
1
First stage
physics
Lec-1
9/12/2015
.د
تيماء
Energy ,Work ,and Power of the Body
We can consider the body to be an energy converter .All activities of the body , including
thinking involve energy changes. The conversion of energy into work such as lifting a
weight or riding a bicycle represents only a small fraction of total energy conversions of
the body .Under resting conditions about 25% of the body’s energy is being used by the
skeletal muscles and the heart , 19 % is being used by the brain , 10 % is used by the
kidneys , and 27 % is being used by the liver and spleen .
The body’s basic energy (fuel) source is food .The food is converted into molecules
chemically .The body uses the food energy to operate its various organs : maintain
constant temperature , do external force , for example ,lifting.
A small percentage (5 %) of the food energy is excreted in the feces and urine ; any
energy that is left over is stored as body fat The energy used to operate the organs
eventually appears as body heat .Some of this heat is useful in maintaining the body at
its normal temperature,but the rest must be disposed of .
Conservation of Energy in the Body
Conservation of energy in the body can be written as a simple equation.
[Change in stored energy ] =[ Heat lost from the body] +[Work done]
[in the body(food energy,]
[body fat,and body heat ]
There are a continuous energy changes in the body both when is doing work and when
it is not .
The first law of thermodynamic equation is :
∆U =∆Q + ∆W ----------(1)
Where ∆U is the change in stored energy
∆Q is the heat lost or gain
∆W is the work done by the body in some interval of time .
A body doing no work(∆W = 0) and at a constant temperature to lose heat to its
surroundings ,and ∆Q is negative .∆U is also negative,indicating a decrease in stored
energy .

2
The change of ∆U , ∆Q and ∆W in a short interval of time ∆ t ,
equation (1) becomes
∆U = ∆Q + ∆W -----------(2)
∆ t ∆t ∆t
where ∆U/∆t is the rate of change of stored energy
∆Q/∆t is rate of change of heat loss or gain,
∆W/∆t is the rate of doing work , that is mechanical work .
Energy Changes in the Body
The unit of energy in SI unit is Joule .
The physiological unit of food energy is Kilocalories .
The unit of heat production = Kcal/minute
1 Kcal =4184 J
Power = Joule / second = Watts
met : is the rate of energy consumption of the body.
1 met =50 Kcal /hour per m² of the body surface area .
A typical man has surface area 1.85 m² of the surface area
A typical women has about 1.4 m² of the surface area
1 met =50 Kcal /hour per m² = 58 watts/m²
OR
1 met =92 kcal /hr
1 met =107 watts
Metabolic rate (MR)
Metabolic rate is define as the rate of oxidation .
In oxidation process within the body heat is released as energy of metabolism.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) : is the lowest rate of energy consumption.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR):Is defined as the amount of energy needed to perform
minimal body functions ( Such as breathing and pumping the blood through the
arteries ) under resting conditions .

3
The energy used for basal metabolism becomes heat which is primarily dissipated from
the skin , so that the basal rate is not related to the surface area but on the mass of the
body .The metabolic rate depends on the temperature of the body if the body
temperature changes by 1 Cº ,there is a change of about 10 % in the metabolic rate .
In oxidation of the glucose , heat energy is released .
Example :
C 6 H12 O6 + 6 O 2 6 H 2 O + 6 CO 2 +686Kcal
1 (mole) + 6 (mole) 6 (mole) + 6 (mole)+ heat energy
180gm 192gm 108gm +64 gm + 686 Kcal
Energy released per gm of glucose = 686/180 = 3.8Kcal /gm
Energy released per liter of O2 used = 686 /6 x22.4 =5.1 Kcal /liters
Liters of O2 used per of fuel = 22.4 x 6/ 180 =0.75liters/gm
Liters of CO 2 produced per gm of fuel = 6 x22.4/180 = 0.75liters /gm
Example (metabolic)
Suppose you wish to lose 4.54 kg either through physical activity or by dieting .
a . How long would you have to work at an activity of 15 kcal/ min to lose 4.54 of fat ?
from table energy release for 1 gm of fat is 9.3 kcal/g . If you work for T minutes ,then
(T min)( 15 kcal/min) = (4.54 x 10³ g)(9.3 kcal/g ) (T min)( 15 kcal/min)
4
( T min)( 15 kcal/min) = 4.2 x 10 kcal
T = 28810 min
T = 47 hour the time taken to lose 4.54 kg of fat
b. It is usually much easier to lose weight by reducing your food intake . If you
normally use 2500 kcal/day , how long must you diet at 2000 kcal/day to lose
4.54 kg of fat . 4
T =energy of 4.54 kg fat = 4.2 x 10 kcal
Energy of deficient per day 5x 10² kcal/day
T = 84 days

