Porcelain GB.. calcified GB..25% CA.
• Limey bile
• Gas in the wall, emphysematous cholecystitis
• Gas in the biliary tree;
• Endoscopic sphincterotomy
• Surgical bilio-enteric anastomsis
• Internal biliary fistula
• Porcelain GB
• Gas in gall bladder
• f• Oral cholecystography
• Once was of first choice in the dx o gall stones
• Intravenous cholangiography
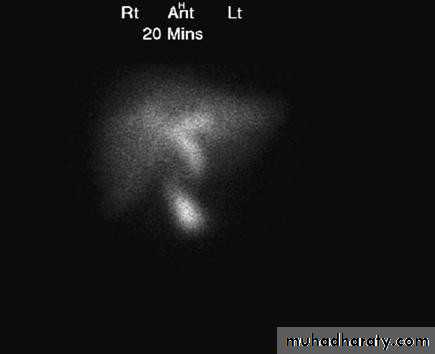
• Radioisotope scanning:
• Tc 99m labelled with derivatives of iminodiactic• acid (HIDA, PIPIDA), that are excreted in the bile.
• Dx of acute cholecystitis GB not visulized
• Bile Leakage, assessment
• Dimethyl iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan.
• INVESTIGATIONS OF THE BILIARY TRACT
• Computerized Tomography scan;• limited usefulness in investigating the biliary tree
• Only when there is a possibility of cancer of gall bladder or bile ducts
• Use of CT scan is an integral part of the differential
• diagnosis of obstructive jaundice
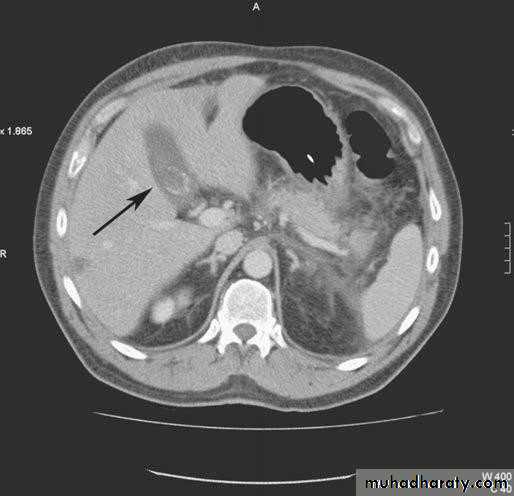
• CT SCAN
• Computed tomography scan demonstrating a gallstone
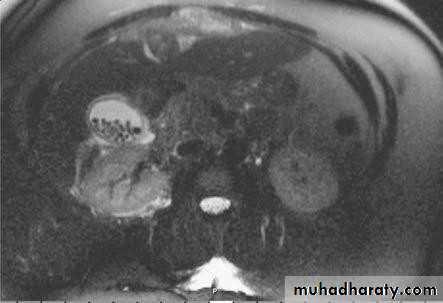
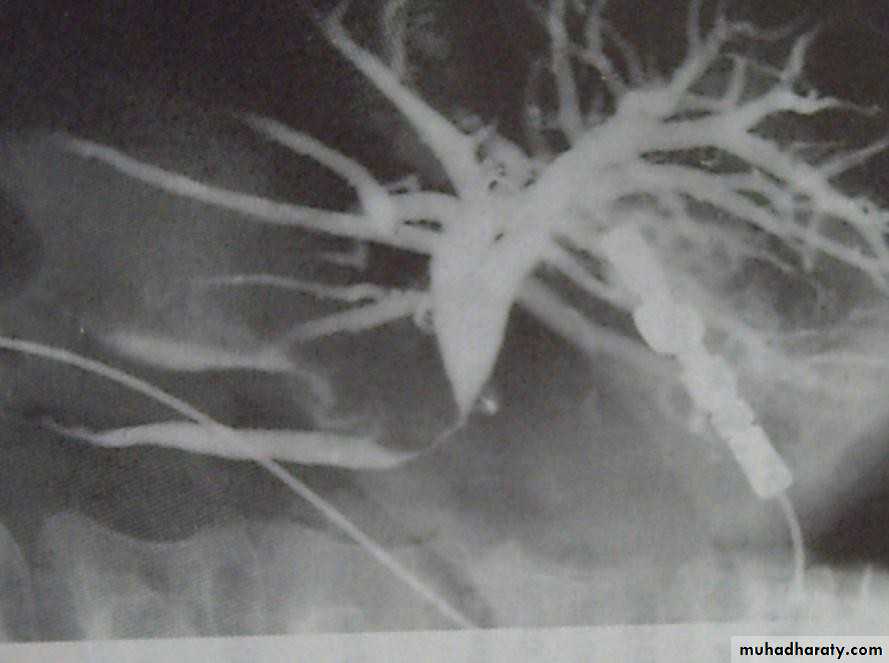
• within the gall bladder (arrowed).• Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatograph:
