

Mouth
1- vestibule
2- mouth proper
lined by strat.sq epitheliumand and contains
numerous salivary glands.
Salivary glands divided into:
1-small
2-large:3 pairs; paroted, submandibular and
sublingual


The pharynx is situated behind the nasal
cavities, the mouth, and the larynx
It is divided into nasal, oral, and laryngeal
parts
Its upper part is wider and lies under the skull
Its lower end is narrow and continues with the
esophagus opposite the sixth cervical vertebra
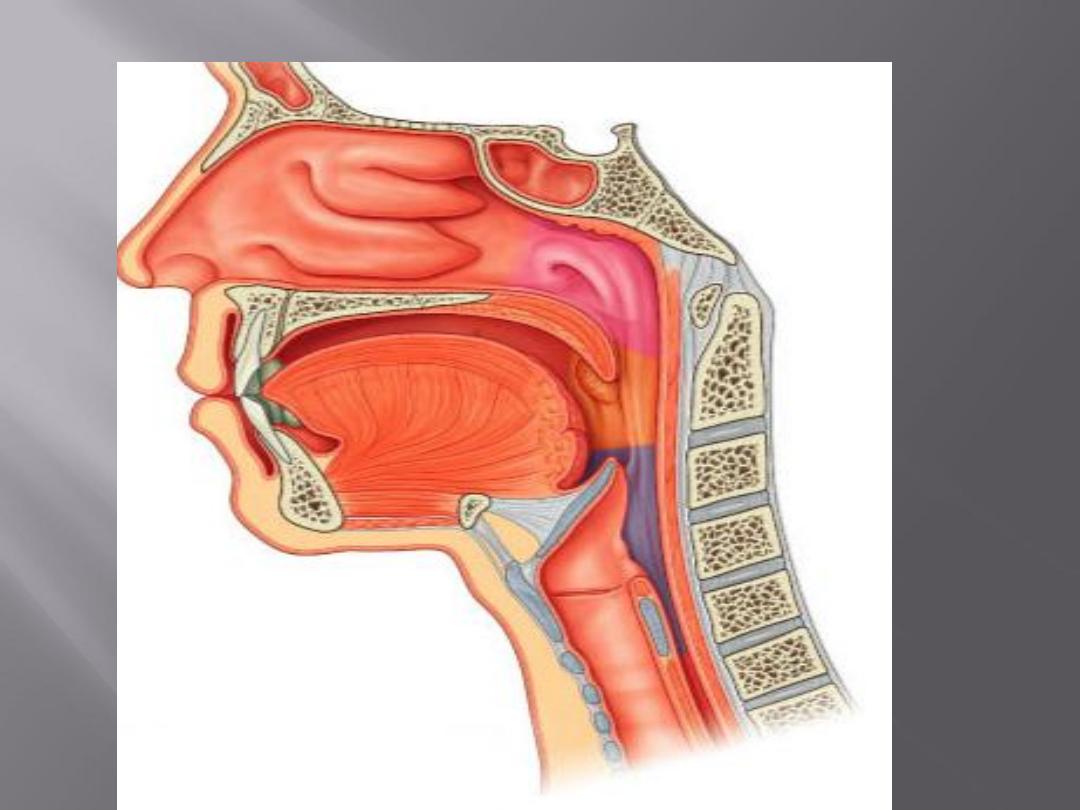
Pharynx

Is a fibro-muscular tube, funnel
shaped being braodest in its
up.part, its lower end
continues with the
esophagus(narrowest part of
the digestive tract).

1- nasopharynx
2- oropharynx
3- laryngopharynx(hypopharynx)

Consists of four layers:
1- Mucous membrane: contains
a- Epithelium
b- Subepith.lymphoid tissues:waldeyers
ring(palatine ,nasopharyngeal, tubal and
lingual tonsils)
2-Apponeurosis (pharyngobasilar fascia)
3- Muscular coat: external and internal layers

a- external : 3 consrictors (sup.,middle and inf.)
b- internal : stylopharyngeuos,palatopharyngeus
and salpingopharyngeus
4- Buccopharyngeal fascia

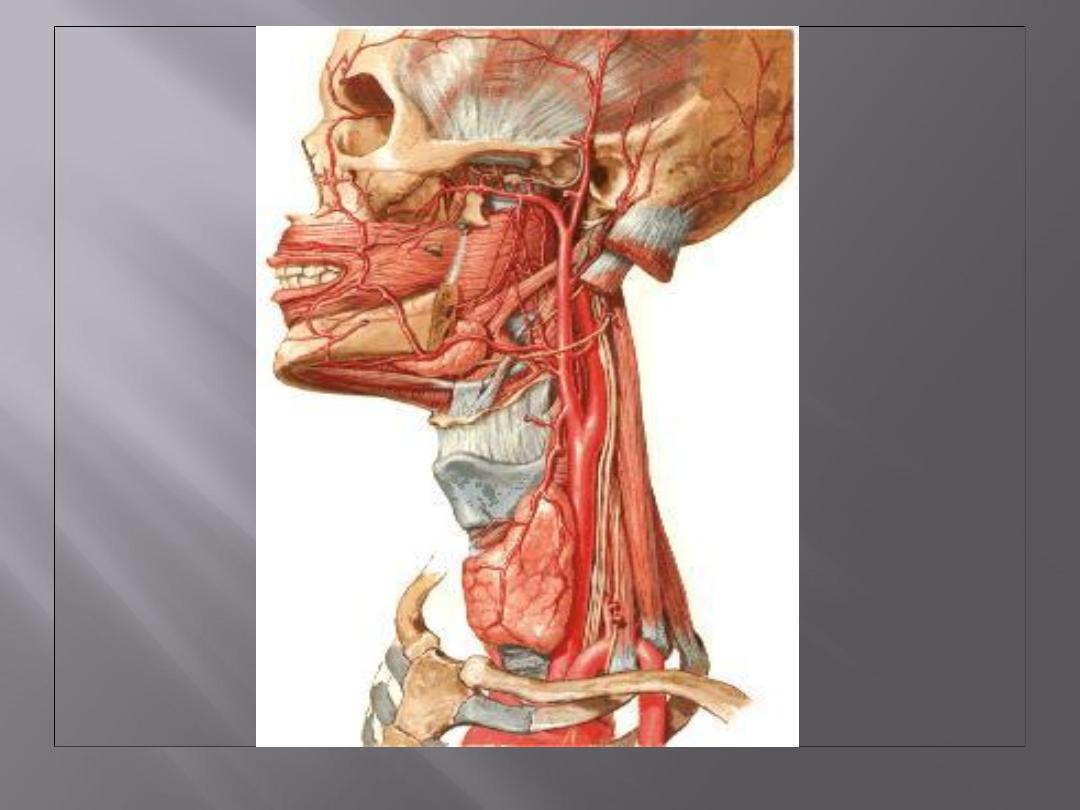
: External caroted a.
Blood supply
: motor(accesory n.)
Nerve supply
Sensory: by 5
th
, 9
th
and 10
th
cranial
nerves.
: deep jugular nodes.
drainage
Lyphatic

This lies above the soft palate and behind the nasal
cavities
In the submucosa of the roof is a collection of
lymphoid tissue called the nasopharyngeal tonsil
The pharyngeal isthmus is the opening in the floor
between the soft palate and the posterior
pharyngeal wall
On the lateral wall is the opening of the auditory
tube, the elevated ridge of which is called the tubal
elevation
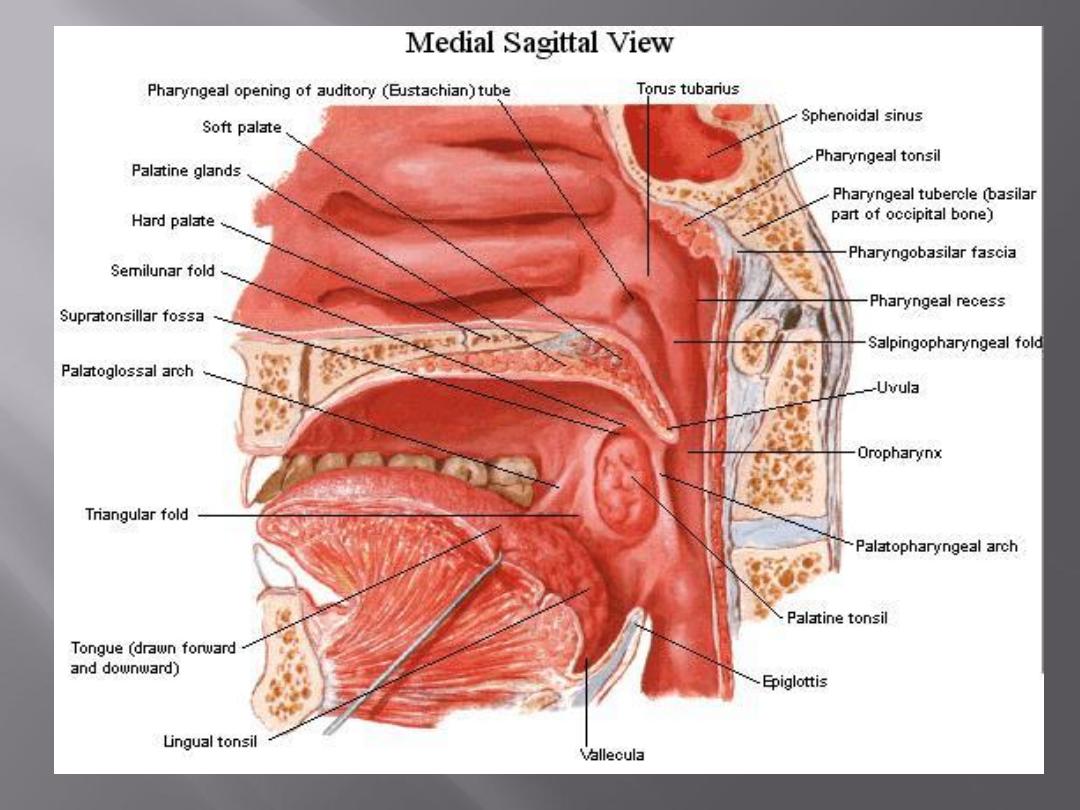

Pharyngeal recess (fossa of Rosen-muller) is a
depression behind the tubal elevation in the
lateral wall of the nasopharynx.
It is the commonest site of a hidden tumor in the
head and neck.

