FERTILITY CONTROL AND
CONTRACEPTION
Asmaa al sanjary
Gynecology
2015

Family planning plays a critical role in promoting personal
health of the women ,optimizing both maternal and fetal well
being
Every year 600000 women die world wide from pregnancy
and pregnancy related causes
.
In developing countries the estimated average annual
risk of dying from causes related to pregnancy and
childbirth may be about 1 85 per 100,000 women not
using contraception
• 3 million women suffer significant perminant disabilities.
• Many STD can be prevented by contraception. (HIV
)infection.

There is no one method that will suit everyone, and
individuals will use different types of contraception at
different stages in their lives.
the ideal contraceptive method should:
• highly effective
• no side effects
• cheap
• rapidly reversible
• widespread availability
• acceptable to all cultures and religions
• easily distributed
• can be administrated by non- health care
personel.

As effective as modern contraceptives have been , they have
not yet achieved their full potential.
• Many
unintended pregnancies still occur in a
women who are using contraception but are not
using their chosen method correctly.

Virtually all methods of contraception occasionally
fail and some are much more effective than others.
Failure rates are traditionally expressed as the
number of failures per 100 woman-years (HwY ),
i.e. the number of pregnancies if 100 women were
to use the method for1 year.
Failure rates for some methods vary considerably,
largely because of the potential for failure caused
By imperfect use (user failure) rather than an
Intrinsic.
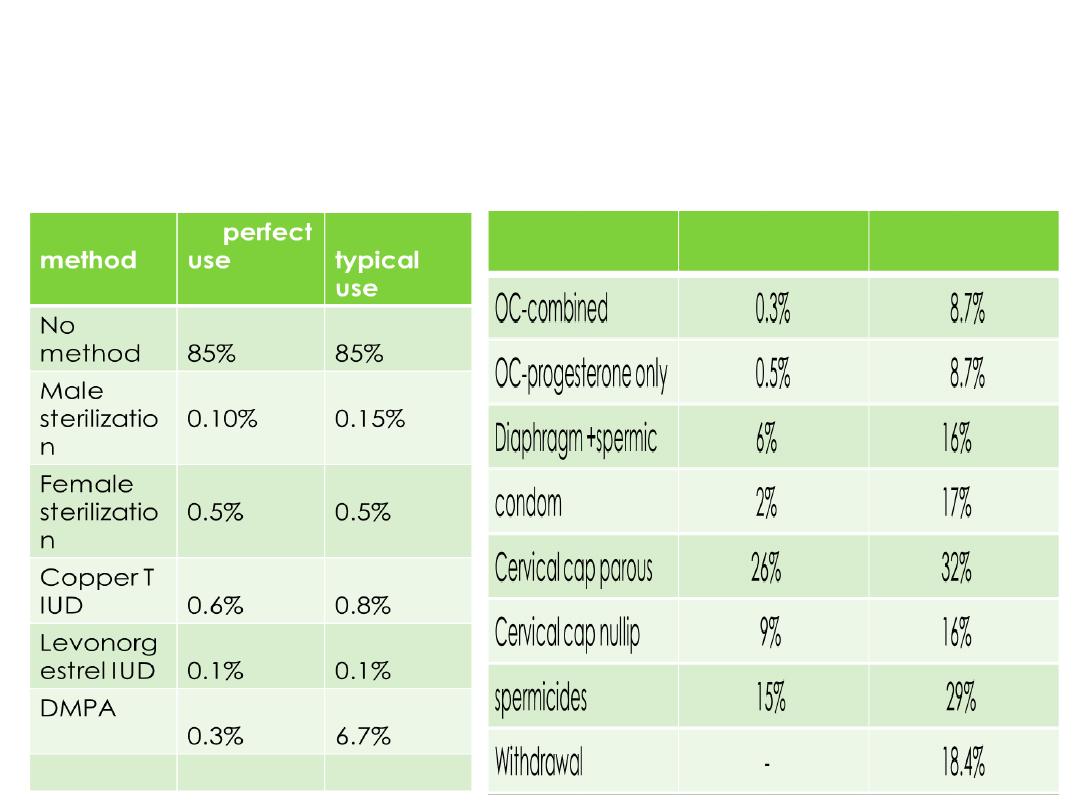
Contraceptive failure rate comparing typical use and
perfect use
:

Classification:
Combined oral contraceptive methods are grouped into
tiers depending on their efficacy with typical use.
Method of contraception
tier
Progesterone implant ,IUD
Longer term
Depot medroxy prog acetate inj.
Vaginal rings,transdermal
patches,oral contraceptice pills.
Malecondom,diaphragm,caps,female
condom,sheild
,spermicide,withdrawal,fertility
awarwness method,natural family
planning.
Combined hormonal
Barrier and behavioral methods

