
1
Forth stage
Surgery
(urology)
Lec-x
د.محمد فوزي
29/11/2015
Renal tumors
• Renal tissue tumors
• Urothelial tumors
Pathology
Benign
Adenoma
Angiomyolipoma
Oncocytoma
Malignant
Primary
Secondary
Benign tumors
:
Renal adenoma
• Small
• Well defined
• asymptomatic
• usually diagnosed accidentally or at autopsy
Renal hamartoma
(Angiomyolipoma)
• Benign
• bilateral with tuberous sclerosis
• Unilateral in normal population
• Usually Asymptomatic
• Symptoms: Bleeding , Pain
• Diagnosis:
US: ecchogenic
CT scan
High fat content Differentiate it from malignant tumors

2
Treatment in symptomatic cases
• Embolization,
• partial nephrectomy
• total nephrectomy
Renal oncocytoma
• Generally benign
• Unifocal 5---6cm
• Malignant elements may be detected
• Clinically presents as other renal tumors
• Spokewhele appearance on angiography
• Treatment: radical nephrectomy is a safe decision
Malignant tumors:
Solid tumors
• Renal cell carcinoma
• Renal sarcoma
• Tranc.cell carcinoma(TCC)
Renal cell carcinoma
• The most common malignant renal tumor(90%)
• 3% of all adult cancer
• M:F = 2:1
• Commonly affects 40-60 year age group
Etiology
• Unknown
• Associated with: Adult polycystic renal disease, acquired renal cysts, horse shoe
kidney
• Risk factors: smoking, analgesic over use, caffeine, petroleum, asbestosis

3
Spread
• Direct: Perinephric fat & nearby viscera: renal vein extension
• Blood : Liver, lung, bone , brain, suprarenal gland
• Lymphatic’s .PARA AORTIC LN
Clinical presentation:
• Symptom less ,accidentally discovered(ABOUT 50 PERCENT)
• Hematuria
• Loin Pain
• Mass
• Wt. loss
Features of metastasis
• Dyspnea ,cough, headache ,bone pain
• Paraneoplastic syndrome
Paraneoplastic presentations
• Polycythemia: Increase erythropoietin
• Hypocalcaemia: Parathormone
