
Dr. Huda Y. K
Saliva

Is a wa t e ry subst a nce loca t e d in t he mout h in cont a ct
wit h t he te e th a nd oral mucosa
Norma lly t he da ily product ion of sa liva ra nge s from
0. 7
to 1 . 5
lite rs
.
Saliva

-
Wit hout st imulat ion
, an ave rage of
0. 25mL pe r minut e is produce d
-
While in
st imulat e d
condit ions an
ave rage 0. 7mL pe r minut e is
produce d.
Saliva

*
Saliva is produce d by
:
1.
Three paired
Major
salivary glands (producing 90%of saliva)
*
Parotid Gland
*
Submandibular gland
*
Sublingual gland
2 . Minor
salivary glands
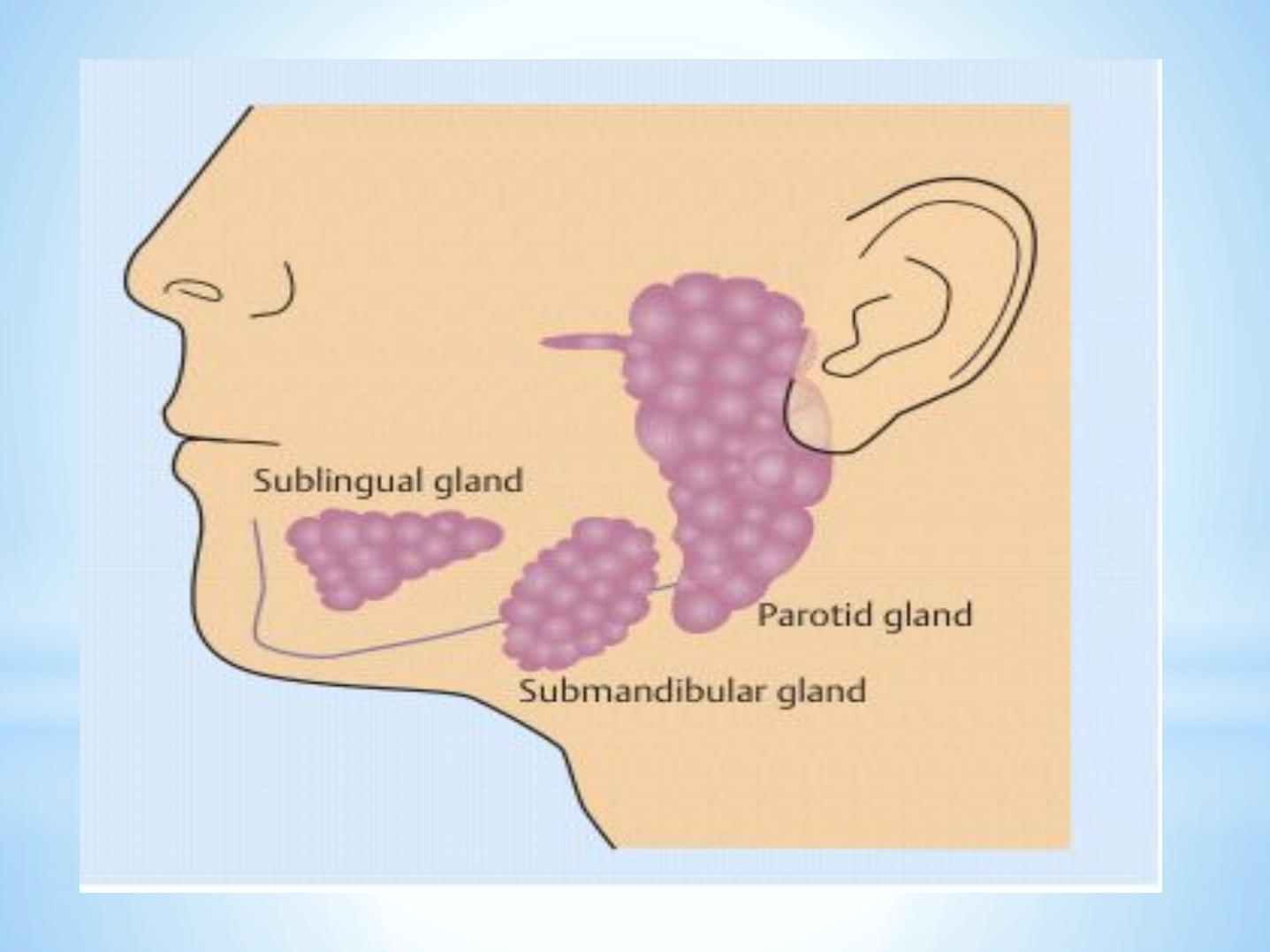

