Neurology: Is the branch of medicine that dealing with diseases of the nervous system .
Nervous system divided into:Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
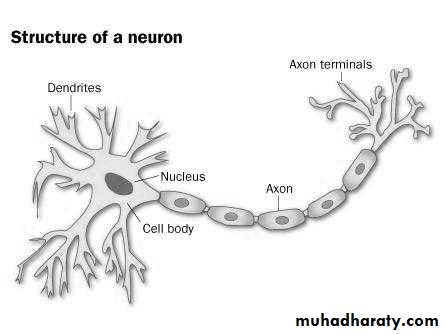
Structure of the neuron:
Divisions of the CNS:
Intracranial ( Cerebrum, Brain stem & Cerebellum)Spinal part ( Spinal cord & Cauda equina)
Cerebrum:
Composed of 2 cerebral hemispheres connected to:Each other by corpus callosum
Brain stem by cerebral peduncles
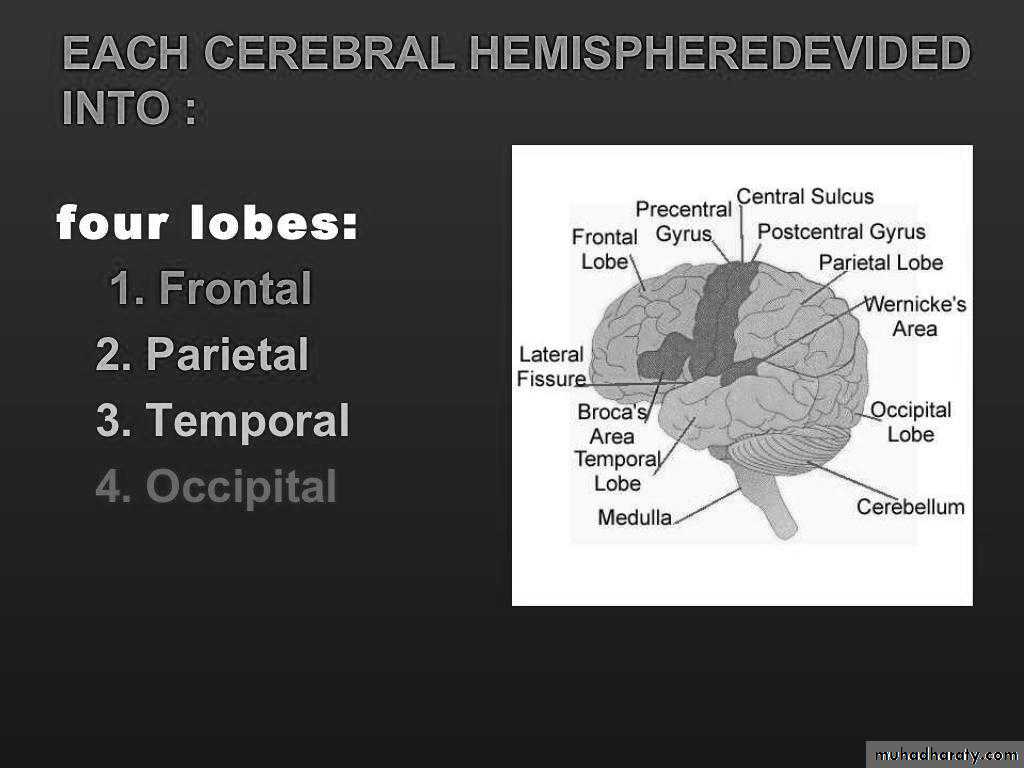
Each Cerebral hemisphere divided into
four lobes:
Frontal lobe
Parietal
Temporal
Occiptal