• (MRCP)
• Standard for biliary tree investigation
• Contrast is not needed
• MRCP
• Magnetic resonance cholangio- pancreatography crosssectional
• image demonstrating a hilar mass (thick• arrow) and gallstones (thin arrow)
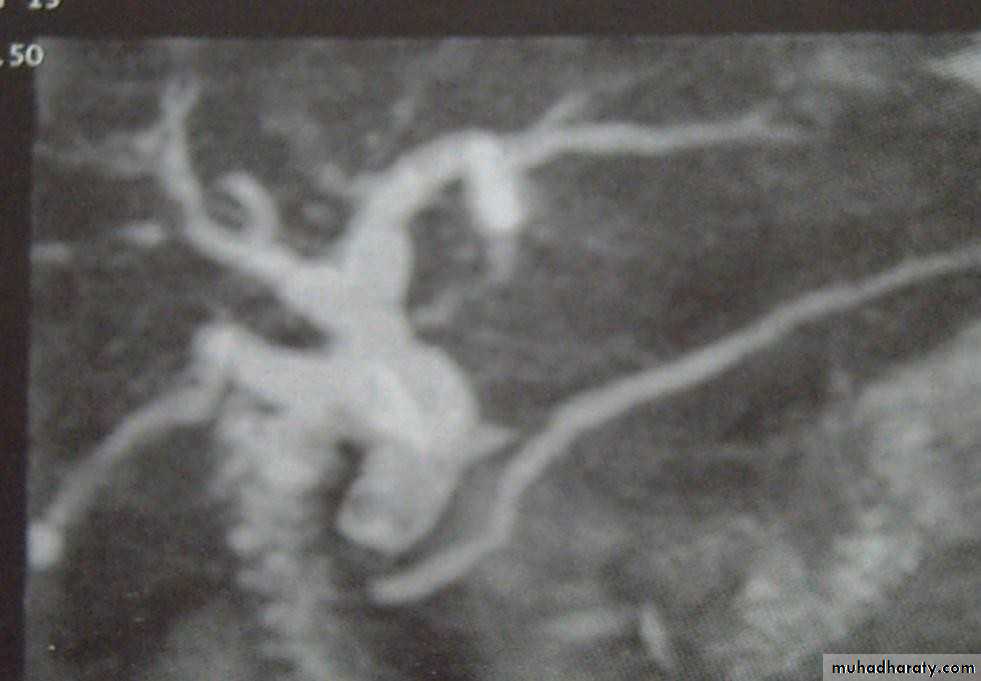
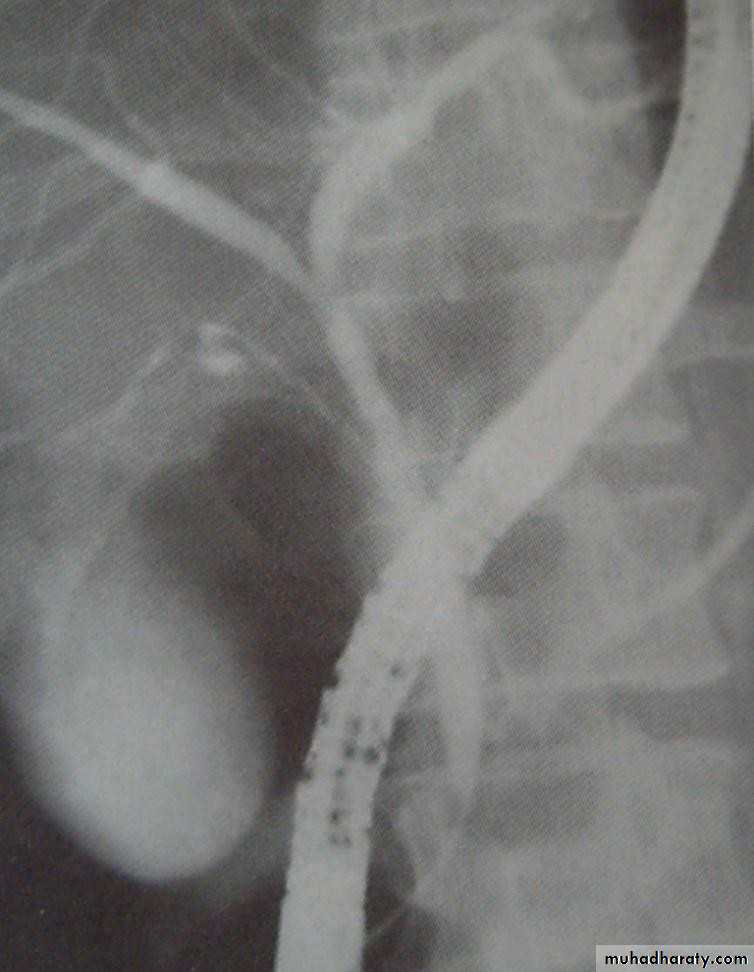
• ENDOSCOPIC RETROGRADE
• CHOLANGIOPANREATOGRAPHY (ERCP)• Side veiwing endoscopie
• Cannulation of ampulla of Vater
• Injection of contrast to visualize the bile
• ducts
• Also bile can be taken for cytological and
• microbiological tests
• Brushings from strictures
• ERCP
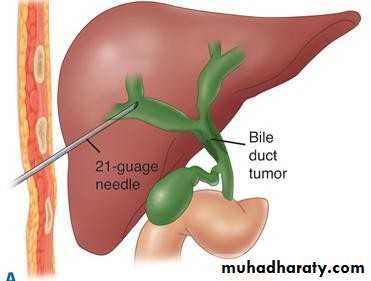
• PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC
• CHOLANGOGRAPHY (PTC):• Preparation;
• Normal PT
• Antibiotics
• DX and therapy;
• Visulization of biliary tree
• Placement of; catheter
• Stenting
• choledochoscope
• PTC
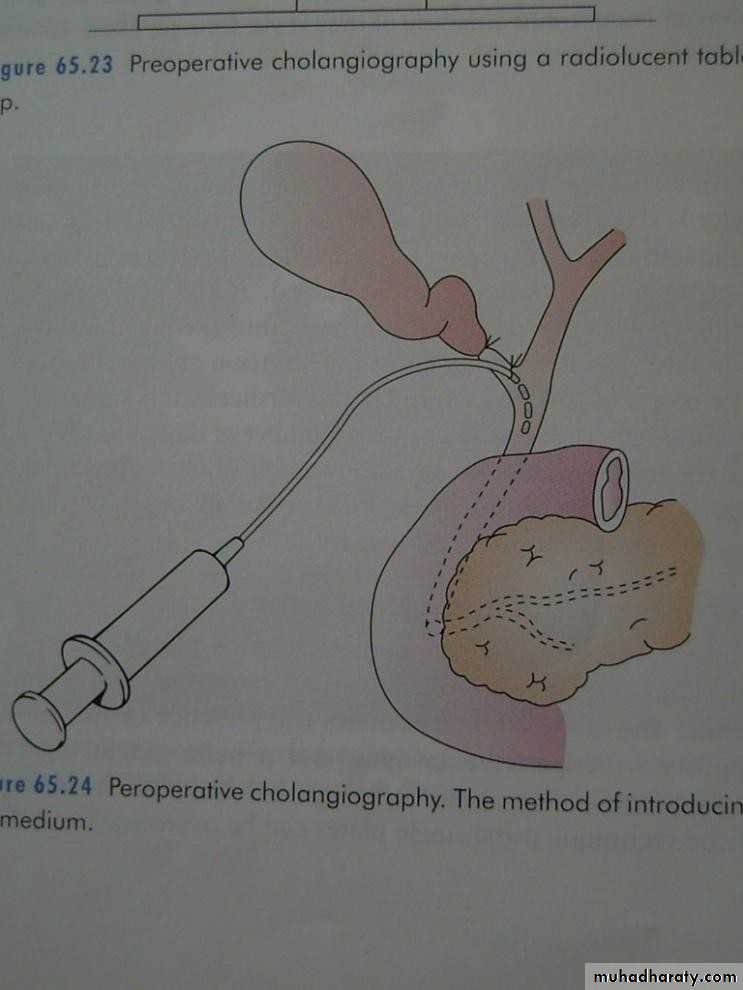
• Peroperative cholangiography
• Operative biliary endoscopy (choledochoscopy)
• DISEASES OF GALL BLADDER AND BILIARY
• PASSAGES• Congenital
• Acquired• CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF THE GB AND BILIARY TREE
• Absence of GB• The phrygian cap