Classification:
Methods not requiring medical consultation:
1-coitus interruptus
2-safe period[Natural family planning]
3-vaginal spermicides
4-barrier methods include :
Male condom
Female barriers
Methods requiring medical supervision:
1-Hormonal contraception:
Combined oral contraceptive methods
Progesterone-only preparations :include
A-progesterone only pills
B-injectables
C-Subdermal implants
D-Hormone-releasing intauterine system
2-Intauterine device
3-Post-coital emergency contraception
4-occlusive diaphragms&caps

Combined oral contraceptive pills(the pill)
first licensed in the UK in 1961. It contains a combination of
two hormones: a synthetic oestrogen and progestogen
available as once daily pill.
Since COC was first introduced, the doses of both
oestrogen and progestogen have been reduced
dramatically,which has considerably improved its safety
profile..
Combined oral contraception is easy to use and
offers a very high degree of protection against pregnancy,
with many other beneficial effects. It is mainly
used by young, healthy

Formulation:
Combined oral contraceptive pills contains both:
1-Synthetic Estrogen (Ethinyl estradiol mostly):
The dose of oestrogen varies from 50 to 15 μg.
2-Synthetic progestogens
Either one of these :
*First generation(e.g. norethindrone).
*Second generation progestins (e.g.
levonorgestrel) .
*Third generation series including gestodene,
desogestrel and norgestimate

• Monophasic pills contain standard daily dosages
of oestrogen and progestogen.
• Biphasic or triphasic preparations have two or
three incremental variations in hormone dose.
Current thinking is that biphasic and triphasic
preparations are more complicated for
women to use and have few real advantages.
.

For maximum effectiveness, COC Most brands
contain 21 pills; one pill to be taken daily,
followed by a 7-day pill-free interval. There are
also some every-day (ED) preparations that
Include seven placebo pills that are taken
instead of having a pill-free interval should
always be taken regularly at roughly the same
time each day. Other are for extended cycle
use to eliminate or minimize the number of
scheduled bleeding episode induced by
placebo pills.this scheduled bleeding is not
medically indicated but desired by some
women for personal reason.

preparation
1.low-dose pills containing 30μg of ethinyl estradiol
2.high-dose pills contain contain 50 μg estrogen.
Higher dosages of oestrogen are strongly linked to
increased risks of both arterial and venous thrombosis
3.Yasmin
contains ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone.
Drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid activity. It can help
prevent bloating, weight gain, and hypertension, but it can
increase serum potassium.
Yasmin is contraindicated in patients at risk for hyperkalemia
and should not be combined with other drugs that can
increase potassium
Mode of action
Combined oral contraception acts both
centrally
And
peri pherally
.
is by far the most
Inhibition of ovulation
centrally
•
important effect. Both oestrogen and progestogen
suppress the release of pituitary FSH and LH,
which prevents follicular development within the
ovary and therefore ovulation .
• Peripheral effects include
atrophic and hostile to an
endomtrium
Making
-
implanting embryo
to prevent sperm
cervical mucus
altering
-
ascending into the uterine cavity.

Contraindication:
absolute:
1• Circulatory diseases:
- iscihaemic heart disease- cerebrovascular accident
- significant hypertension
- arterial or venous thrombosis
- any acquired or inherited pro-thrombotic tendency
- any Significant risk factors for cardiovascularpisease
2• Acute or severe liver disease
3• Oestrogen-dependent neoplasms, particularly breast
cancer
4.Breastfeeding <6 weeks post-partum
5.Smoking ≥15 cigarettes/day and age ≥35
6.Focal migraine

Relative contraindications
• Generalized migraine
• Long-term immobilization
• Irregular vaglinal bleeding (until a diagnosis has
been made)
• Less severe risk factors for cardiovascular
disease,e.g. obesity, heavy smoking, diabetes

Side effect:
1-Venous thromboembolism:
VTE is the major measurable risk other wise the
combined
oral contraceptive pills are very safe.
Oestrogens alter blood clotting and coagulation in a
way that induces a pro-thrombotic tendency, although
the exact mechanism of this is poorly understood.
The higher the dose of oestrogen within COc, the
greater the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE)...
Type of progestogen also affects the risk of VTE, with
users of COC containing third-generation progestogens
being twice as likely to sustain a VTE.

The risks of VTE are:
• 5 per 100 000 for normal population,
•
15 per 100 000 for users of 2
nd
generation.
•30 per 100 000 for users of 3
rd
generation.
•
60 per 100 000 for pregnant women.