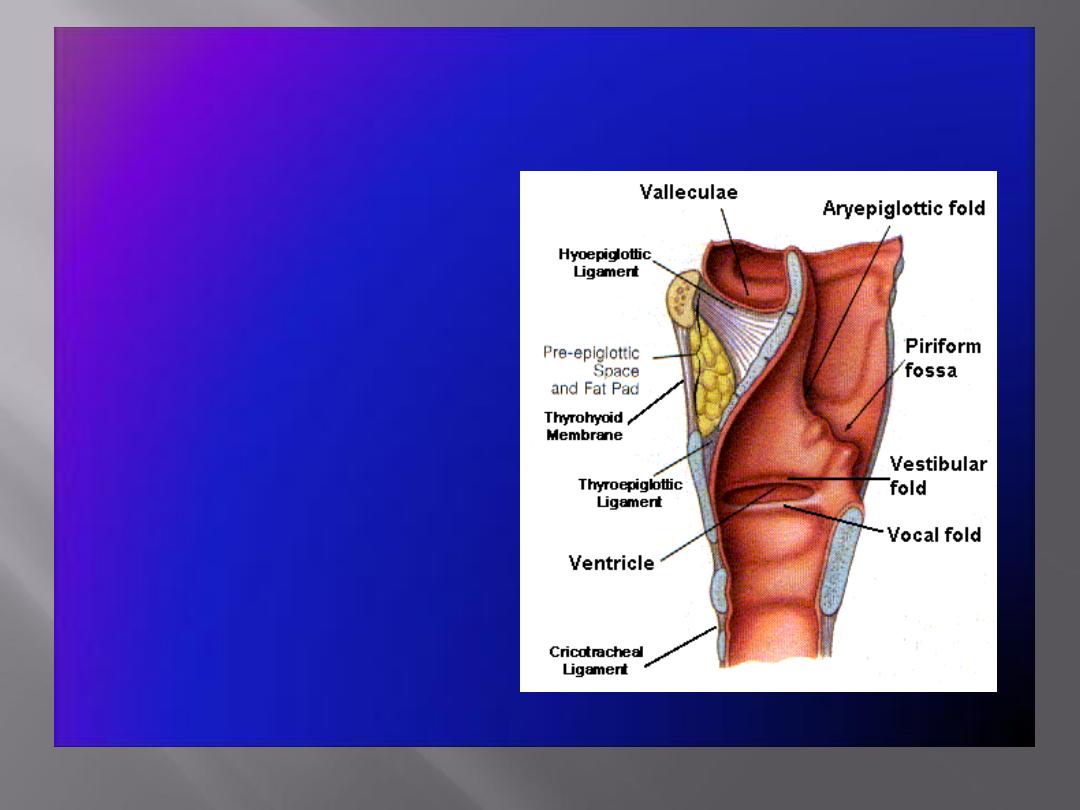
This lies behind the oral cavity
The floor is formed by the posterior one third of
the tongue and the interval between the tongue
and epiglottis
The tongue and epiglottis are connected by 3
mucosal folds, one median and two lateral
glossoepiglottic folds.
The depression on each side of the median
glossoepiglottic fold is called the vallecula
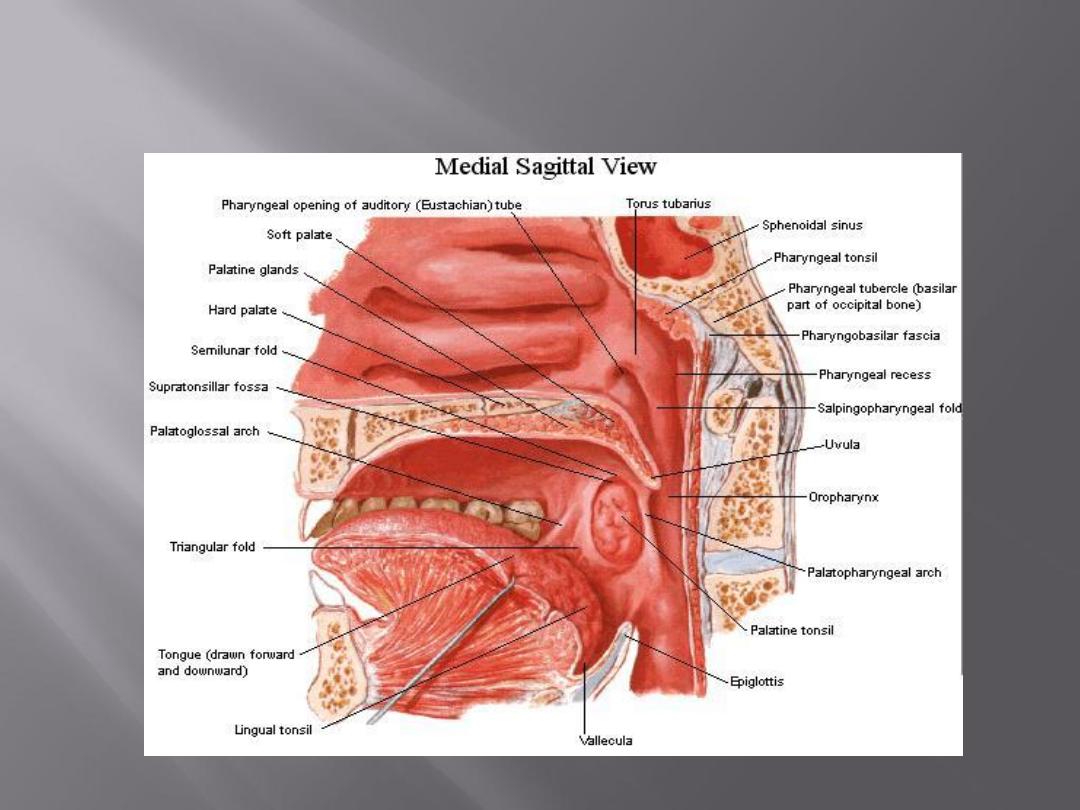

On the lateral wall on each side are the palatoglossal
and the palatopharyngeal arches or folds and the
palatine tonsils between them
The palatoglossal arch is a fold of mucous membrane
covering the palatoglossus muscle
The interval between the two palatoglossal arches is
called the oropharyngeal isthmus
It marks the boundary between the mouth and
pharynx

The palatopharyngeal arch is a fold of mucous
membrane covering the palatopharyngeus
muscle
The recess between the palatoglossal and
palatopharyngeal arches is occupied by the
palatine tonsil

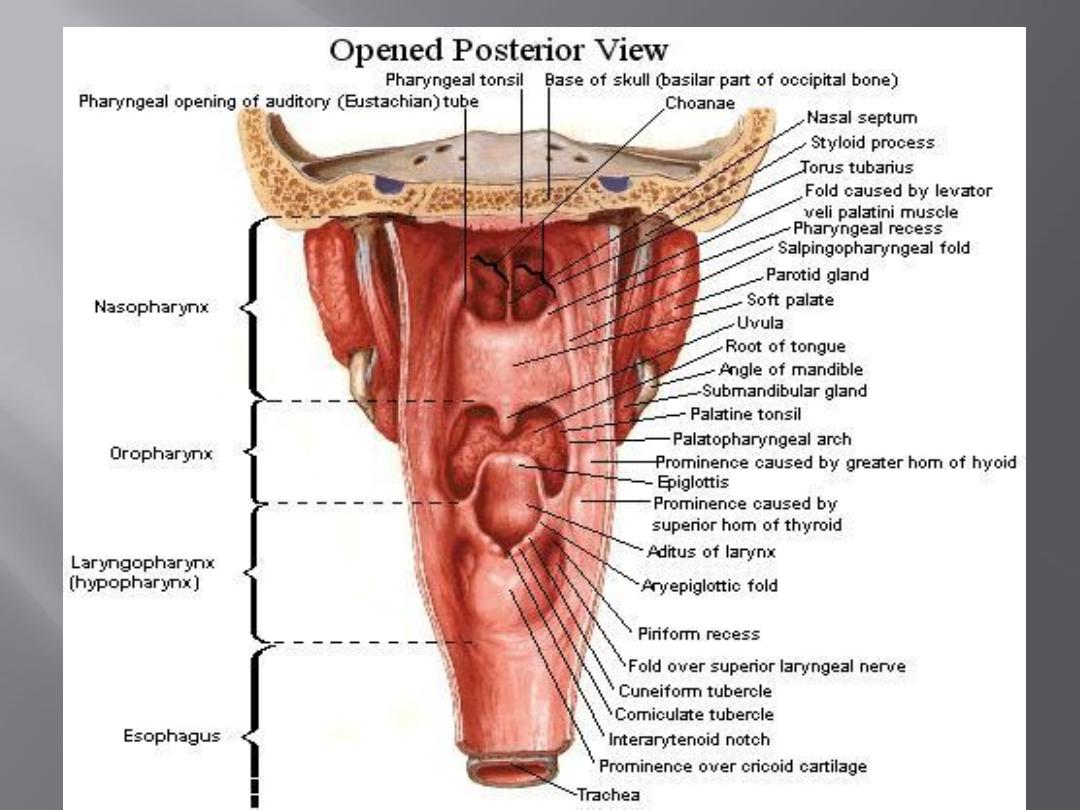
This lies behind the opening into the larynx
The lateral wall is formed by the thyroid cartilage
and the thyrohyoid membrane. It consists of 2
pyrifom sinuses (fossae), postcricoid region
and posterior pharyngeal wall.
The pyriform fossa is a depression in the mucous
membrane on each side of the laryngeal inlet

Nasal pharynx: The maxillary nerve
Oral pharynx: The glossopharyngeal nerve
Laryngeal pharynx: The internal laryngeal branch
of the vagus nerve

Ascending pharyngeal, tonsillar branche of
facial artery, and branches of maxillary and
lingual arteries (branches of external carotid
artery)