• Floating GB
• Double GB
• Absence of CD
• Low insertion of CD
• An accessory cholecystohepatic duct ( small ducts of
Luschka)
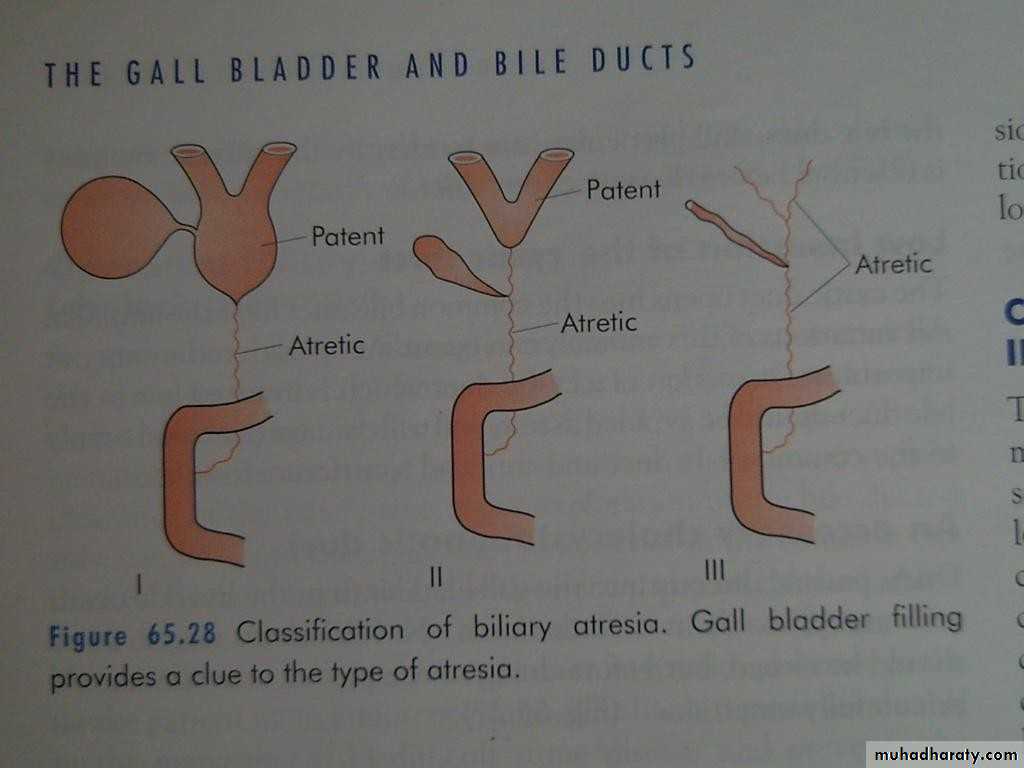
• EXTRAHEPATIC BILIARY ATRESIA
• Aetiology and pathology:• 1 per 14000 live birth
• Equal and female
• If untreated the child dies before the age of 3 years
• 20% associated anomalies, cardiac, situs inversus, absent vena cava
• Classification:
• Type I: atresia restricted to the CBD• Type II: atresia of the CHD
• Type III: atresia of the right and left HD
• Clinical features:
• 1/3 jaundiced at birth• All jaundiced by the end of first week
• Meconium little bile stained
• Pale stool and dark urine
• Osteomalacia
• Pruritis
• Clubbing, skin xanthoma
• Diff. Dx.:
• Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency• Choledochal cyst
• Inspissated bile syndrome
• Neonatal hepatitis
• Traetment:
• Roux-en Y anastomosis• Kasai procedure
• CHOLEDOCHAL CYST
• Weaknes of part or whole of the wall of the• CBD
• Anomalous junction of the biliary pancreatic junction;
• High amylase
• Repeated attacks of panreatitis
• Clinical features: premalignant
• At any age, Attacks of;• juandice
• Cholangitis
• Swelling in the right hypochondrium
