
Connective Tissue:
5
th
lecture
November 19, 2015

Connective Tissue:
Connective tissue is the most abundant and widely distributed
tissue type found in the human body.
The main role of connective tissue is to
1- Enclose organs as a capsule and separate organs into layers.
Areolar
2- Connect tissues to one another. Tendons and ligaments.
3- Support and movement. Bones.
4- Storage. Fat.
5- Insulation. Fat.
6- Transport. Blood.
7- Protection. Bone, cells of the immune system.

The main characteristics of connective tissue
are as the following:
• Connective tissues tend to be very vascular (have a rich blood
supply). Some exceptions, such as tendons, ligaments, and
cartilages, are less vascularized, but overall, connective tissues
possess a great blood supply than the epithelial tissue previously
discussed.
• Connective tissues are made up of many types of specialized cells.
• Connective tissues contain a large amount of non-living material
referred to as the matrix (composed of ground substance and
fibers). Typically, this material is manufactured and secreted by the
cells of the specific connective tissues Fig (1).
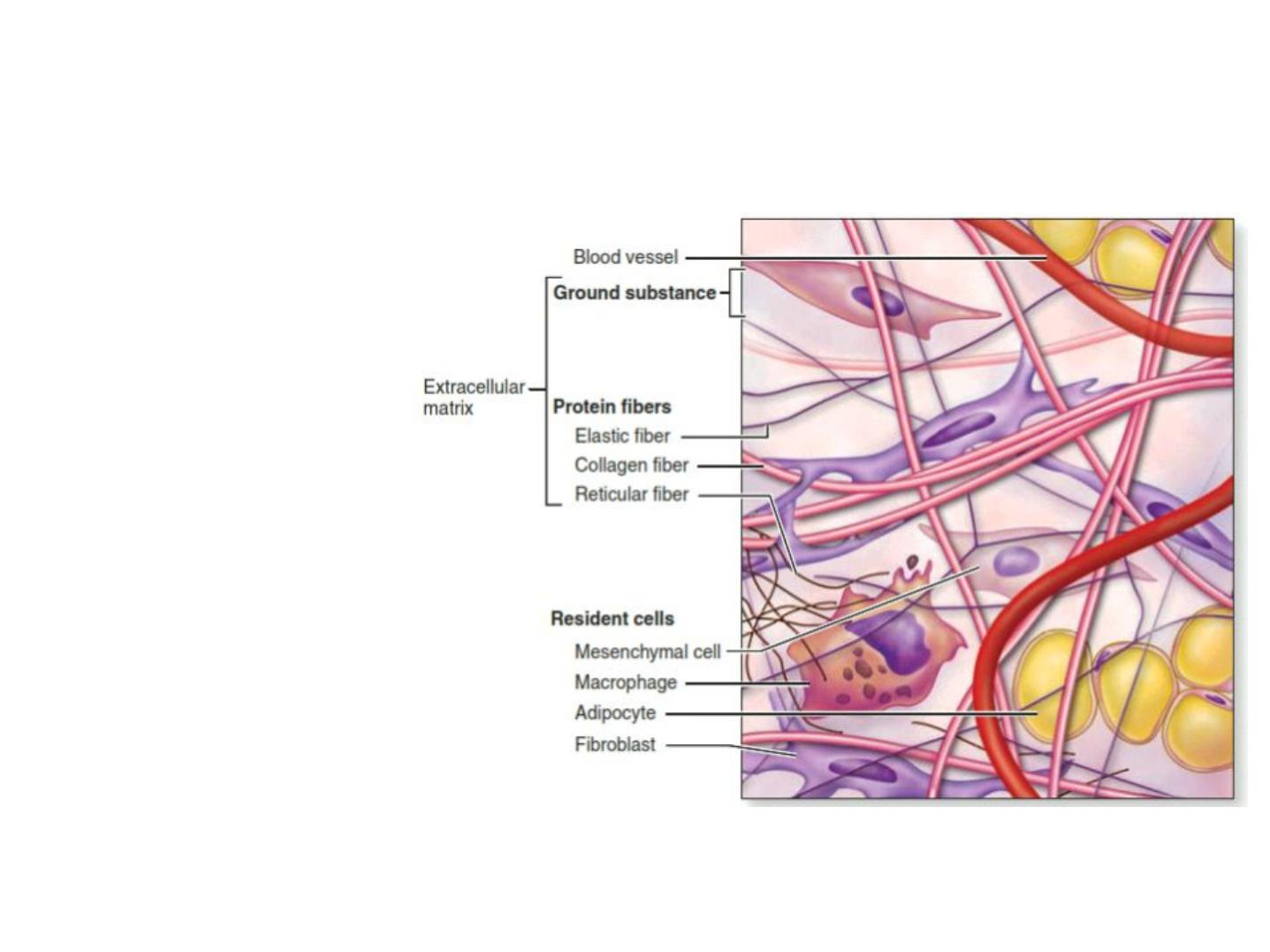
Connective tissue component
Figure (1): Cellular and extracellular components of connective tissue
1- Ground substance –
unstructured material
that fills the space
between cells
2- Fibers –collagen,
elastic, or reticular
3- Cells –fibroblasts,
chondroblasts,
osteoblasts,
hematopoietic stem
cells, and others
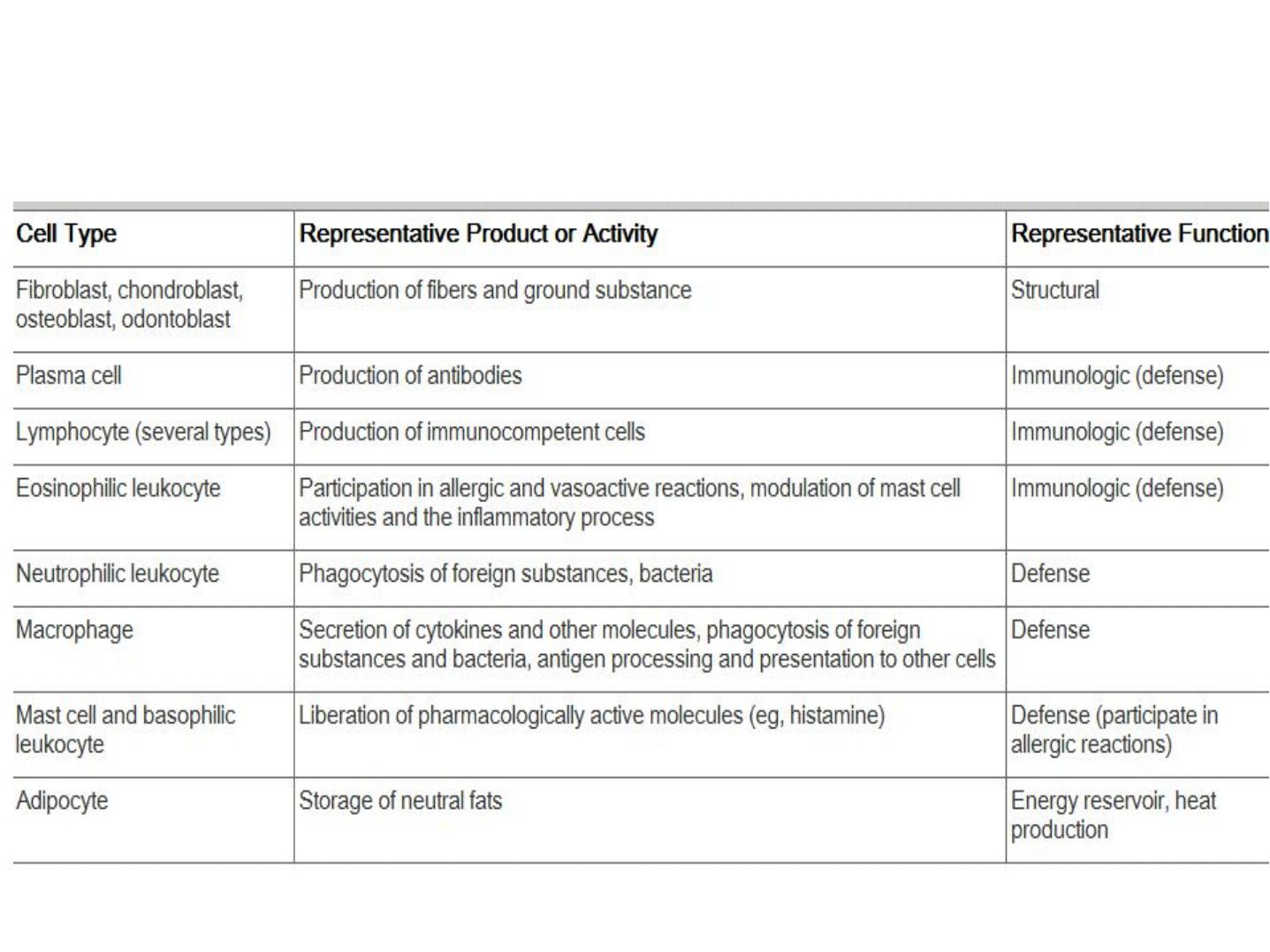
Function of connective tissue cell

Extracellular Matrix - ECM
ECM has 3 major components
1. Protein fibers
2. Ground substance
3. Fluid
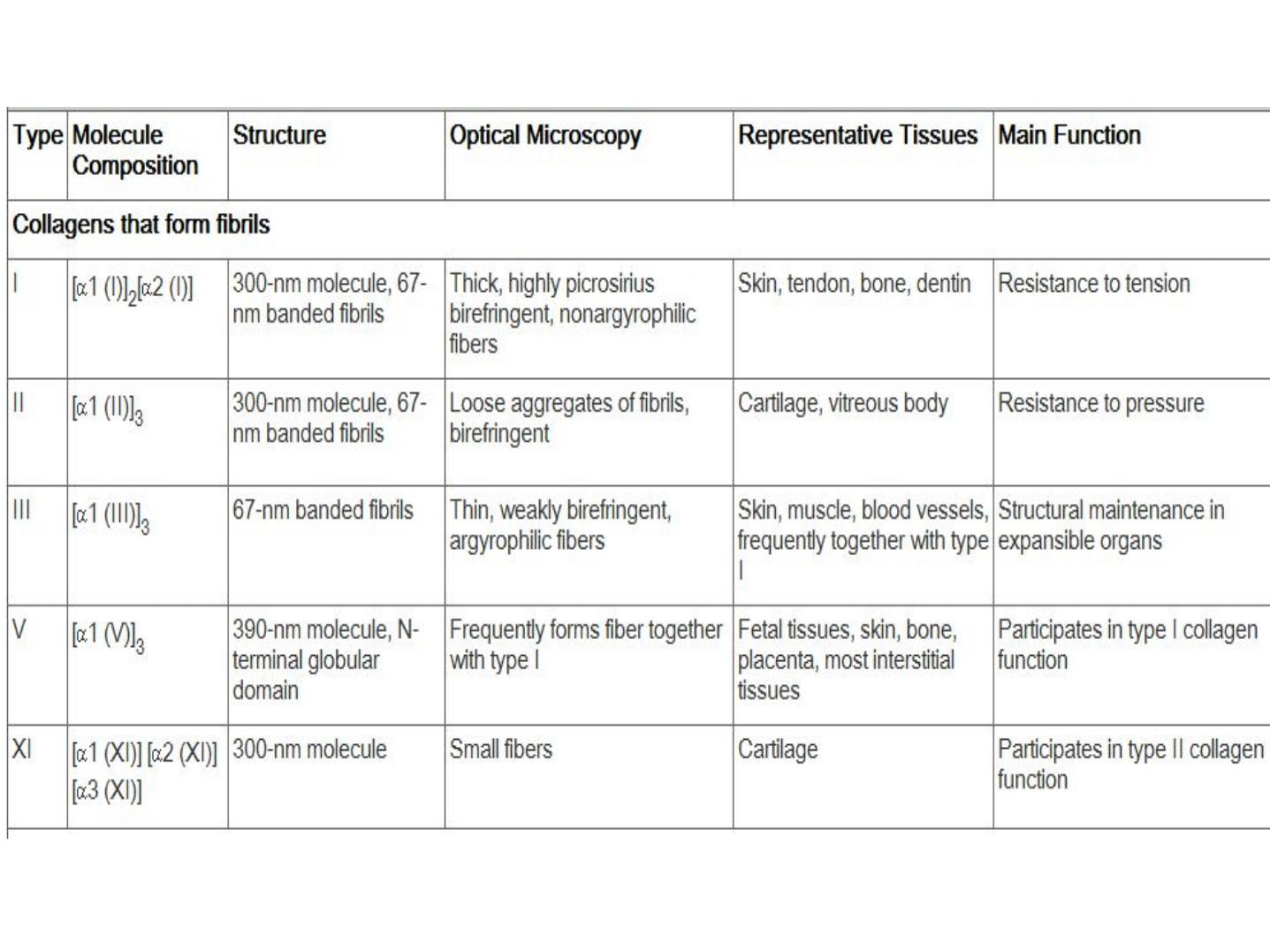
Protein fibers
Collagen fibers. Composed of the protein collagen.