• Hepatic dysfunction
• Hypertension : increased rennin
• Polyneuropathy
• Anemia
Diagnostic aids
• GUE: Haematuria ?
• Hematology: Anemia, Polycythemia, raised ESR.
• Paraneoplastic features
• Imaging: US. IVU. CT scan. MRI. Angiography
• Bone scan
• FNAC (fine needle aspiration cytology)
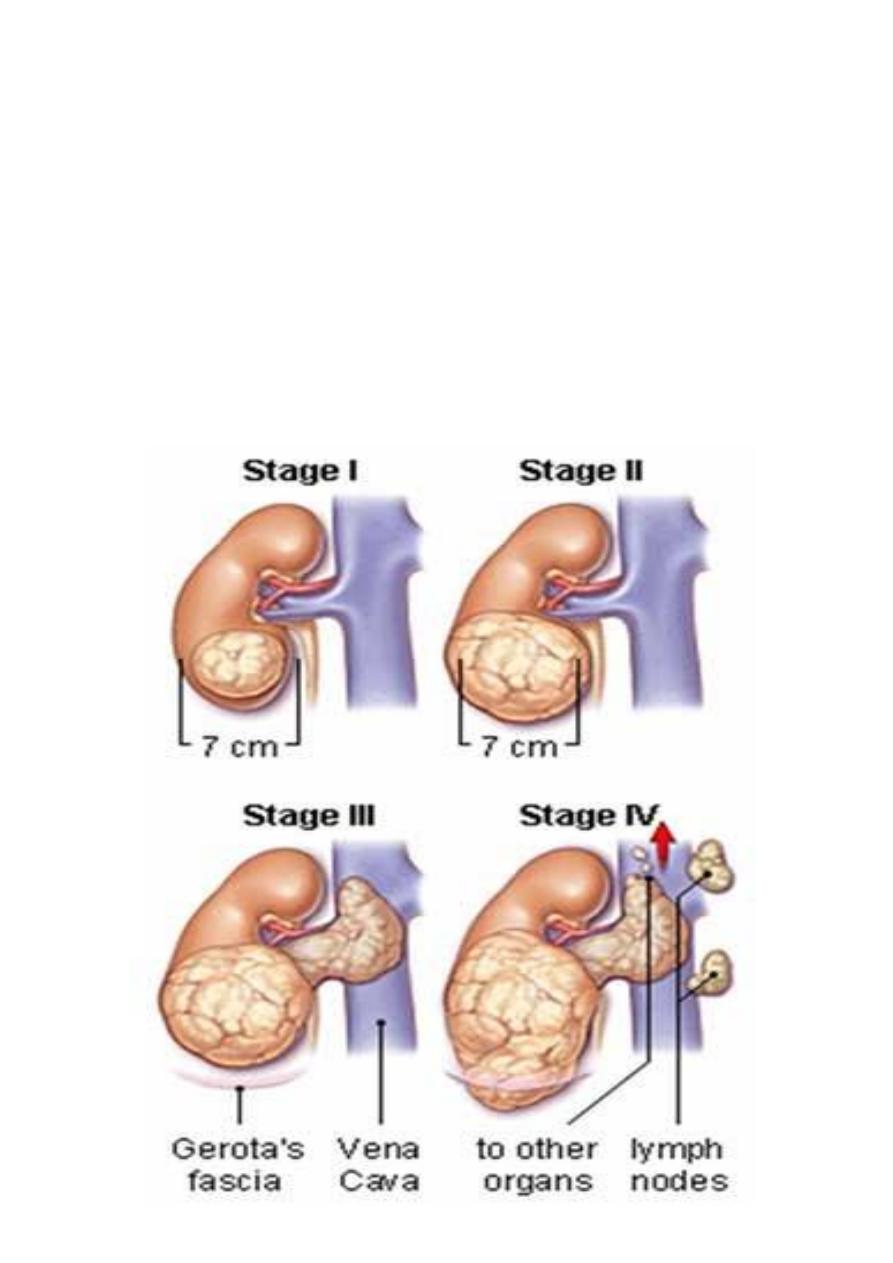
Staging
• To select the suitable therapy
• To provide the prognostic data
4
Staging systems:
Robson
TNM staging
Robson staging
• St1 T within the renal tissue
• St2 T within gerotas fascia, perinephric fat invaded
• St3a renal vein involved
• St3b regional LN involved
• St3c vessels & nodes involved
• St4a nearby organs involved
• St4b Distant metastasis
5
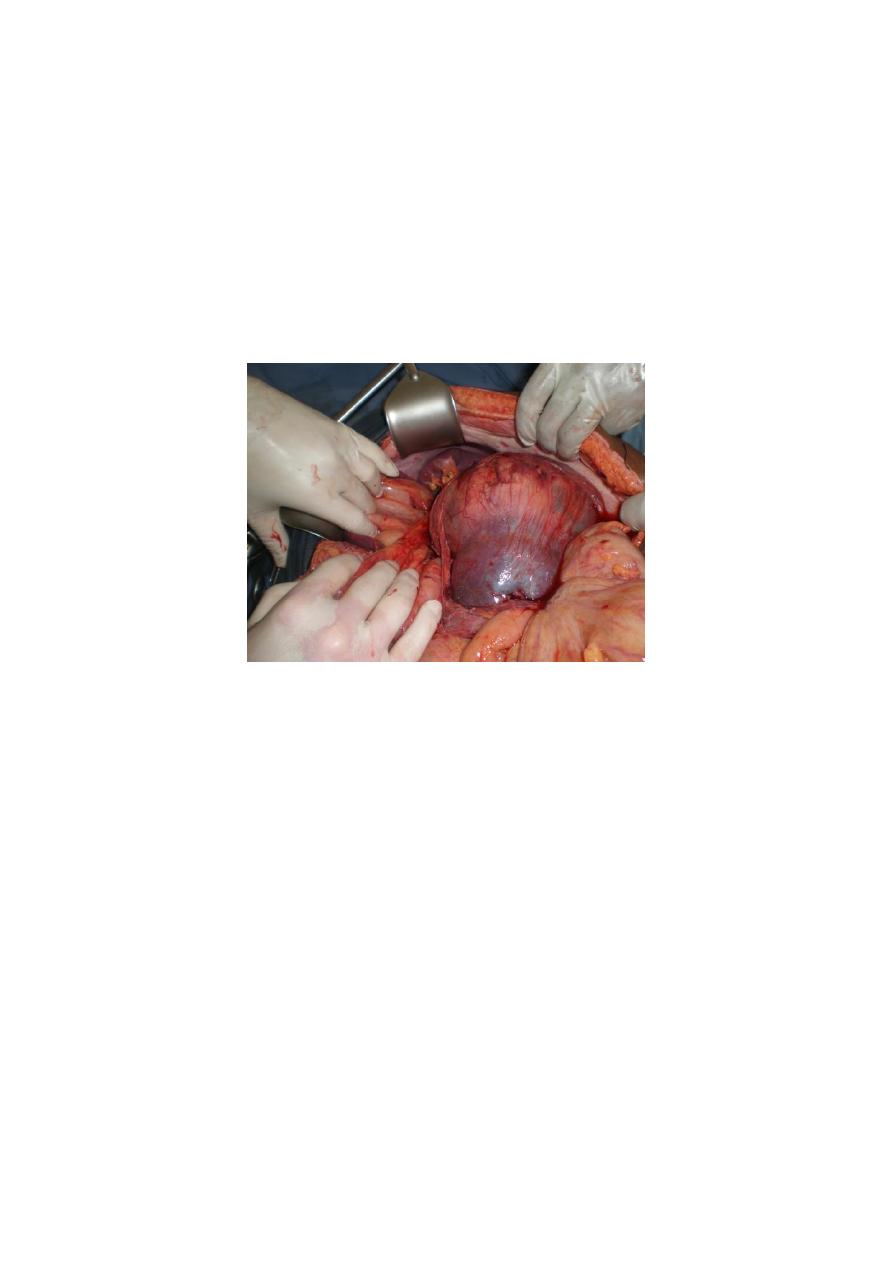
Treatment
for localized tumor
T1, T2, T3a
Radical nephrectomy
Removal of the kidney, perinephric fat, and gerotas fascia altogether