• US –abnormal cyst
• MRI– clear anatomy
• Treatment:
• Radical excision of the cyst and reconstruction of
• the biliary tract using Roux en Y jejunal loop
• TRAUMA
• Iatrogenic• Accidental, is rare, penetrating or crushing
• Presentation of acute abdomen
• Treatment:
• GB—cholecystectomy• Bile ducts:
• Drainage using T tube
• –Roux-en-Y
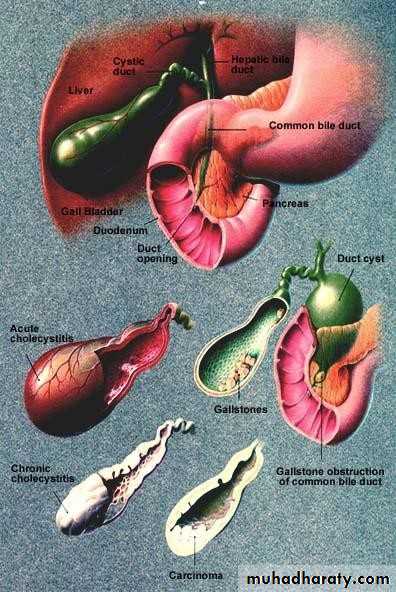
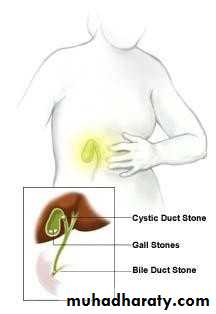
• GALL STONES (CHOLELITHIASIS)
• Most common pathology• Affecting about 10–15% of the adult population.
• Mostly asymptomatic in >80%
• Cholecystectomy is one of the most common operations
• performed by general surgeons.
• AETIOLOGY OF GALLSTONES
• Metabolic• Infective
• Stasis
• RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH FORMATION OF GALL STONES
• Age > 50 years• Female sex (twice risk in men)
• Genetic or ethnic variation
• High fat, low fibre diet
• Obesity
• Pregnancy (risk increases with number of pregnancies)
• Hyperlipidaemia
• Bile salt loss (ileal disease or resection)
• Diabetes mellitus
• Cystic fibrosis
• Antihyperlipidaemic drugs (clofibrate)
• Gallbladder dysmotility
• Prolonged fasting
• Total parenteral nutrition
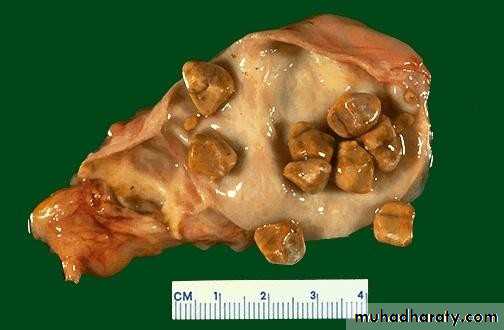