Strong, flexible, inelastic; great tensile strength (i.e.
resist stretch). Perfect for tendons, ligaments
Elastic fibers. Contain molecules of protein elastin that
resemble coiled springs. Returns to its original shape
after stretching or compression. Perfect for lungs,
large blood vessels
Reticular fibers. Formed from fine collagenous fibers;
form branching networks. Fill spaces between tissues
and organs.

Ground Substance
• Interstitial (tissue) fluid within which are one or more of the
molecules listed below:
- Hyaluronic acid: a polysaccharide. Very slippery; serves as
a good lubricant for joints. Common in most connective
tissues.
- Proteoglycans: protein and polysaccharide complex.
Polysaccharides called glyocosaminoglycans (chondroitin
sulfate, keratin sulfate). Protein part attaches to
hyaluronic acid. Able to trap large amounts of water.
- Adhesive molecules: hold proteoglycan aggregates
together. Chondronectin in cartilage, osteonectin in bone,
fibronectin in fibrous connective tissue.
• Functions as a molecular sieve through which nutrients
diffuse between blood capillaries and cells
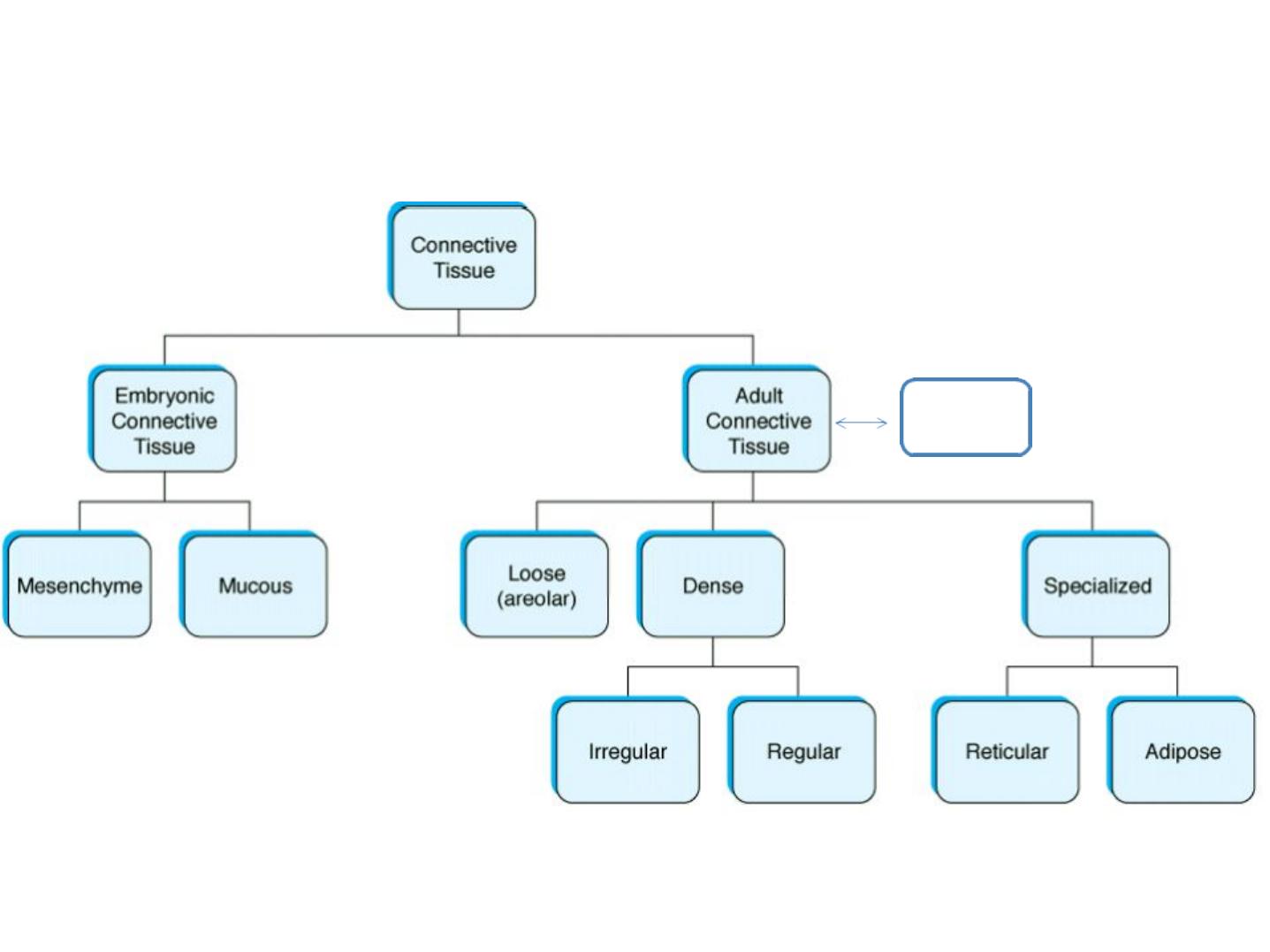
Types of connective tissue
Proper
CT
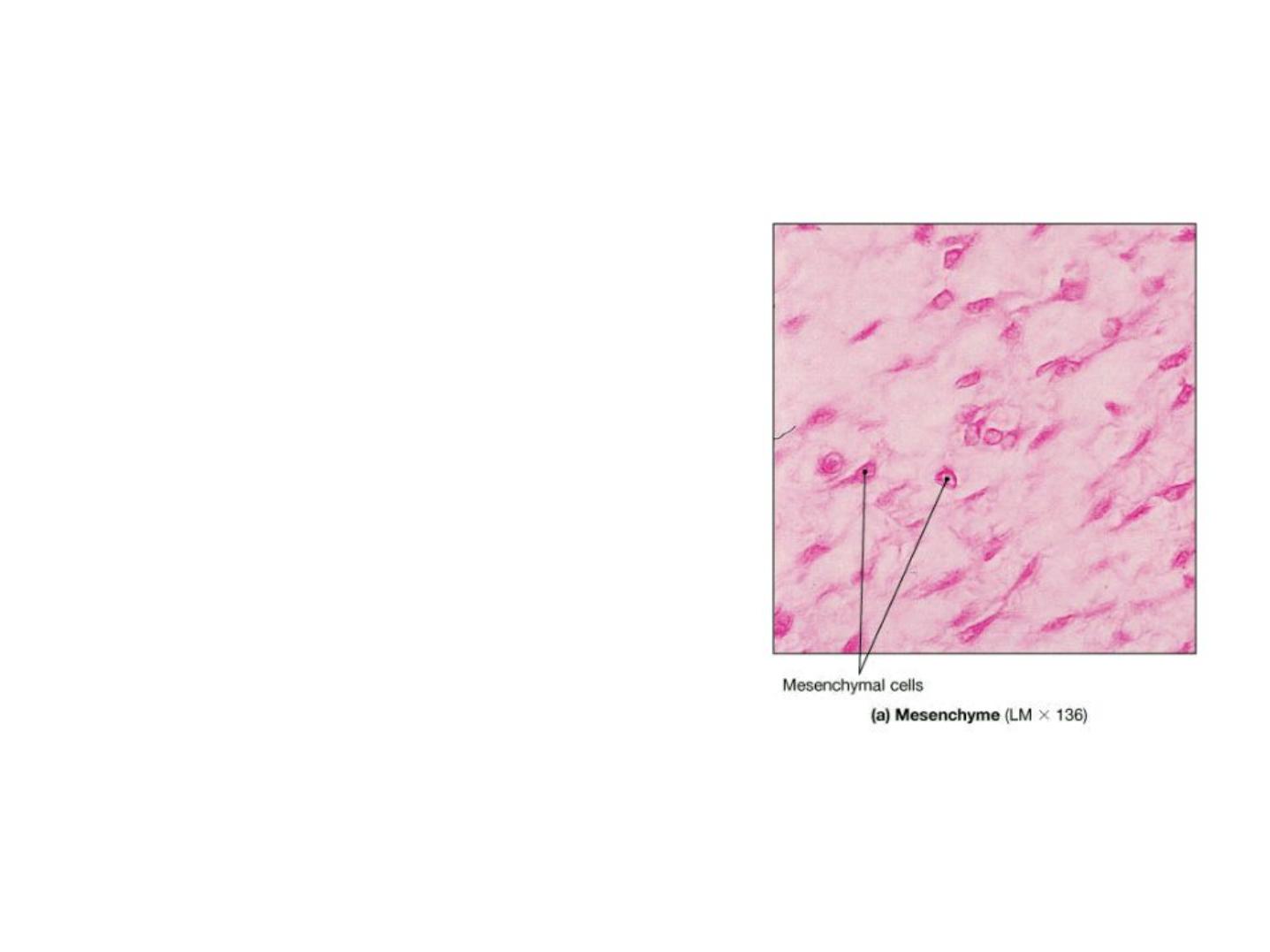
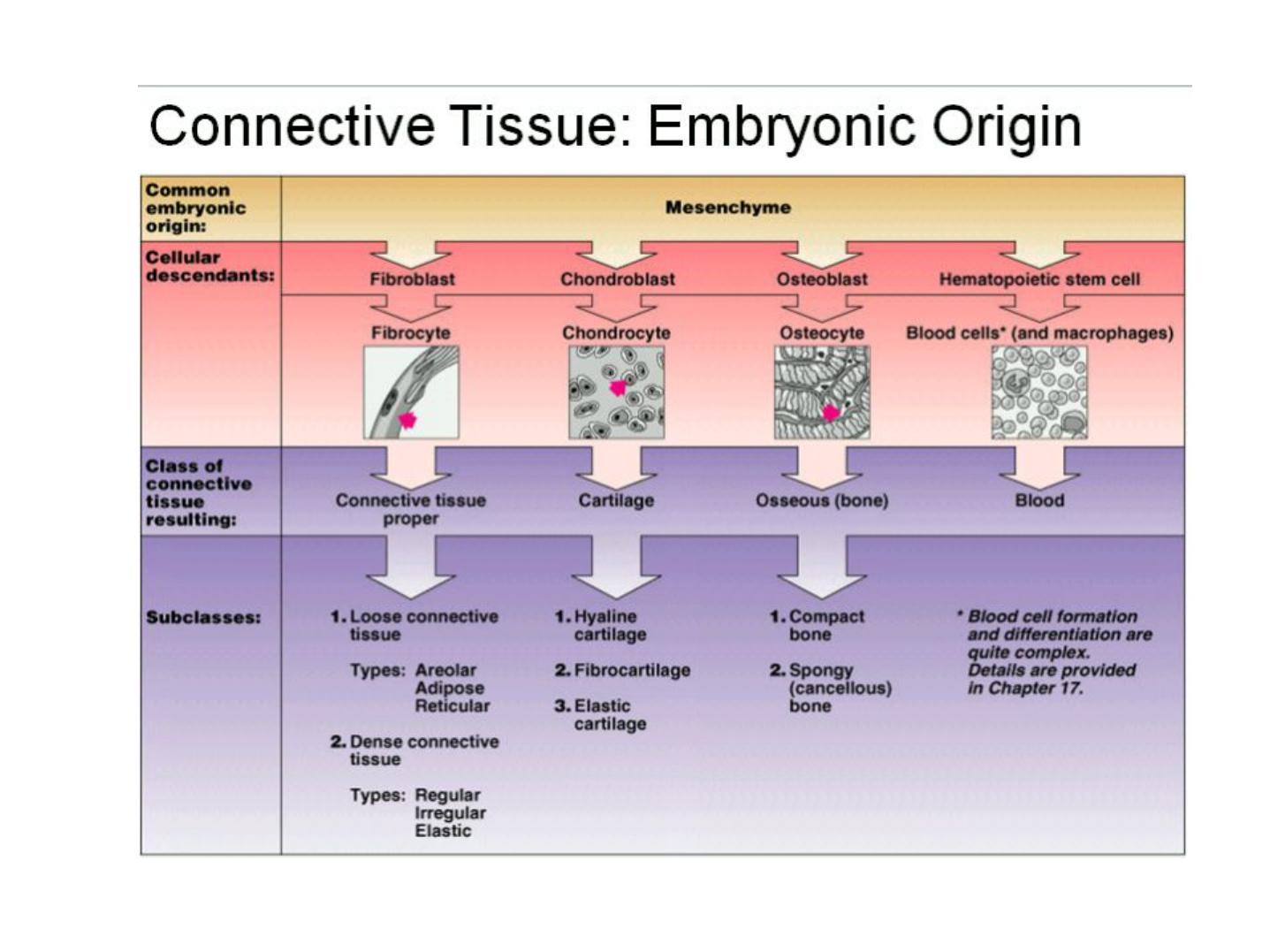
Connective Tissue in Embryos
Mesenchyme tissue consists of a population of
undifferentiated cells, generally elongated but
with many shapes, having large euchromatic
nuclei and prominent nucleoli that indicate
high levels of synthetic activity. These cells are
called Mesenchymal cells. Mesenchymal cells
are surrounded by an ECM that they produced
and that consists largely of a simple ground
substance rich in hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid),
but with very little collagen.