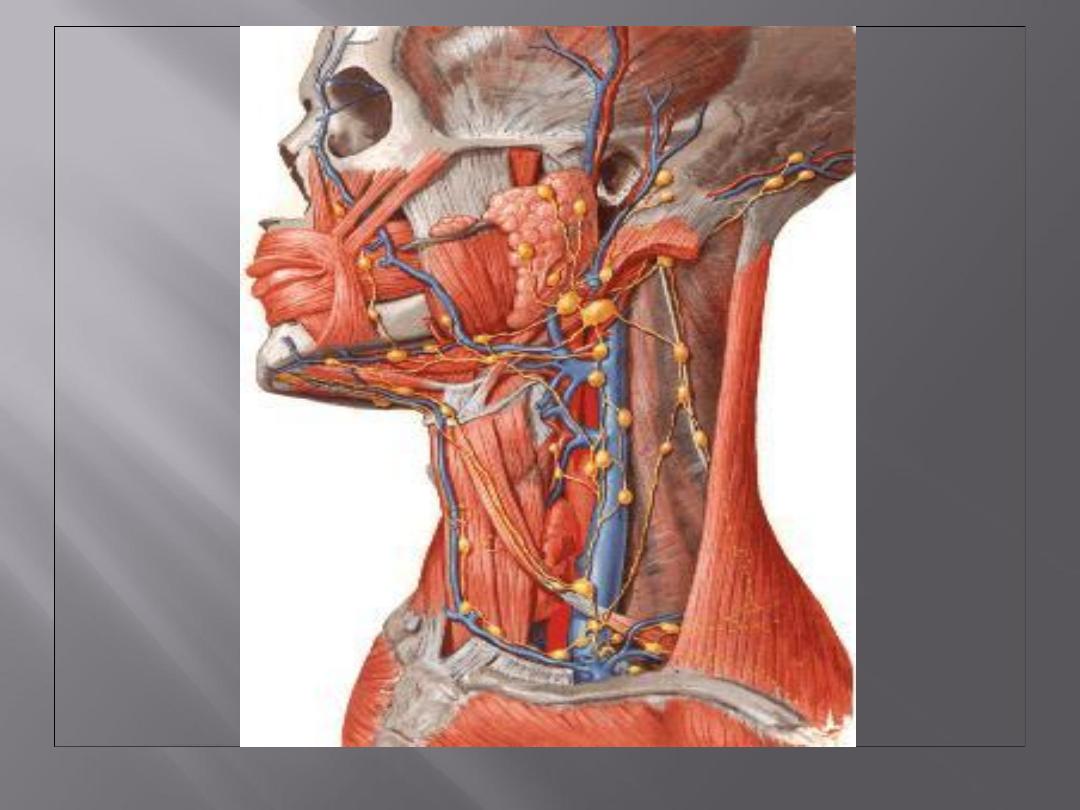
Directly into the deep cervical lymph nodes or
indirectly via the retropharyngeal or
paratracheal nodes into the deep cervical nodes
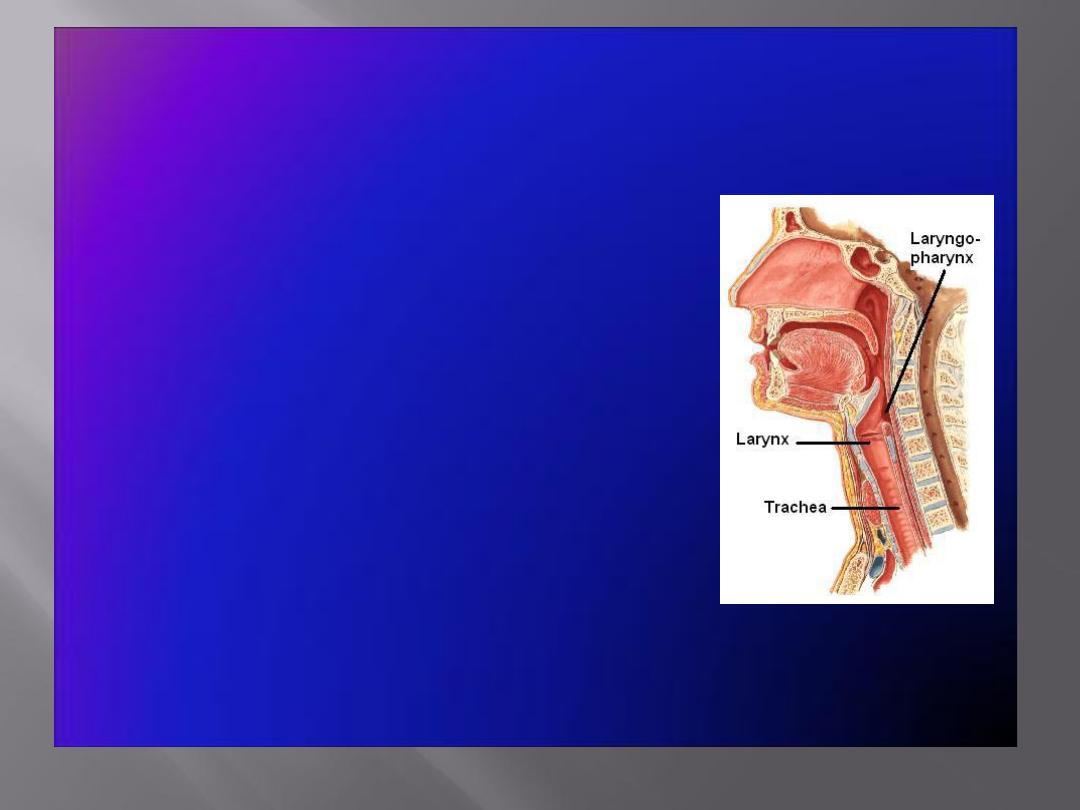
The Larynx
• The larynx is the
portion of the
respiratory tract
containing the vocal
cords
• A
2-inch-long
, tube-shaped organ,
opens into the
laryngeal part of the
pharynx
above and is continuous
with the
trachea
below
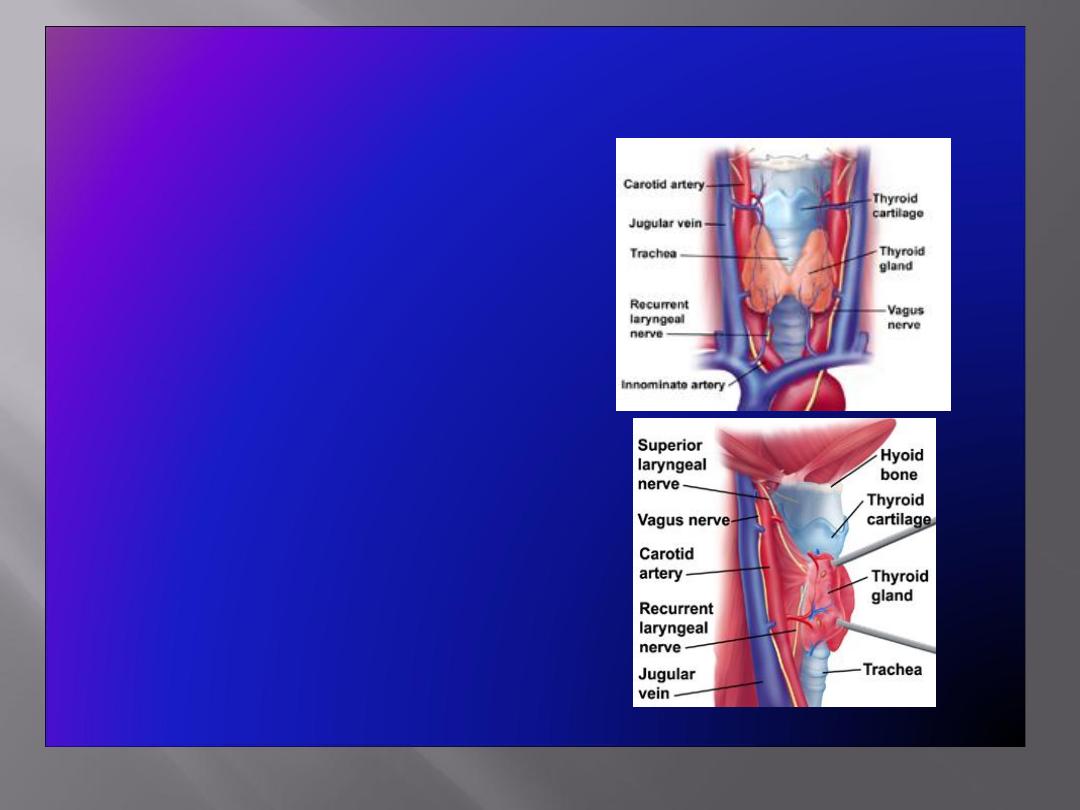
The Larynx: Important Relations
• The larynx related to
major critical structures:
Carotid arteries , jugular
veins, and vagus nerve
Superior and inferior
thyroid arteries
Superior and recurrent
laryngeal nerves
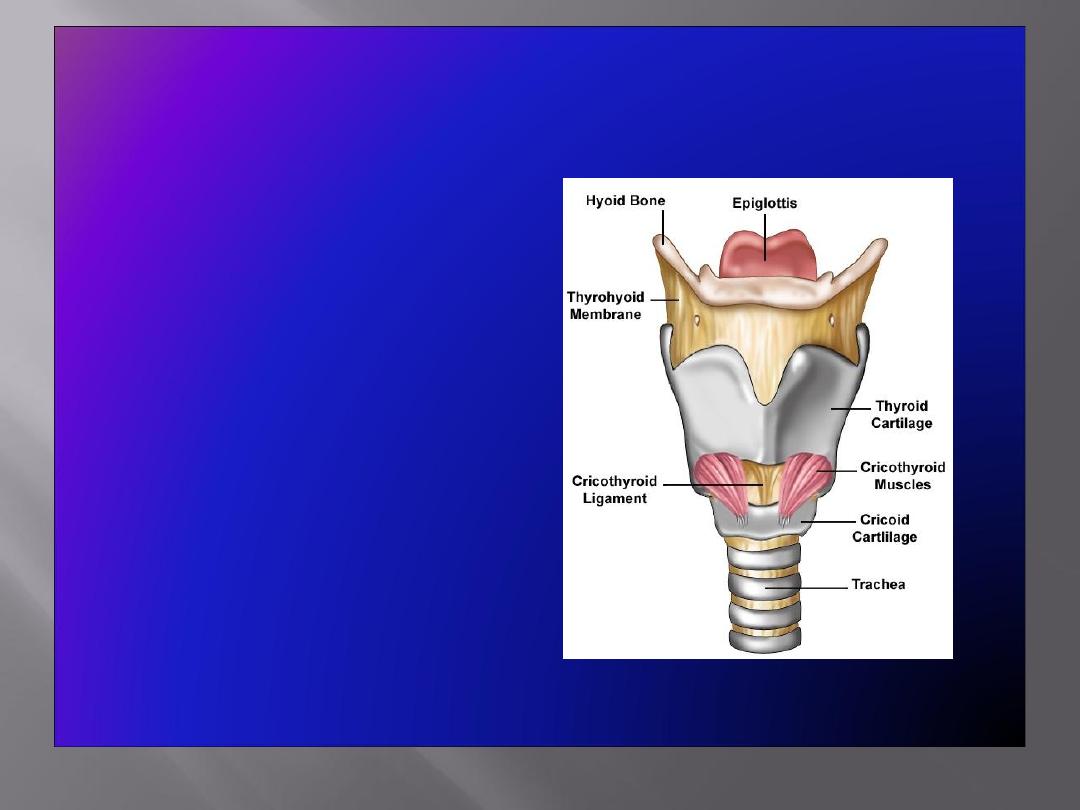
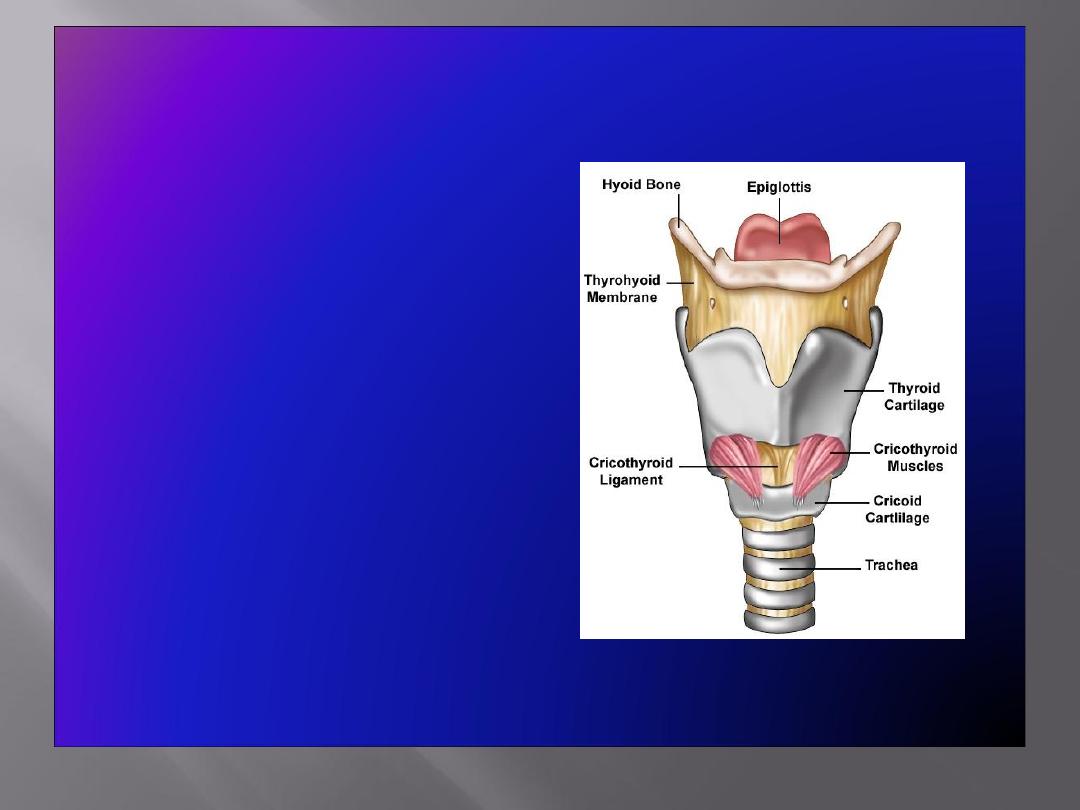
Structure
• The larynx consists of
four basic components:
A cartilaginous
skeleton
Membranes and
ligaments
Intrinsic and extrinsic
muscles
Mucosal lining
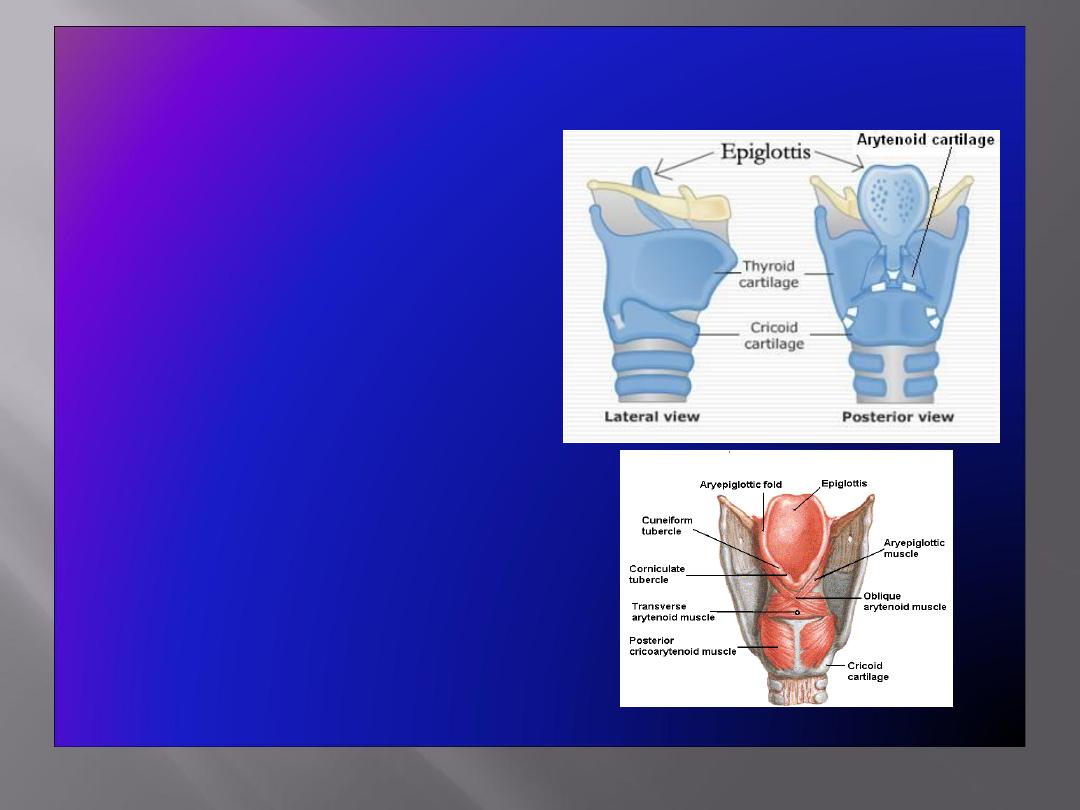
The Cartilages
• The cartilaginous
skeleton is comprised
of :
Single Cartilages
:
Thyroid
Cricoid
Epiglottis
Paired Cartilages
:
Arytenoid
Corniculate
Cuneiform
• All the cartilages,
except the epiglottis,
are of