2-Arterial disease
*risk of hypertention:
will become significantly
per cent of COC users
1
hypertensive and they should be advised to stop
taking COC
*risk of myocardial infarction and thrombotic
stroke :
in young, healthy women using low-dose COC
is extremely small.
Cigarette smoking
will, however, increase the
arterial risk, and any woman who smokes must
be advised to stop COC at the age of 30years.

3-Mortality
There is increased mortality in women using
the pills over women not using it, related to
age&smoking habits.
Death is most often the result of pulmonary
embolism,cerebral or coronary thrombosis.
Women who are under 35 years, do not
Smoke nor have hypertention or diabetes have
no exess mortality
otherwise women over 35 years ,women who
Smoke or have hypertention there is excess
mortality .

4.Carcinogenic effect:
• Breast cancer
Most data do show a slight increase in the risk of
developing breast cancer among current COC users
(relative risk around l. 24).
This is not of great significance to young women, as the
background rate of breast cancer is very low at their age.
However, for a woman in their forties, these are more
relevant data, as the background rate of breast cancer is
Higher, but beyond 10 years after stopping coc
there was no increase in breast cancer risk for former
coc users.

• Cervical cancer
More than five years of pill use may be
associated with small increase risk of
cervical carcinoma.
• Liver cancer
Benign hepatic adenoma is a rare
consequence of COC use
Minor side effects
CNS
Gastrointestinal
Genitourinary
system
Breast
miscellaneous
Depression
Headaches
Loss of libido
Nausea and vomiting
Weight gain
Bloatedness
Gall-stones
jaundice
Cholestatic
Cystitis
Irregular bleeding
Vaginal discharge
Growth of fibroids
Breast pain
Increased risk of
breast cancer
Chloasma (facial pigmentation)
Leg cramps

• Method of use
• The patient begins taking the pills on the first
day of menstrual cycle then in the next cycles
they are administered in fifth day of the cycle
and continue for 21 days, each day at the
same time, then discontinued for 7 days to
allow for withdrawal bleeding that mimics the
normal menstrual cycle which occur after 3-5
days from stopping pills

If pills are missed ????
How late
are you???
Less than
12 hours
late
Don't worry
. Just take
the delayed pill at
once, and further
pills as usual
More than
12 hours
late
• Take the most
recently
delayed pill now
• Use extra
precautions
(condom, for instance)
for the next 7 days

Drug interaction
*This can occur with enzyme-inducing agents
Such as some anti-epileptic drugs increase
activity of hepatic enzyme so reduce efficacy
of COC.Higher dose oestrogen coc
containing 50 Mg ethinyl oestradiol may need
to be prescribed
*Some broad-spectrum antibiotics Ampicillin,
Amoxicillin, Tetracycline , Neomycin can alter
intestinal absorption of COC and reduce its efficacy.
Additional contraceptive measures should therefore
be recommended during antibiotic therapy and for 1
week thereafter.

• *Steroids ,Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) and
acetaminophen may elevate plasma ethinyl
estradiol so increase its efficacy.

Positive health benefits
*COC users generally have light, pain -free, regular
bleed and therefore COC can be used to treat heavy
or painful periods
( menorrhagia & dysmenorrhea )
*It will also improve premenstrual syndrome(PMS)
*reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease(PID).
*decreased incidence of benign breast lump.
*decrease number of functional ovarian cyst.
*less endometriosis.
*COC offers long-term protection.
against both ovarian and endometrial cancers.
*It can also be used as a treatment for acne.