Without stimulation, 2/ 3 of t he t ot al sa liva is
se cre t e d by t he
sub ma ndibula r
gla nds.
50%of stimulate d sa liva is se cre t e d by t he
pa rot id
g
la nds a nd 35%come s from t he sub
ma ndibula r gla nds
Saliva

*
Saliva consist s of mucus and se rous fluids
*
The parotid gland produce s pure ly se rous saliva.
*
The ot her maj or salivary glands produce mixe d (se rous and
mucus) saliva .
Saliva


The
Parot id
gland se cre t e s t hin, wat e ry saliva rich in
amylase (an e nzyme t hat bre aks down st arch int o sugar).
The
Submandibular
glands se cre t e viscous, slimy saliva
rich in mucin (a prot e in lubrica nt ).
The
Sublingual
glands produce viscous saliva.
Saliva
99.4 % Water
0.2 % Soluble inorganic substances:
sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride,
bicarbonate, phosphate, fluoride
0.3% Soluble organic substances:
proteins, digestive enzyme (amylase), mucins,
antibodies (immunoglobulins), urea, peroxidases,
antioxidantenzymes
0.1 % insoluble substances
Saliva
The Composition of Saliva

The composition of saliva :
a. Inorganic compone nts .
B. Organic compone nts .
Saliva

Inorganic compone nts
•
Calcium
•
Phosphat e
•
Hydrogen Carbonat e
•
Ot her Ions (Fluoride )

Organic compone nts of saliva
*
Mucins
*
Amylase
*
Lysozyme
*
Lact oferrin
*
Secre t ory IgA
*
Proline-rich prot eins
*
Hist at ins
*
St at herin

*
Function of Saliva
1.
Lubrica t ion and prot e ct ion
2.
Buffe ring act ion and cle arance
3.
Maint e nance of t oot h int e grit y
4.
Ant ibact e rial and ant ifungal act ivit y
5.
Tast e and dige st ion.

As a se romucous coat ing, saliva lubrica t e s and prot e ct s oral
t issue s, act ing as a barrie r against irrit ant s.
The be st lubrica t ing compone nt s of saliva are mucins: t he y
have t he prope rt ie s of low solubilit y, high viscosit y, high
e last icit y, and st rong adhe sive ne ss.
1. LUBRICATION AND PROTECTION

Mucins
*
Prot enic
Product s of submandibular, sublingual and some minor
salivary glands.
Mucin Functions
1.
Tissue Coat ing
*
Prot ect ive coat ing for hard and soft t issues
*
Primary role in format ion of
acquired pellicle
2.
Lubricat ion
*
Increase s lubricat ing qualit ies(Mast icat ion, speech, and
swallowing).
3.
Bact erial adhesion
*
Mucin-coat ed bact eria may be
unable
t o
at t ach
t o surface .
Mucin react wit h
bact erial adhesors,
t here by
blocking
t hem .

