الاحد 24/11/2013
LEC.5أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطي
NEURO ANATOMY
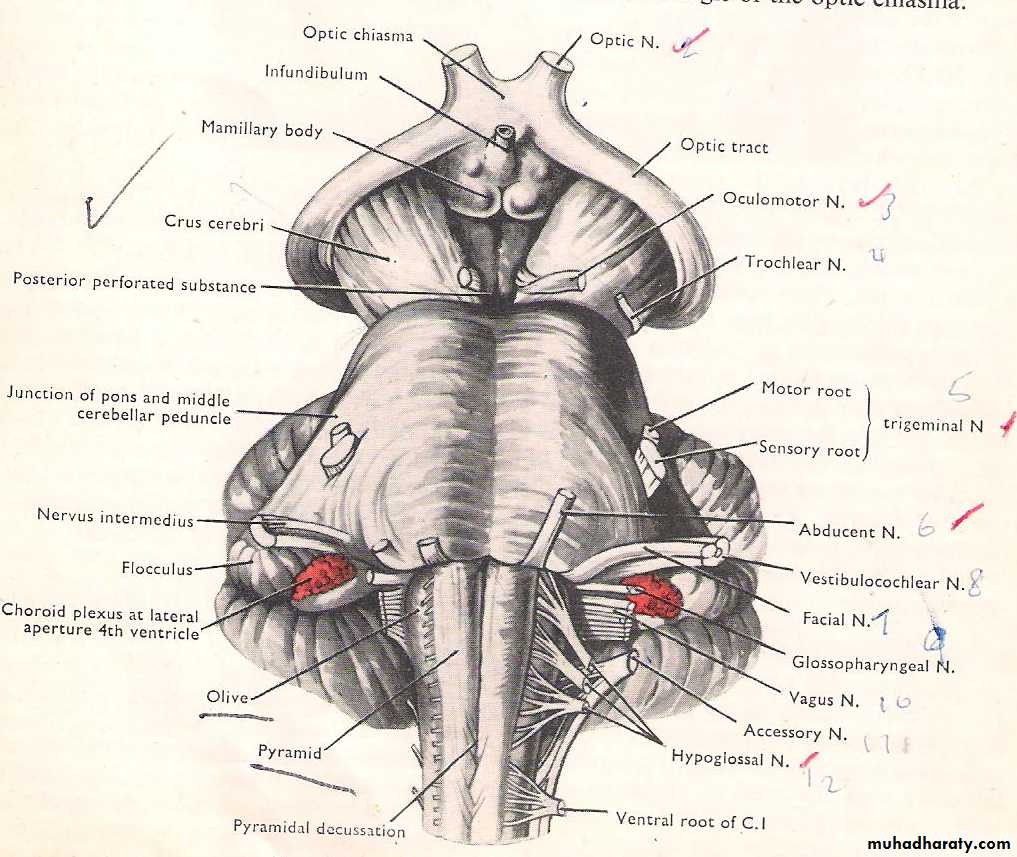
The medulla oblongata:Is the part of the brain stem (also part of the hind brain) extending from the foramen magnum below; to lower border of the pons above, it is 2.5cm long which lies against the basilar part of the occipital bone, being wider above & narrower below. It consists of 2 parts; a closed lower ½ (traversed by the central canal) & opened upper 1/2, which has no central canal & forms the lower ½ of the floor of 4th ventricle
it show the following features
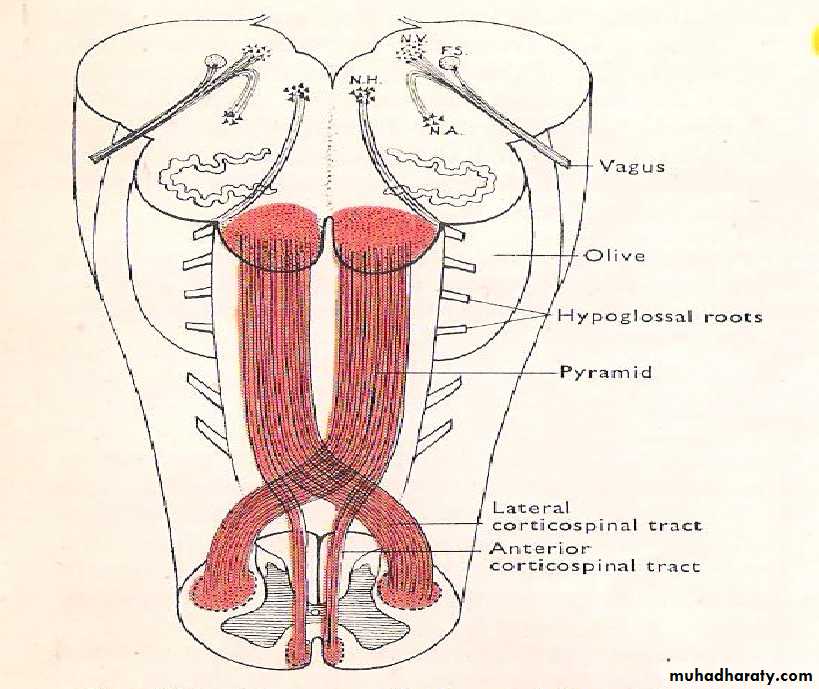
Anterior median fissure which continues below with the anterior median fissure of the spinal cord, this fissure is interrupted inferiorly by the motor decussation (pyramided decussation).On each side of the fissure we can see a vertical band of elevated area known as pyramid, which is formed by the descending motor fibers (cortico-spinal) coming from the pre-central gyrus, 80-85% of these fibers
decussate to the opposite side forming the lateral cortico-spinal tract (descends to the white mater of spinal cord), while the remaining 15-20% of fibers descends as uncrossed fibers to form anterior cortico-spinal tract (also descend to the white mater of the spinal cord).
