Genus Trichomonas
Its includes a group of flagellated protozoa which infect humans and animalHumanTrichomonad
3 species of trichomonads found in human
Two are normally harmless
Trichomonastenexfound in buccal cavity
Trichomonashominisfound in large intestine
TrichomonasvaginalisThe common parasite of man
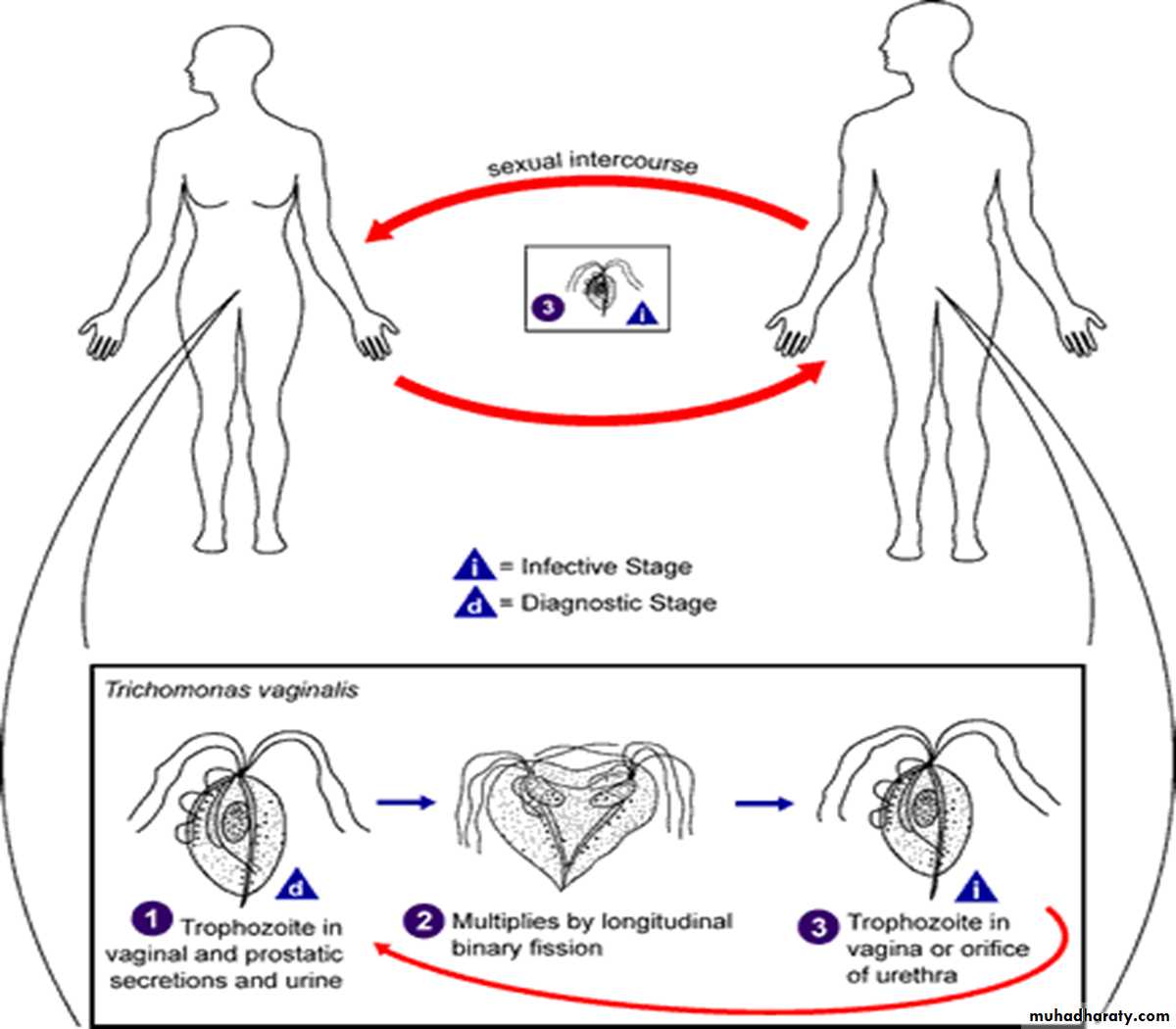
Trichomonasvaginalis
Trichomoniasis is perhaps the most common curable sexually transmitted disease worldwide. It is associated with potentially serious complications such as preterm birth and human immunodeficiency virus transmission.
although trichomoniasis is easily treated with oral metronidazole, there is concern that the number of strains resistant to this antibiotic are increasing
INTRODUCTION
Trichomonas vaginalis is the causative agent of trichomoniasis, a common cause of vaginitis. More recently, however, appreciation of the high rates of disease and of associations of trichomoniasis in women with adverse outcomes of pregnancy and increased risk for human immunodeficiency virus HIV infection suggest a need for increased control efforts.
MORPHOLOGY AND LIFE CYCLE
The shape of T. vaginalis in culture is typically pyriform, although amoeboid shapes are evident in parasites adhering to vaginal tissues in vivo. T. vaginalis is about 9 by 7 μm, and non-dividing organisms have four anterior flagella. In addition to the undulating membrane, one recurrent flagellum. Internal organelles include a prominent nucleus and a rigid structure, the axostyle, that runs through the cell from the anterior end to the posterior end. Unique energy-producing organelles, the hydrogenosomes, are present as para-Axostylar chromatic granules by light microscopy.