1- Mesenchyme CT
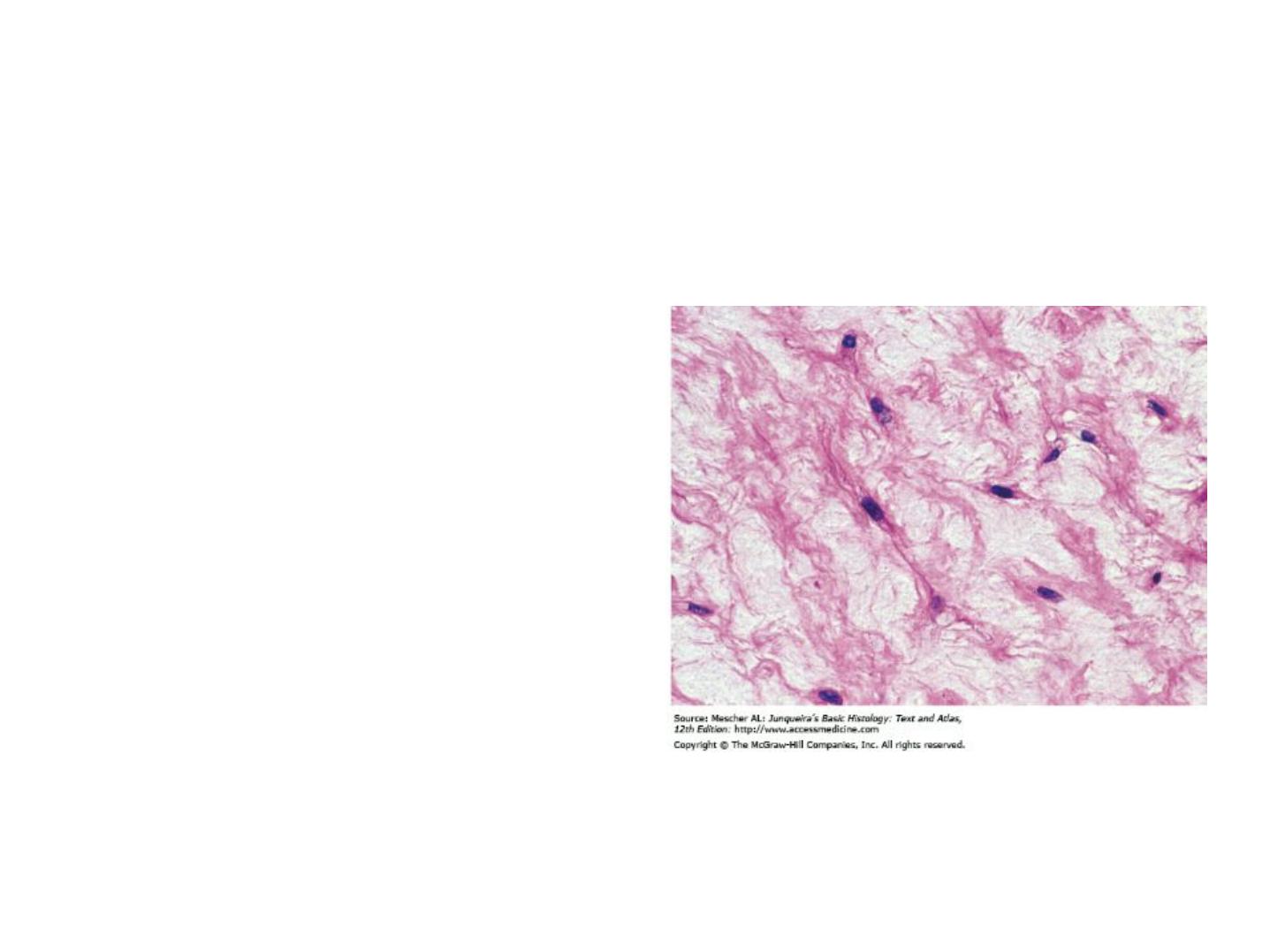
Mucous tissue is found mainly in the
umbilical cord and fetal tissues. Mucous
tissue has an abundance of ground
substance composed chiefly of hyaluronic
acid, making it a jellylike tissue containing
very few collagen fibers with scattered
fibroblasts. Mucous tissue is the principal
component of the umbilical cord. A
similar form of connective tissue is also
found in the pulp cavity of young teeth.