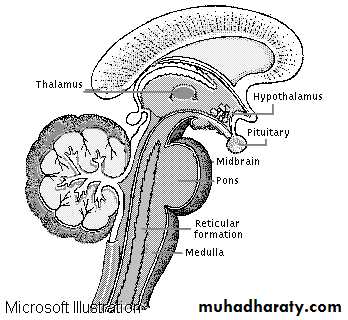
Brain stem:
Formed of:
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Connected to:
Cerebral hemishphere by cerebral peduncles
Cerebellum by cerebellar peduncles
The brain stem contains:
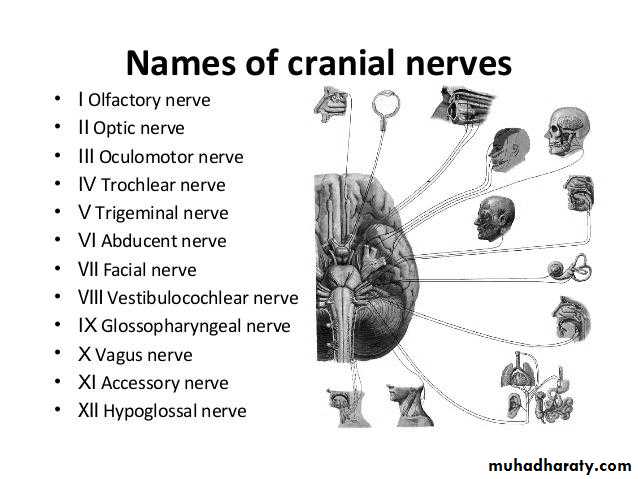
Cranial nerve 3&4 (in midbrain)
Cranial nerve 5,6,7&8 (in pons)
Cranial nerve 9,10,11&12 (in medulla)
Cerebellum:
Behind the brain stemFormed of: medline vermis & two cerebellar hemispheres
Composed of: outer grey matter & inner white matter
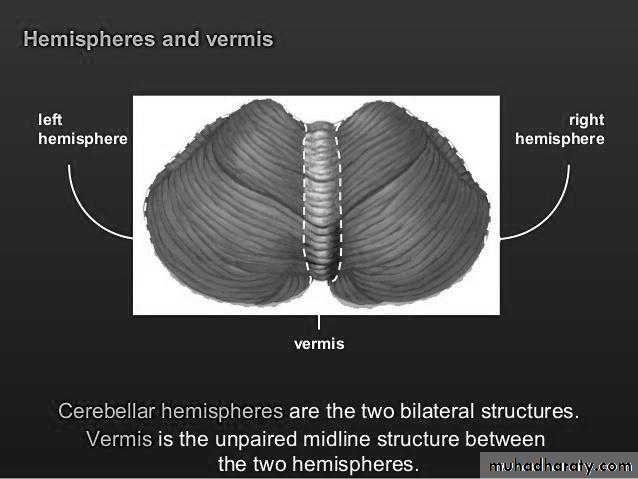
Hemispheres and vermis