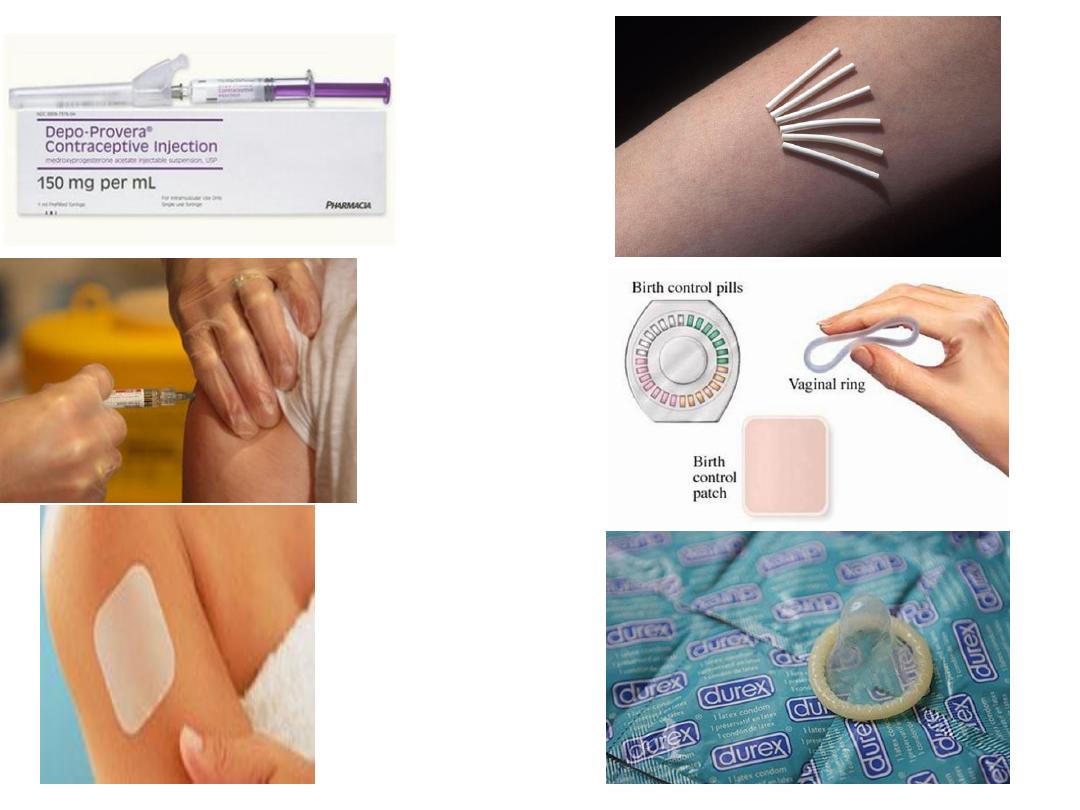
Combined oestrogen and progesterone
vaginal ring
It is soft ring that a woman can insert into
vagina; and the Women who use Ring
leave the ring in place for 3 weeks during a
month. During the 4th week, the ring is
removed for 7 days.
A new ring is used for each cycle.

Combined hormonal patches
A contraceptive transdermal patch containing
Oestrogen and progestogen has been
Developed and releases norelgestromin 150 Mg
and ethinylestradiol 20 Mg per 24 hours.
Patches are applied weekly for 3 weeks, after
which there is a patch-free week.
Contraceptive patches have the same risks and benefits
as COC and, although they are relatively more
expensive, may have better
compliance.

Progesterone only contraception:
All other types of hormonal contraception in
current use in the world are progestogen -only
and share many similar features in terms of mode
of action and side effects.
Because they do not contain oestrogen, they
are extremely safe & can be used if woman
has cardiovascular risk factors.
The dose of progestogen within them varies from
very low to high

The current methods of progestogen-only
contraception are
• progestogen-only pill, or 'mini-pill'
• subdermal implant Implanon®
• injectables.
• hormone-releasing intrauterine system

Mechanism of action
1-peripheral effects:
*local effect on cervical mucus making it hostile
to ascending sperm.
*Local effect on the endometrium making it thin
& atrophic thereby preventing implantation
*Progestin use also causes decreased tubal and
endometrial motility.
2-central effects
Higher dose progestogen-only methods can act
centrally & inhibit ovulation .

Side effects
• Menstrual disturbances either irregular vaginal
bleeding or amenorrhea.
• Functional ovarian cyst
• Increase risk of ectopic pregnancy :this has not been
confirmed,although it is probably that POP protect
much more effectively against intrauterine than
ectopic pregnancy.

Progestogen-only pills
The progestogen-only pill (POP) is ideal for
Women who like the convenience of pill
taking but cannot take COC. Although the
failure rate of the POP is greater than that
Of COC , it is ideal for women at times of
lower fertility.
If the POP fails, there is a slightly higher risk of
ectopic pregnancy

they contain
*the second-generation progestogen
norethisterone or norgestrel (or their derivatives)
*or the third-generation progestogen desogestrel.
The POP is taken every day without a break

Injectable progestogens
Two injectable progestogens are marketed.
• Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate 150 mg
(Depo-Provera or DMPA) which lasts around 12-
13 weeks .
• Norethisterone enanthate 200 mg (Noristerat)
which only lasts for 8 weeks and is not nearly
so widely used.

Depo-Provera is a highly effective method
Of contraception and it is given by deep
intramuscular injection Most women who
use it develop very light or absent
menstruation. Depo-Provera will improve
PMS and can be used to treat menstrual
problems such as painful or heavy periods.
It is particularly useful for women who have
difficulty remembering to take a pill

Particular side effects of Depo-Provera
• weight gain of around 3 kg in the first year,
• delay in return of fertility - it may take
Around 6 months longer to conceive compared
to a woman who stops COC,
• persistent menstrual irregularity ,irregular vaginal
bleeding may occur or amenorrhea in prolonged
use of this injection
• very long-term use may slightly increase the
Risk of osteoporosis (because of low oestrogen
levels)

Particular indications for depo provera
-contraindication to estrogen
-Following rubella vaccination in peurperium.
-Husband waiting for effect of vasectomy.
-Mental retarded women. .
-Breast-feeding.
-population control in developing countries.