2- Mucous CT
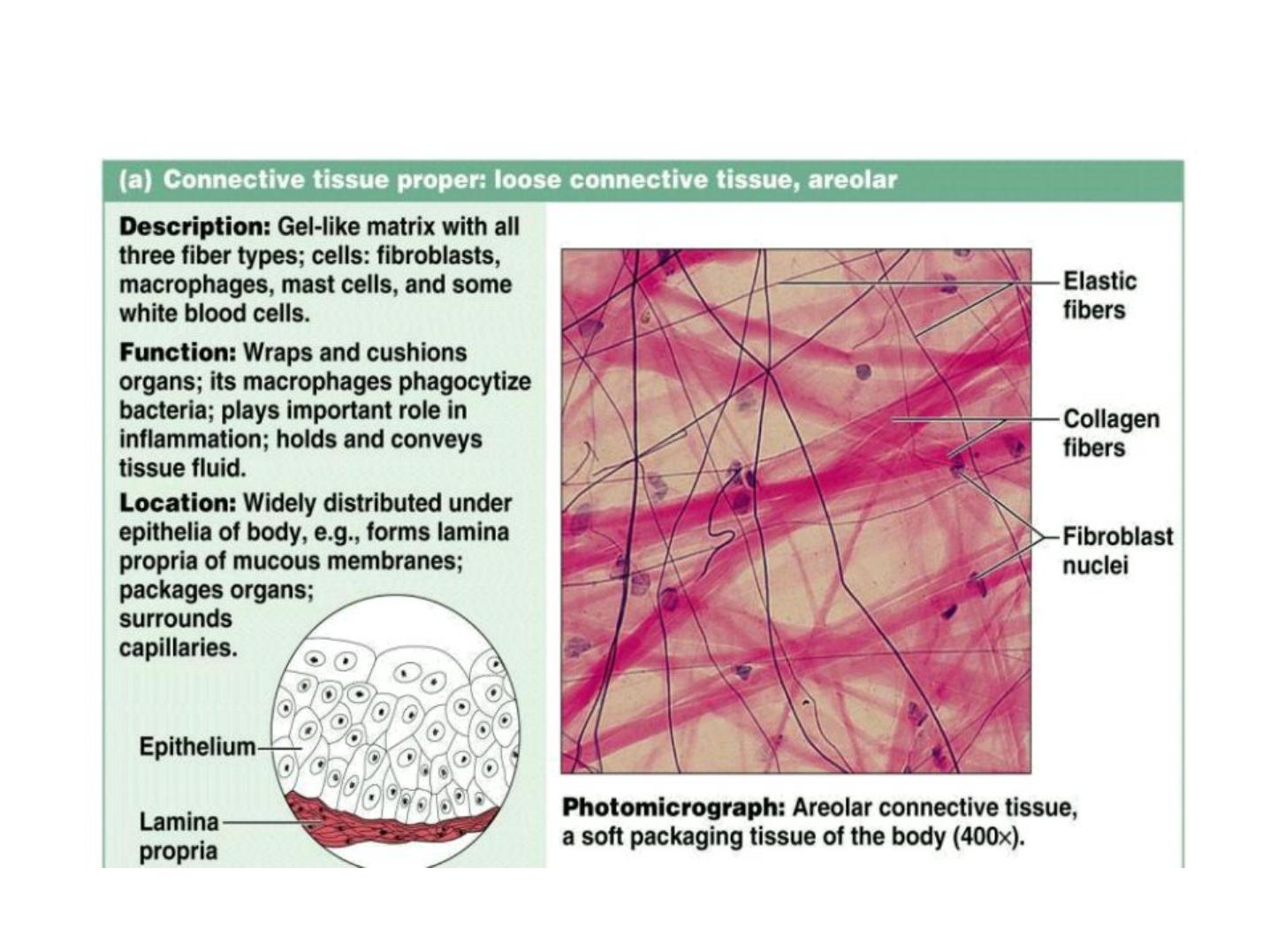
proper CT (Loose CT) Areolar Tissue:
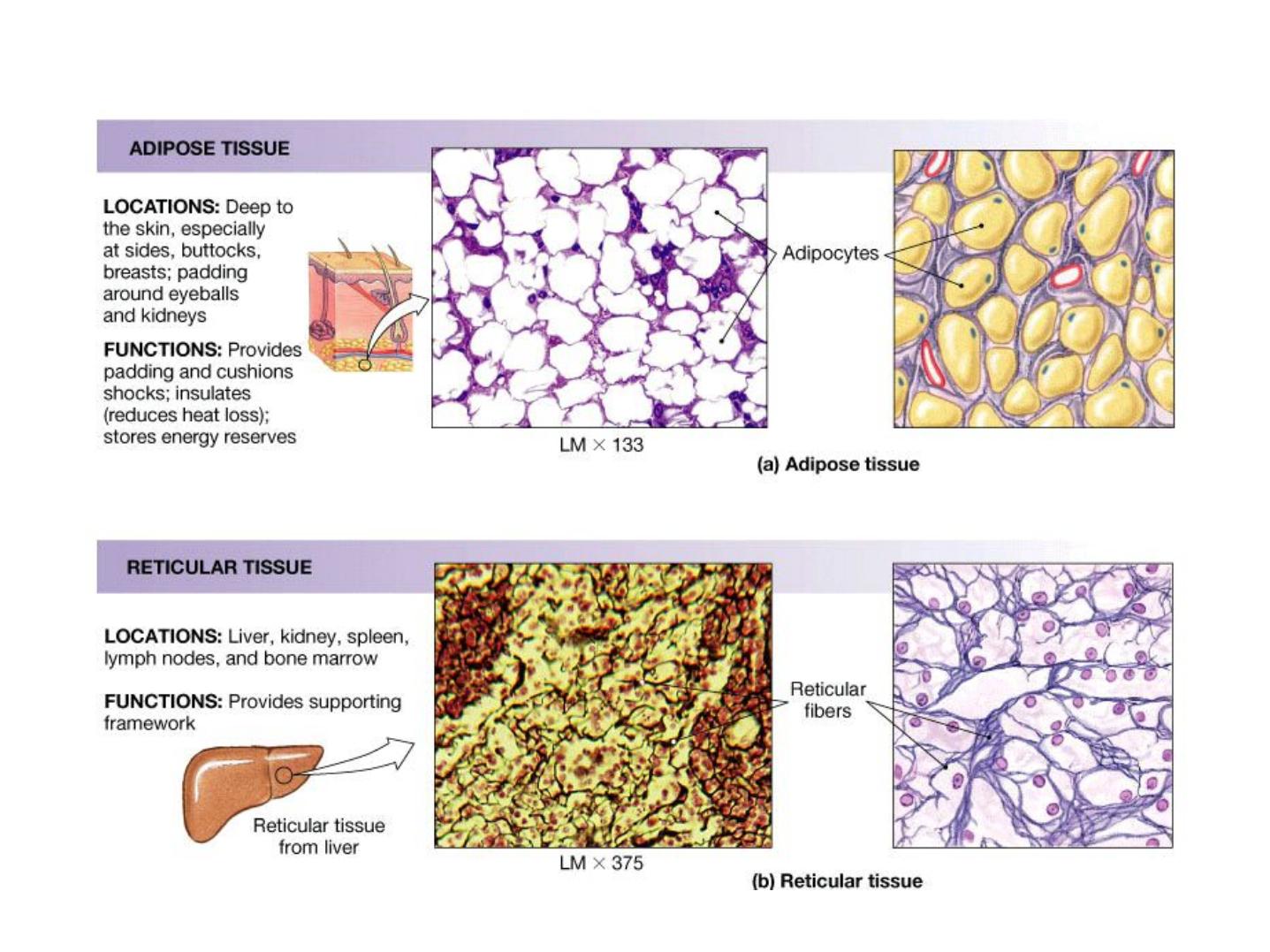