• TYPES OF GALL STONES:
• Cholesterol• Pigment stones
• Mixed stones• CHOLESTEROL STONES
• Contain mainly pure cholesterol• •Mostly single ( cholesterol solitaire)
• •Obesity,
• •high-calorie diets
• •certain medications
• PIGMENT STONES:
• Black stones• Contents:
• insoluble bilirubin pigment polymer mixed with calcium
• phosphate and calcium bicarbonate.
• < 30% cholesterol
• Hemolysis;
• Hereditary spherocytosis
• Sickle cell anaemia
• PIGMENT STONES:
• Brown stones:• calcium bilirubinate, calcium palmitate and calcium
• stearate, as well as cholesterol
• form in the bile duct and are related to bile stasis and
• infected bile.
• MIXED STONES:
• Cholesterol major component• Ca bilirubinate, Ca palmitate, Ca carbonate, Ca
• phosphate, and proteins
• Account for 90%
• Multiple
• Faceted
• INCIDENCE OF GALL STONES
• Female• Fat
• Fertile
• Fifty
• Flatulent
• CAUSAL FACTORS IN GALL STONE FORMATION
• Metabolic• Infective
• Stasis
• Metabolic:
• Cholesterol
• Bile salts
• Phospholipid
• High cholesterol “Supersaturated” or
• “lithogenic” bile• Aging
• Female contraceptives
• Obesity
• Clofibrate
• Interruption of enterohepatic circulation of bile salts
lead to low bile salts.