For T1 PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY IS ANOTHER OPTION
For metastatic tumor
• Immunotherapy : BCG , Interferon, Interleukin_2
• DXT Palliation of metastasis
• Hormonal therapy
• Chemotherapy renal tumor is very chimoresistant
Indication of palliative nephrectomy in metastatic renal adenocarcinoma
• Severe hemorrhage
• Pain not respond to opiate
• Debulking of tumor before immunotherapy
• When there is resectable single pulmonary metastasis
Prognosis
5 years survival
80-100% T1
60% T2-T3b
0-15% M1
6
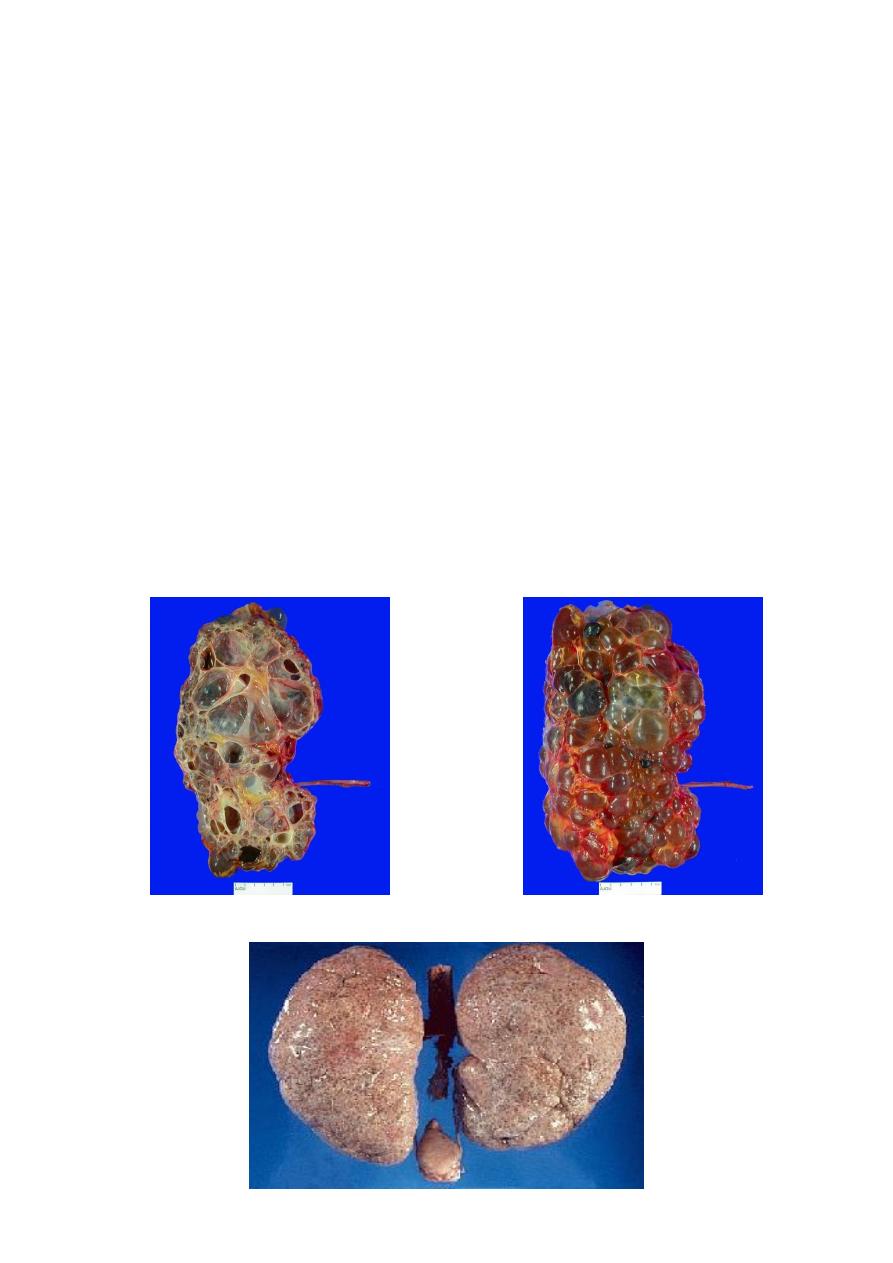
Cystic disease of the kidney
Classification:
Adult polycystic renal disease:
Genetic
•
Autosomal recessive (infantile)
polycystic kidney disease.
• Autosomal dominant (adult)
polycystic kidney disease. )
Non genetic
• Multicystic kidney
(multicystic dysplastic
kidney).
• Simple cysts.
• Medullary sponge kidney.
• Acquired renal cystic disease.