Cerebellar hemispheres are the two bilateral structres
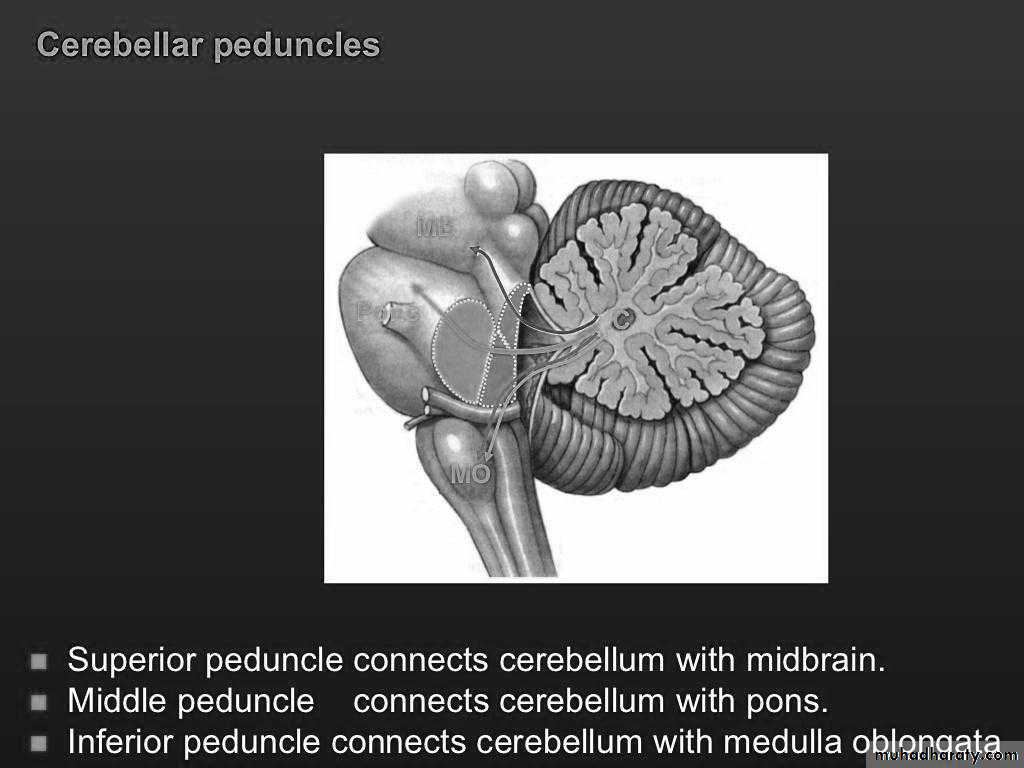
Vermis is the unpaired midline structure between the two hemispheresCerebellar peduncles
Superior peduncle connects cerebellum with midbrain
Middle peduncle connects cerebellum with ponsInferior peduncle connects cerebellum with medulla oblongata
Blood supply and driange of the brain:
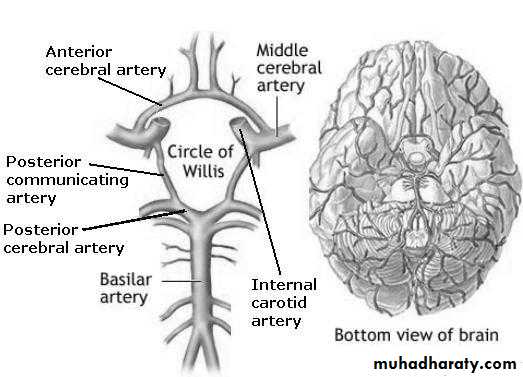
Blood supply of the brain through the circle of willis.
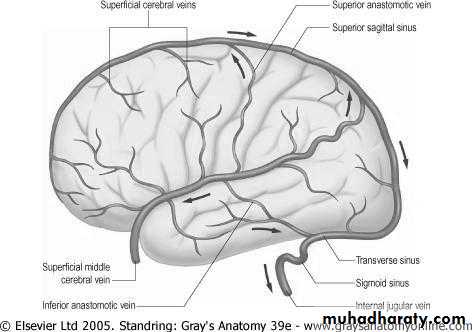
Blood drainage though deep and superfacial venous system (venous sinuses).
Ventricular system filled with CSF.