hyaline
type.
• Epiglottis is formed of
elastic
cartilage
• The cartilages are:
Connected by
joints
,
membranes
&
ligaments
Moved by
muscles
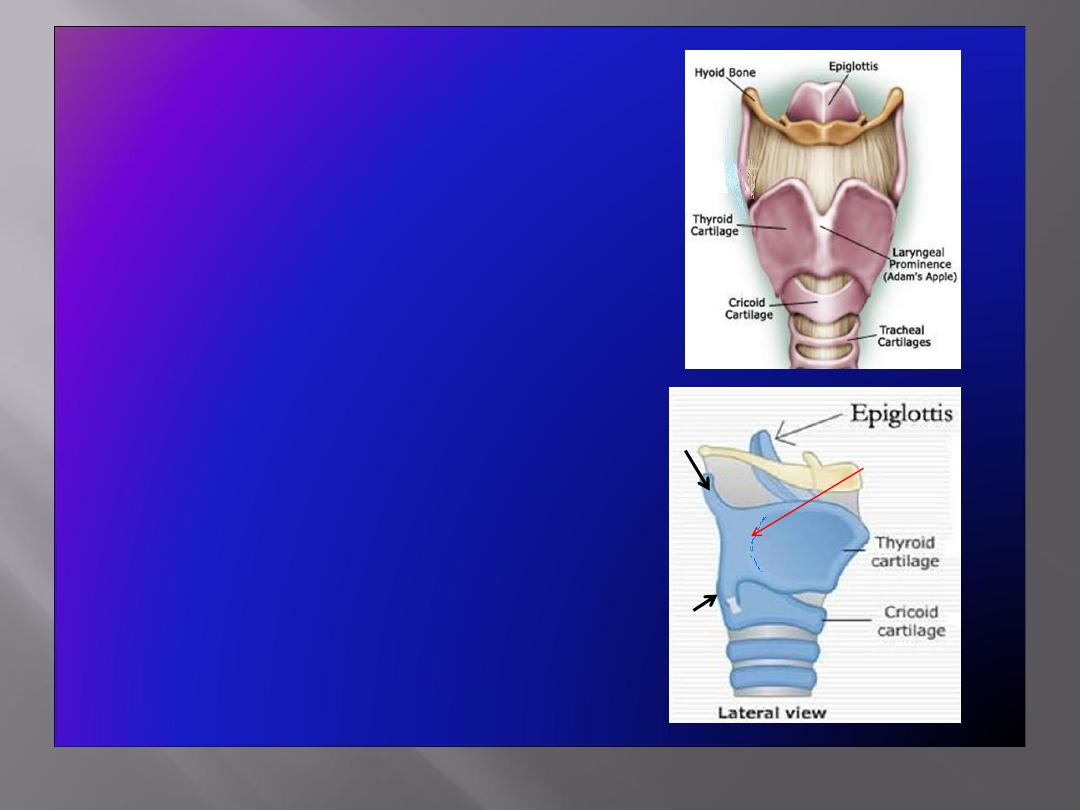
Thyroid Cartilage
• Has
two laminae
, which meet in the
midline and form a prominent angle,
called
laryngeal prominence
(
Adam’s
apple
) and the
superior thyroid notch
at
the rostral margin of the
• The
posterior border
of each lamina
forms
superior & inferior cornu
(horns)
• Outer surface of each lamina shows an
oblique line
which gives attachment to
thyrohyoid
,
sternothyroid
&
inferior
constrictor of the pharynx
• The
superior border
gives attachment to
the
thyrohyoid membrane
Oblique
line
superior
cornu
inferior
cornu
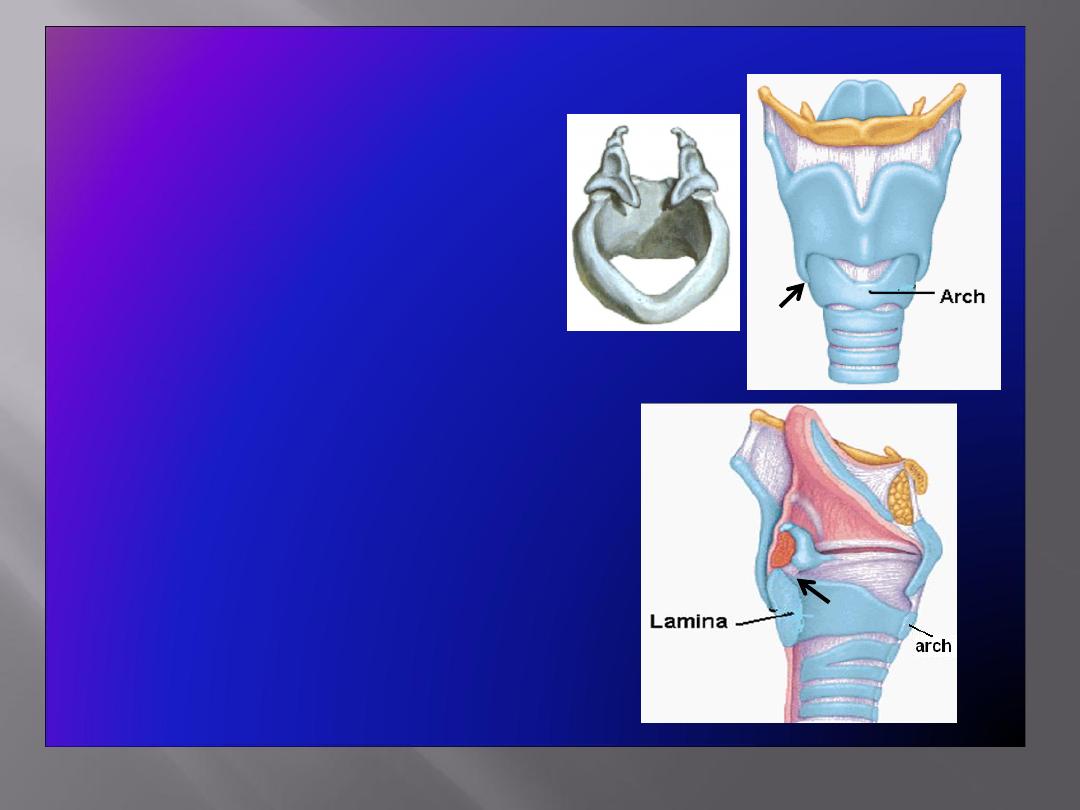
Cricoid Cartilage
• Lies below the thyroid
cartilage
• Forms a complete ring
• Has a
narrow anterior arch
& a
broad posterior lamina
• Has an articular facet on its:
• Lateral surface
for
articulation with
inferior
cornu of the thyroid
cartilage
(a synovial joint)
• Upper border
for
articulation with base of
arytenoid cartilage
(a
synovial joint)
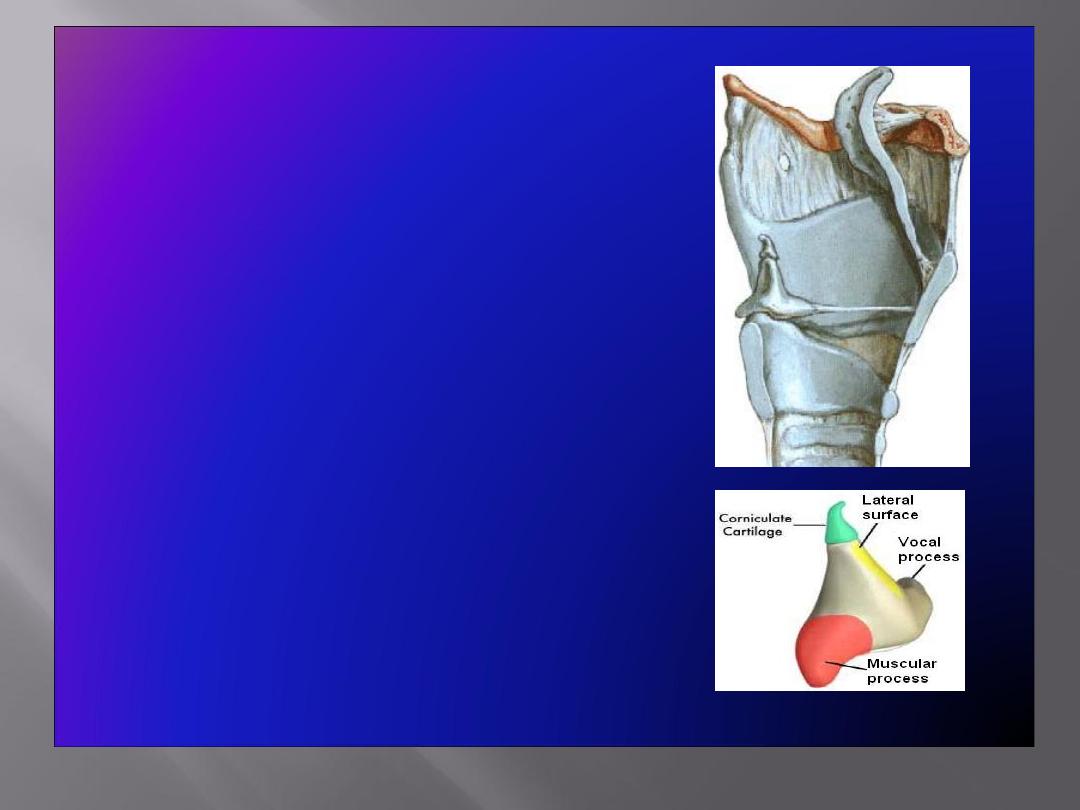
Arytenoid Cartilages
• Small,