7
Dysplasia
Acquired renal cystic disease
Usually occur in patient with end stage renal failure especially those on hemo or
peritoneal dialysis
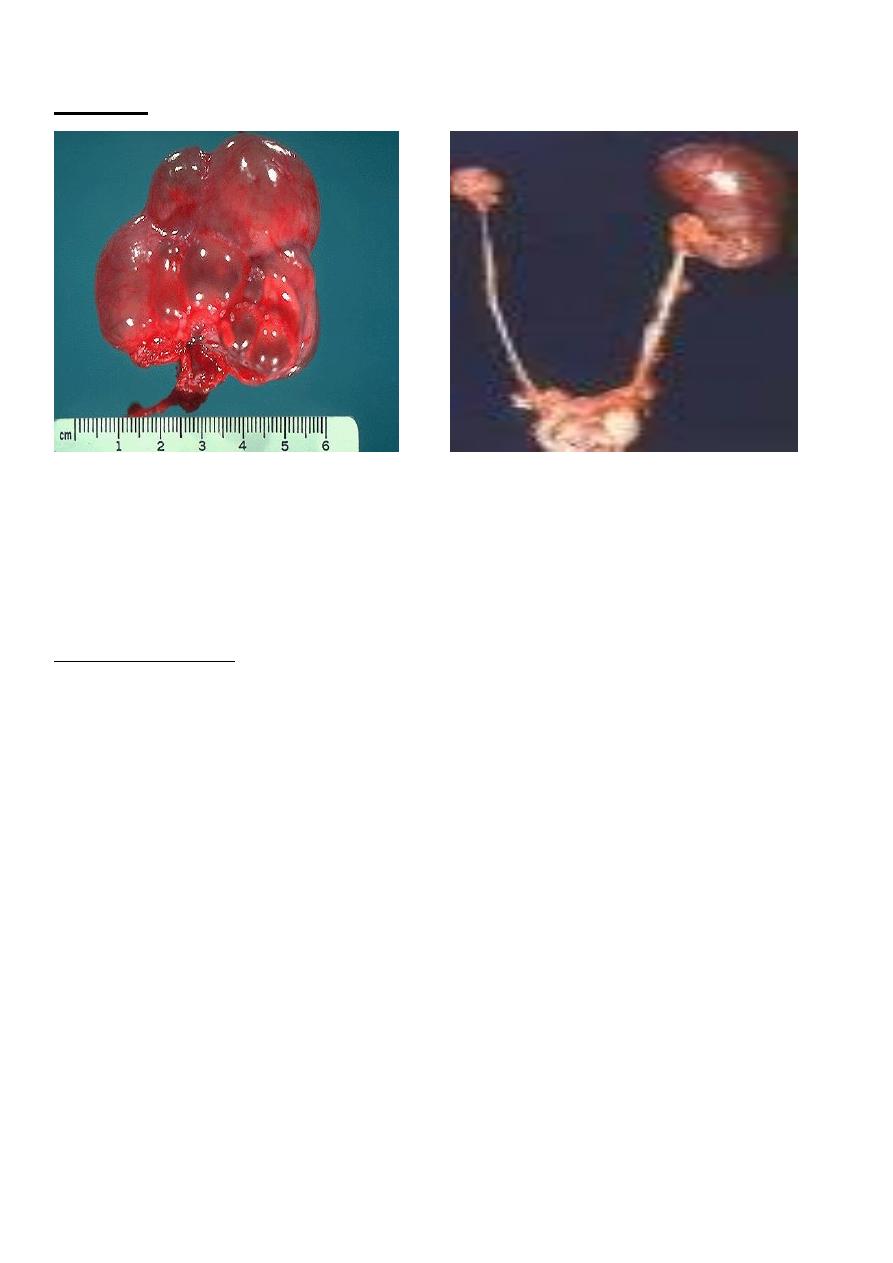
1-SIMPLE (SOLITARY) CYST
• Simple cyst of the kidney is usually unilateral and single but may be multiple and
multilocular and, more rarely, bilateral.
• It differs from polycystic kidneys both clinically and pathologically.
• Congenital or acquired
Pathology
Simple cysts usually involve the lower pole of the kidney. Those that produce symptoms
average about 10 cm in diameter, but a few are large enough to fill the entire flank.
