Dr. Fatima Alkhaledy
M.B.Ch.B,F.I.C.M.S/C.M.NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
• Objectives
• Introduction• Magnitude Of The Problem
• Age Distribution of NCDs
• Common Risk Factors
• Coronary Heart Disease
• Hypertension
• Stroke
• Obesity
• Diabetes
• Accidents and Injuries
• Malignancies
• Blindness
• Psychiatric disorders
• Other NCDs Among Elderly
• Prevention of NCDs
Index
Objectives
To get an idea about the magnitude of the problem
To know the risk factors responsible
Methods of prevention of NCDs
Introduction
Synonyms: “Chronic” diseases”,“Lifestyle Diseases”
With rapid urbanization, industrialization and increasing level
of affluence (the so called “modernization”), the price that thesociety is paying is a tremendous load of “Non - Communicable”
diseases.
Global phenomena -not simply restricted to the developed, rich countries.
In the context of our country, too, the problem of lifestyle and its
consequent diseases is assuming the position of a new “EPIDEMIC”.
Magnitude Of The Problem
Prevalence is INCREASING in most of the Developed as well as Developing Countries. A New “Epidemic” REASON?Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer - Leading causes of death in most of the developed countries (70 to 75% of total Deaths).
Developing Countries- Following the same steps to the trap(!!) in a far more pitiable fashion. HOW?-Cause, we have CDs, NCDs and Poverty- all 3 burdens to be taken SIMULTANEOUSLY.
Younger Age-group
Accidents and InjuriesRheumatic Heart Disease
Diabetes
Blindness
Psychiatric disorders
Elderly
HypertensionCoronary Heart Disease
Diabetes
Stroke
Malignancies
Obesity
Blindness
Psychiatric disorders
Others
Age Distribution of NCDs
NON-MODIFIABLE
Age
Sex
Family History
Genetic Factors
Personality
MODIFIABLE
Cigarette Smoking
Alcohol Abuse
Dyslipidemia
Sedentary Life Style
Stress
Environmental Risk Factors
Inability to avail preventive health care services
Common Risk Factors
Coronary Heart DiseaseProblem Statement: 30% of deaths in men; 25% of death in female in Western Countries.
Leading cause of death in coming years
Presentations:
Angina Pectoris
Myocardial Infarction
Arrhythmia
Cardiac Failure
Sudden Death
Hypertension
Classification:
Category Systolic BP Diastolic BP
(mm Hg) (mm Hg)
Normal <130 <85
High Normal 130-139 85-90
Hypertension
Stage 1(Mild) 140-159 90-99
Stage 2(Moderate) 160-179 100-109
Stage 3(Severe) >180 >110
Hypertension (Contd..)
GLOBAL BURDEN: About 10% to 20% population.Male Female
Urban 6% 7%Rural 3.5% 3.6%
Hypertension (Contd..)
Rule of Halves.
Non hypertensive
Hypertensive (Not diagnosed)
Diagnosed but Untreated Hypertensive
Inadequately Treated Hypertensive
Adequately Treated Hypertensive
Hypertension (Contd..)
“Tracking” of Blood Pressure.Blood Pressure
TimeStroke
Problem Statement: 10% to 12% of all deaths in Developed Countries.The proportion of stroke among young age-group is significantly more.
Stroke (Contd..)Etiopathological types:
Hemorrhagic
Thrombotic
Embolic
TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACKS (TIA)
Sudden onset
Focal
Reversible neurological deficit
Duration<24 hours
Cause: Micro-emboli
Significance: WARNING SIGN OF STROKE!!!
Obesity
Abnormal growth of adipose tissue.OBESITY
Hypertrophic Hyperplastic
OBESITYAndroid Gynoid
Obesity (Contd..)Magnitude: (Developed Countries)
Adults 20% to 40%
Children 10% to 20%
Assessment of Obesity:
BMI
Skinfold Thickness
Waist Circumference & WHR
Others (Total body Water
Total body Potassium
Body density
Measuring fat cells)
Obesity (Contd..)
Complications of Being an Obese:
Hypertension
Dyslipidemia
Glucose intolerance
Coronary heart disease
Arthritis
Breast, colon carcinoma
Gall stone diseases
Depression and Withdrawal into self
Diabetes
Around 150 million Diabetic World-wide. Predicted to DOUBLE by 2025.Screening Methods:
Venous Blood Sugar testing
Random
Fasting
Post-prandial
Urine Glucose Examination
Accidents and Injuries
What is Accident?-Unpremeditated event resulting in recognizable damage.
A significant cause of morbidity, mortality, disability among the productive age group population of a country.
Etiological factors:
Irresponsible usage of machines
Risk-taking behavior
Weak legislation
Accidents and Injuries (Contd..)
Driving vehicles under influence of alcohol
Poor maintenance of machines/vehicles
Over-crowding, poor illumination, inadequate layout in the road
Low driving standards
Not using protective measures
Lack of concentration while operating machines/vehicles.