• Infection:
• mucus plug as nidus• Unclear
• Radiolucent centre of stone
• for stone formation
• unconjugated insoluble
• B glucuronidase
• bilirubin.
• Bile stasis:
• Decrease contractility of gall bladder
• Estrogen in pregnancy
• Parenteral nutrition
• Truncal vagatomy
• EFFECTS AND COMPLICATIONS OF GALL STONES
• In the GB:• Silent up to 80%
• Chronic cholecystitis
• Acute cholecystitis
• Gangrene
• Perforation
• Empyema
• Mucocele
• carcinoma
• In the bile ducts:
• Obstructive jaundice
• Cholangitis
• Acute panreatitis
• In the intestine:
• Acute intestinal obstruction ( gall stone ileus)
• Acute cholecystitis
• Biliary Colics• Chronic cholecystitis
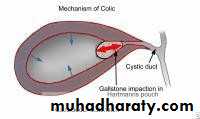
• ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS
• Right hypochondrial pain• Radiate to back, chest
• Referred right shoulder pain
• Occ. Start at epigastrium or left subcostal
• Start at night
• Other symptoms;
• Dyspeptic symptoms• Vomiting
• fever
• ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS
• BILIARY COLIC• Several hours to few days
• Fever
• leucocytosis
• Few minutes to few hours
• No fever
• No Leucocytosis
• DIFFERENTIAL DX
• Common:• Appendicitis
• Perforated peptic ulcer
• Acute pancreatitis
• Uncommon:
• Acute pyelonephritis
• MI
• Pneumonia, right lower lobe
• DIAGNOSIS
• Physical examination:• Murphy’s sign
• Palpable tender gall bladder.
• DIAGNOSIS
• Ultrasound• Liver function test
• Bilirubin
• WBC
• pneumonia ,air under diaphragm
• CXR
• ECG
• GUE and urine culture
• TREATMENT
• Conservative• Urgent cholecystectomy
• Early cholecystectomy
• Elective cholecystectomy
• CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
• IV fluids• NPO with
• NG tube
• Analgesia
• Antibiotics
• Follow up
• CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
• 90% respond to conservative treatment.• Subsequent treatment:
• Early cholecystectomy next op. list 5-7 days
• Elective cholecystectomy 6 weeks
• URGENT CHOLECYSTECTOMY
• •Increasing:
• •pain and tenderness
• •pulse and temperature
• •leucocytosis
• When to stop conservative treatment:
• Conservative treatment is not advised
• •Uncertinity about the dx• EMPYEMA OF THE GALL BLADDER
• Pus filled gall bladder• A sequel to acute cholecystitis or Mucocele
• Treatment:
• Cholecystectomy
• Disturbed anatomy---- drainage (Cholecystostomy)
• later cholecystectomy
• Acalculous cholecystitis
• Acute or chronic• Dx by:
• Radioisotope in acute cholecystitis
• Acute acalculous can occur in patients after major
• surgery, trauma, burn
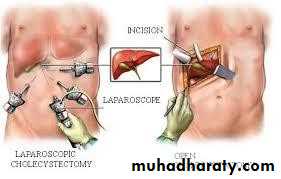
• CHOLECYSTECTOMY
• Indications• Preperation
• procedure
• CHOLECYSTECTOMY
• Indications• Symptomatic cholelithiasis
• Trauma
• Part of other operation -----Whipple’s procedure
• Neoplasia of Gall Bladder
• Preparation for operation
• ■ Full blood count• ■ Renal profile and liver function tests
• ■ Prothrombin time
• ■ Chest X-ray and electrocardiogram (if over 45
• years or medically indicated)
• ■ Antibiotic prophylaxis
• ■ Deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis
• ■ Informed consent
• CHOLECYSTECTOMY
Laparoscopiccholecystectomy
Open
• colecystectomy
• •Gold standard
• COMPLICATIONS OF CHOLECYSTECTOMY
• Inraoperative:• Biliary injuries
• Iatrogenic injuries to near by organs
• Bleeding.
