Fourth stage
Surgery (urology)Lec-
Dr.Alshahwani
29/11/2015
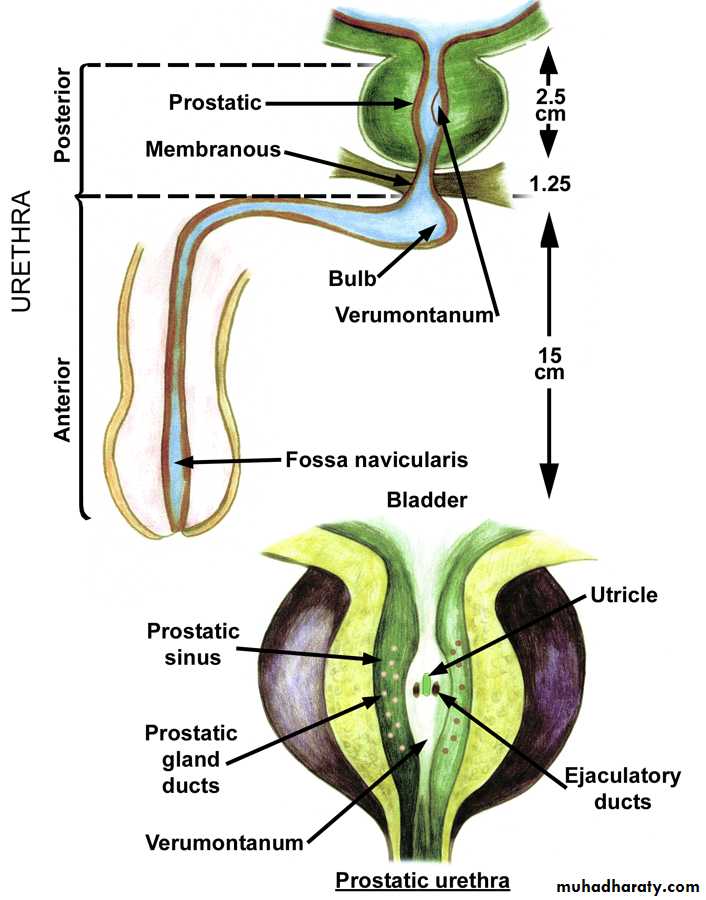
Male urethral injuries and bladder injuryUrethral injury divided into
Anterior Urethral injuryposterior Urethral injury
Anterior urethral injury (bulbar urethral injury)
Causesblow to the perineum
Stradal injury: cycling, loose manhole covers
Clinical features
Suspect urethral injury after blunt perineal trauma when;
The man goes into retention
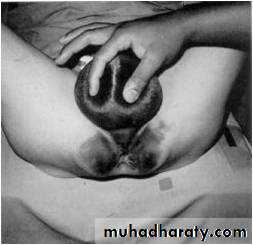
There is perineal swelling "butterfly hematoma"
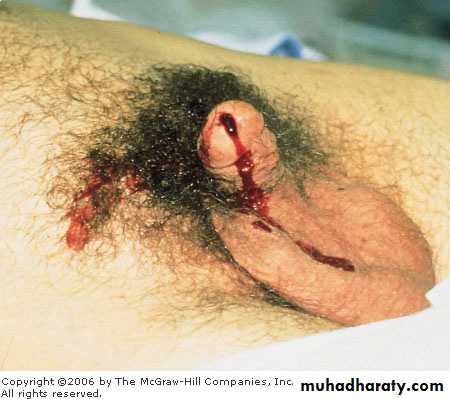
There is blood at urethral meatus
Treatment
Once urethral injury is suspectedDont allow the patient to urinate
Dont insert a foleys cathter
unless after doing retrograd urethrography
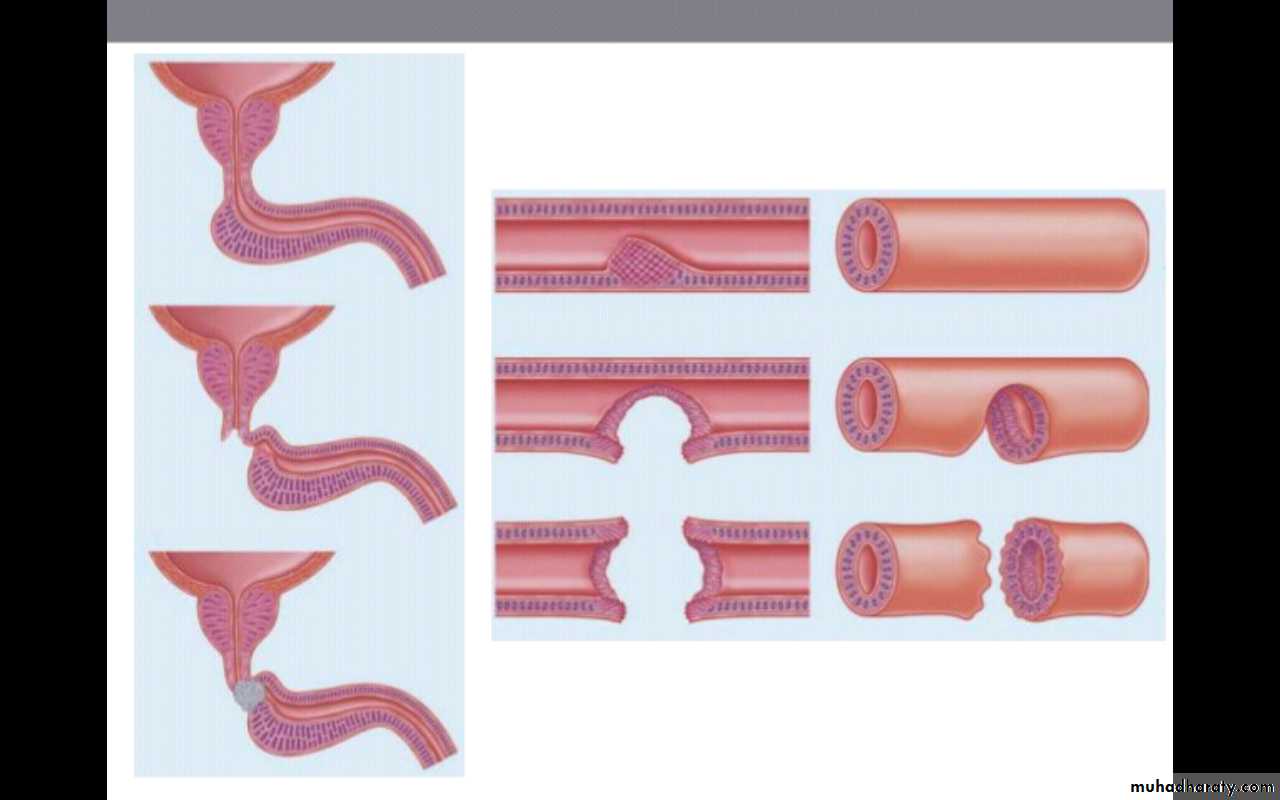
Accordingly the injury can be divided into
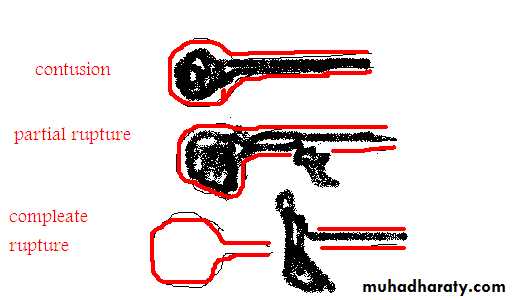
Contusion : the dye pass to bladder ,no exravasation
Partial rupture : the dye pass to bladder ,with exravasation
Complete rupture : the dye did not pass to bladder ,with exravasation
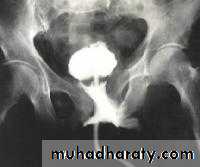
"Retrograde ureththrography show Anterior partial urethral injury"
Contusion --->analgesic and antibiotic
Partial and compleat rupture -->
"suprapubic cystostomy"
analgesic and antibiotic