pyramidal
in shape
• Situated at the back of the larynx
Has:
• A
base
articulating with the upper
border of the cricoid cartilage
• An
apex
supporting the corniculate
cartilage
• A
vocal process
projecting forward,
gives attachment to the vocal
ligament
• A
muscular process
projecting
laterally, gives attachment to
muscles
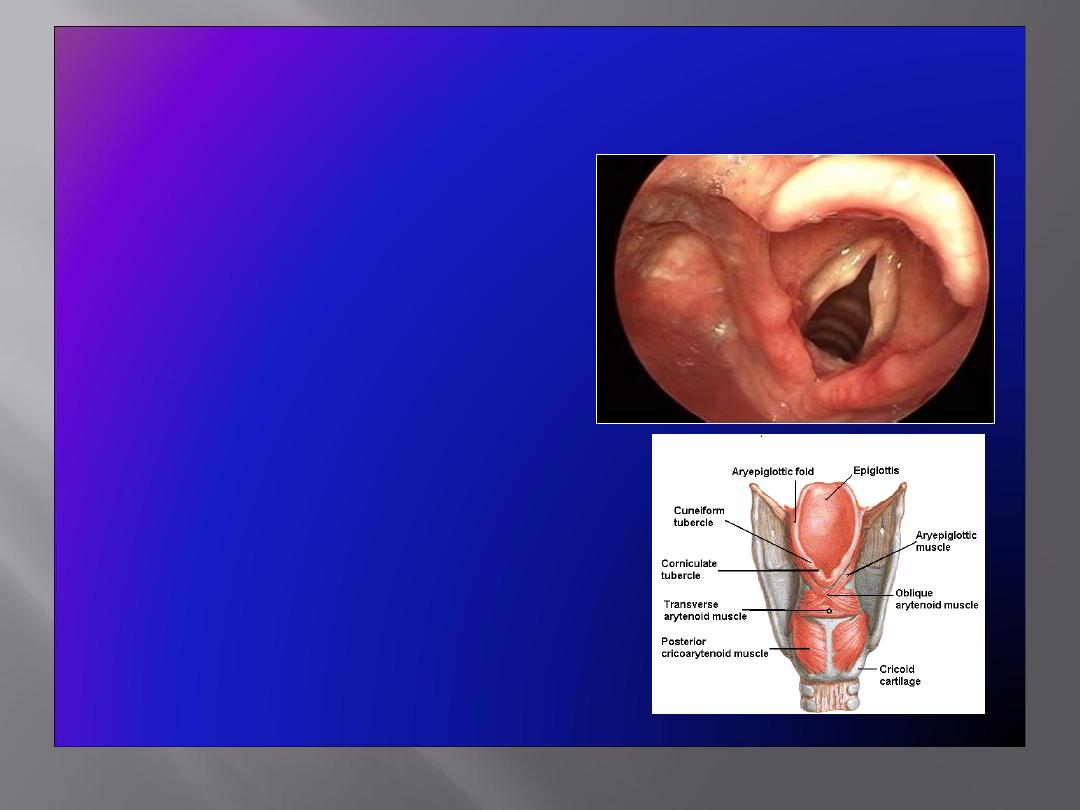
Corniculate & Cuneiform Cartilages
Corniculate Cartilages
• Small nodules
• Articulate with the apices of
arytenoid cartilages
Cuneiform Cartilages
• Small rod shaped, placed in each
aryepiglottic fold, producing a
small elevation
• Do not articulate with any other
cartilage
Serve as support for the ary-
epiglottic fold
E
CU
CO
V
F
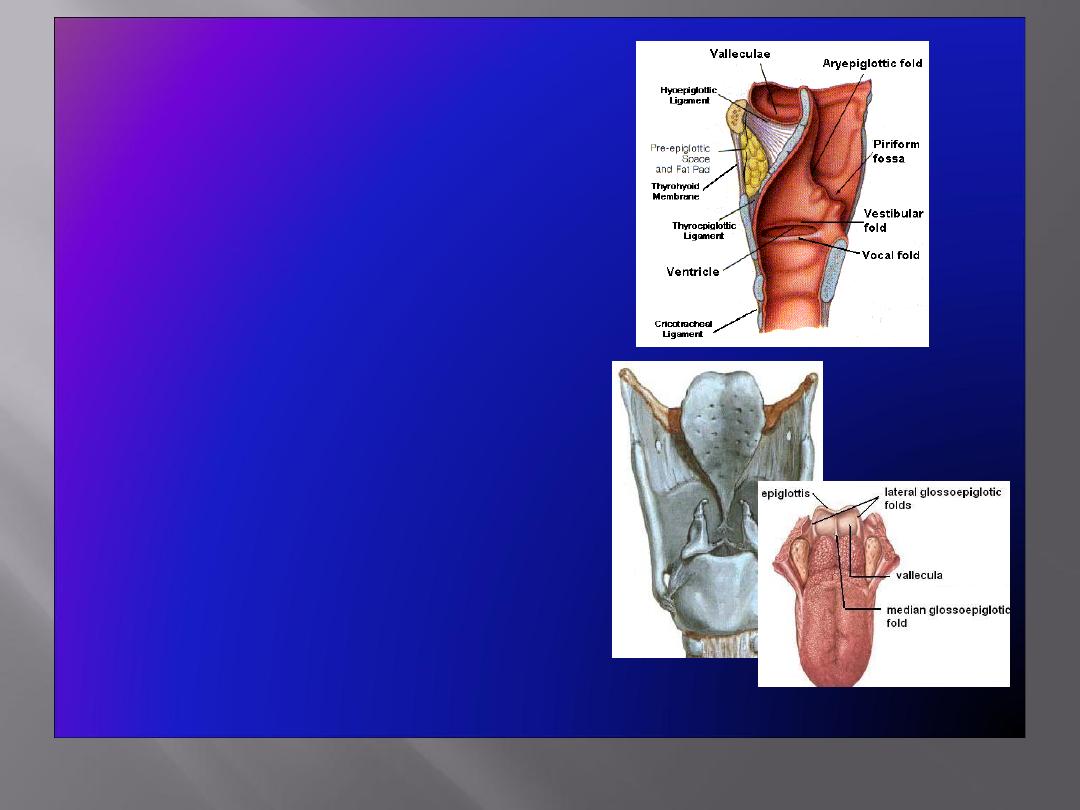
Epiglottis
• Leaf shaped, situated behind the root
of the tongue
• Connected:
In front to the body of hyoid bone
by the
hyoepiglottic ligament
By its stalk to the back of thyroid
cartilage by the
thyroepiglottic
ligament
• Upper edge is free.
• Laterally
gives attachment to
aryepiglottic fold
• Anteriorly mucosa is reflected onto the
tongue forming three
glossoepiglottic
folds & valleculae
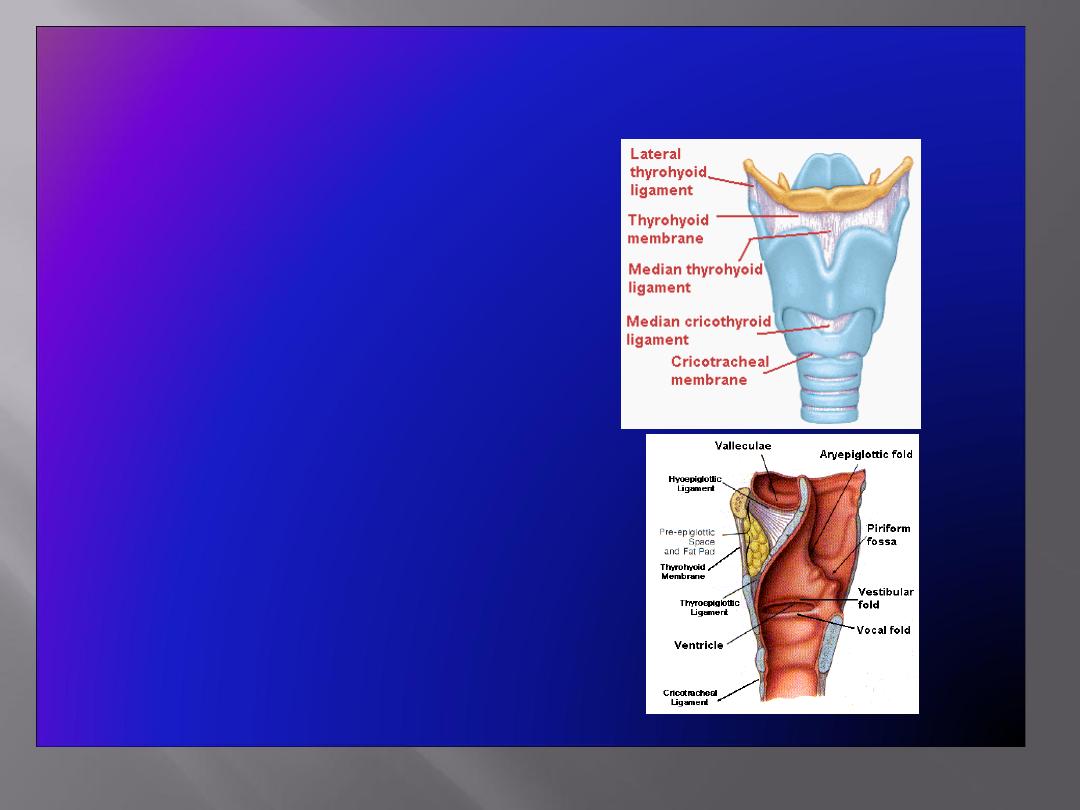