• Early postoperative:
• CBD obstruction------------Jaundice
• CBD injury --------------Collection , Biliary peritonitis
• Bleeding ---------------Local hematoma, Shock
• Missed stone in CBD
• COMPLICATIONS OF LAPAROSCOPIC
• CHOLECYSTECTOMY• access complications
• bile duct injuries• Biliary injury:
• Bile leakage• Local collection or excessive bile drainage if drain is present
• Biliary peritonitis
• PAIN AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY
• Causes:• Incorrect preoperative diagnosis - for example, irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcer, gastro.oesophageal reflux
• Retained stone in the CBD or CD stump
• Iatrogenic biliary injury
• stricture of common bile duct
• Papillary stenosis or dysfunctional sphincter of Oddi
• ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT
• Criteria for non-surgical treatment of gall stones• Cholesterol stones < 20 mm in diameter
• Fewer than 4 stones
• Functioning gall bladder
• Patent cystic duct
• Mild symptoms
• SUMMARY POINTS
• Gall stones are the commonest cause for emergency hospital• admission with abdominal pain
• Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has become the treatment of choice for gallbladder stones
• Risk of bile duct injury with laparoscopic cholecystectomy is
• around 0.2%
• Asymptomatic gall stones do not require treatment
• Cholangitis requires urgent treatment with antibiotics and biliary decompression by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
• OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE
Attributed to CBD obstruction• Stone in CBD
• Carcinoma of CBD
• Tumor of head of pancreas
• FB inside the CBD
• Paracitic
• MANAGEMENT OF CBD OBSTRUCDTION
Following cholecystectomy• Jaundice ---- immediate action
• Ultrasound
Dilatation
• Collection at porta hepatis
• Biochemical investigations
• Immediate MRCP:
• If stone detected endoscopic extraction(ERCP)• If CBD obstruction --- surgery
• If bile leakage :
• Percutaneous drainage
• Stenting
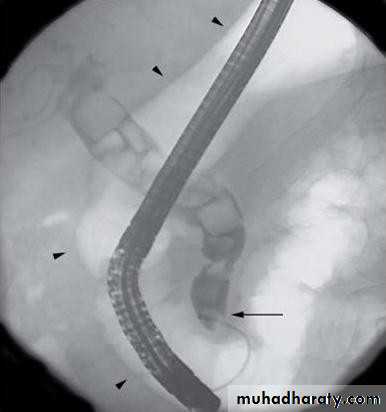
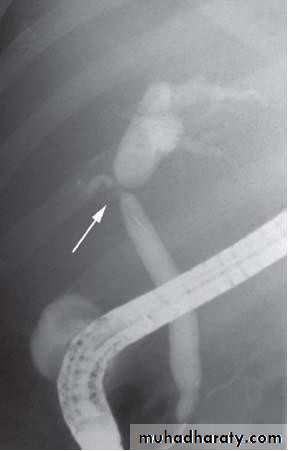
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Several years after cholecystectomy• CBD infestation by Ascaris lumbricoides or
• clinorchis sinensis
• STONES IN THE CBD
Clinical presentation:• Asymptomatic
• Jaundice
• Cholangitis ( Charcoat triad )
• Fever and rigor
• Jaundice
• Pain
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Signs:• Tenderness upper abdomen and RUQ
• STONES IN THE CBD
Management:• Dx
• Ultrasound
• Liver function test
• Liver biopsy
• MRCP
• ERCP
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Resuscitaion• Relief of obstruction
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Resuscitaion• Rehydration
• Broad spectrum Antibiotics
• Attention to clotting Vit K
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Relief of obstruction• Endoscopic sphincterotomy
• Extraction of stone by Dormia basket or balloon catheter
• Some times stent placement
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography:• then drainage
• Percutaneous choledochoscopy
• STONES IN THE CBD
• Surgery:• Choledochotomy
• CHOLEDOCHOTOMY
• Indications:• Preoperative:
• Stone in CBD
• Dilatation of CBD
• History of jaundice
• Peroperative:
• Palpable stone
• Dilated CBD
• STRICTURE OF CBD
• Benign stricture:• 80% postoperative
• 20% inflammatory
• Malignant stricture
• CAUSES OF BENIGN BILIARY STRICTURE
• Congenital• ■ Biliary atresia
• Bile duct injury at surgery
• ■ Cholecystectomy
• ■ Choledochotomy
• ■ Gastrectomy
• ■ Hepatic resection
• ■ Transplantation
• Inflammatory
• ■ Stones
• ■ Cholangitis
• ■ Parasitic
• ■ Pancreatitis
• ■ Sclerosing cholangitis
• ■ Radiotherapy
• Trauma
• Idiopathic
• POSTOPERATIVE STRICTURE
• Technical error during cholecystectomy• Blind control of bleeding in Calot triangle