Subdermal implants
Implanon consists of a single silastic rod that is
inserted subdermally under local anaesthetic into
the upper arm. It releases the progestogen
etonogestrel 25-70 Mg daily (the dose released
decreases with time), which is metabolized to the
Third-generation progestogen desogestrel.
Implanon was introduced into the UK in the late
1990s.
Other type of implant is the six-rod implant, Norplant,
which is withdrawn from the market
It lasts for 3 years and thereafter can be easily
removed or a further implant inserted.
Implanon is particularly useful for women who
have difficulty remembering to take a pill and
Who want highly effective long-term
contraception. There is a rapid return of
fertility when it is removed.

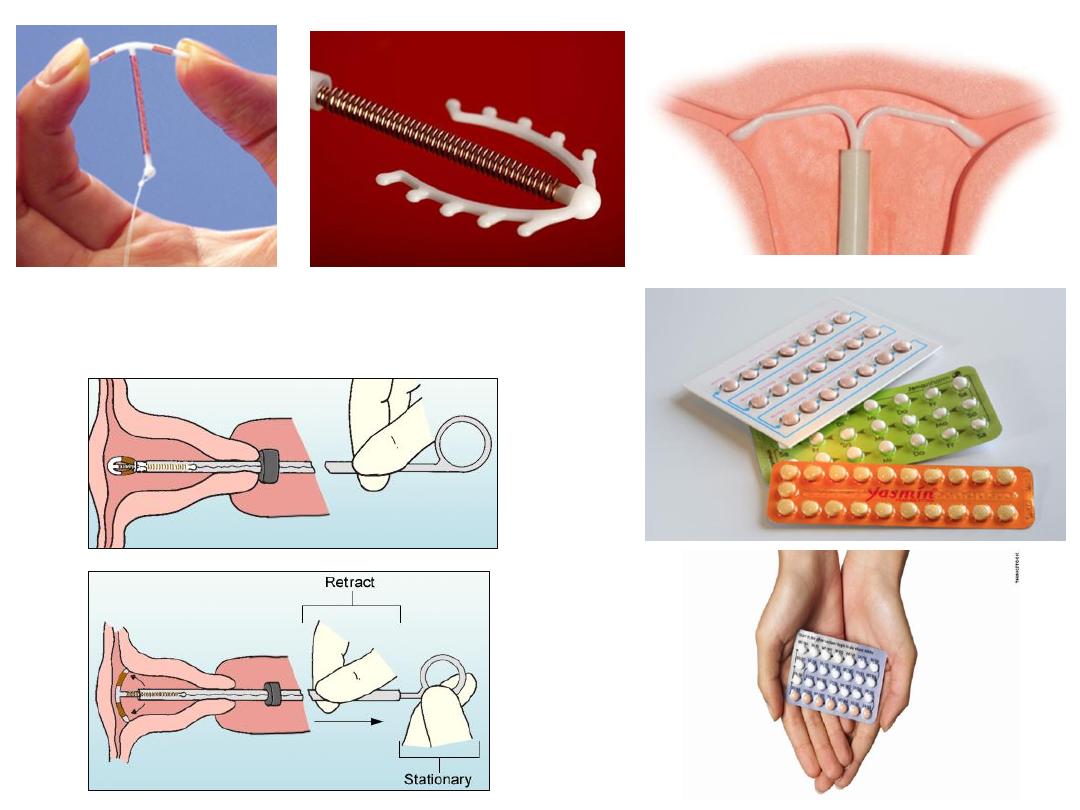
Intrauterine device
IUDs can be classified as either:
Medicated,
copper-bearing T380A(copper T IUD)
levonorgestrel hormone-releasing (LNG-IUD)
Unmedicated, or inert
The majority of the IUDs now widely used
are copper-bearing.