LIFE CYCLE
The life cycle of T. vaginalis is simple in that the trophozoite is transmitted through coitus and no cyst form is known. The trophozoite divides by binary fission and, in natural infections, gives rise to a population in the lumen and on the mucosal surfaces of the urogenital tracts of humans.Non venereal transmit ion despite reported but its very rare and occur via toilet seats and fomites.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Humans are the only natural host of T. vaginalis. Trichomoniasis is an extremely common infection worldwide. AlthoughTrichomoniasis is far exceeds the incidence of chlamydia and gonorrhea, trichomoniasis is not a public health priority. The World Health Organization has estimated that this infection accounts for almost half of all curable infections worldwide.Epidemiologically, T. vaginalis infections are commonly associated with other STDs and are a marker of high-risk sexual behavior. Trichomoniasis is frequently seen concomitantly with other STDs, particularly gonorrhea. The majority of women with trichomoniasis also have bacterial vaginosis. Unlike other STDs, which have a higher prevalence among adolescents and young adults, the rates of trichomoniasis are more evenly distributed among sexually active women of all age groups
Although survival on fomites is documented, the organism is thought to be transmitted almost exclusively by sexual activity. The incubation period of this infection is unknown; however, in vitro studies suggest an incubation period of 4 to 28 days .
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Women who are symptomatic from trichomoniasis complain of vaginal discharge, pruritus, and irritation. Signs of infection include vaginal discharge (42%), offal fishy odor (50%), and edema or erythema (22 to 37%). The discharge is classically described as frothy. The color of the discharge may vary from white, pale yellow to dark green .strawberry cervix is a specific clinical sign for this infection but is detected with reliability only by colposcopy and rarely during routine examination.
Other complaints may include dysuria and lower abdominal pain; the etiology of the latter is unclear. The urethra is also infected in the majority of women. Nearly half of all women with T. vaginalis are asymptomatic. Therefore, if these women are not screened, the diagnosis will be missed. The extent of the inflammatory response to the parasite may determine the severity of the symptoms. Factors that influence the host inflammatory response are not well understood but may include hormonal levels, vaginal PH, the coexisting vaginal flora, and the strain and relative concentration of the organisms present in the vagina.
In male
prevalence and spectrum of disease are less well characterized; the infection appears to be asymptomatic, but it has been suggested as an increasingly important cause of non-gonococcal urethritis.
Common symptoms include
Urethral discharge ( ranging from scant to purulent), Disuria
Urethral pruritis, some man experience burning immediately after coitus
The lesser prevalence in male may attributed to flushing effect of urine and the trichmonocidal effect of prostate and seminal vesicle glands fluids.
The urine usually flushes out the parasites before they colonize the urethra and if migration of the parasite occur toward prostateit usually killed by lysozyme which present in high conc. In the fluid of prostate gland
However colonization of the parasite in the prostate may lead to infertility to affected male
HOST RESPONSE AND IMMUNOLOGY
Natural infection seems to produce immunity that is only partially protective, since reinfection of patients can be 30% on follow-up .
innate immune responses and acquired cellular immune responses are likely to be important.
PATHOGENESIS
pathogenesis and virulence in human trichomoniasis not fully understood, progress has been made in identifying parasite products that can damage host cells and tissues, parasite can secretes toxic sub-stance which kill target cell
Parasite also have receptors to vaginal wall cells that helps parasite to adhere to target cell
The PH of vagina play crucial role in development of the disease despite parasite can live in PH 4-4.5 yet it cannot multiplicate in such PH degree factor affect PH in the vagina will affect parasite development
Lactobacillus which is normal micro-flora of vagina of healthy women can metabolize the glycogen which present in squamous cells of vaginal wall to be lactic acid which in turn acidificate the vaginal environment
DIAGNOSIS:
Vaginal Ph
Whiff test
Wet mount
vaginal smear
Culture
Direct immunoflouresence assay and ELISA
Polymerase chain reaction
Evaluation for other STDs
whiff test
The whiff test (addition of potassium hydroxide to vaginal fluid for olfactory detection of amines) is variable. Currently, the “gold standard” for the diagnosis of trichomoniasis is culture.
Wet mount tech.
The most common means of diagnosis is visualization of the motile trichomonads in a saline preparation of the vaginal fluid. This must be performed within 10 to 20 min of collection of the sample, or the organisms will lose viability. The organisms are about the size of a white blood cell and may be actively motile or may be seen beating their flagella at rest. Although quick and inexpensive, the test has limited sensitivity, ranging from 60 to 70% . There are often white blood cells in the vaginal fluid that are indicative of accompanying inflammation.The vaginal pH is elevated (greater than 4.5) in the majority of cases, but it may be normal.
Vaginal smear
direct fixation and staining of the parasite on slide
Culture of the parasite
by inoculation of the parasites for specific culture mediaand result obtained after 3-4 daysELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay demonstrated a sensitivity and specificity of 78.5 and 98.6%PCR
TREATMENT
Metronidazole was the most efficacious antibiotic available the treatment of trichomoniasis.The recommended dose is 2 g orally in a single dose, and the reported cure rate is 97%. Sexual partners should also be treated.
Although there continues to be some controversy about the safety of metronidazole in pregnancy, there has never been a documented case of fetal malformation attributed to its use, even when it is used in the first trimester
Tinidazole may be useful for resistant infections. Women with asymptomatic infection should be treated.
Tinidazole may be a good option for patients with infection resistant to metronidazole.
The acidification of vaginal environment may needed in some patients who give little response to metronidazole tinidazole treatment this can be done by vinegar douche
Treatment both sexual partner is very important as husband could be asymptomatic.
Prevention and control
Save sex using condoms very effective tool to prevent infection
Asymptomatic cases should diagnosed and treated