Membranes & Ligaments
• Thyrohoid membrane
,
median & lateral thyrohoid
ligaments
• Median cricothyroid
ligament
• Cricotracheal membrane
• Hyoepiglottic ligament
• Thyroepiglottic ligament
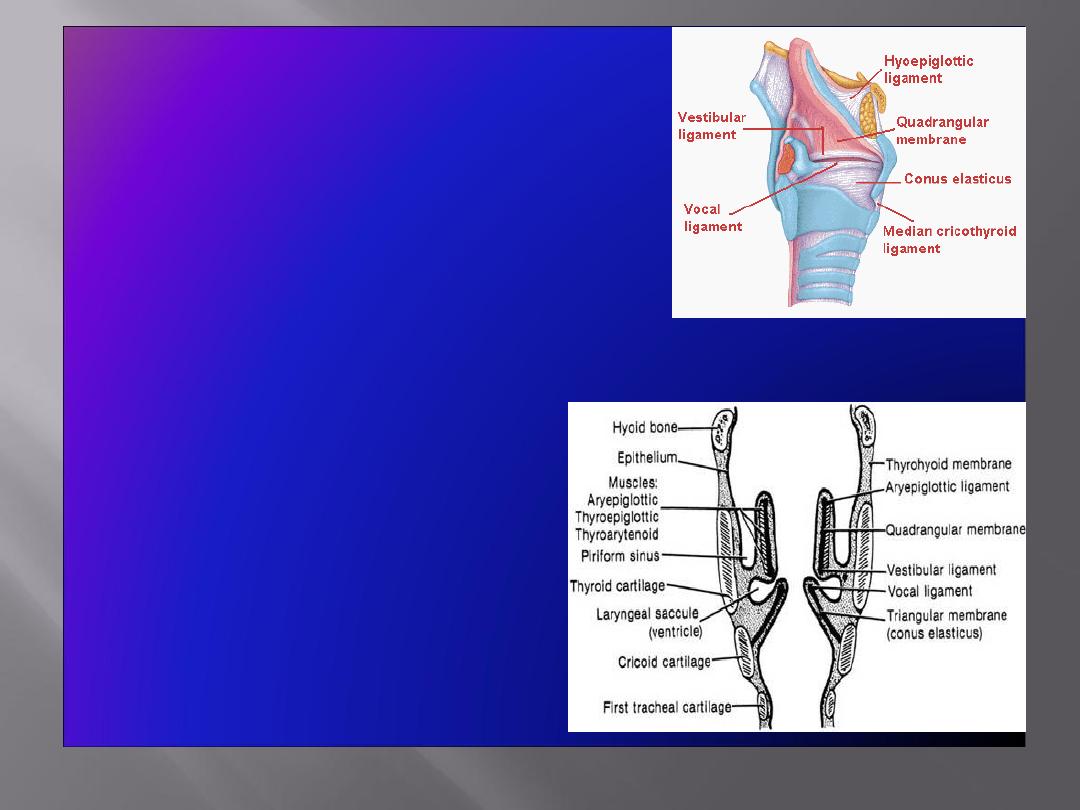
• Quadrangular membrane:
• Extends between the epiglottis
and the arytenoid cartilages
• Its lower free margin forms the
vestibular ligament
that lies
within the vestibular fold
• Cricothyroid membrane
(conus elasticus):
• Lower margin is attached to upper
border of cricoid cartilage
• Upper free margin forms
vocal
ligament
that is attached
anteriorly
to deep surface of
thyroid cartilage &
posteriorly
to
the vocal process of arytenoid
cartilage
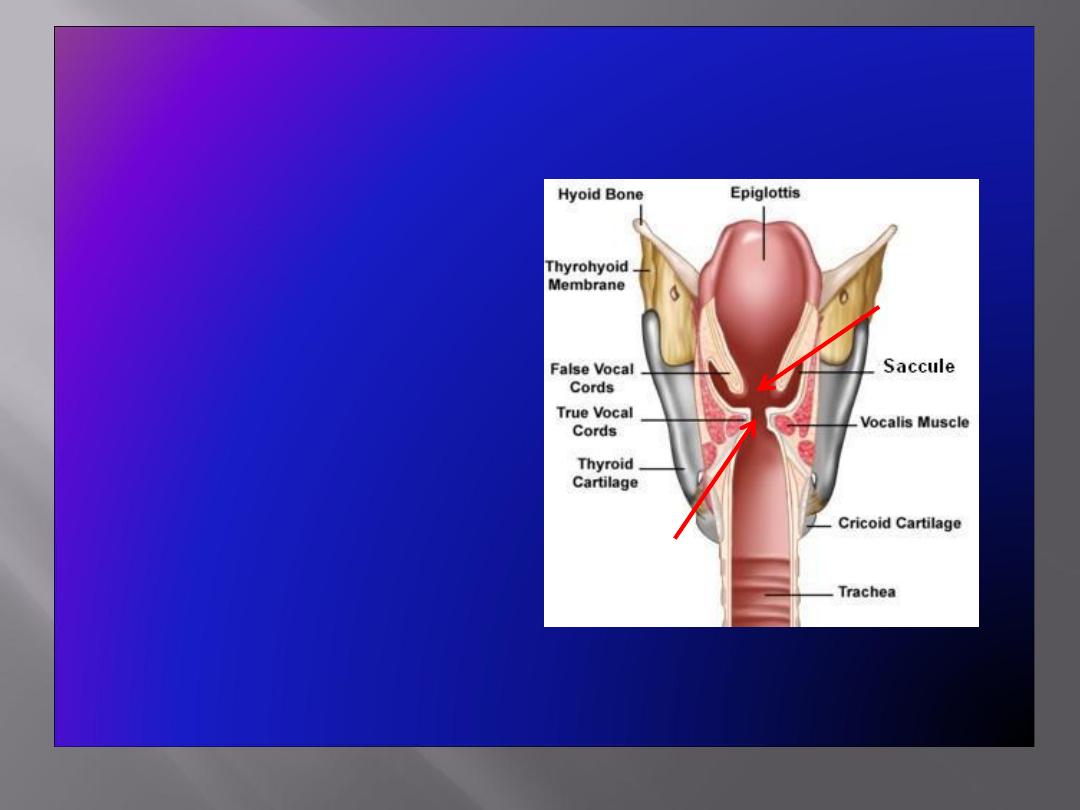
Laryngeal Cavity
• Extends from laryngeal
inlet to lower border of
the cricoid cartilage
• Narrow in the region of
the vestibular folds
(
rima vestibuli
)
• Narrowest in the
region of the vocal
folds (
rima glottidis
)
Rima
vestibuli
Rima
glottidis
Laryngeal Cavity cont’d
• Divided into
three
parts
:
A. Supraglottic part
,
the part above the
true vocal cords
B. Glottis
: The true
vocal cords
C. Subglottic part
, the
part below the true
vocal cords.
A
B
C