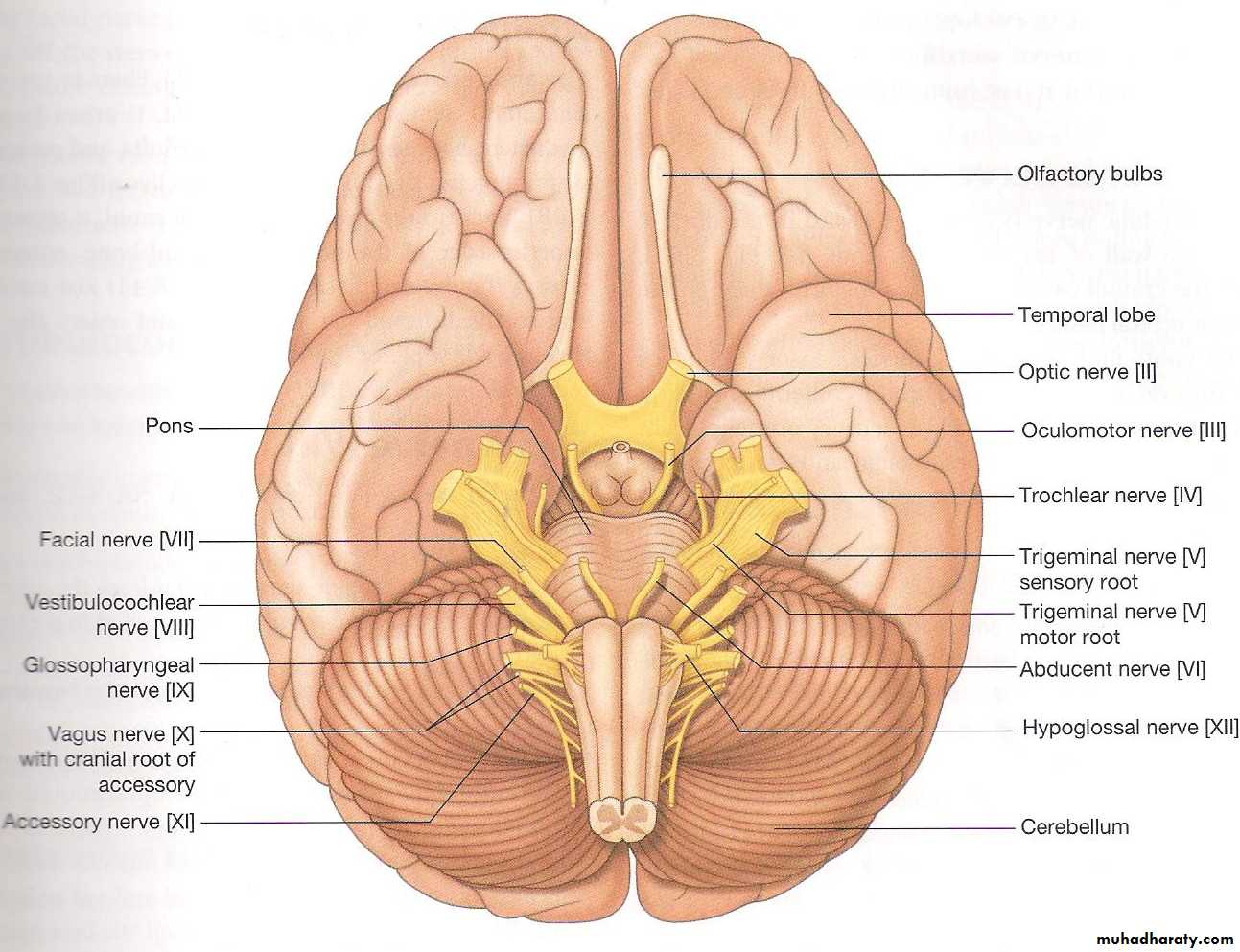
Just lateral to the pyramid, there is an olive like elevation known as olive (it is produced by the underlying inferior olivary nucleus). The hypoglossal nerve (rootlets) emerges from the groove between the pyramid & olive.
Just lateral to olive there is inferior cerebellar peduncle, connecting the medulla oblongata with the cerebellum. In the groove between the olive & inferior cerebellar peduncle 3 cranial nerves emerge the glossopharyngeal, vagus & cranial part of accessory nerve. The inferior cerebellar peduncle is a route of communication between the cerebellum & both the medulla oblongata & spinal cord.