after 3 weeks retrograde urethrography done to asses the urethra,usually there will be a stricture which should be treated by dilatation,or urethrotomy,or urethroplasty
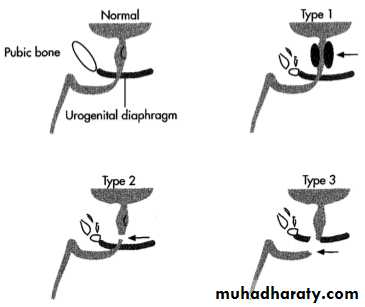
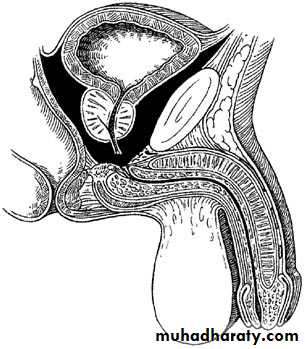
Posterior urethral injyry (membranous urethral injury)
Intra pelvic rupture of membranous urethra occur near the apex of prostateMost comonlly due to blunt trauma withe pelvic fracture
Clinical picture
History or trafic accident,fallBlood at external urethral meatus
There may be associated injury to head,chest,abdomin,fracture of long bones,which may take priority in management to keep the pationt a live
KUB : usually there is pubic bone fracture
PR examination : very high prostate, pelvic hematoma
Retrograde urethrography :extravasation of dye
Treatment
ABC "Espicially when there is multiple injury"Suprapubic cystostomy should be formal type when associated intraperitoneal bladder injury is suspected to repair the bladder at the same time
Some surgion prefer rail roading method to realign the seperated urethral ends
after 6 to 8 weeks asses the uretha by urethrography or urethroscopy
Complication of post urethral injury
Urethral stricture
Urinary incontinence
Impotence
Bladder injuries
CausesPeroperative TURP..TURBT,,cystolitholapaxy,cystoscopic bladder biobsy,caeserean section,