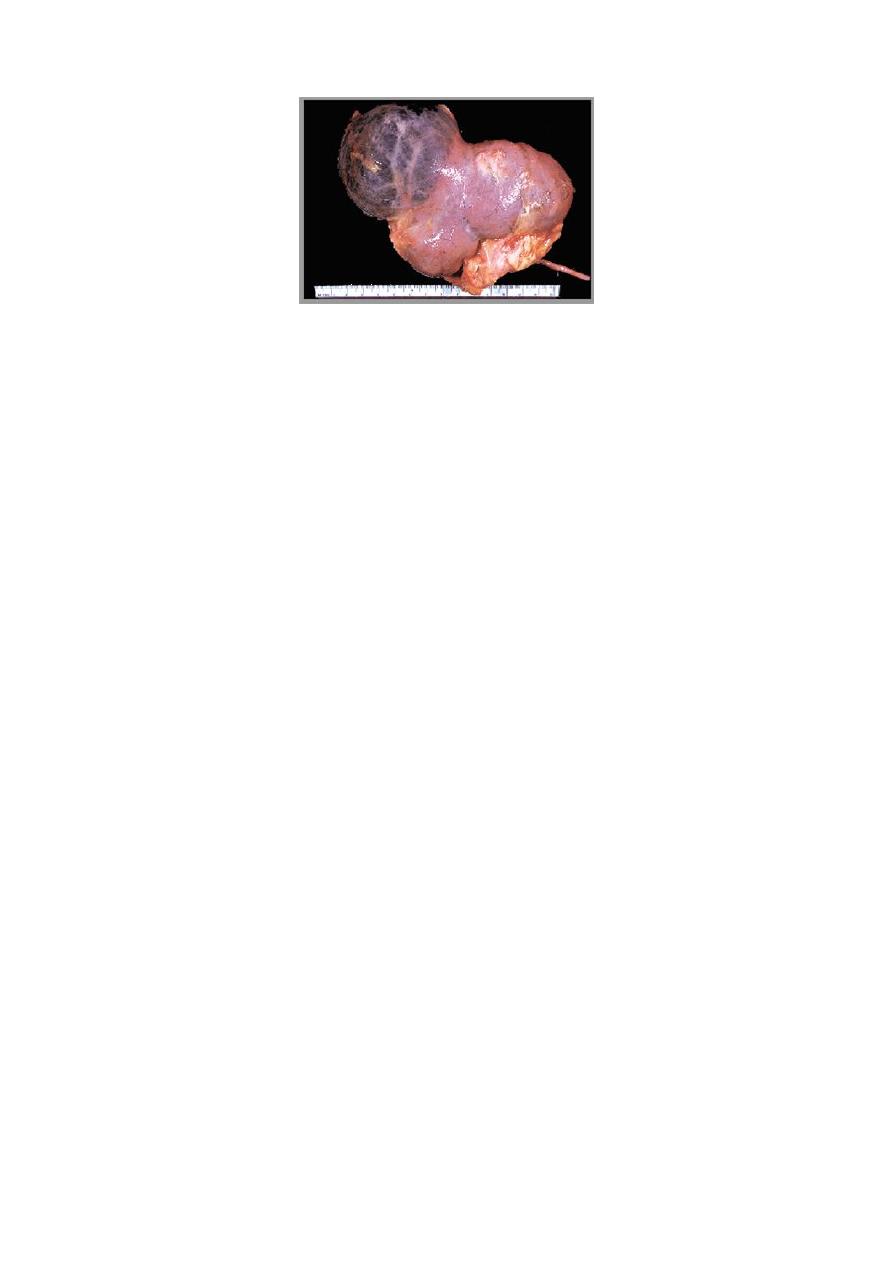

8
Simple renal cyst
• They usually contain a clear amber fluid.
• Their walls are quite thin, and the cysts are “blue domed” in appearance.
• Calcification of the sac is occasionally seen.
• About 5% contain hemorrhagic fluid, and possibly one-half of these have papillary
cancers on their walls.
•
Cysts do not communicate wit renal pelvis
.
Clinical Findings
1usuqlly symptomless and discovered accedentally
Pain in the flank or back, usually intermittent and dull. If bleeding suddenly distends
the cyst wall, pain may come on abruptly and be severe.
2- Gastrointestinal symptoms.
3- A mass in the abdomen.
4- Infected cyst, the patient usually complains of pain in the flank, malaise, and fever.
Diagnosis
1- LAB. INVESTIGATIONS
GUE, and KFT usually normal.