Malignancies
An important cause of mortality, disability world-wide.(10 million mew cases diagnosed/year, 6 million die of cancers/annum)
3 most common malignancies worldwide:
• Lung cancer (12.3% of all cancers)
• Breast cancer (10.4%)
• Colorectal cancer (9.4%)
Top 3 “killers” among the malignancies:
• Ca Lung
• Ca Stomach
• Ca Liver
Blindness
WHO defines Blindness as:“Visual Acuity of less than 3/60 (Snellen) or its equivalent in the better eye”.
Low Vision:
Visual acuity poorer than 6/18 but better than 3/60.
0.7% people are blind. Among them, 62.6% are due to Cataract.
Blindness (Contd..)
Other important causes (in decreasing order of prevalence):
• Refractive error
• Glaucoma
• Posterior segmental pathology
• Corneal opacity
• Miscellaneous
Vision 2020: “Right to sight”
Psychiatric disorders
With the ever-increasing stress in today’s day-to-day life, psychiatric disorders are assuming more significant dimension.Prevalent almost in all age-groups.
Increased life expectancy
More population reside in the elderly group
Hence problems of poor mentation (Alzheimer’s, Dementia, Insomnia, Irritability etc.) warrant special attention.Other NCDs Among Elderly
ArthritisOsteoporosis
Chronic Respiratory Diseases (e.g. Chronic Bronchitis, Emphysema, Asthma)
Renal Failure
Chronic liver diseases
Hearing Impairment
Prevention of NCDs
Prevention
Primary Secondary Tertiary
Prevention Prevention PreventionPopulation High Risk
Strategy StrategyExercise Recommendation for Weight control
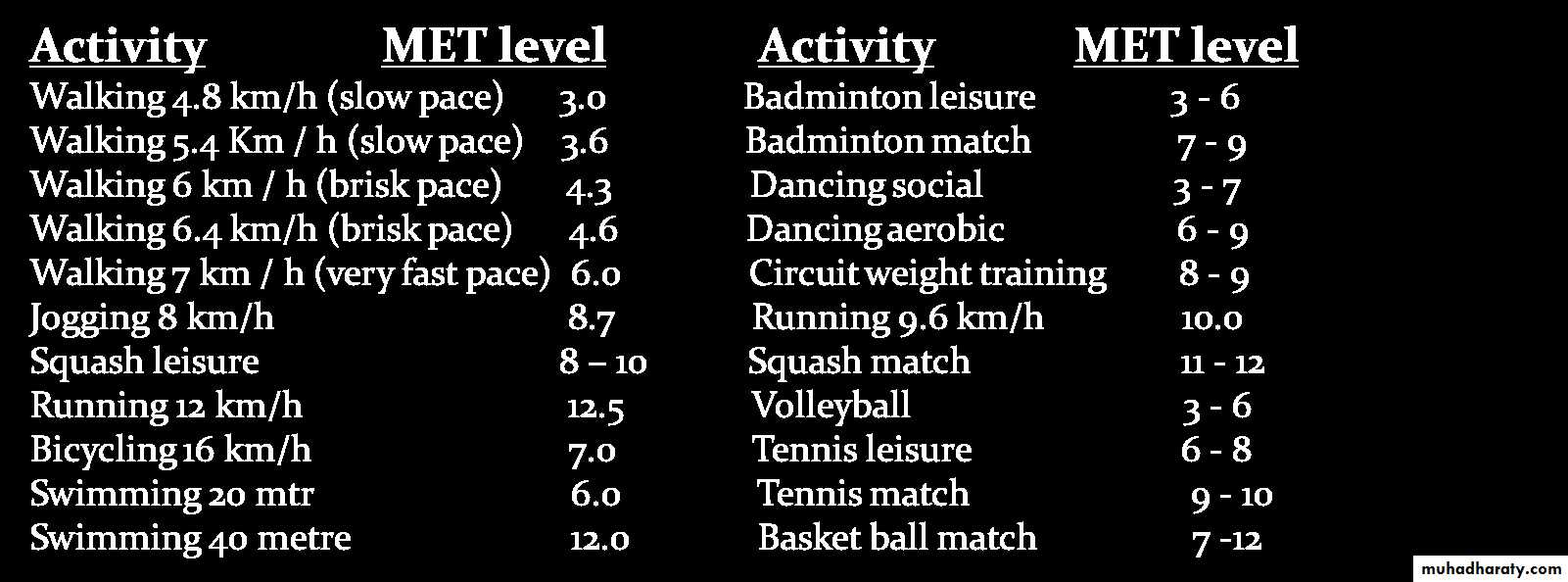
4 to 5 sessions per week,MET level 5 to 8 (moderate intensity exercises )
45 to 60 minutes/session.
Other Activities and MET Levels
Just a moment…..
“….The Japanese smoke a lot and suffer fewer heart attacks than Australians or New Zealanders;The French eat a lot of fat and suffer fewer heart attacks than Australians or New Zealanders;
The Italians drink a lot of wine and also suffer
fewer heart attacks than Australians or New Zealanders…..”
(Conclusion : NEVER COPY OTHERS’ BAD HABITS BLINDLY; DIFFERENT POPULATION HAS DIFFERENT LEVEL OF SUSCEPTIBILITY !!!!!!!!)