4
Work and power
Chemical energy stored in the body is converted into external mechanical work as well
as into life –preserving functions .
External work
External work is defined as a force moved through a distance Δx
ΔW = F Δx
where W is the work
Δx is the distance
The force and the motion x must be in the same direction .
External work is done when a person is climbing a hill or walking up stairs ,
We can calculate the work done :
Work done = persons weight x vertical distance moved
W = m g h
When a man is walking or running at a constant speed on a level surface , most of the
forces act in the direction perpendicular to his motion . Thus , the external work which
done by him appears to be zero .However , his muscles are doing internal work which
appears as heat in the muscle and causes a rise in its temperature .this additional heat
in the muscle is removed by blood flowing through the muscle , by conduction to the
skin , and by sweating .
We can measure the external work done and power supplied by a subject ,
for example :riding a fixed bicycle we can also measure the oxygen consumed during
this activity , the total food energy consumed can be calculated since
5 kcal are produced for each liter of oxygen consumed .

5
Power
Power is the rate of doing work
P = ΔW
Δt
where P is the power
The change in work is
ΔW = F Δx
P = F Δx
Δt
Power is the rate of doing work
P = ΔW
Δt
where P is the power
The change in work is
ΔW = F Δx
P = F Δx
Δt
P = F Δx
Δt
Where Δ x / Δ t is
P = F v
6
Efficiency of the human Body
We can consider the human body as a machine in doing external work.
The efficiency of the human body as a machine can be obtain from the usual definition
of the efficiency ( ε ):
Efficiency ( ε ) = Work done
Energy consumed
Efficiency ( ε ) is lowest at low power ,but can increase to 20 % for trained individuals
in activities such as cycling and rowing .Table 1 shows the efficiency of man for several
activities along with the efficiency of several mechanical engines.
Table 1 Shows the efficiency of
man for several activities
•
17
Steam engine
~3
Shoveling
<2
~4
Swimming(on surface)
( under water)
~20
Cycling
Efficiency
%
Task or Machine
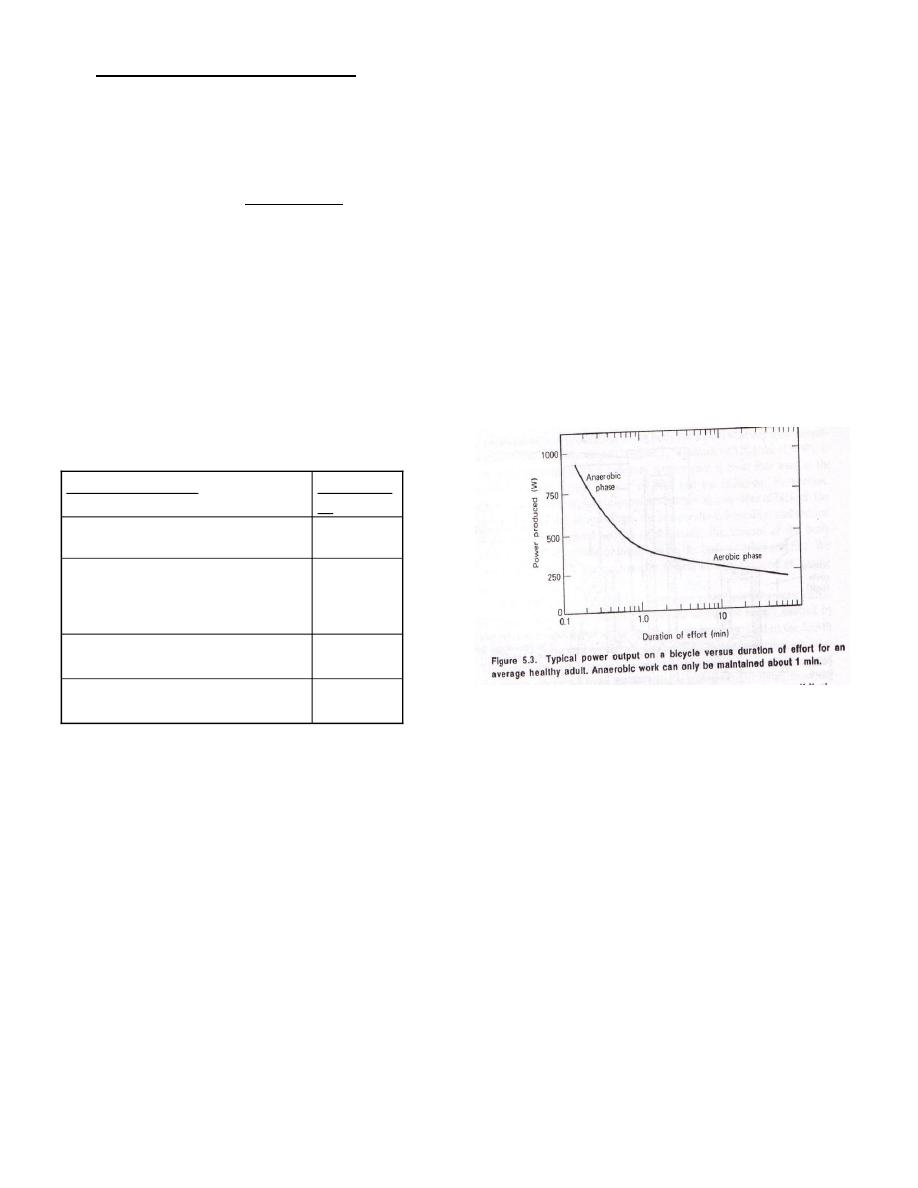
The maximum work capacity of the
body is variable
Figu
re 1
Figure1:phases of
work
The maximum work capacity of the body is variable .For short periods of time the body
can perform at very high power levels , but for long – term efforts it is more limited.
Experimentally it has been found that long -term power is proportional to the maximum
rate of oxygen consumption in the working muscles .
The body supplies instantaneous
energy for short - term power needs by splitting energy - rich phosphates and glycogen ,
leaving an oxygen deficit in the body .This process can only last about a minute and is
called the anaerobic ( without oxygen ) phase of work; long –term activity requires
oxygen ( aerobic work ) as shown in figure 1 .