• Failure to identify the anatomy at Calot triangle
Acute inflammation
• Mirizzi syndrome
• Short or absent cystic duct
• Anatomical anomalies
• POSTOPERATIVE STRICTURE
• CBD obstruction• Deeping jaundice
• Partial obstruction delayed jaundice
• POSTOPERATIVE STRICTURE
• Radiological investigations:• Ultrasound
• MRCP
• Cholangiography
• Through tube
• PTC
• ERCP
• POSTOPERATIVE STRICTURE
• Treatment• Supportive
• Relief of obstruction
• Temporary:
• ERCP stenting
• Transhepatic external drainage and stenting
• For strictures of recent onsent:
• ERCP --- guide wire---- balloon dilatation---stent placement
• POSTOPERATIVE STRICTURE
• Definite relief of obstruction:• Choledocho-jejunostomy
• Late complications:
• syndrome• CBD stricture
• Stone in CBD
• Post cholecystectomy pain
• Wrong preoperative diagnosis
• Complication of cholecystectomy
• PARASITIC INFESTATION OF THE
• BILIARYBILIARY TRACT• ascariasis
• The round worm, Ascaris lumbricoides, commonly
• infests the intestine
• Complications:
• strictures,
• suppurative cholangitis,
• liver abscesses and empyema of the gall bladder
• HYDATID DISEASE
• Jaundice:• Cyst near porta hepatis
• Rupture of cyst into the biliary passages
• TUMOURS OF THE BILE DUCT
• Benign tumours of the bile duct:• Rare
• Symptoms not distinguished from common biliary problems
• Malignant tumours of the bile duct
• Rare, but incidence increasing• Presents with jaundice and weight loss
• Diagnosis by ultrasound and CT scanning
• Jaundice relieved by stenting
• Surgical excision possible in 5%
• Prognosis poor – 90% mortality in 1 year
• the tumour is usually an adenocarcinoma
• (cholangiocarcinoma).• predominantly in the extrahepatic biliary
• RISK FACTORS
• ulcerative colitis, hepatolithiasis, choledochal• cyst ,sclerosing cholangitis.
• liver fluke infestations in the Far East
• CLINICAL FEATURES
• Jaundice• Abdominal pain, early satiety
• weight loss
• palpable gall bladder
• INVESTIGATIONS
• Biochemical investigations• tumour marker CA19-9
• ultrasound and CT scanning define:
• the level of biliary obstruction
• the locoregional extent of disease
• the presence of metastases
• percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
• ERCP
• TREATMENT
• Most patients are inoperable, but 10–15% are• suitable for surgical resection
• CARCINOMA OF GALL BLADDER
• Risk factors• Comon in india Incidence 9%
• Gall stones less than 1%
• 90% of Ca GB have gall stones
• CARCINOMA OF GALL BLADDER
• Pathology:• Schirrous adenocarcinoma
• Squamous cell
• Mixed sq adenocarcinoma
• CARCINOMA OF GALL BLADDER
• Spread:• Direct invading the liver
• Lymphatics
• Peritoneal seedlings
• Clinical features:
• Mostly elderly 70 years
• Females more than males 5:1 ratio
• Same as cholecystitis
• Suspected during cholecystectomy then preoved by
• histopathology• CARCINOMA OF GALL BLADDER
• Jaundice:• Mass in liver
• late sign
• INVESTIGATION
• non-specific findings such as anaemia, leucocytosis, mild elevation of transaminases and increased erythrocyte sedimentation• rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP).
• Elevated CA19-9
• US and CT scan
• percutaneous biopsy
• Laparoscopy• CARCINOMA OF GALL BLADDER
• Treatment:• Usually discovered after cholecystectomy and so no further surgical treatment required If tumor confined to mucosa good prognosis
• transmural disease, a radical en bloc resection of the gall bladder fossa and surrounding liver along with the regional lymph nodes.
• PATHOGENESIS OF STONE FORMATION
• For cholesterol stones:• Supersturation of bile with cholesterol
• Low bile acid concentration
• For pigment stones:
• Usually accompany haemolysis like in:• Spherocytosis
• Sickle cell disease
• Prosthetic heart valves
• For mixed(brown) stones:
• insoluble• Stasis
• Infection—beta glucuronidase
• unconjugated bilirubin