*
Most import ant carie s-pre ve nt ive funct ions of saliva are t he
flushing and ne ut ralizing e ffe ct s, commonly re fe rre d t o as
"salivary cle arance “
.
*
Oral cle arance can be de fine d as t he dilut ion and e liminat ion
of subst ance s in t he oral cavit y which can be fast or slow.
*
Accordingly, a high salivary flow rat e result s in a high clearance
and t he highe r t he buffer
.
2. BUFFERING ACTION AND CLEARANCE

Oral Clearance
-
Relies on flow rat e.
- Higher salivary flow rat e = increased clearance.
- Unst imulat ed flow rat e < 0. 2ml/ min = prolonge d
clearance.
- Prolonged clearance = great er risk of caries and
great er risk of acid erosion.

*
St udie s have shown t hat
che wing sugar-fre e gum
aft e r me als
re sult s in a significant de cre a se in t he incide nce of de nt al
carie s and t hat t he be ne fit is due
t o st imulat ing
salivary flow
rat he r t han any che wing gums.
Oral Clearance

*
In t he de ve lopme nt of carie s dise ase t he t wo
following buffe r syst e ms are import ant :
1.
The phosphat e syst e m
2.
The bica rbonat e syst e m
Buffering Capacity
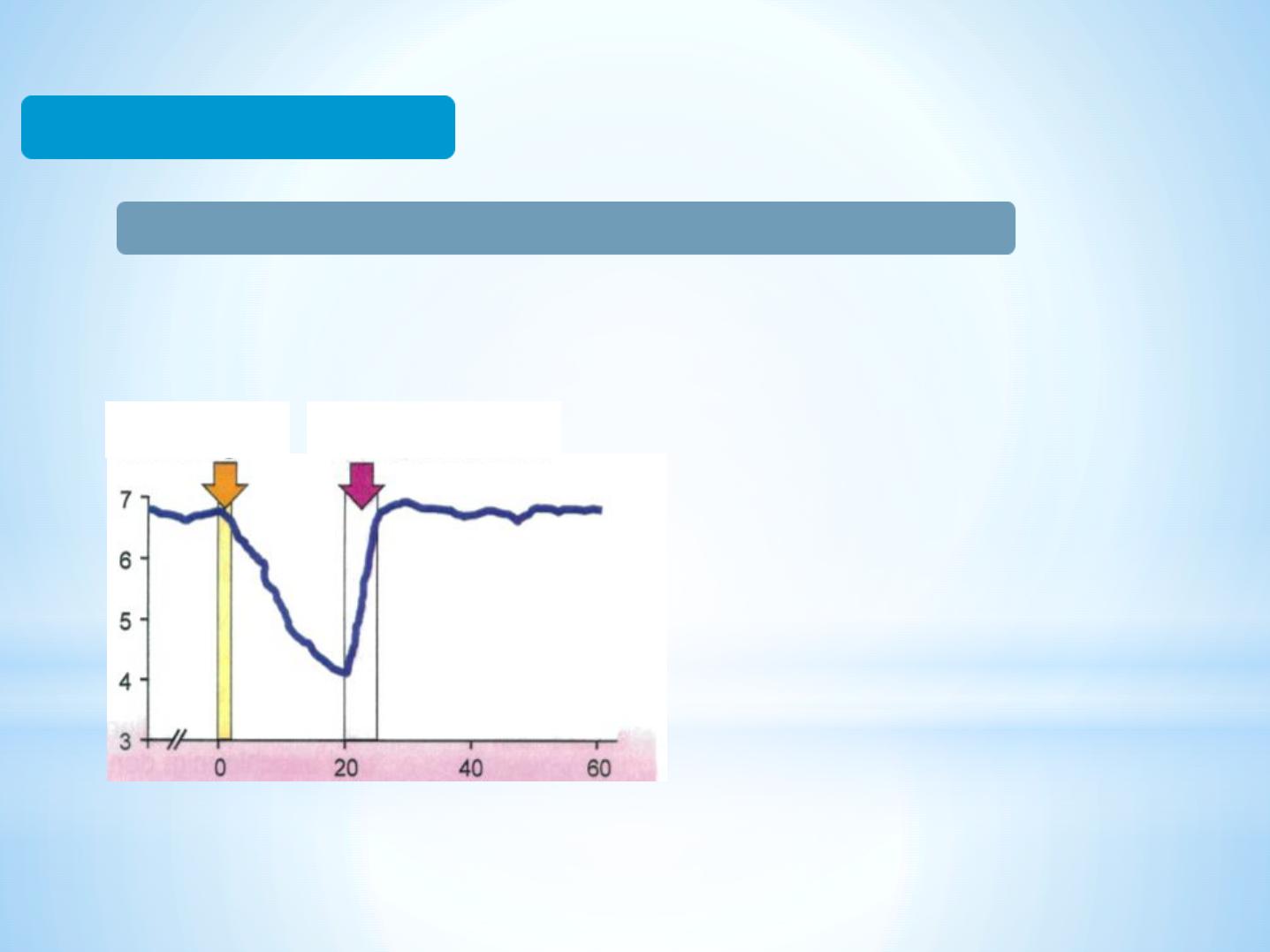
Buffering Capacity
Saliva stimulation and buffering of acids by chewing gum
p
H
va
lu
e
10% sugar
solution
Chewing gum with sugar
substitute
Time in minutes
(Stoesser 1996)
-
Buffer capacity is the ability to
neutralise acids (buffering).
-
The pH value is raised due to the
increased concentration of
bicarbonate in stimulated saliva.
(Bicarbonate increases from 5.47
unstimulated to 16.03mmol/L in
stimulated saliva).
-
Increased flow rate exposes hard
tissues to low pH for a shorter period.
(Flow rate increases from 0.32
ml/min unstimulated to 2.08ml/min
in stimulated saliva).
Fast flowing saliva neutralises plaque (pH value increases).