Adipose and Reticular Tissues
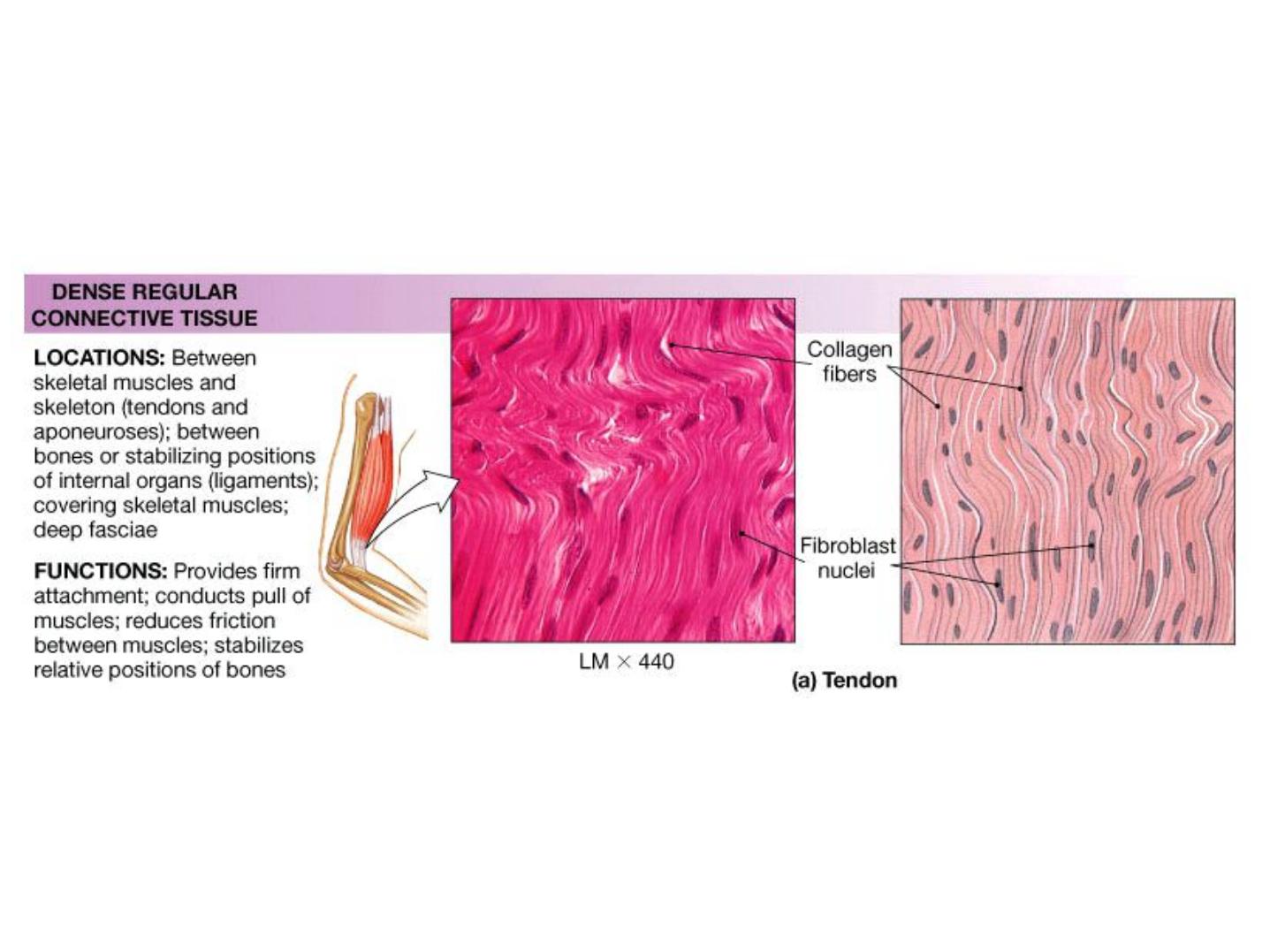
Dense Connective Tissues