7
Solution
Q.3 For a hypothetical animal that has a mass of 700 kg (the basal metabolic
rate = 10000 kcal /day ).Assuming 5 kcal/g of food , estimate the
minimum amount of food needed each day ?
The basal metabolic rate of mass 700kg = 10000 kcal/day
10000 = 2 x 10³ g/day
5
amount of food needed each day = 2 kg/day
Q5.5 (a) What is the energy required to walk 20 km at 5 km/hr ?
From the table , the energy rate of walking activity at 5km/hr is
3.8 kcal /min .
The energy required to walk 20 km =3.8 kcal/min x 20km x 60 min/hr
5km/hr
Energy = 912 kcal
(b) Assuming 5 kcal /g of food ,calculate the grams of food needed for
walk .
The amount of food needed for walk =[ Energy ]
[ Energy /gm ]
= 912 kcal
5 kcal/gm
= 182 gram
Q 5.7 Suppose that the elevator is broken in the building in which you work
and you have to climb 9 stories – a height of 45 m above ground
level .How many extra calories will this external work cost you if
your mass is 70 kg and your body at 15% efficiency ?
External work = m g h
= 70 x9.8x 45
since 1 kcal = 4.2 x10³ J
External work = 70 x9.8x 45
4.2 x10³
= 7.3 kcal
calories needed = 7.3 kcal = 7.3
efficiency 0.15
= 49 kcal
8
5.9 A 70 Kg hiker climbed a mountain 1000 m high . He reached the peak
in 3 hr .
a . calculate the external work done by the climber .
External work = m g h
= 70 x 9.8 x 10³
= 6.9 x 10 J
b. Assuming the work was done at a steady rate during the 3 hr
period ,calculate the power generated during climb.
Power = Work
Time
Power = 6.9 x 10 J = 64 watts
3x 3600 sec
c. Assuming the average O2 consumption during the climb was 2 liter /min
(corresponding to 9.6 Kcal /min ), find the efficiency of the hiker’s body .
Energy consumed =( 9.6 Kcal /min )(180 min )(4.2 x 10³J/kcal)
6
= 7.3 x 10 J
Efficiency = work done
Energy consumed
€ = 6.9 x 10
6
7.3 x 10
€ = 0.094
€ = 9.4%
d . How much energy appeared as heat in the body ?
Δ U =Δ Q + Δ W
6
7.3 x 10 J = Δ Q + 6.9 x 10
6
Δ Q = 6.6x 10 J

9
Q.15 Consider a man on a beach in Florida .It is a sunny day so he is
receiving radiation from the sun at the rate of 30 Kcal/hr .He has an
effective body surface of 0.9 m² ,Ts = 32 °C , and the temperature of
his surrounding is 30 °C.
a. Find the net energy gained by radiation per hour .
b. If there is a breeze at 4m/sec ,find the energy lost by convection
per hour .
c. If he loses 10 Kcal/hr , and his metabolic rate is 80 kcal/hr , how
much heat is lost by evaporation?
a. Hr = Kr Ar e (Ts –Tw)
Since Kr = 5Kcal/ m². hr .°C
e=1
Hr = 5x 0.9 (32 -30)
=9 Kcal/hr
b . Hc = Kc Ac (Ts – T α)
Kc =10.45 – v + 10 √ v
Kc = 10.45 - 4 + 10 √4
Kc = 6.45 +20
Kc = 26.5 Kcal /hr.m² .°C
Hc = 26.5 x 0.9 (32 – 30 )
Hc = 48 Kcal /hr
c. Heat lost = Heat gain
Heat lost by radiation +evaporation +convection +respiration
Heat lost = 9 +evaporation +48 +10
Heat lost =67 + evaporation
Heat gain = 80 +30 = 110
110 =67 + evaporation
Heat lost by evaporation =110 -67
Heat lost by evaporation = 43 Kcal /hr