3. MAINTENANCE OF TOOTH INTEGRITY
*
Maint aining t oot h int e grit y is a t hird funct ion of saliva,
one t hat facilit at e s t he re mine ralizat ion proce ss aft e r
de mine ra lizat ion
From t he carie s dise ase angle , t he most import ant
e le ct rolyt e s are calcium, inorganic phosphat e , bi-
carbonat e , and fluoride .
The conce nt rat ion of t he various salivary e le ct rolyt e s is
st rongly de pe nde nt on t he salivary flow rat e

The pH of unst imulat ed and st imulat e d saliva is be t we e n
6
and
7
.
De mine raliza t ion occurs whe n acids diffuse t hrough plaque and t he
pe llicle int o t he e name l. Re sult ing in cryst alline dissolut ion t hat
occurs at a pH of 5 t o 5. 5, which is t he crit ical pH range for t he
de ve lopme nt of carie s.
Demineralization

Caries
Demineralisation-Remineralisation
- When the pH value is <5.5
- Calcium (Ca
2+
) and Phosphate
(PO4
3
-) are withdrawn from the
dental enamel.
Demineralisation
- When the pH value is >6.5
- Calcium (Ca
2+
) and Phosphate
(PO4
3
-) migrate back into the dental
enamel.
Remineralisation
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
F
-
F
-
F
-
Ca
++
PO
4
-
F
-
F
-
Demineralisation
Low pH
Ca
+ +
PO
4
-
Remineralisation
Increased pH
Ca
+ +
PO
4
-
©R e e v e s 20 14
Ca
++
PO
4
-
- A dynamic equilibrium exists between demineralization and remineralisation.
- A neutral pH value promotes remineralisation.
Remineralization

4. ANTIBACTERIAL AND ANTIFUNGAL
ACTIVITY
Ant imicrobial e nzyme s t hat kill bact e ria
*
Lysozyme
*
Lact ofe rrin
*
Salivary lact ope roxidase
*
Immunoglobulin A

Lactofe rrin
*
Iron
-binding prot e in
*
Pre ve nt s iron
from be ing
use d
by
microorga nism
t ha t re quire it
for me t a bolism
Lyzozyme
*
Ant imicrobia l a ct ivit y by de st ruct ion of ba ct e ria l
ce ll me mbra ne s

5. TASTE AND DIGESTION
*
saliva can e nhance t ast e and be gin t he dige st ive proce ss.
*
Tast e is a main st imulant for format ion of saliva. On t he
ot her hand, pre se nce of saliva in t he oral cavit y is also
e sse nt ial for t ast e pe rce pt ion
*
Dige st ion will st art most ly by Amylase e nzyme .

