UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF HUMANITIESTechnical Lab Analysis Department. Lectures of Histopathology .# Cell Structure and Function:
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Cell Structure and Function
Learning Objectives :At the end of this lecture , the student must be able to know 1- the characteristics of all cells. 2- types of cells and difference between them . 3- the cells overall structures . 4- define shape , position , and functions of each structure .
Cell Structure and Function
Characteristics of All Cells:A surrounding membrane
Protoplasm or cytoplasm – cell contents in thick fluid
Organelles – structures for cell function
Nucleus - Control center with DNA
Cell Structure and Function
Cell Types:PROKARYOTES
EUKARYOTES.
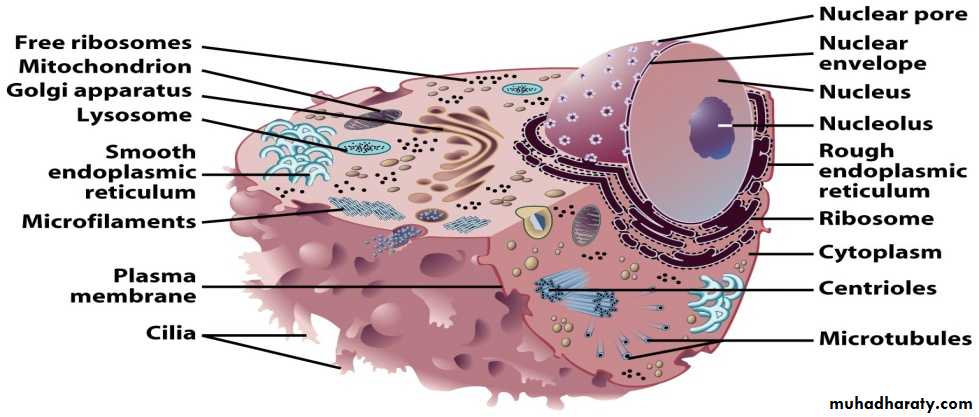
Animal Cell Structure and Function
Animal Cell
Cell Structure and Function
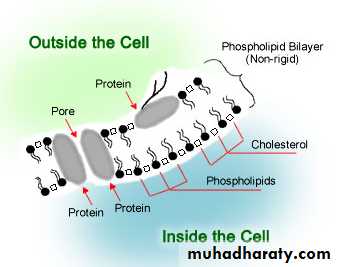
1- Cell Membrane( plasma membrane ).the cell membrane functions in 1-transport of materials in and out of cell, 2-recognition, 3-communication, and 4-homeostasis.
Receptors and communication # cells communicate with each other through surface protein ( markers) .
# Cell membranes often include receptor sites for interaction with specific biochemicals
Homestasis:
is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant , examples: regulation of temperature , PH , and various solutes across the cell membrane .Glucose regulation
2- Nucleus:
Nucleus is the control center or "brain" of cell (controls cell functioning and reproduction). Contains the DNA and is site of manufacture of RNA. The DNA is contained by a number of chromosomes, which consist of long strands of DNA tightly arranged into coils with proteins called histones. The combination of DNA andhistone proteins is known as CHROMATIN.
The nucleus, therefore, determines the metabolism, growth, differentiation, structure, and reproduction of cell.