The brain envelope by meninges
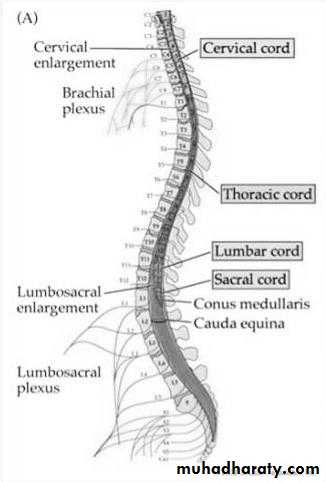
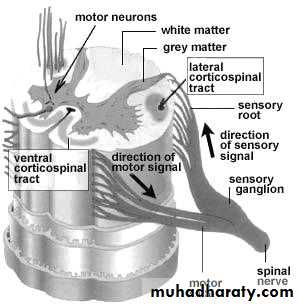
Spinal cord
Inside spinal canalEnd at lower border of L1
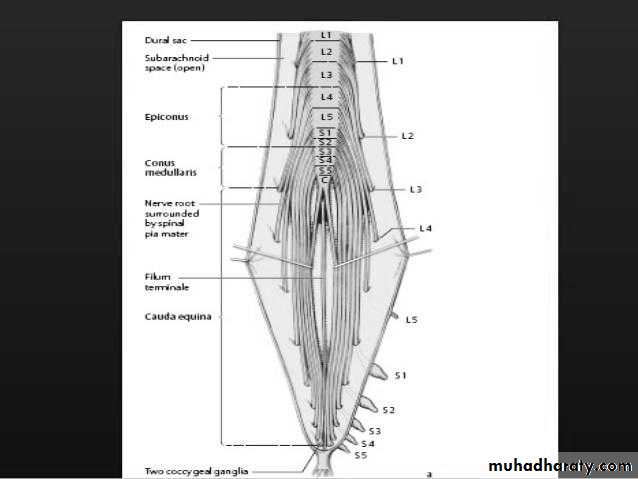
The lowest 3 segments = Conus
The above 4 segemens = Epiconus
Inner grey matter and outer white matter
Cauda equina
Lumbosacral roots collection fills the lower part of the spinal canal below L1