Amylase s
*
Produced by
maj or
salivary glands
*
Me tabolize s starch
int o glucose & malt ose
“
Appears”to have
digest ive
funct ion inside t he oral cavit y ,
inact ive
in
st omach
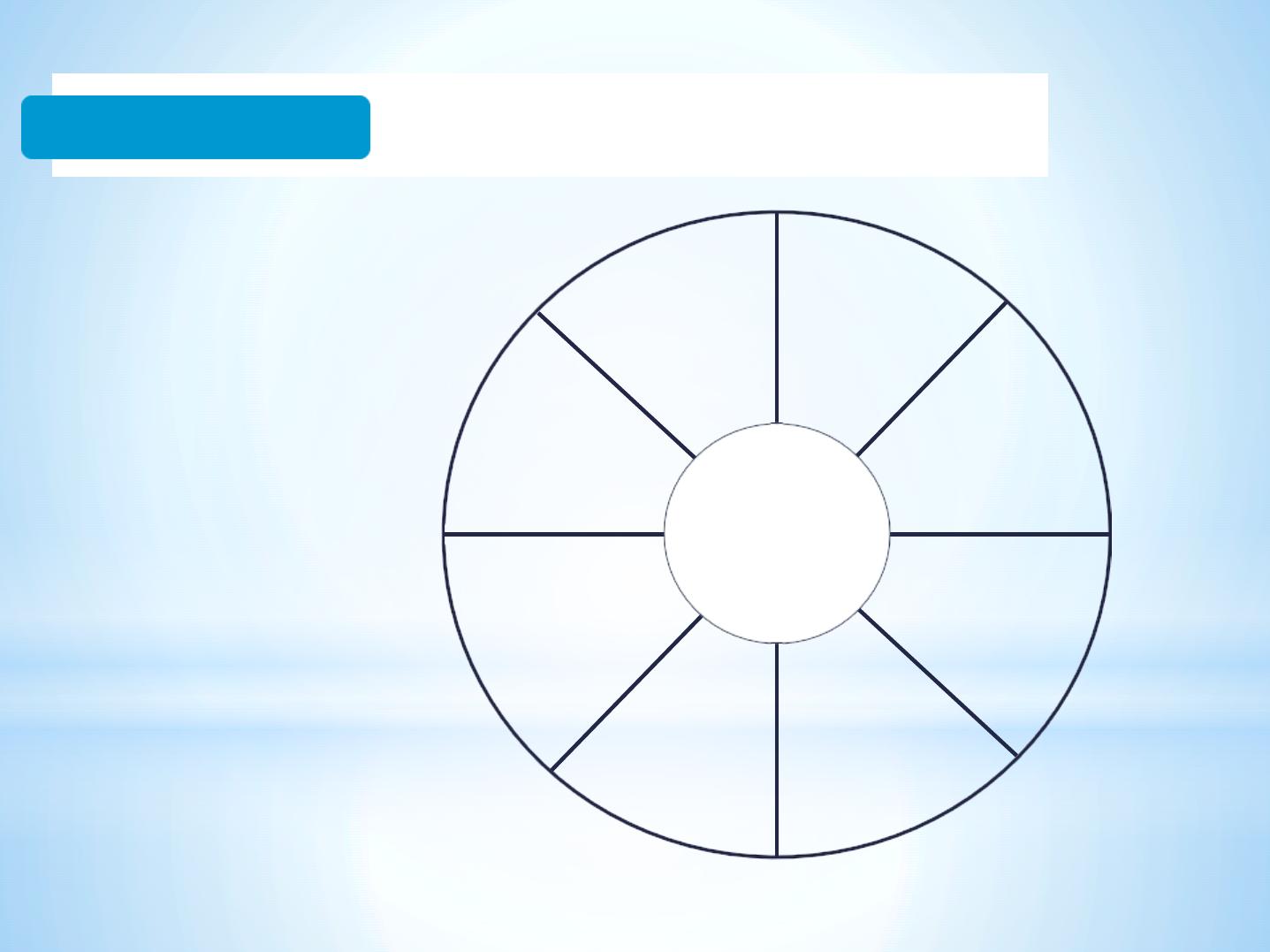
S
S
a
a
l
l
i
i
v
v
a
a
r
r
y
y
F
F
u
u
n
n
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
A
nti
-B
ac
te
ria
l
sIg
A
Pe
ro
xid
as
es
Bu
ffe
ri
ng
C
ar
bo
ni
c
an
hy
dr
as
es
H
CO
3
Dig
est
ion
lipa
se,
am
yla
se
mu
cin
s
Mineraliz
ation
Ca, Fl,
PO
4
Lub
rica
tion
Vis
cos
ity
Ela
s tic
ity
Mu
c in
s
Sta
the
rin
s
Ti
s s
ue
C
oa
tin
g
M
uc
ins
, P
RP
s
Am
yl
as
e s
An
ti-
Fu
ng
a l
Ca
nd
ida
: H
ist
a ti
ns
Anti-Viral
Saliva
The Multiple Functions of Saliva