Mucous Membrane
• The cavity is lined with
ciliated columnar epithelium
• The surface of
vocal folds
, because of exposure to continuous trauma
during phonation, is covered with
stratified squamous epithelium
• Contains many
mucous glands
, more numerous in the saccule (for
lubrication of vocal folds)
Muscles
Divided into two groups:
• Extrinsic muscles
: divided into two groups
• Elevators
of the larynx
• Depressors
of the larynx
• Intrinsic muscles
: divided into two groups
• Muscles
controlling the laryngeal inlet
• Muscles
controlling the movements of the vocal cords
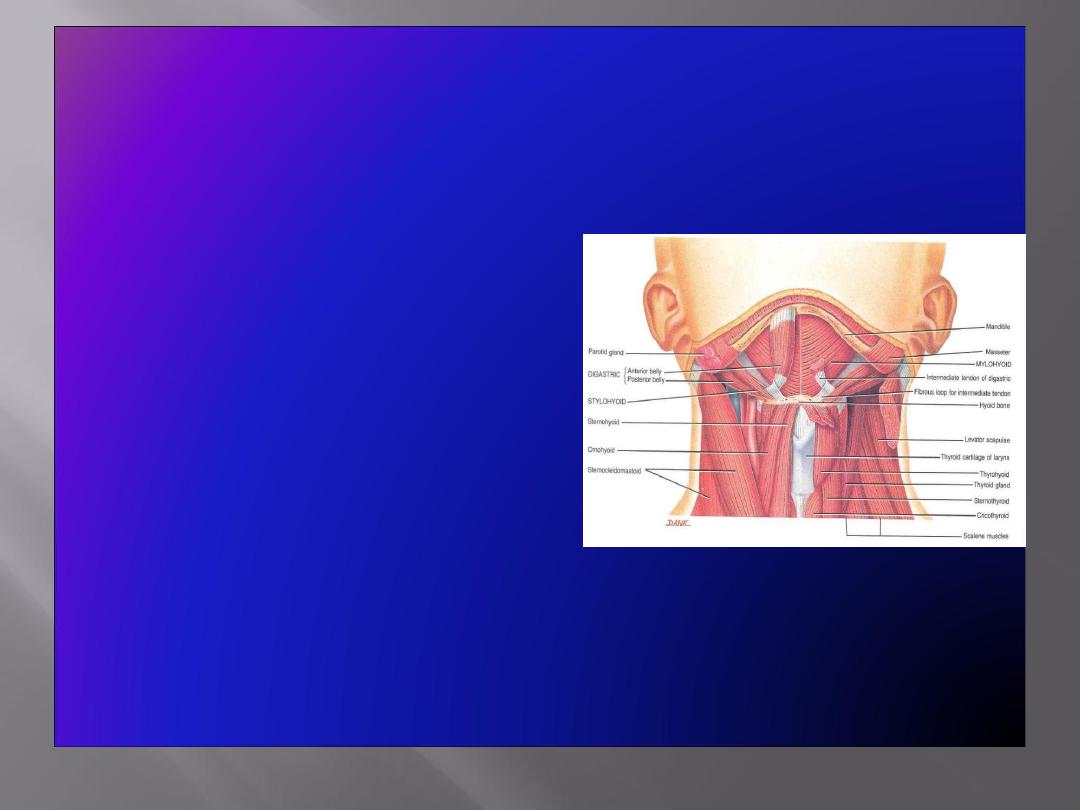
Elevators of the
Pharynx
• The Suprahyoid Muscles
Digastric
Stylohyoid
Mylohyoid
Geniohyoid
• The Longitudinal Muscles of the
Pharynx
Stylopharyngeus
Salpingopharyngeus
Palatopharyngeus
Depressors of the Pharynx:
• The Infrahyoid Muscles
Sternohyoid
Sternothyroid
Omohyoid
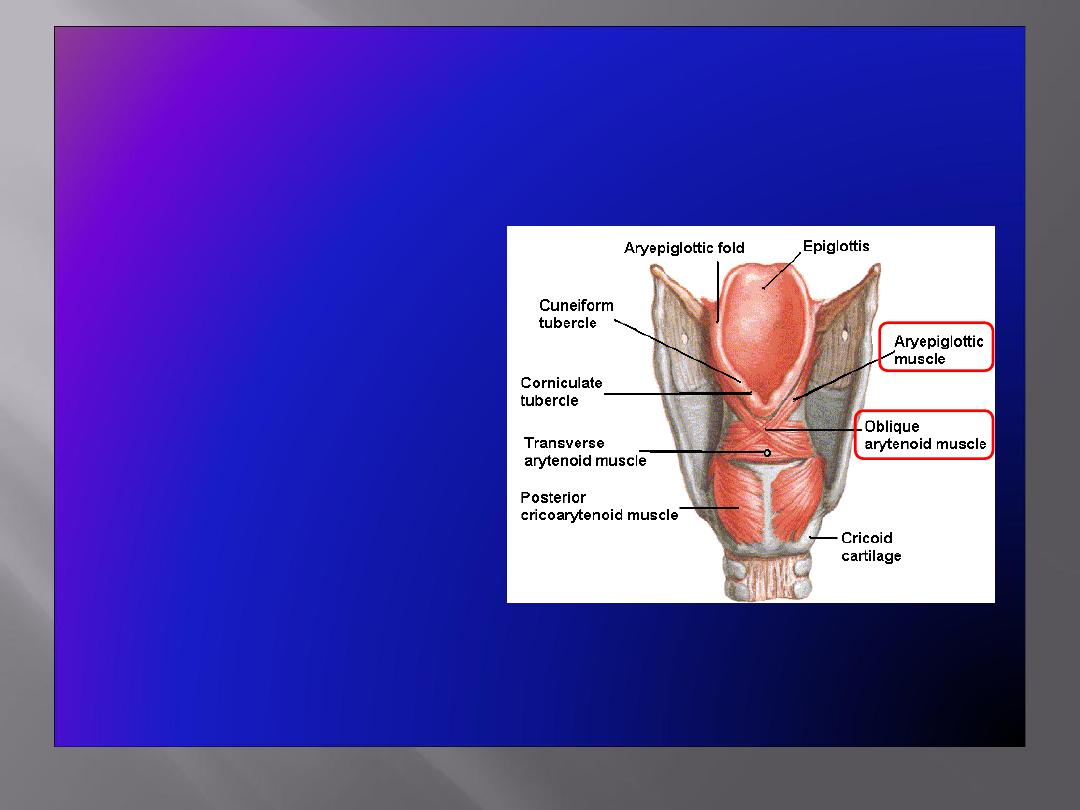
Muscles Controlling the Laryngeal Inlet
• Oblique arytenoid
• Aryepiglottic muscle
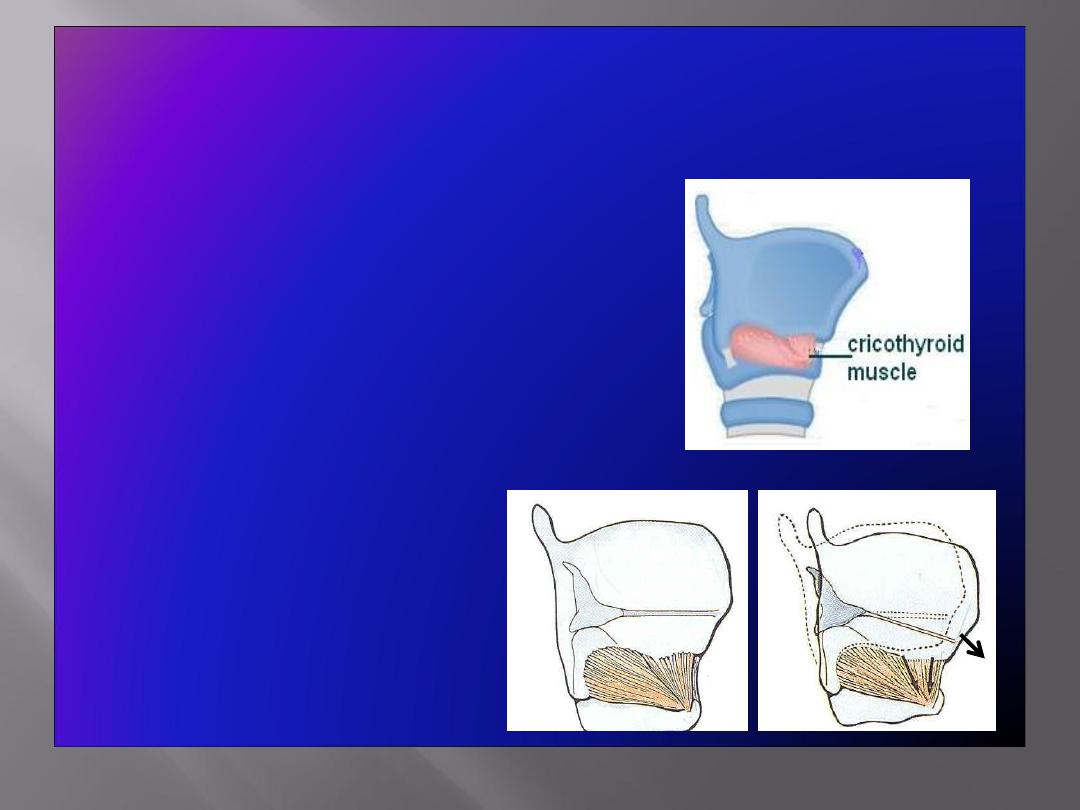
Muscle Increasing the Length & Tension of the
Vocal Cords
• Cricothyroid
: increases the
distance between the
angle of
the thyroid cartilage
& the
vocal
processes of the arytenoid
cartilages,
and results in
increase
in the
length & tension
of the vocal cords
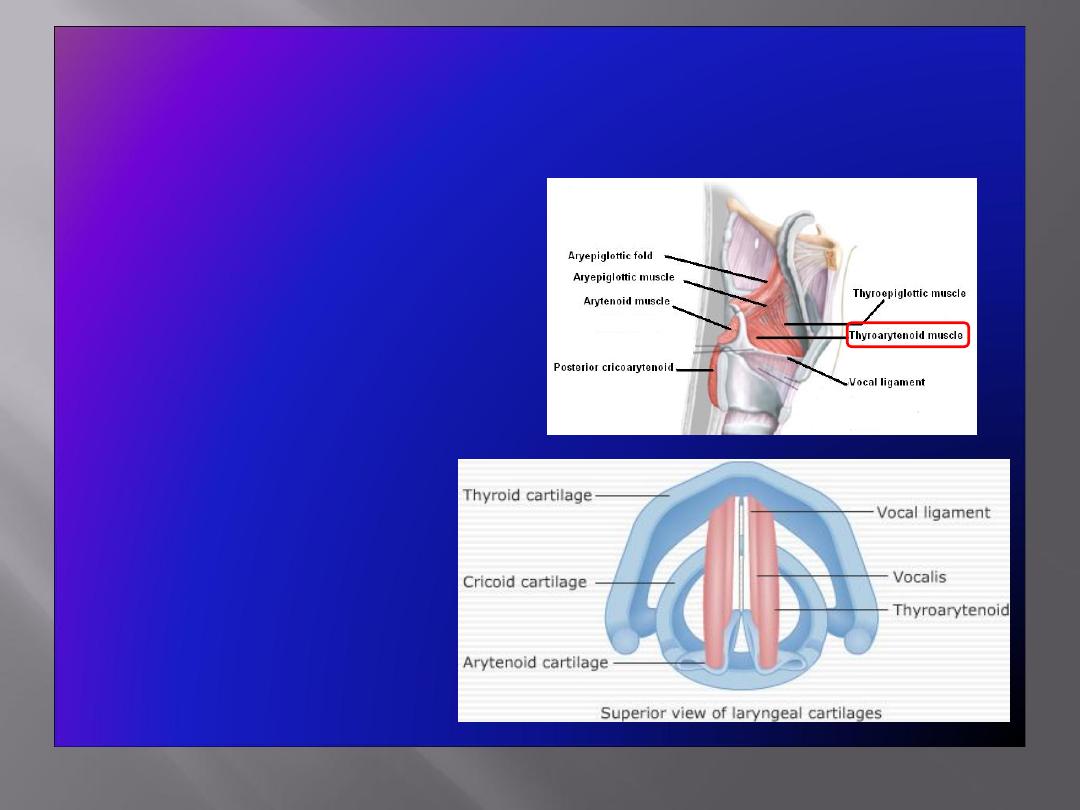
Muscle decreasing the Length & Tension of Vocal
Cords
• Thyroarytenoid
(vocalis)
: pulls the