Peripheral nervous system
Anterior horn cellsRoots
Plexuses
Peripheral nerves
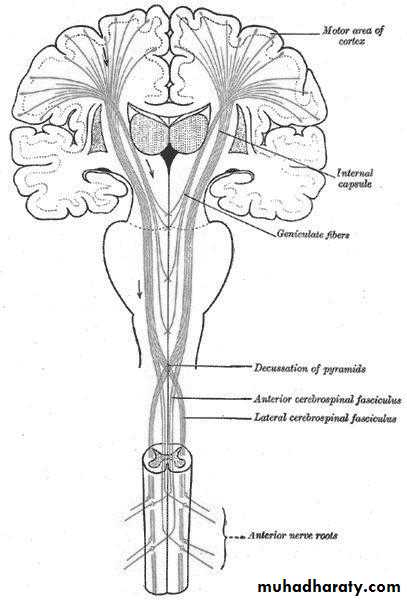
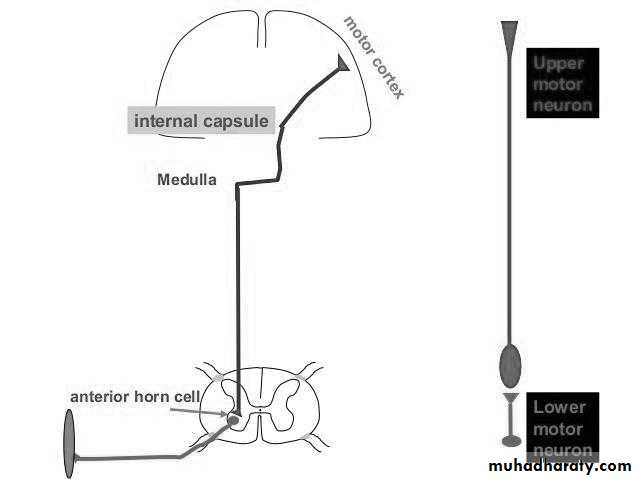
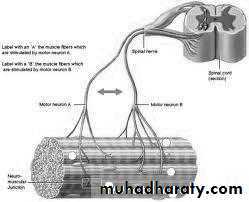
Motor pathway:
Neuro mascular junction and muscle
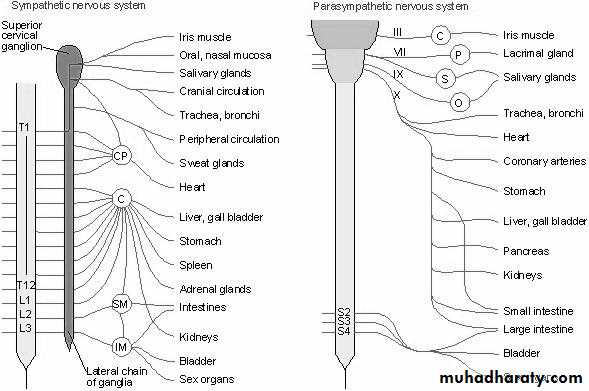
Autonomic nervous system which divided into:
SymathaticParasymathatic
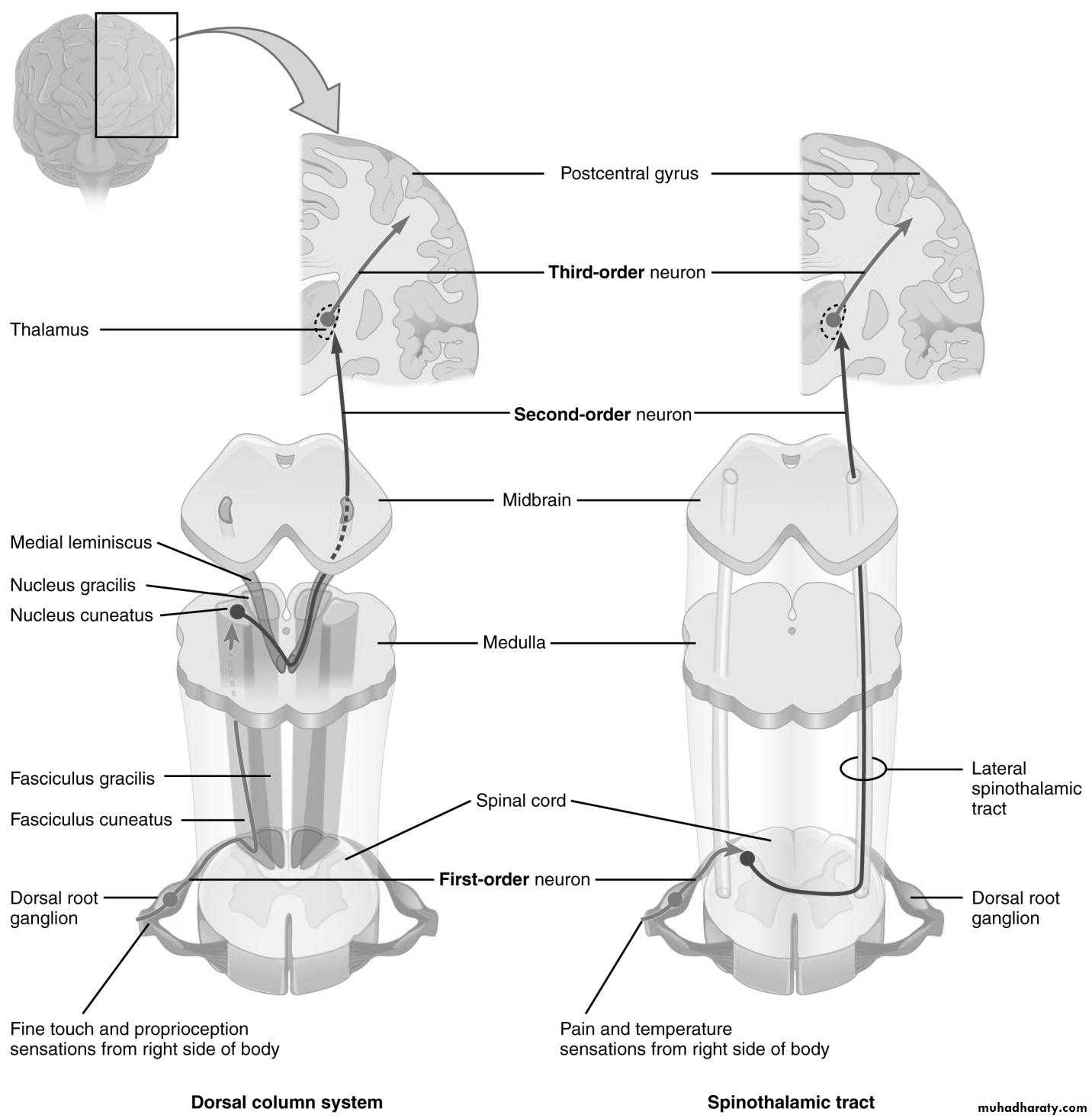
Sensory Pathway
End