*
Hyposalivation
Is a diagnosis made whe n:
*
The unst imulat ed salivary flow rat e is le ss t han
0. 1ml/ min and/ or
*
Whe n t he st imulat e d flow rat e is le ss t han
0. 7ml/ min
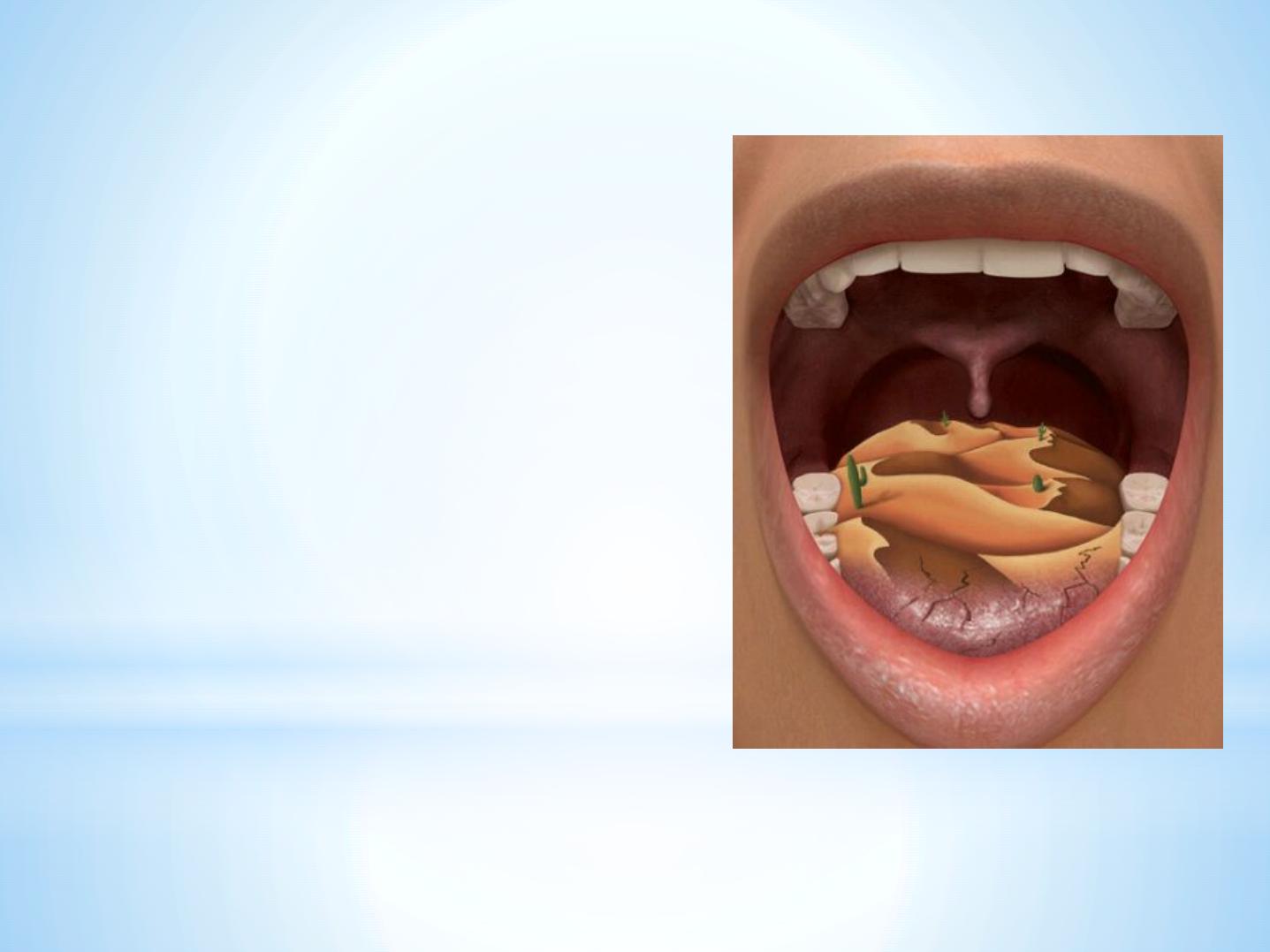
*
Xe rostomia
*
Xe rost omia is t he subj e ct ive
fe e ling (sympt om) of a se nsat ion
of oral dryne ss, which oft e n
impa irs oral funct ion and e ve n
t he ove rall qualit y of life .
*
A salivary flow rat e be low
0. 16mL/ min incre ase s t he risk of
de ve loping carie s