This IUD provides excellent pregnancy protection
that is convenient and rapidly reversible.
1
st
year failure rates are 0.7% and cumulative
10- to 12-year pregnancy rate are 1.4% to 1.9%.
most women are candidate for IUD use including
those with serious medical problems as
Hypertension, morbid obesity, diabetes, stroke
,MI , and even cancer.
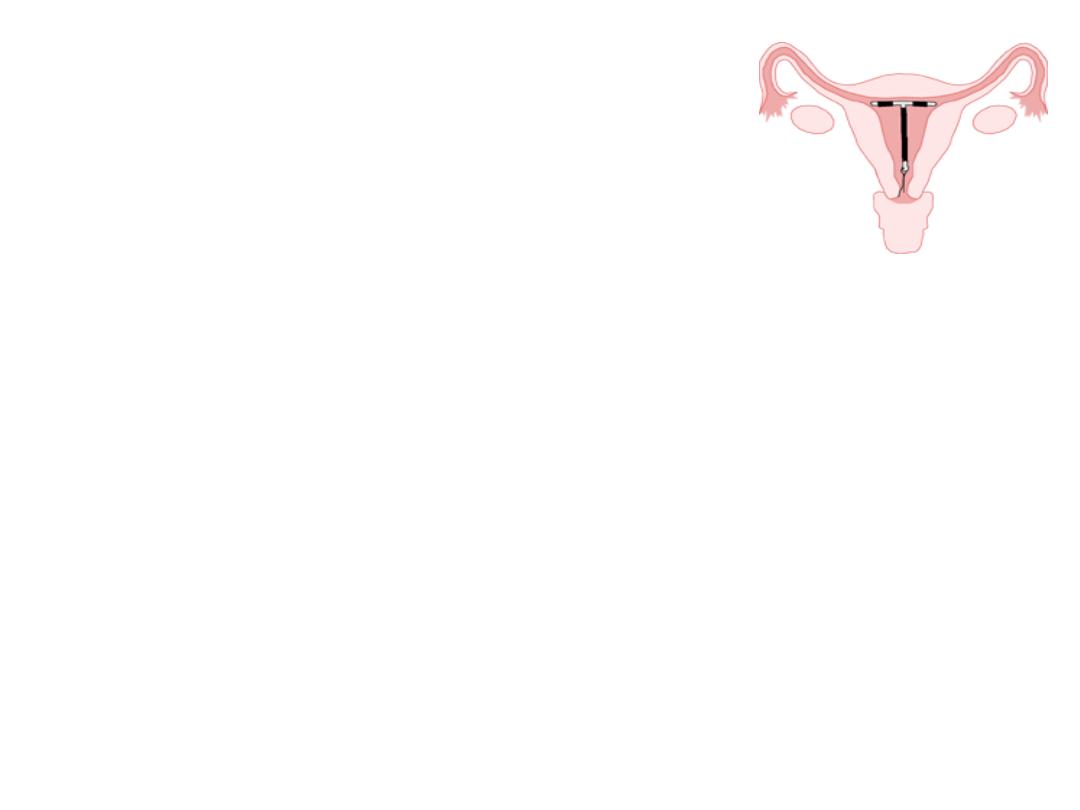
Mechanism of action
of copper T IUD
• Induce inflammatory reaction within
the endometrium make the cavity
and tube fluid that is toxic to the sperm ,oocyte and the embryo,
• Copper ions released from copper IUD reach a level in the
uterine cavity fluid that is toxic to the sperm oocyte and embryo.
• It appear that IUD mainly interfere with the fertilization, that’s
only few sperms reaching the fallopian tube by cervical mucos
hostility and by interfering with sperm motility,and affecting
tubal motility,
and if reaching are incapable of fertilization,
even the oocyte is incapabale to be fertilized.
• IUD interfere with sperm motility , oocyte capability of
fertilization and implantation.

Complication of IUD:
Bleeding and pain
Increased menstrual bleeding, often
with pain, is the most common problem
of IUD use and the most common
medical reason for removing lUDs
Older women and women with children
generally have lower rates of removal
due to bleeding and pain.

Unlike other IUDs, hormone-releasing
devices decrease menstrual blood flow
or,
may
even
stop
menstruation
altogether
With all IUDs, abnormal bleeding and
pain may be due not to the IUD itself but
to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID),
ectopic pregnancy, malignancy, or other
conditions

IUD use has not been proved to induce
clinical anemia
In a study of the TCu-380Ag carried out
in several developing countries and the
US, the proportion of women with
anemia rose only from 24% to 25.4%
during four years of use

Infection(PID):
• Many studies have confirmed that the risk of
infection and infertility among IUD users is
very low (2004). However, studies also
indicate that the insertion process and not
the IUD or its strings, pose the temporary
risk of infection.
• Good infection prevention procedures should
be practiced.
• Antibiotic prophylaxis should not be used
routinely prior to insertion.
• The risk of infection following IUD insertion
returns to a very low or normal level after 20
days (1992).

perforation
•
Perforation of the uterus occurs when
the IUD, the inserter tube, the sound, or
another gynecological instrument used
during insertion pierces the uterine
muscle wall, most often at the fundus,
or top of the uterus
•
Careful insertion technique can prevent
most perforations