Note: - Between the inferior border of the pons & upper part of medulla oblongata 3 cranial nerves emerges (Abducent, Facial & Vestibulocochlear nerves) the Abducent emerges between the pons & upper border of the pyramid.
The posterior surface of the medulla oblongata:
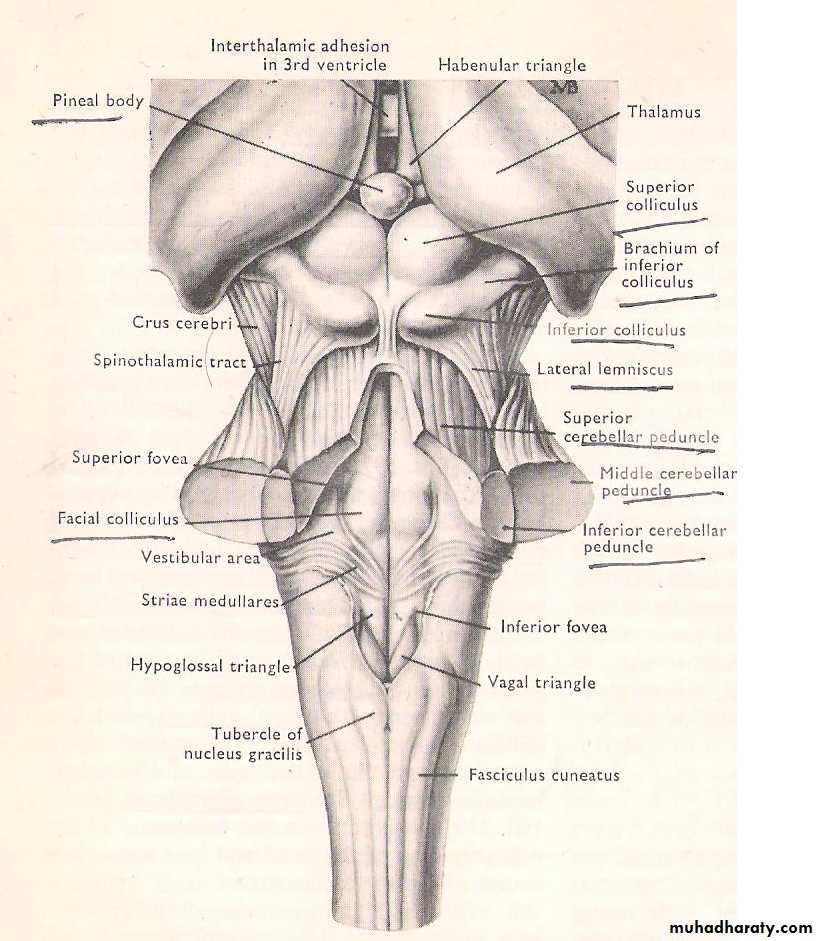
• On the upper half (open medulla) which forms the lower part of the floor of the 4th ventricles. It shows the following features: -• V shaped depression called inferior fovea with the following triangles & areas: -
• Hypoglossal triangle lies adjacent to the posterior median sulcus; it overlies the nuclei of both the hypoglossal & the glossopharyngeal nerves.
• Vestibular area produced by vestibular nuclei.
• Vagal triangle: - a depressed area between the hypoglossal triangle & the vestibular area, it overlies the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve.
• 2- On the lower half (closed medulla) we see: -
• Gracile tubercle & its associated tract or fasiculus. The fibers of the gracile tract arise in the cells of the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal nerves of the same side (first order neurones) carry proprioceptive sensation as well as fine touch from lower 1/2 of the body.• Cuneate tubercle & its associated fasculus contains fibers from dorsal spinal root ganglia which carry proprioceptive and fine touch sensation of the upper 1/2 of the body.
Nuclei in the M.O.
• inferior olivery nucleus gives rise to: -• Olivo-cerebellar tract.
• Olivo-spinal tract.
• Gracile & cuneate nuclei: -
The fibers of both fasciculi terminate at these ganglia,then
internal arcuate fibers passes up ward from here,they
decussate (forming sensory decussation) and after the
decussation continues as the medial lemniscus (2nd order
neurons) which relay (terminates) in the thalamus.
• Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve which lies medial to
• spinal tract of trigeminal, it carries pain & temperature
• sensations from the same side of the face.
It also receives general sensation via the 9th & 10th cranial nerves:
• 4. Nucleus ambigues which is amotor nucleus
• which give rise to the motor fibers joining the
• emerging 9th-11th cranial nerve to supply the ms
• of pharynx,, larynx & soft palate.
• Dorsal nucleus of vagus which is a parasympathetic
• nucleus gives rise to the secretomotor fibers of the
• vagus n.
• Inferior salivary nucleus gives rise to secretomotor of
• glossopharyngeal which relays in otic ganglion to
• reach the parotid gland.
• Nucleus solitarius:-receive taste sensations from 7th,
• 9th & 10th cranial n.
• 8. Hypoglossal nucleus & glossopharyngeal n.