*
Signs and symptoms
*
De nt al carie s (xe rost omia re lat e d carie s)
*
Acid e rosion.
*
Oral candidia sis
*
Dysge usia –alt e re d t ast e se nsat ion
*
Int raoral halit osis
*
Dysphagia –difficult y swallowing and che wing

The following condit ions can influe nce t he flow rat e and
le ad t o hyposalivat ion:
*
Me dicat ions—for e xample , ant ide pre ssant s, diure t ics,
ant ihist amine s, ant ihype rt e nsive s, ant ie me t ics, narcot ics
*
Radia t ion
*
Aut oimmune dise ase s, AIDS, diabe t e s me llit us
*
Me nopause
*
Eat ing disorde rs
*
Salivary gland st one s
*
Aging

*
Change s in Saliva
with Aging
*
What happe ns t o saliva compone nt s wit h age ?
*
The re are change s in t he st ruct ure of t he salivary glands
due t o age
*
But it se e ms t hat t he se change s are not sufficie nt t o
significant ly influe nce t he t hre e compone nt s (wat e r,
e le ct rolyt e s, and organics) in such a way t hat t he t e nde ncy
for de ve loping carie s incre ase s.

35
*
Aging
*
If t he qualit y and quant it y of saliva doe sn’
t change wit h
age , t he n what account s for t he incre ase d incide nce of
xe rost omia and associat e d morbidit y among t he e lde rly?
*
Medicat ions, diseases, and ot her environme nt al
insult s affect bot h t he qualit y and quant it y of
saliva
*
An incre ase in incidence of t hese insult s generally
associat ed wit h an incre ase in age