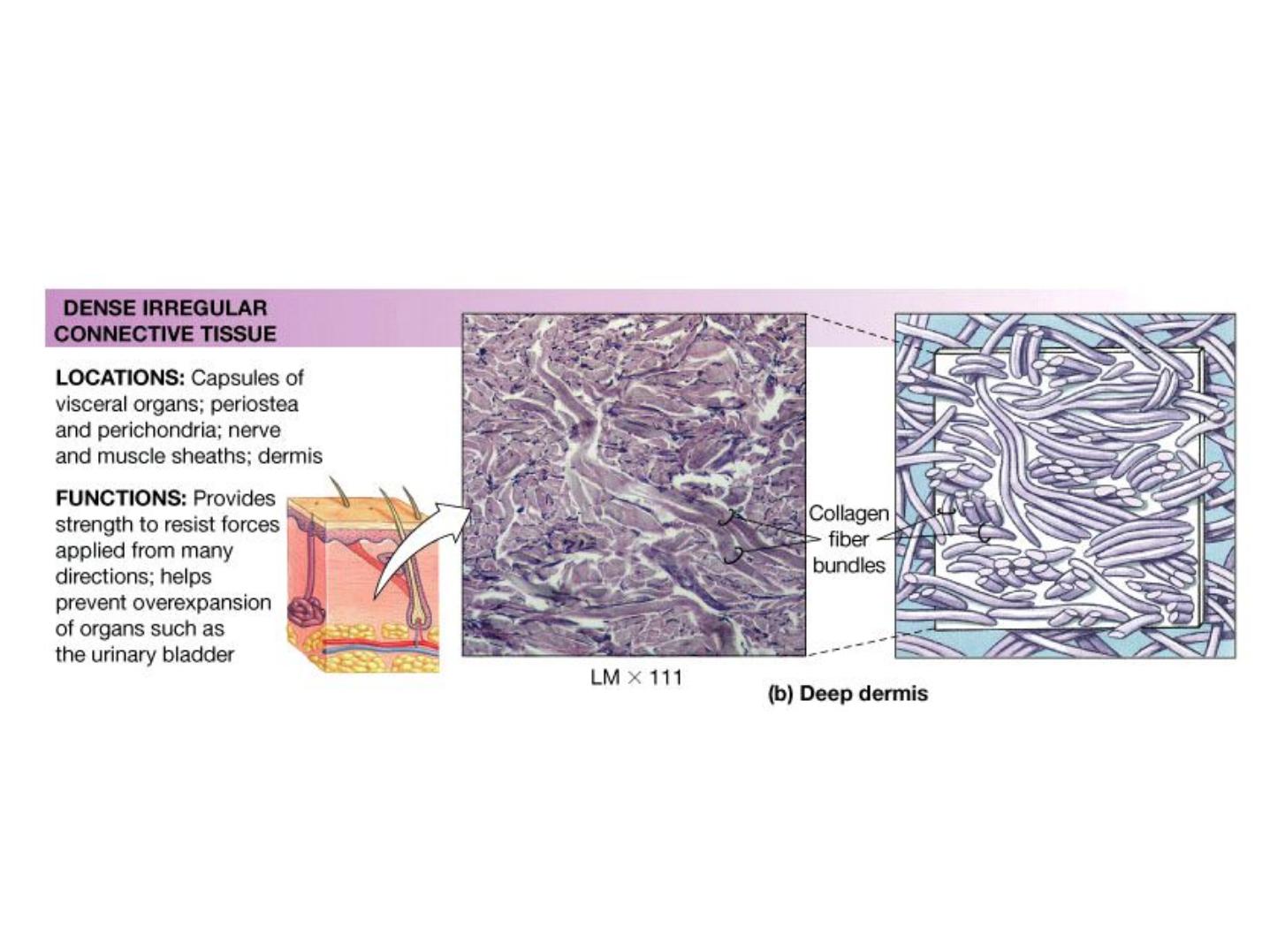
Dense Connective Tissues
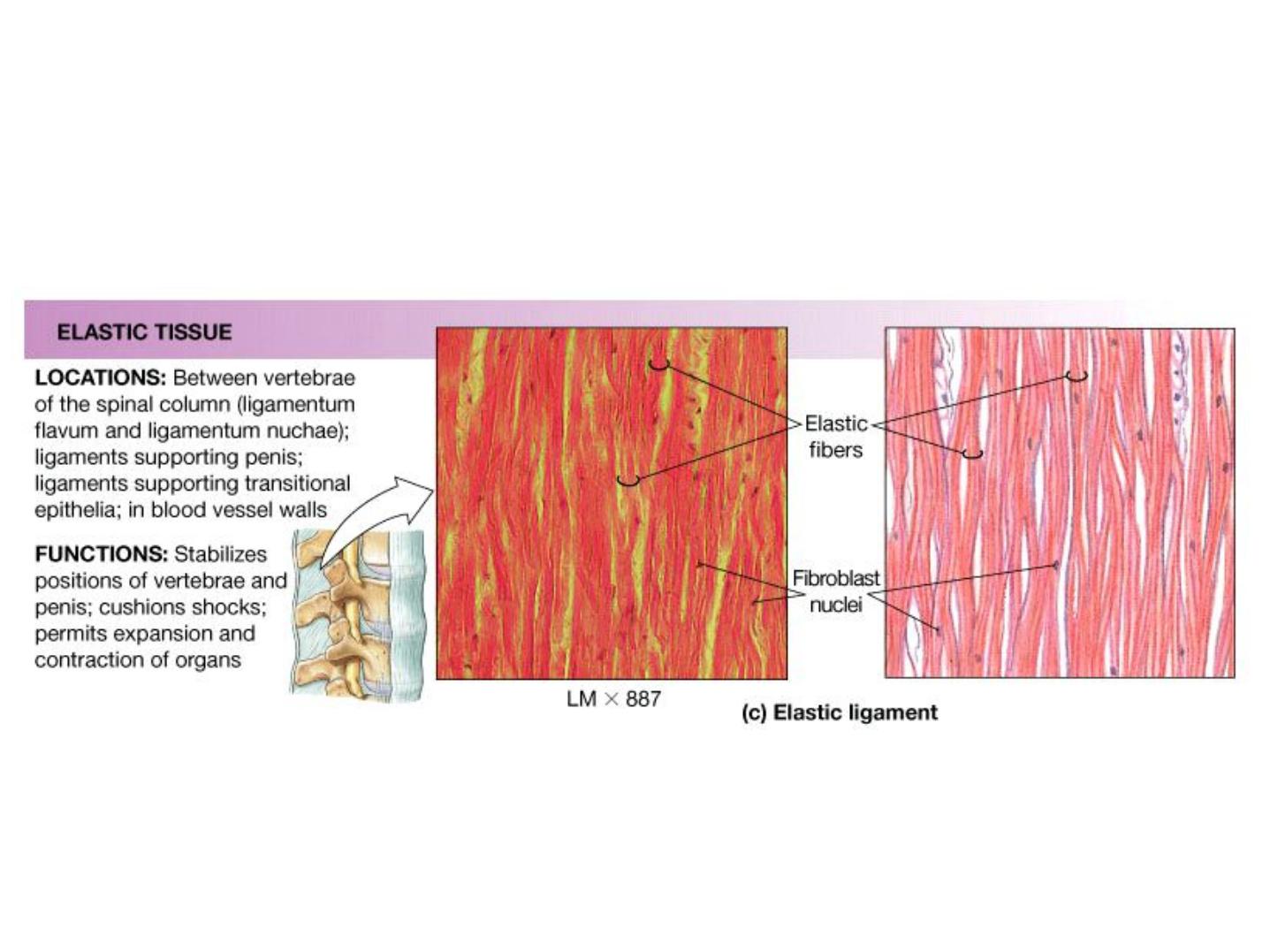
Dense Connective Tissues