•
Perforations may go unnoticed at the
time of insertion
•
Over time lUDs may become embedded in
the uterine wall without perforating it
• Expulsion
• After IUD insertion, uterine contractions can
push the device downward, causing partial or
complete expulsion
• Most expulsions occur in the first year and
especially the first three months after insertion

•
Younger women and women who have
never been pregnant or have never had
children are more likely to expel their lUDs
•
Women who had painful menstruation or
abnormally large menstrual flows were
more likely to expel copper-T IUDs
•
Correct insertion, with the IUD placed up to
the fundus, is thought to reduce the
chances of expulsion

Intrauterine pregnancy
•
If pregnancy does occur, potentially
severe complications can result. Medical
attention is always needed
•
Spontaneous abortion is the most
frequent complication of pregnancy with
an IUD in place
•
the IUD should be removed as soon as
pregnancy is confirmed

• An IUD left in place during pregnancy also
increases the risk of premature delivery.
It does not increase the risk of other
complications-birth defects, genetic
abnormalities, or molar pregnancy

Ectopic pregnancy
Mounting evidence indicates that most
lUDs help to protect against ectopic
pregnancy while they are in use
IUD users were half as likely to
experience ectopic pregnancies as
women using no contraception

A recent analysis of randomized trials
found that second-generation copper
lUDs and the LNG-20 reduce ectopic
pregnancy rates to 10% of the level
among women using no contraception
lUDs provide less protection against
ectopic pregnancy than consistently used
oral contraceptives or barrier methods

Any pregnancy in an IUD user is
uncommon, however. The ectopic
pregnancy in an IUD user is rare
TCu-380A and MLCu-375, have the lowest
ectopic pregnancy rates – 0.25 and close
to 0 per 1,000 woman years

Clinical implications:
Women using lUDs should be told about
the signs of ectopic pregnancy
If an IUD user conceives or shows signs of
pregnancy, health care providers should
always look for ectopic pregnancy
A woman who has had an ectopic
pregnancy can use an IUD
• There is no evidence that IUDs cause any
type of cancer

• among IUD users. WHO and US researchers
have/estimated about one to two deaths per
100,000 IUD users per year from infection,
ectopic pregnancy, or second-trimester
septic abortion.
• The IUD is one of the safest family planning
methods, according to estimates of annual
death rates among US women using various
family planning methods or no method.

Containdication:
• Nulliparity and infertility: higher rate of expulsion
and discomfort,,,infertility ???
• Active infection,,if IUD Increased risk of
actinomyces which is recovered after removal and
re insertion.
• Uterine anomalies increase risk of expulsion and
perforation.
• gynecologic malignancy.
• genital bleeding of unknown cause.
• gestational trophoblastic disease.

Levonorgestrel releasing IUD
• The LNG IUS is made of flexible
plastic
• The LNG IUS contains a progestin
hormone called levonorgestrel which
has been used in birth control pills
since the 1970s
• The safety of levonorgestrel has been
proven by clinical use also in sub-
dermal implants and intrauterine
systems since decades