blunt pelvic trauma
Penetrating trauma
Types of perforation
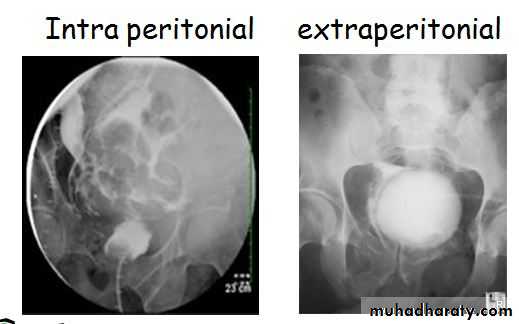
Intraperitoneal perforation : the urine escape to the peritoneal cavity
Extraperitoneal perforation : the urine escape into the space around the bladder
Diagnosis
If injury occur During endoscopic operation the diagnosis is clear on visual inspiction alone,a dark hole or loop of bowel is seen
In case of blunt trauma ,The classicall symtoms and sign are
1-suprapubic pain and tenderness
2-in ability to pass urine
3-haematuria
these sign and symtoms are indication for retrograde cystography
Retrograde cystogram
300 to 400 cc of contrast is ingecteto the bladder and film is takin then another film post evacuation is takinIn intraperitoneal perforation loop of bowel may be out line by the contrast
In extraperitoneal perforation the cotrast is limitted to immediate area surrounding the bladder
Treatment
Extraperitoneal ----> Blader drainage with a urethral drainage for 2 weeks followed by cystogram to conferm healing of perforationIndication for surgical repair
1. a bone spike protruding to the bladder
2. associated rectal or vaginal perforation
Intraperitoneal ----> Usually required surgically to prevent complications from leakage of urine to the peritoneal cavity