Human chromosomes
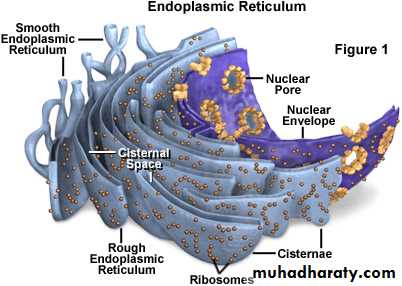
3. Organelles: A- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
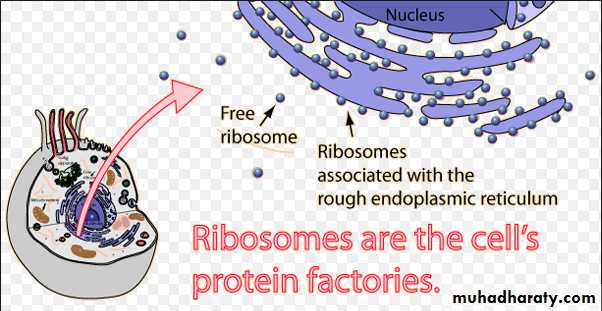
• the ER is a system of MEMBRANOUS TUBULAR CANALS that begins just outside the nucleus and branches throughout the cytoplasm. • if ribosomes are attached to the ER, it is called ROUGH Endoplasmic Reticulum. The function of rough ER is protein synthesis. if no ribosomes are attached to the ER, it is called SMOOTH Endoplasmic Reticulum. The function of smooth ER is synthesis of lipids (Lipids are required for the growth of the cell membrane and for the membranes of the organelles within the cell and are often used to make hormones).Ribosomes:
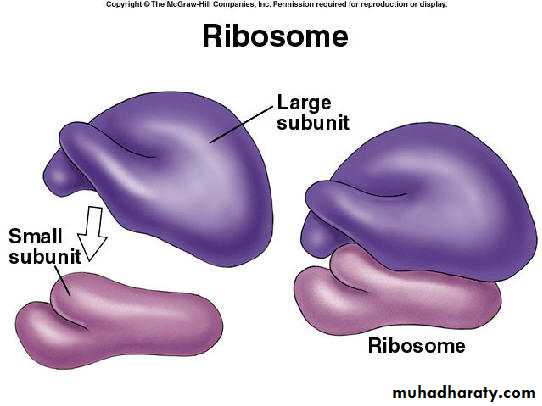
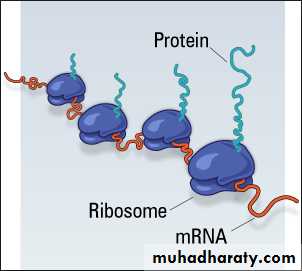
A ribosome is a cell organelle. It functions as a micro-machine for making proteins. Ribosomes are composed of special proteins and nucleic acids. The TRANSLATION of information and the Linking of AMINO ACIDS are at the heart of the protein production process ,Vacuoles and Vesicles: Storage Depots
A VESICLE is a small vacuolevacuoles and vesicles are formed by: 1) pinching off from the Golgi apparatus 2) endocytosis of the cell membrane
• they are used for transport and storage of materials.
Lysosomes: Cellular “Stomach”
• special vesicles which are formed by the Golgi apparatus. • contain powerful hydrolytic enzymes • functions in 1) cellular digestion 2) autodigestion or disposal of damaged cell components like mitochondria. 3) breakdown of a whole cell (by releasing their contents into the cell cytoplasm). For this reason, they are sometimes called “suicide sacs.”
• 4-destroy invading bacteria.
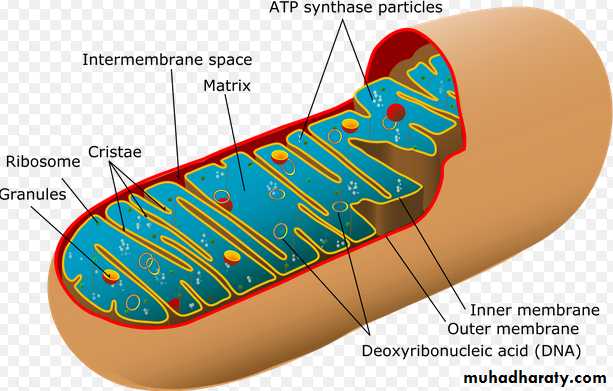
Mitochondria: the Cell’s Powerhouse
• function is AEROBIC ENERGY METABOLISM (also called CELLULAR RESPIRATION). Converts glucose and fatty acids to ATP, the cell's primary energy molecule, as well as lesser amounts of other energy rich molecules. The overall formula for cellular respiration is:Carbohydrate + O2 " CO2 + H2O + ENERGY (i.e. ATP)
Cytoplasm:
Viscous fluid between nucleus and cell membrane Function as protected environment for various structures of cells and suitable environment for various process of cells to take place.components of cytoplasm
Interconnected filaments & fibers
Fluid = cytosol
Organelles (not nucleus)
storage substances