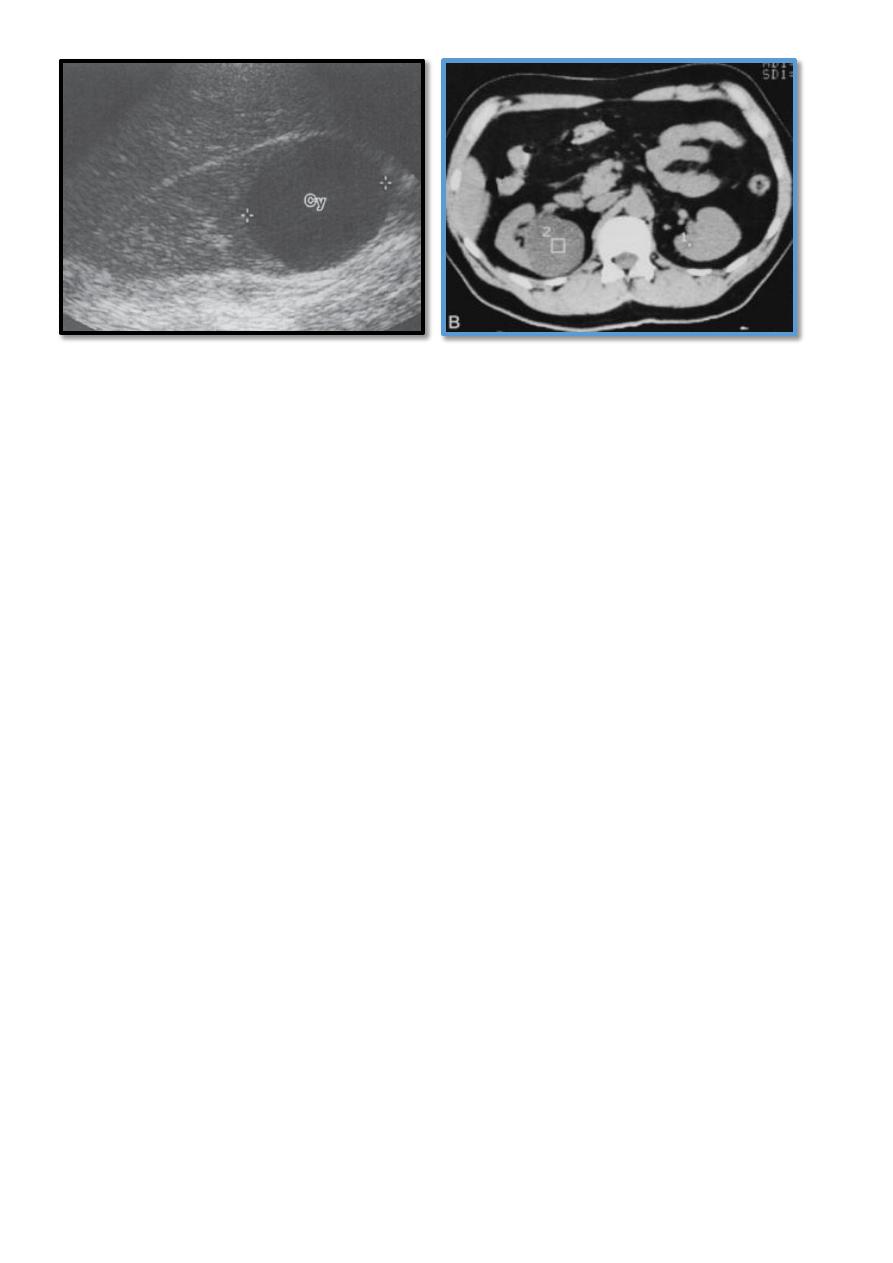
2- RENAL ULTRASONOGRAPHY
:
Differentiates between a cyst and a solid mass .usually the cyst have regular shape, thin
walls ,no calcifications or internal echos.
3- CONTRASTED CT: appears to be the most accurate means of differentiating renal cyst
and tumor.
4
-
ISOTOPE SCANNING
:
it appears as cold area (avascular).
9
Differential Diagnosis
1 Carcinoma of the kidney.
2- Polycystic kidney disease.
3- Renal cortical abscess.
4- Hydronephrosis.
5- Echinococcal (hydatid) Cyst.
6- Acquired cystic disease of the kidney.
Complications (Rare)
1- Infections.
2- Hemorrhage into the cyst.
3- Hydronephrosis.
4- Hypertension.
5- Severe Pain.
TREATMENT
Is usually expectant , unless complications developed which should be treated
accordingley.( antibiotics , drainage , open or lap. Marcipulization (rovsing op.)
A.L.Y