arytenoid cartilage
forward toward the
thyroid cartilage and
thus
shortens
and
relaxes
the vocal cords
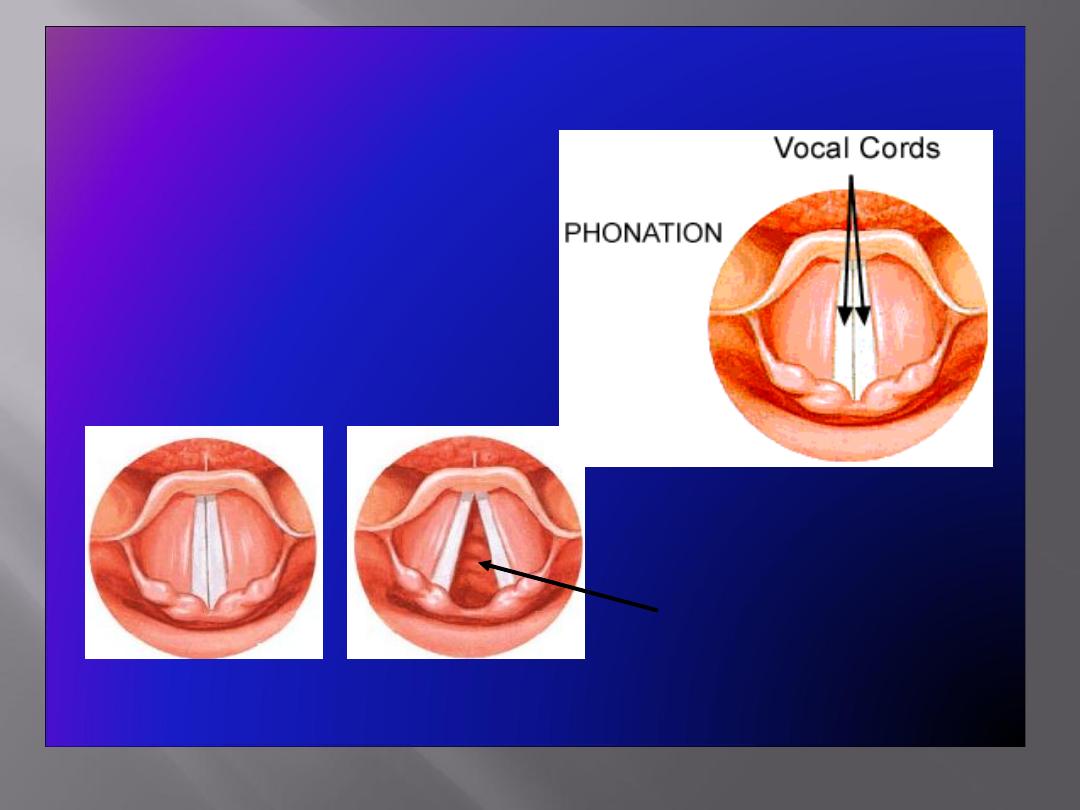
Movements of the Vocal Cords
• Adduction
• Abduction
Folds closed (adducted) Folds open (abducted
)
(View from above)
Glottis (space between folds)
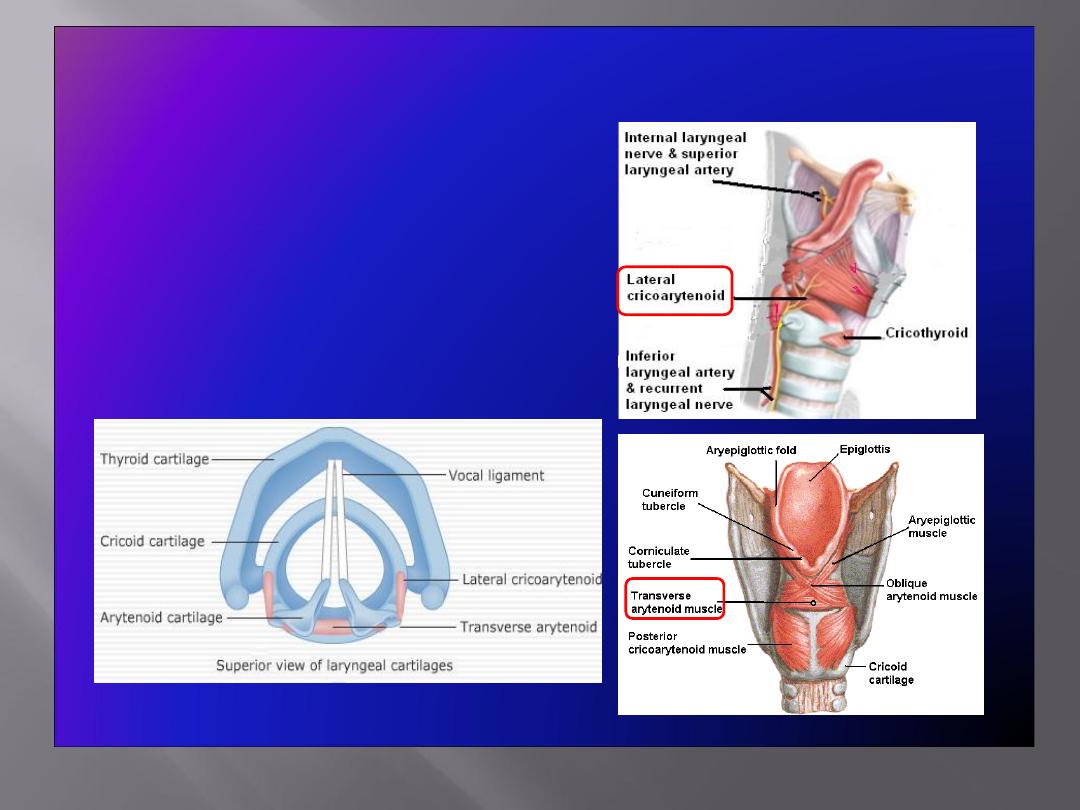
Adductors of the Vocal Cords
• Lateral
cricoarytenoid
• Transverse arytenoid
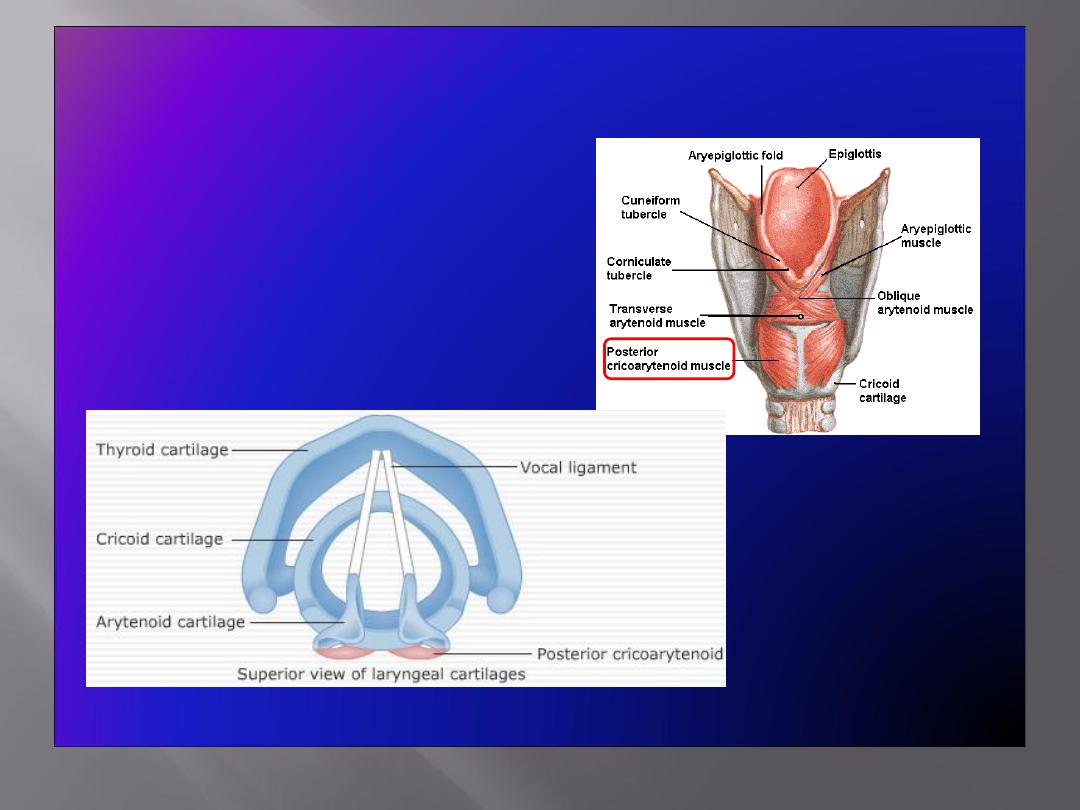
Abductor of the Vocal Cords
• Posterior
cricoarytenoid
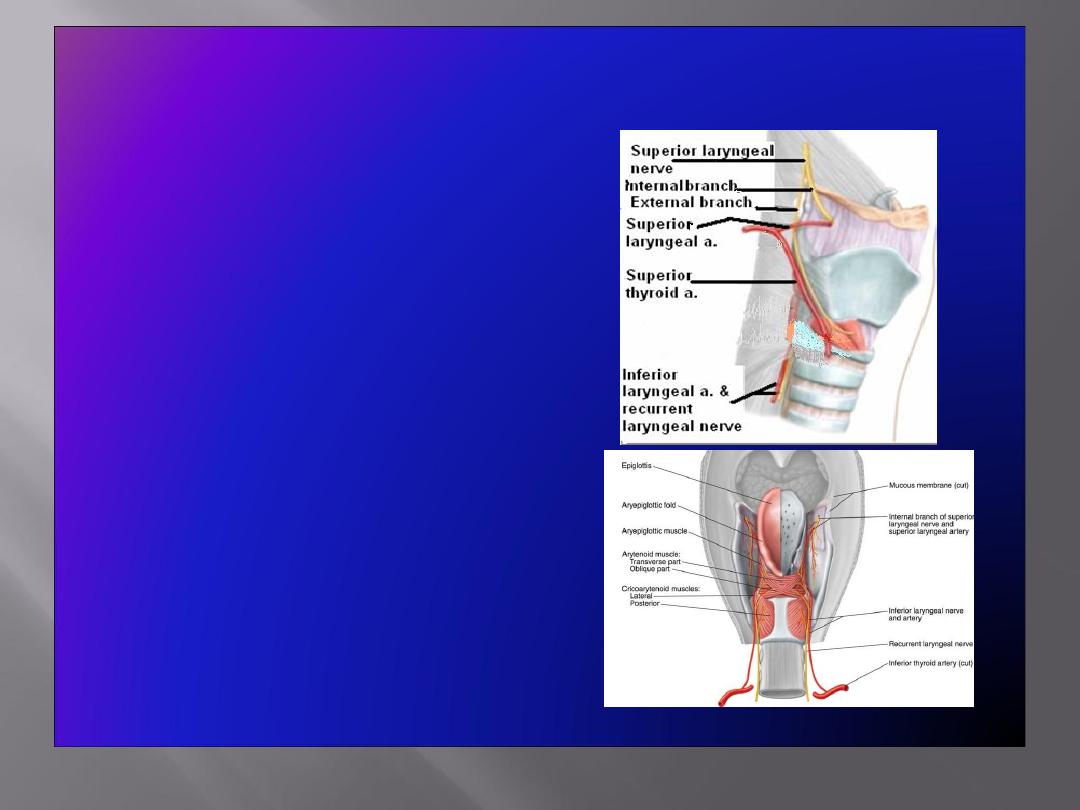
Blood Supply & Lymph Drainage
• Arteries:
Upper half:
Superior laryngeal
artery
, branch of superior
thyroid artery
Lower half
:
Inferior laryngeal
artery
, branch of inferior
thyroid artery
• Veins:
Accompany the corresponding
arteries
• Lymphatics:
The lymph vessels drain into
the
deep cervical lymph nodes
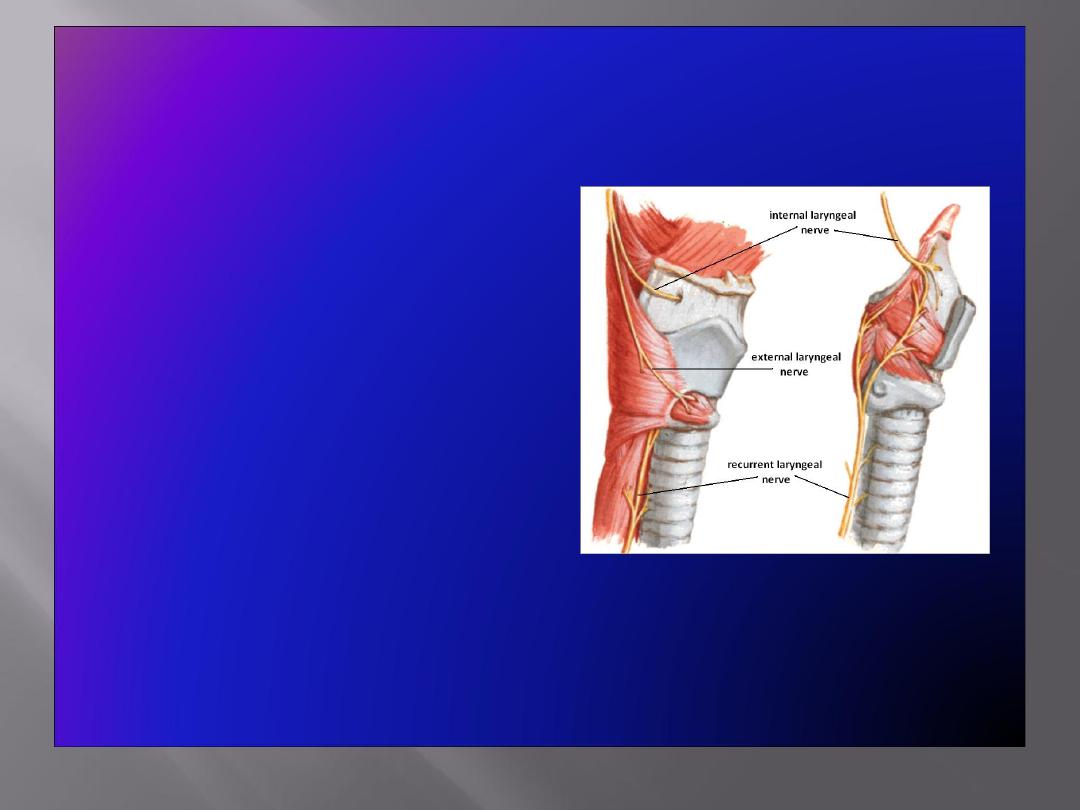
Nerve Supply
• Sensory
Above the vocal cords:
Internal
laryngeal nerve
, branch of the
superior laryngeal branch of
the vagus nerve
Below the vocal cords:
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
,
branch of the vagus nerve
• Motor
All intrinsic muscles, except
cricothyroid
, supplied by the
recurrent laryngeal nerve
The
cricothyroid
muscle is
supplied by the
external
laryngeal nerve,
a branch of the
superior laryngeal branch of
vagus nerve

1- protection of lower air passages
2- phonation
3- respiration
4- fixation if the chest

THANX