• in every country LNG-IUD is approved for
contracepttion with an effect comparable to
sterilization
with an ability for regret, and is
approved for treatment of heavy prolonged
menstrual bleeding ,and is effective as
endometrial ablation
.
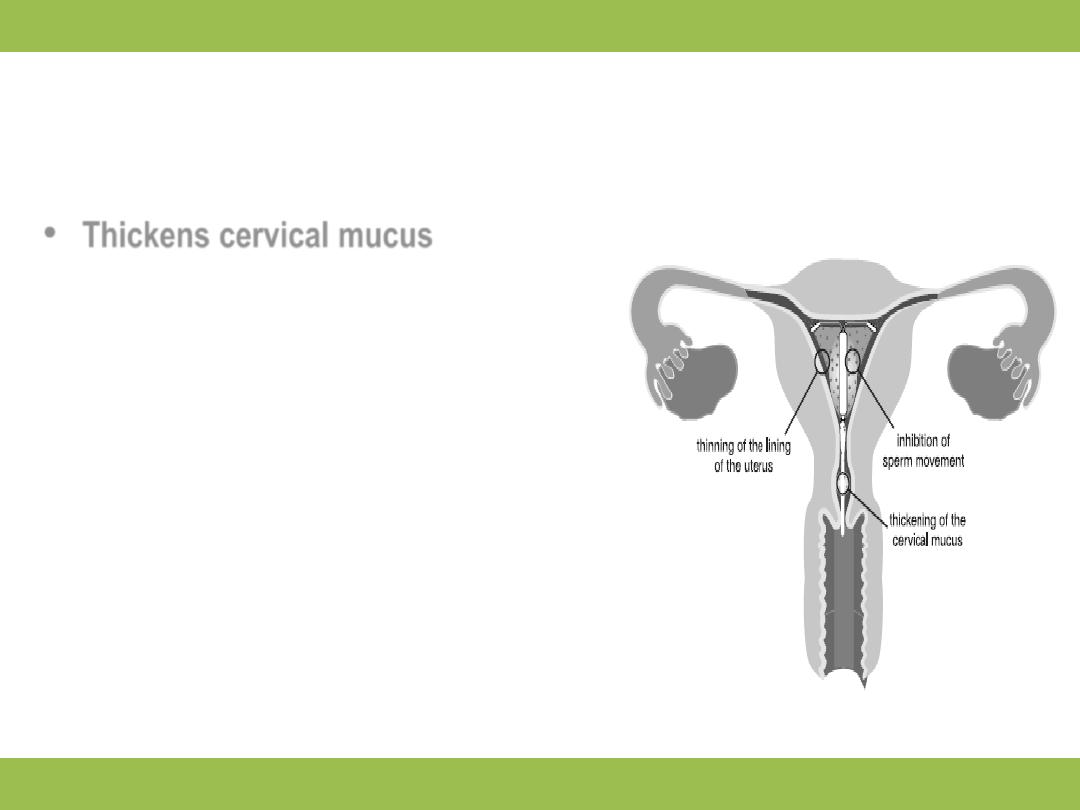
LNG IUS MECHANISMS OF ACTION
•
Thickens cervical mucus
•
Inhibits sperm function in uterus
•
Reduces monthly growth of the
lining of the uterus making periods
lighter and shorter; there is no
evidence that LNG IUS has any
impact on implantation
•
LNG IUS can also lessen menstrual
blood loss in women who have
heavy menstrual flow

Treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding
•
Use of LNG IUS makes periods lighter, shorter and less painful
•
Over 12 months, blood loss reduced by 80-96% in women with
menorrhagia
•
Clinical improvement in associated anemia:
Hemoglobin levels rise 1.8g/L in one year of use with LNG IUS,
compared to a decrease of 1.2g/L with Copper-T.
•
Irregular bleeding or spotting common in first 3-6 months; 20%
with amenorrhea at 12 months. Sometimes the amenorrhea rate
can be higher than 20% e.g. up to 50% at 12 and 24 months of
use.

What are the most common
side-effects of the LNG IUS?
10+ in every 100 women are likely
to experience the following:
•
Headache
•
Abdominal/ pelvic pain
•
Bleeding changes
•
Vulvovaginitis (inflammation of the
external genital organs or vagina)
•
Genital discharge
1 to 10 in every 100 women are likely to
experience the following:
•
Depression
•
Migraine
•
Nausea
•
Acne
•
Hirsutism (excessive body hair)
•
Back pain
These side effects are common among OC Pill
users as well.
Source: Luukkainen 1995

LNG-and risk of ectopic pregnancy
•
It is very rare to become pregnant while using LNG IUS
•
However, if you become pregnant while using LNG IUS, the
risk having an ectopic (extra-uterine) pregnancy is relatively
increased
•
About 1 in a 1000 women correctly using LNG IUS have an
ectopic pregnancy per year. This rate is lower than that
among women not using any contraception (about 3 to 5 in a
1000 women per year)
•
Woman who have already had an extra-uterine pregnancy,
pelvic surgery or pelvic infection carry a higher risk of
experiencing an ectopic pregnancy

Emergency contraception
Post-coital contraception is any drug or device
used prevent pregnancy after unprotected
intercourse
There are two types of emergency
contraception[EC]

A-hormonal emergency contraception
1-Combined oestrogen&progesterone[CEP]:
Combination of 100 microgram ethinyl estradiol &0.5
mg levonorgestrel is taken twice the two doses
being 12 hours apart & started within 72 hours of
unprotected intercourse
Nausea & vomiting are common side effects.
The precise mechanism of action is not known but
probably involves disruption of ovulation or corpus
luteal function depending on the time in the cycle
when hormonal EC is taken so it inhibit ovulation
or interfere with implantation.

2-Levonorgestrel alone:
Levonorgestrel 0.75 mg taken twice with two
doses separated by 12 hours ,it may be more
effective & better tolerated
It has to be taken within 72 hours of an episode
of unprotected intercourse and is more effective
the earlier it is taken
•

B -intrauterine device
A copper-bearing IUD is highly effective post-
coital contraceptive with failure rate less than
1%,used up to five days after the estimated
day of ovulation.It prevent implantation &the
copper exerts an embryotoxic effect
The hormone-releasing IUS has not been shown
to be effective for EC and should not be used
in this situation
Ultrasound imaging
Copper IUD
LNG IUD